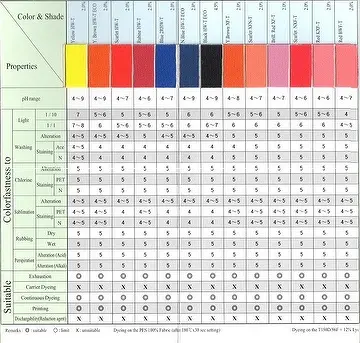
The global disperse dye market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand from the textile industry—particularly in synthetic fiber applications such as polyester. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global disperse dye market size was valued at USD 1.12 billion and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increased textile production in Asia-Pacific, especially in countries like China, India, and Vietnam, which dominate both dye manufacturing and textile exports. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects steady market expansion due to advancements in dyeing technologies and a growing focus on eco-friendly and low-impact disperse dyes. As demand rises, manufacturers are scaling production, improving sustainability, and innovating formulations to meet regulatory and performance standards. In this competitive landscape, the following eight companies have emerged as leading disperse dye manufacturers, distinguished by their market presence, technological capabilities, and product portfolios.
Top 8 Disperse Dye Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Disperse Dyes TAICRON
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tntind.com.tw
Key Highlights: A specialized manufacturer and supplier of Disperse Dyes TAICRON in Taiwan. Welcome to visit our website to browse more Disperse Dyes TAICRON relative products….
#2 Disperse Dye Suppliers and Manufacturers in USA
Domain Est. 2005
Website: chemworldintl.com
Key Highlights: Disperse Dye Suppliers and Manufacturers in USA. Looking for a disperse dye supplier from the USA? We provide high quality disperse dyes at competitive ……
#3 Hangzhou Flariant Co.,Ltd. –Folanthene
Domain Est. 2008
Website: flariant.com
Key Highlights: Flariant is the leading disperse dyes manufacturer, providing solutions for dyeing and finishing. · Steady development. Strong performance, competitive advantage ……
#4 Disperse Dyes Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2009
Website: tiankunchemical.com
Key Highlights: Tiankun offers a wide range of high-quality disperse dyes suitable for dyeing polyester and synthetic fibers. We are a trusted wholesale supplier of ……
#5 Disperse Dyes
Domain Est. 2019
Website: polyventive.com
Key Highlights: Disperse dyes are a type of synthetic dye primarily used for coloring synthetic fibers such as polyester & nylon. Widely used in textile & apparel ……
#6 Disperse dye additives
Domain Est. 1997
Website: borregaard.com
Key Highlights: Our sustainable lignin-based dyestuff dispersants are used either alone or in blended formulations to meet your specific requirements….
#7 DISPERSE DYES
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pylamdyes.com
Key Highlights: Disperse dyes are typically used for coloring synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, acrylic, and acetate rayon….
#8 Disperse dyes
Domain Est. 2001
Website: solutions.cht.com
Key Highlights: Universal Rapid Dyeing dye with excellent combinability and dispersion stability, suitable for dyeing large and densely wound packages. BEMACRON SEL/SEB…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Disperse Dye

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Disperse Dye
The global disperse dye market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving textile industry demands, technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and shifting regional production dynamics. As synthetic fibers—particularly polyester—continue to dominate the global textile market, disperse dyes, which are primarily used for dyeing these materials, are expected to maintain strong demand. Key market trends shaping the disperse dye sector in 2026 include:
-
Growing Demand from the Textile and Apparel Industry
The rise in global consumption of polyester-based textiles, especially in fast fashion and sportswear, is fueling demand for disperse dyes. Asia-Pacific, particularly countries like China, India, and Vietnam, remains the epicenter of textile manufacturing, contributing significantly to disperse dye consumption. Increasing urbanization and disposable incomes in emerging economies are expected to sustain this demand through 2026. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Dyes
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness are compelling manufacturers to develop low-impact and eco-friendly disperse dyes. By 2026, there will be a notable shift toward dyes with reduced water and energy consumption, lower effluent toxicity, and compliance with global standards such as ZDHC (Zero Discharge of Hazardous Chemicals) and OEKO-TEX®. Bio-based and non-azo disperse dyes are gaining traction as brands seek greener supply chains. -
Technological Innovation and Digitalization
Advancements in dyeing technologies—such as supercritical CO₂ dyeing and digital inkjet printing—are influencing disperse dye formulation and application. These technologies reduce water usage and waste, aligning with sustainability goals. By 2026, integration with Industry 4.0 tools like AI-driven color matching and automated dyeing systems will enhance precision and efficiency in disperse dye usage. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The disperse dye market is witnessing increased consolidation as major chemical companies acquire niche players to expand product portfolios and geographic reach. Strategic partnerships between dye manufacturers and textile mills are also on the rise, aimed at co-developing customized, high-performance dyes that meet specific application needs. -
Regulatory Pressures and Supply Chain Transparency
Stringent environmental regulations in Europe and North America are pushing manufacturers to reformulate disperse dyes to eliminate hazardous substances. By 2026, traceability and compliance with REACH, EPA, and other regulatory frameworks will be critical for market access. This is prompting investment in green chemistry and closed-loop production systems. -
Rising Competition from Asia-Based Producers
China and India are not only major consumers but also leading producers of disperse dyes. By 2026, these regions are expected to strengthen their dominance through cost-effective production, innovation in mid-tier dye products, and expanding export capabilities. However, environmental crackdowns in China may shift some manufacturing to Southeast Asia. -
Impact of Circular Economy and Recycled Polyester
The growing use of recycled polyester (rPET) in textiles presents both challenges and opportunities for disperse dyes. Dyeing recycled fibers often requires modified formulations due to variability in polymer quality. By 2026, dye manufacturers will increasingly offer specialized disperse dyes tailored for rPET, supporting the circular economy in fashion and textiles.
In conclusion, the 2026 disperse dye market will be characterized by a balance between performance, sustainability, and innovation. Companies that invest in eco-friendly technologies, comply with global regulations, and adapt to digital and circular economy trends are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Disperse Dyes (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing disperse dyes, essential for dyeing polyester and other hydrophobic fibers, involves navigating significant challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to production failures, legal disputes, reputational damage, and financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Color Fastness & Performance:
- Pitfall: Dyes from different batches or suppliers may exhibit significant variations in critical performance attributes like light fastness, wash fastness, sublimation fastness, and rubbing fastness.
- Consequence: Garments or textiles fail quality control, leading to customer complaints, returns, and brand damage. Products may fade prematurely or bleed color during use/washing.
- Root Cause: Poor raw material control, inconsistent synthesis processes, inadequate quality control (QC) testing by the supplier, or use of substandard additives.
-
Batch-to-Batch Color Variation (Shade Variation):
- Pitfall: Even within the same dye type (e.g., Disperse Red 167), the exact hue, strength, and brilliance can vary noticeably between production batches from the same or different suppliers.
- Consequence: Inability to achieve consistent dyeing results across production runs, leading to off-shade fabrics, production delays, and significant rework or scrappage costs. Critical for brands requiring color consistency.
- Root Cause: Lack of rigorous process control, insufficient spectrophotometric matching, or variations in the isomer ratio of the dye molecule.
-
Presence of Impurities & Undeclared Additives:
- Pitfall: Dyes may contain harmful impurities (e.g., carcinogenic amines from incomplete synthesis, heavy metals) or excessive, undeclared dispersing agents/fillers.
- Consequence: Violation of stringent regulatory standards (REACH, Oeko-Tex, ZDHC MRSL), leading to shipment rejections, product recalls, fines, and legal liability. Impurities can also negatively impact dyeing performance and final product quality.
- Root Cause: Use of non-compliant starting materials, poor purification processes, or deliberate adulteration to reduce costs.
-
Poor Solubility & Dispersion Stability:
- Pitfall: The dye formulation may not disperse well in water or form stable dispersions, leading to sedimentation or agglomeration.
- Consequence: Uneven dyeing (streaking, speckiness), nozzle blockages in jet dyeing machines, reduced dye uptake efficiency, and increased waste. Requires higher dispersant levels, potentially impacting other properties.
- Root Cause: Inadequate milling process, incorrect choice or dosage of dispersing agents, or poor formulation design.
-
Lack of Comprehensive & Accurate Technical Data:
- Pitfall: Suppliers provide incomplete, generic, or inaccurate technical data sheets (TDS) lacking crucial information like exact chemical composition (CAS number), detailed fastness profiles under relevant conditions, compatibility data, or specific application guidelines.
- Consequence: Difficulty in formulating recipes, predicting performance, troubleshooting dyeing problems, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Increases risk of application failures.
- Root Cause: Reluctance to disclose proprietary information, lack of rigorous testing infrastructure, or poor communication.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
-
Sourcing Patented Dyes Without License:
- Pitfall: Procuring and using a disperse dye that is protected by an active patent (composition, process, or application patent) without obtaining a proper license from the patent holder (often a major chemical company like Huntsman, Archroma, or DyStar).
- Consequence: High risk of patent infringement lawsuits. This can result in injunctions halting production/sales, significant damages (potentially tripled for willful infringement), legal costs, and reputational harm. Liability often extends to the user of the dye, even if the supplier provided it.
- Root Cause: Lack of IP due diligence, reliance on unverified supplier claims (“generic”), sourcing from obscure suppliers who may be infringing, or misunderstanding the scope of patent protection.
-
“Generic” Dye Misrepresentation:
- Pitfall: Suppliers market dyes as “generic” equivalents of patented dyes, implying they are legally free to use, when they may actually infringe on formulation, process, or application patents, or contain restricted substances.
- Consequence: The buyer is lulled into a false sense of security and unknowingly uses infringing products, exposing them to full legal liability. The “generic” dye might also have inferior quality.
- Root Cause: Unscrupulous suppliers exploiting the term “generic” without legal validity. Lack of independent verification by the buyer.
-
Unclear or Opaque Supply Chain:
- Pitfall: Purchasing through multiple intermediaries (traders, brokers) without knowing the actual manufacturer. The final manufacturer might be producing infringing dyes.
- Consequence: Difficulty in tracing the origin, verifying IP status, and holding the responsible party accountable if infringement occurs. Dilutes quality control.
- Root Cause: Complex global supply chains, desire for lowest price leading to indirect sourcing, lack of supplier transparency requirements.
-
Inadequate Supplier Warranties & Indemnification:
- Pitfall: Supplier contracts lack strong warranties guaranteeing the dye is free from IP infringement and clauses where the supplier indemnifies the buyer against any resulting legal claims and costs.
- Consequence: The buyer bears the full brunt of legal and financial consequences of IP infringement, even if the supplier was at fault. Recourse against the supplier may be difficult or impossible.
- Root Cause: Standard purchase terms favoring the supplier, lack of legal review of contracts, or power imbalance in negotiations.
Mitigation Strategies:
* Rigorous Supplier Vetting: Audit suppliers (quality systems, certifications like ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ZDHC), demand full disclosure of manufacturing sites.
* Comprehensive Testing: Implement incoming QC testing for color strength/shade, fastness properties, and regulatory compliance (e.g., GC-MS for amines, ICP-MS for metals). Use certified labs.
* Demand Transparency: Require detailed, accurate TDS and Safety Data Sheets (SDS). Insist on CAS numbers.
* Conduct IP Due Diligence: Consult legal/IP experts. Verify patent status of key dyes (using databases like Espacenet, USPTO). Require suppliers to warrant non-infringement.
* Secure Strong Contracts: Include robust quality specifications, IP warranties, and indemnification clauses. Prefer direct sourcing from reputable manufacturers.
* Prioritize Reputable Suppliers: Build relationships with established, transparent suppliers known for compliance and quality, even at a higher initial cost.
By proactively addressing these H2-level pitfalls in quality and IP, companies can secure reliable, compliant, and legally safe disperse dye supplies, protecting their operations, products, and brand reputation.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Disperse Dyes
Disperse dyes are non-ionic, water-insoluble dyes primarily used for dyeing synthetic fibers such as polyester, acetate, and nylon. Due to their chemical nature and application, the logistics and compliance requirements for handling, transporting, and storing disperse dyes must adhere to international, national, and industry-specific regulations. This guide outlines key considerations under H2 (Health, Safety, and Environmental Hazards) to ensure safe and compliant operations.
1. Chemical Classification & Identification
- Chemical Name: Disperse Dyes (varies by specific compound, e.g., Disperse Blue 79, Disperse Red 60)
- CAS Number: Varies by dye; must be specified per product
- UN Number: Typically UN3077 (Environmentally hazardous substance, solid, n.o.s.) or UN3082 (Liquid, hazardous to the environment), depending on formulation
- GHS Classification:
- Hazard Statements (H-codes):
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation
- H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects
- Precautionary Statements (P-codes):
- P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray
- P273: Avoid release to the environment
- P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection
- P391: Collect spillage
2. Packaging & Labeling Requirements
- Packaging:
- Use sealed, moisture-resistant containers (e.g., multi-wall paper bags with polyethylene lining or HDPE drums).
- Ensure packaging is UN-certified for transport if classified as hazardous.
- Labeling:
- GHS-compliant labels including:
- Product identifier
- Signal word (e.g., “Warning” or “Danger”)
- Hazard pictograms (e.g., exclamation mark, environment)
- H- and P-statements
- Supplier information
- Transport labels per IMDG (sea), ADR (road), IATA (air), or 49 CFR (USA) as applicable.
3. Transportation Regulations
- Mode-Specific Compliance:
- Air (IATA DGR):
- Classify under Class 9 (Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods) if environmentally hazardous.
- Packing Group III typically applies.
- Shipper must provide a completed Dangerous Goods Declaration.
- Sea (IMDG Code):
- Entry under UN3077 or UN3082; marine pollutant marking required if applicable.
- Road (ADR/EU):
- Requires orange placards if quantity exceeds thresholds.
- Transport documents must include hazard class, UN number, and emergency contact.
- Rail (RID):
- Follows ADR regulations with additional rail-specific provisions.
4. Storage & Handling
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight.
- Keep containers tightly closed to prevent dust formation.
- Segregate from strong oxidizers and foodstuffs.
- Handling Precautions:
- Use local exhaust ventilation when handling powders.
- Avoid generating dust; use wet methods or vacuum systems for cleanup.
- Prohibit eating, drinking, or smoking in handling areas.
5. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Minimum PPE:
- Chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile)
- Safety goggles or face shield
- Dust mask (NIOSH-approved N95 or equivalent) for powders
- Protective clothing (lab coat or coveralls)
- Engineering Controls:
- Use closed systems or glove boxes where feasible.
- Install dust collection systems.
6. Spill & Emergency Response
- Spill Procedure:
- Evacuate non-essential personnel.
- Wear full PPE.
- Contain spill with absorbent material (e.g., vermiculite).
- Collect waste in labeled, sealed container for disposal.
- Do not allow entry into sewers or waterways.
- Fire Hazards & Extinguishing:
- Disperse dyes are generally combustible solids.
- Use water spray, foam, dry chemical, or CO₂ for extinguishing.
- Avoid dry sweeping—creates airborne dust.
7. Waste Disposal
- Dispose of waste in accordance with local, national, and international regulations (e.g., Basel Convention for transboundary movement).
- Label waste containers as hazardous.
- Use licensed waste disposal contractors.
- Document disposal manifests and retain records.
8. Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU):
- Ensure registration of substances if manufactured/imported >1 ton/year.
- Review SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) status.
- TSCA (USA):
- Confirm substance is listed on the TSCA Inventory.
- CLP Regulation (EU):
- Classify, label, and package according to CLP (aligned with GHS).
- GHS Implementation:
- Countries vary in adoption; ensure SDS and labels meet local requirements.
9. Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Requirements
- Maintain up-to-date, GHS-compliant SDS (16-section format).
- Include:
- Section 1: Identification
- Section 7: Handling and storage
- Section 8: Exposure controls/PPE
- Section 13: Disposal considerations
- Section 14: Transport information
- Section 15: Regulatory information
10. Environmental & Sustainability Considerations
- Prevent runoff into water bodies.
- Monitor wastewater treatment for dye residues.
- Consider biodegradability and eco-toxicity profiles when selecting dyes.
- Explore certified eco-friendly alternatives (e.g., OEKO-TEX® STANDARD 100 compliant dyes).
Conclusion
Disperse dyes require careful management throughout the supply chain due to health, safety, and environmental risks. Adherence to H2-related compliance standards ensures the protection of workers, communities, and ecosystems. Always consult the specific SDS and local regulatory authorities before shipping or handling.
Note: This guide provides general information. Always verify requirements based on the exact chemical composition, concentration, and regional regulations applicable to your operation.
Conclusion for Sourcing Disperse Dyes
Sourcing disperse dyes requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and compliance with industry standards. As the primary choice for dyeing synthetic fibers such as polyester, disperse dyes play a critical role in the textile manufacturing process. When sourcing these dyes, it is essential to partner with reliable suppliers who adhere to environmental regulations, ensure consistent dye performance, and provide technical support.
Key considerations include the dye’s color fastness, dispersion stability, and eco-compliance, particularly in meeting REACH, ZDHC, and Oeko-Tex standards. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on their production capacity, innovation in low-impact dyes, and commitment to sustainable practices can enhance long-term supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of disperse dyes involves thorough due diligence, ongoing supplier evaluation, and alignment with both technical requirements and sustainability goals. By prioritizing responsible sourcing, textile producers can achieve high-quality dyeing results while supporting environmental and regulatory compliance in a competitive global market.