The global manufacturing landscape is undergoing a strategic shift as companies reevaluate their procurement models to enhance resilience, reduce costs, and improve supply chain transparency. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global sourcing market was valued at USD 6.7 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% through 2029, driven by increasing demand for cost-efficient and agile supply chains. A critical component of this evolution is the balance between direct and indirect sourcing—two procurement strategies with distinct implications for scalability, risk management, and operational efficiency. Direct sourcing, where organizations procure goods and services directly from manufacturers or raw material suppliers, is gaining traction amid rising interest in vertical integration and supplier relationship control. In contrast, indirect sourcing—which involves acquiring non-core inputs such as maintenance, IT services, and facilities management—continues to account for a significant portion of operational spend, often representing 20–30% of total organizational expenditures, as reported by Grand View Research. As supply chain leaders navigate inflationary pressures, geopolitical disruptions, and ESG compliance mandates, understanding the strategic differences and performance outcomes of sourcing directly versus indirectly from manufacturers has become critical. This analysis explores the top nine global manufacturers redefining the direct and indirect sourcing paradigms, leveraging data on procurement spend, supply chain structure, and operational KPIs to highlight best practices and emerging trends.
Top 9 Direct Vs Indirect Sourcing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
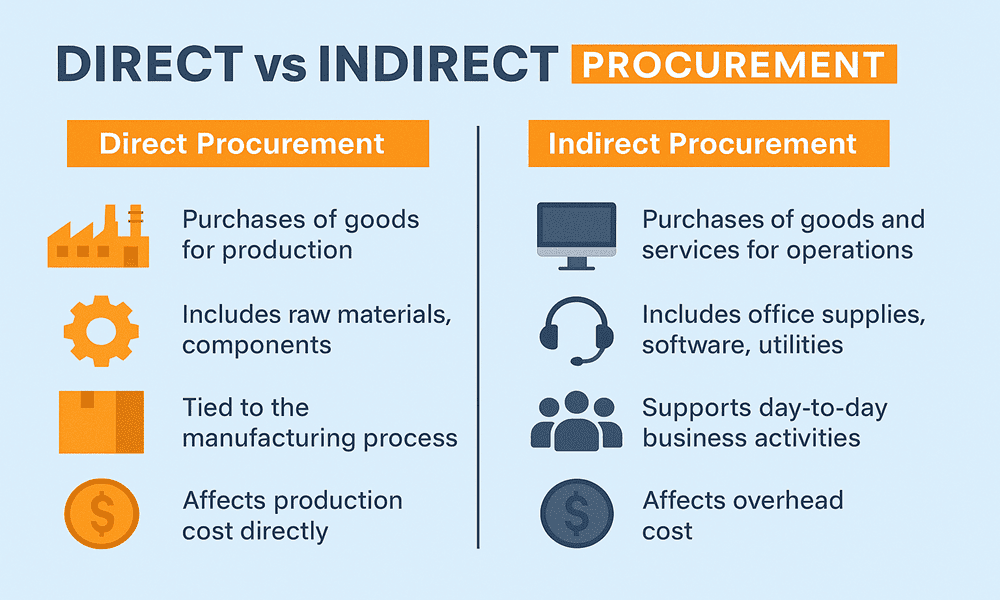
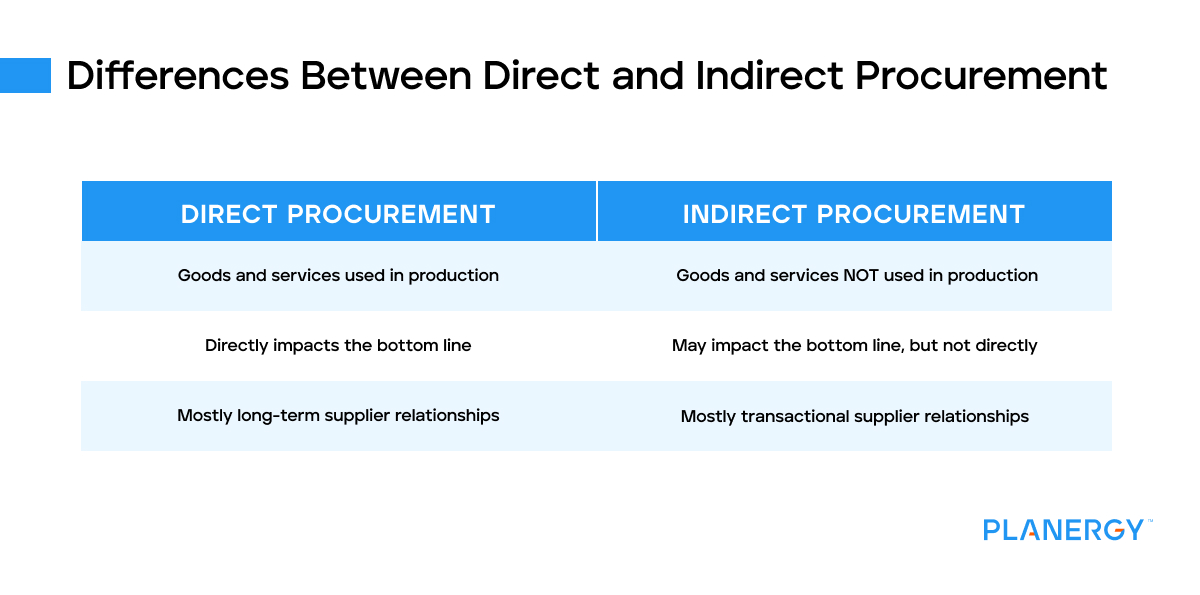
#1 Direct & Indirect Procurement Explained
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cips.org
Key Highlights: Indirect procurement is the expense of day-to-day operations and does not contribute to profit. However, indirect procurement does help to drive efficiency….
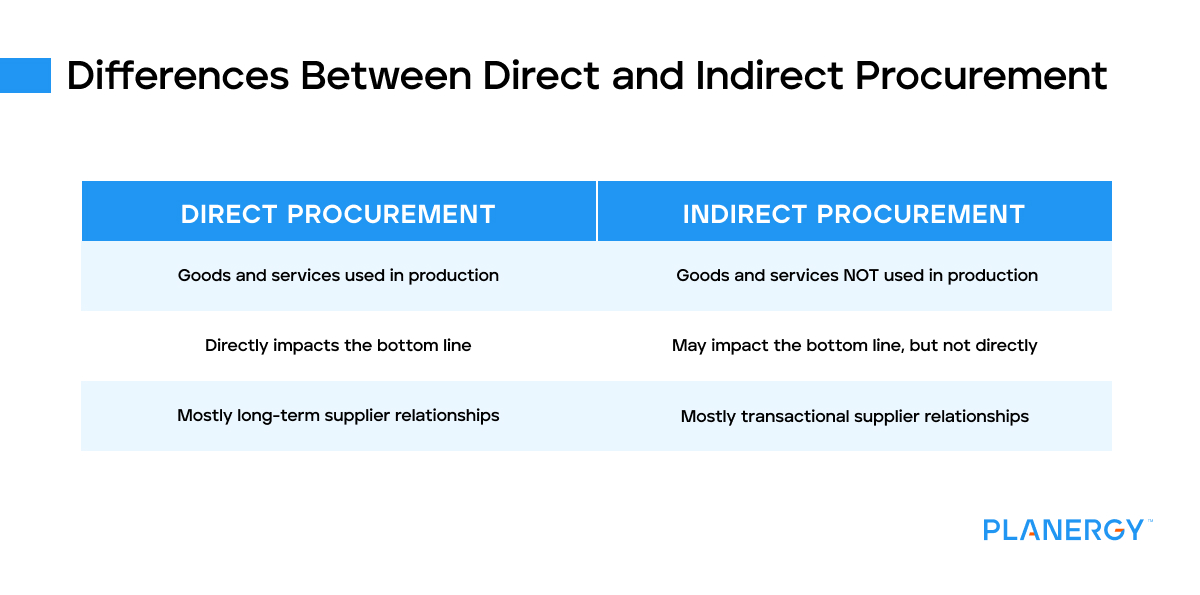
#2 Direct vs Indirect Procurement
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ivalua.com
Key Highlights: Direct procurement focuses on production-critical materials and suppliers, directly impacting margin and operational resilience. Indirect ……
#3 Direct vs indirect procurement: key differences explained
Domain Est. 2004
Website: fraxion.biz
Key Highlights: The key difference between direct and indirect procurement is the function they address. Direct procurement focuses on securing the core supplies that are ……
#4 Direct vs. Indirect Procurement
Domain Est. 2005
Website: drydengroup.com
Key Highlights: Usually, direct spend procurement is focused on the purchase or acquisition of tangible items. It can also be focused on the services that ……
#5 What Is Indirect Procurement? Understanding the Basics
Domain Est. 2010
Website: tipalti.com
Key Highlights: Exact differences between direct and indirect spend are: Company policy. Direct purchasing typically occurs over a centralized management team and a rigid ……
#6 Direct vs Indirect Procurement: What’s the Difference?
Domain Est. 2012
Website: procurify.com
Key Highlights: Direct procurement refers to the process of purchasing materials, goods, or services that are directly incorporated into a final product or service offering….
#7 Direct vs. Indirect Procurement: How to Manage Both
Domain Est. 2015
Website: precoro.com
Key Highlights: Direct procurement refers to acquiring goods and services directly involved in producing a company’s final product or service (hence the name)….
#8 Direct vs. Indirect Procurement
Domain Est. 2021
Website: getfocalpoint.com
Key Highlights: Direct procurement directly impacts your end product while indirect procurement supports general operations and infrastructure. Each procurement ……
#9 Indirect Sourcing vs Direct Sourcing
Domain Est. 2023
Website: cpgsourcing.com
Key Highlights: Direct Sourcing means contacting and benchmarking suppliers directly, negotiating contracts and pricing, ensuring quality conformity ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Direct Vs Indirect Sourcing
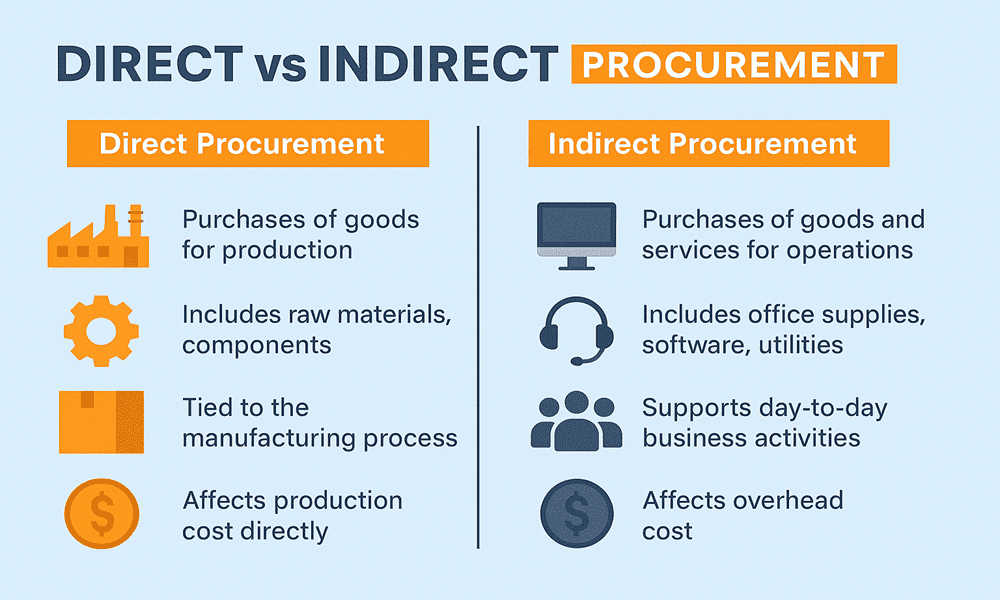
H2: Direct vs Indirect Sourcing Market Trends in 2026
As global supply chains evolve amid technological advancements, economic shifts, and increasing focus on sustainability, the dynamics between direct and indirect sourcing are expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026. Companies are reevaluating their procurement strategies to balance cost-efficiency, resilience, and strategic agility. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the direct versus indirect sourcing landscape in 2026.
1. Rise of Strategic Direct Sourcing
By 2026, direct sourcing—procuring raw materials, components, or goods directly from manufacturers or suppliers—is gaining prominence, especially in industries like automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. Organizations are increasingly bypassing intermediaries to gain better control over quality, lead times, and costs.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Post-pandemic disruptions and geopolitical tensions have led companies to shorten supply chains and reduce dependency on third-party distributors. Direct sourcing enables greater transparency and traceability, critical for compliance and risk mitigation.
- Cost Optimization: Eliminating middlemen reduces procurement costs and improves margin control. With rising inflation and input costs, businesses are leveraging direct relationships to negotiate better pricing and long-term contracts.
- Sustainability & ESG Goals: Direct engagement allows firms to monitor environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices at the source, supporting sustainability commitments. This is particularly important in sectors under regulatory scrutiny.
2. Digital Transformation and Supplier Enablement
Technology is a key enabler of direct sourcing growth. By 2026, digital procurement platforms, AI-driven supplier discovery tools, and blockchain for supply chain transparency are mainstream.
- Supplier Portals & E-Procurement: Enterprises are investing in integrated digital ecosystems that connect directly with suppliers, enabling real-time collaboration, order tracking, and performance analytics.
- AI & Predictive Analytics: Artificial intelligence helps identify optimal suppliers, forecast demand, and mitigate risks, making direct sourcing more scalable and efficient.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Especially in food, fashion, and high-tech, blockchain ensures authenticity and ethical sourcing, reinforcing consumer trust.
3. Indirect Sourcing Efficiency through Consolidation
While direct sourcing grows, indirect sourcing—procurement of non-core goods and services such as office supplies, IT services, marketing, and facilities management—remains essential. However, the approach is maturing toward consolidation and strategic partnerships.
- Category Management & Bundling: Companies are consolidating indirect spend across categories to negotiate volume discounts and reduce administrative overhead. Third-party procurement service providers (PSPs) and managed service providers (MSPs) are playing a growing role.
- Focus on Compliance & Risk Control: Indirect sourcing involves a broader, more fragmented supplier base. By 2026, organizations emphasize compliance, cybersecurity, and vendor risk management, especially for IT and professional services.
- Outsourcing and Vested Outsourcing Models: Many firms are adopting outcome-based contracting models, where vendors are incentivized by performance, blending indirect spend with strategic outcomes.
4. Geographic and Sectoral Shifts
- Nearshoring and Regionalization: To reduce lead times and tariffs, direct sourcing is shifting toward nearshoring in regions like North America (Mexico, Canada), Eastern Europe, and Southeast Asia. This trend supports direct relationships over complex, multi-tiered indirect channels.
- High-Tech and Energy Sectors Leading Direct Adoption: In semiconductors and renewable energy, direct sourcing of rare earth materials and critical components is becoming a strategic imperative due to supply scarcity and national security concerns.
5. Talent and Organizational Readiness
By 2026, procurement teams are evolving from transactional roles to strategic partners. The shift toward direct sourcing demands specialized skills in supplier relationship management, contract negotiation, and supply chain analytics. Conversely, indirect sourcing requires expertise in category management and cross-functional alignment.
- Upskilling Procurement Teams: Organizations are investing in training and hiring talent skilled in digital tools, data analysis, and sustainability standards.
- Integration of Procurement Functions: Leading companies are integrating direct and indirect sourcing under unified procurement platforms to leverage synergies and enhance spend visibility.
Conclusion
In 2026, direct sourcing is poised for growth driven by resilience, cost control, and sustainability imperatives, particularly in strategic supply chains. Indirect sourcing, while remaining critical, is becoming more efficient through consolidation, digital enablement, and strategic outsourcing. The future belongs to organizations that can balance both models—leveraging direct sourcing for core materials and indirect strategies for operational flexibility—supported by digital tools and a strategic procurement mindset.

Common Pitfalls in Direct vs Indirect Sourcing (Quality, IP)
When organizations choose between direct and indirect sourcing models, they often face critical challenges related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Understanding the pitfalls inherent in each approach is essential for mitigating risk and ensuring successful outcomes.
Quality Risks in Direct Sourcing
In direct sourcing, companies engage suppliers or manufacturers without intermediaries. While this offers greater control, it also introduces specific quality-related pitfalls:
- Inconsistent Quality Standards: Without internal expertise or standardized procedures, organizations may struggle to maintain consistent quality across production batches, especially when working with overseas suppliers.
- Limited Oversight and Monitoring: Direct relationships may lack the infrastructure for regular audits or real-time quality monitoring, increasing the risk of defects or non-compliance.
- Supplier Capability Misjudgment: Companies may overestimate a supplier’s technical capabilities during selection, leading to poor product quality or delivery delays.
- Lack of Scalability Readiness: A supplier that delivers high quality at a small scale may fail to maintain standards when production volumes increase.
Quality Risks in Indirect Sourcing
Indirect sourcing relies on intermediaries such as distributors, agents, or third-party vendors. This model introduces different quality challenges:
- Reduced Transparency: The presence of middlemen can obscure visibility into manufacturing processes, making it harder to trace quality issues back to their source.
- Dilution of Specifications: Intermediaries may not fully communicate or enforce technical requirements, resulting in deviations from original product specifications.
- Dependency on Third-Party Oversight: Quality assurance becomes reliant on the intermediary’s standards and diligence, which may not align with the buyer’s expectations.
- Higher Risk of Counterfeit or Substandard Goods: Indirect channels increase exposure to unauthorized resellers or gray market products, especially in complex supply chains.
Intellectual Property Risks in Direct Sourcing
Direct engagement with suppliers can expose companies to significant IP vulnerabilities:
- IP Theft or Misappropriation: Suppliers may copy designs, formulas, or technologies, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, and use them to create competing products.
- Inadequate Legal Agreements: Poorly drafted contracts may fail to clearly define ownership of IP, confidentiality obligations, or restrictions on reverse engineering.
- Lack of IP Protection Infrastructure: Direct suppliers, particularly in emerging markets, may not have internal controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Joint Development Ambiguities: When co-developing products, unclear IP clauses can lead to disputes over ownership and usage rights.
Intellectual Property Risks in Indirect Sourcing
While indirect sourcing may distance a company from the manufacturer, it does not eliminate IP risks—often shifting or compounding them:
- Increased Exposure Through Multiple Touchpoints: Each intermediary in the chain represents a potential point of IP leakage, especially if NDAs or security protocols are inconsistently applied.
- Unclear Chain of Custody for IP: With multiple parties involved, tracking who has access to proprietary information becomes complex, increasing the risk of unauthorized use.
- Limited Control Over Subcontracting: Intermediaries may subcontract work to unauthorized or unvetted parties, potentially exposing IP to unsecured environments.
- Difficulty Enforcing IP Rights: Legal recourse may be complicated by jurisdictional issues and layered contractual relationships, making it hard to hold the right party accountable.
Mitigation Strategies
To address these pitfalls, organizations should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on both suppliers and intermediaries.
– Implement robust IP protection clauses in contracts (e.g., clear ownership, confidentiality, audit rights).
– Establish quality control protocols, including on-site audits and third-party inspections.
– Limit access to sensitive information on a need-to-know basis.
– Use trusted partners with proven track records in IP and quality management.
Choosing between direct and indirect sourcing requires a strategic assessment of these risks. By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, businesses can build resilient, secure supply chains.
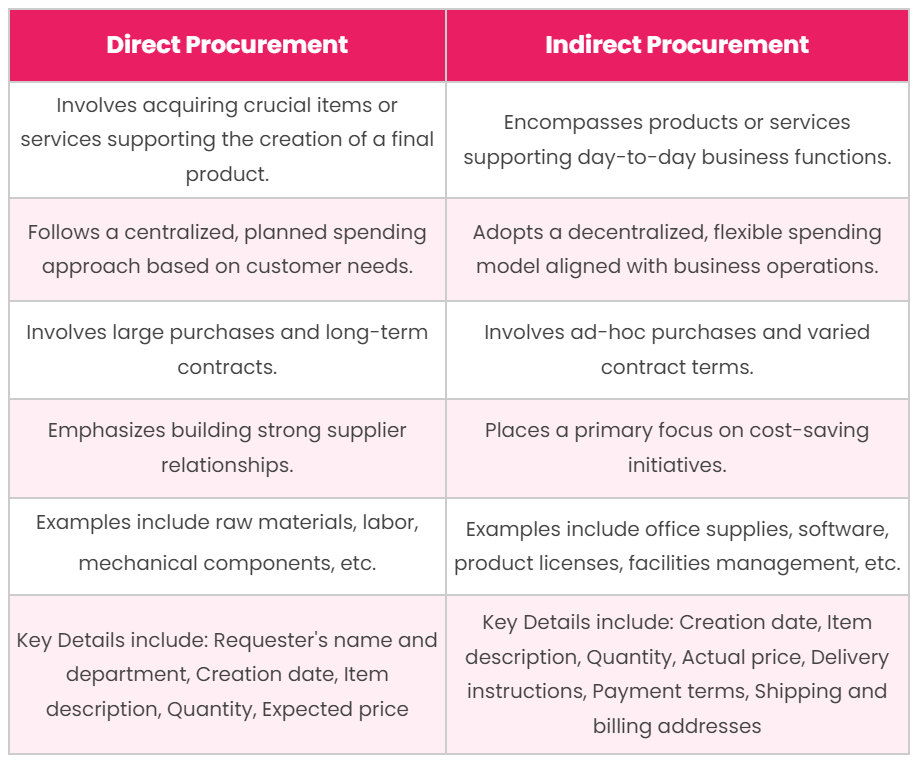
Logistics & Compliance Guide: Direct vs Indirect Sourcing
Understanding Direct and Indirect Sourcing
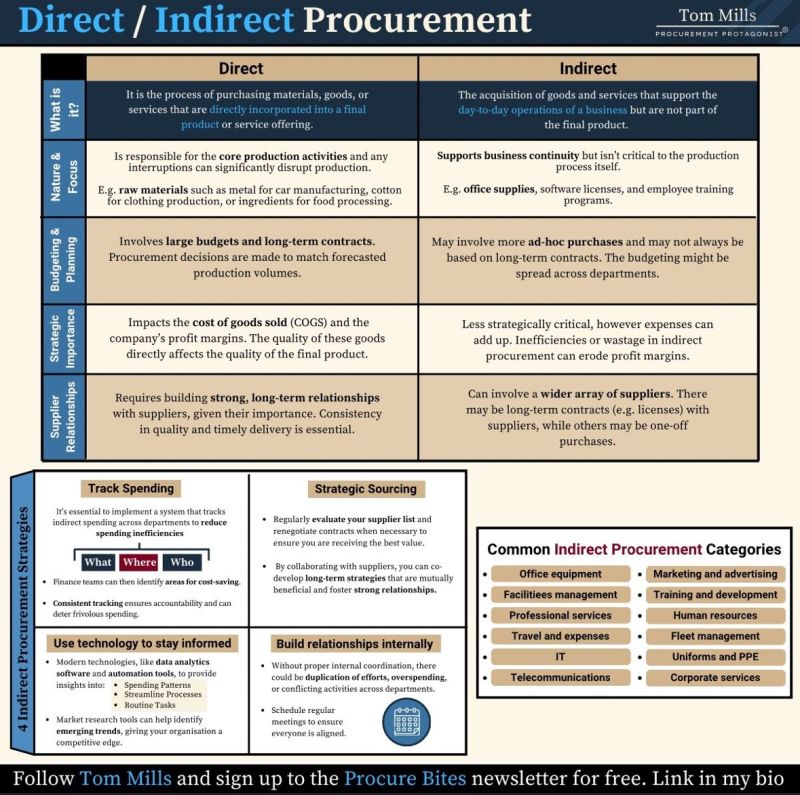
Direct Sourcing involves procuring raw materials, components, or finished goods directly from manufacturers or suppliers, often bypassing intermediaries such as distributors or wholesalers. This model provides greater control over costs, quality, and lead times but requires more internal resources and logistical expertise.
Indirect Sourcing refers to the procurement of goods and services that support business operations but are not part of the final product—such as office supplies, IT equipment, maintenance services, or logistics providers. These purchases are typically made through third parties like distributors, resellers, or service vendors, reducing operational complexity but potentially increasing costs and reducing visibility.
Logistics Implications: Direct Sourcing
Direct sourcing places significant demands on internal logistics infrastructure. Companies must manage international shipping, customs clearance, warehousing, and inventory planning. Key considerations include:
- Supply Chain Visibility: Requires robust tracking systems to monitor shipments from origin to destination.
- Lead Time Management: Longer lead times due to direct factory coordination; necessitates accurate demand forecasting.
- Inventory Holding: Often results in larger order volumes, increasing warehouse space needs and inventory carrying costs.
- Transportation Complexity: Responsibility for freight forwarding, Incoterms negotiation (e.g., FOB, CIF), and multimodal transport planning.
- Reverse Logistics: Handling returns, defects, or recalls directly with manufacturers adds complexity.
Logistics Implications: Indirect Sourcing
Indirect sourcing typically simplifies logistics by outsourcing fulfillment. Distributors or service providers manage delivery, returns, and inventory replenishment. Advantages include:
- Faster Delivery: Localized distribution networks enable shorter lead times.
- Reduced Operational Burden: Vendors manage transportation, warehousing, and last-mile delivery.
- Flexible Order Sizes: Easier to order smaller quantities, reducing inventory risk.
- Integrated Fulfillment: Many indirect suppliers offer drop-shipping or just-in-time delivery options.
- Scalability: Rapid scaling without adding internal logistics capacity.
Compliance Considerations: Direct Sourcing
Direct sourcing increases compliance responsibilities, especially in cross-border transactions. Critical compliance areas include:
- Customs and Import Regulations: Responsibility for accurate tariff classifications, import documentation (e.g., commercial invoices, packing lists), and duty payments.
- Trade Sanctions and Restrictions: Must ensure suppliers and goods comply with OFAC, EAR, or other regulatory lists.
- Product Standards and Certifications: Verification of compliance with local safety, environmental, and labeling requirements (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS).
- Supply Chain Due Diligence: Adherence to anti-bribery laws (e.g., FCPA), labor standards (e.g., Modern Slavery Act), and environmental regulations.
- Incoterms and Legal Liability: Clear understanding of risk transfer points, insurance, and liability under agreed Incoterms.
Compliance Considerations: Indirect Sourcing
While indirect sourcing reduces direct compliance burden, organizations remain ultimately liable for regulatory adherence. Key aspects include:
- Vendor Compliance Oversight: Ensuring third-party suppliers adhere to relevant regulations and pass audits.
- Indirect Tax Management: Responsibility for sales tax, VAT, or GST compliance on non-inventory purchases.
- Data Privacy and Cybersecurity: Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, etc., when using third-party IT or cloud services.
- Contractual Protections: Contracts must define compliance obligations, audit rights, and indemnification clauses.
- Ethical Sourcing: Monitoring vendors for adherence to sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) standards.
Risk Management Strategies
Both sourcing models entail distinct risks requiring tailored mitigation:
- Direct Sourcing Risks: Supplier dependency, geopolitical disruptions, quality inconsistencies, and logistical delays.
-
Mitigation: Diversify suppliers, conduct on-site audits, implement supply chain monitoring tools, and secure cargo insurance.
-
Indirect Sourcing Risks: Hidden costs, reduced control over quality, vendor lock-in, and compliance gaps.
- Mitigation: Standardize procurement processes, consolidate vendors, conduct regular performance reviews, and maintain compliance checklists.
Choosing the Right Model
The decision between direct and indirect sourcing depends on:
- Product Criticality: Core production materials often justify direct sourcing for control and cost savings.
- Volume and Scale: High-volume procurement benefits from direct supplier negotiations.
- Internal Capabilities: Companies with strong logistics and compliance teams can manage direct sourcing effectively.
- Regulatory Environment: Highly regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, aerospace) may prefer direct oversight.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Weigh total landed costs, including logistics, compliance, and risk mitigation.
Best Practices for Hybrid Approaches
Many organizations adopt a hybrid model, using direct sourcing for strategic items and indirect for operational needs. Best practices include:
- Categorize Spend: Classify procurement needs into direct vs. indirect for targeted strategy development.
- Leverage Technology: Use procurement platforms with logistics tracking and compliance modules.
- Centralize Oversight: Maintain a centralized procurement or supply chain team to manage both models.
- Regular Audits: Conduct supplier compliance and logistics performance audits annually.
- Train Procurement Teams: Ensure staff understand Incoterms, customs processes, and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Direct and indirect sourcing each offer distinct logistical and compliance challenges and benefits. Direct sourcing provides greater control and cost efficiency but demands robust logistics and compliance frameworks. Indirect sourcing reduces operational complexity but requires vigilant vendor management and oversight. By understanding these differences and implementing appropriate strategies, organizations can optimize their supply chains for efficiency, resilience, and regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, the decision between direct and indirect sourcing depends on a company’s strategic goals, resources, supply chain complexity, and risk tolerance. Direct sourcing offers greater control over quality, costs, and supplier relationships, often leading to improved transparency and long-term savings, especially for high-volume or critical components. However, it requires significant time, expertise, and investment in supplier management.
On the other hand, indirect sourcing, typically through intermediaries such as distributors or third-party vendors, provides flexibility, faster procurement, and access to a broader range of products and services with reduced administrative burden. While it may result in higher costs and less control, it is advantageous for non-core items or when speed and convenience are prioritized.
Ultimately, an optimized sourcing strategy often involves a balanced approach—leveraging direct sourcing for strategic materials and indirect sourcing for lower-risk or indirect procurement needs. Companies that align their sourcing method with business objectives, supplier capability, and market dynamics are better positioned to achieve efficiency, resilience, and competitive advantage in their supply chains.