The global digital fingerprinting equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for biometric authentication across law enforcement, civil identification, and commercial sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 2.35 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.8% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 5.4 billion by the end of the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by rising government initiatives for national ID programs, heightened security concerns, and the integration of fingerprint technology in consumer electronics and access control systems. As digital identity becomes increasingly critical, the need for high-accuracy, rapid, and secure fingerprint capture devices has elevated the role of leading manufacturers in shaping the future of identity verification. Below are the top 10 digital fingerprinting equipment manufacturers leading innovation and market share in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Top 10 Digital Fingerprinting Equipment Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Fingerprint Identification: Biometric Authentication
Domain Est. 1986
Website: nec.com
Key Highlights: NEC is the world’s leading supplier of fingerprint biometrics for identity management applications. NEC fingerprint identification technology is empowered by a ……
#2 Fingerprint
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fingerprint.com
Key Highlights: The Fingerprint device intelligence platform works across web and mobile applications to identify all visitors with industry-leading accuracy — even if …Missing: equipment manuf…
#3 Area Touch and Swipe Fingerprint Sensors
Domain Est. 1989
Website: synaptics.com
Key Highlights: A family of fingerprint-authentication sensors enabling applications such as PC and Auto with the highest levels of security, ease of use, and cost efficiency….
#4 Fingerprint Cards
Domain Est. 1992
Website: fpc.com
Key Highlights: Discover how FPC is driving the future of identity with trusted biometric solutions – enabling secure, seamless authentication across devices and platforms….
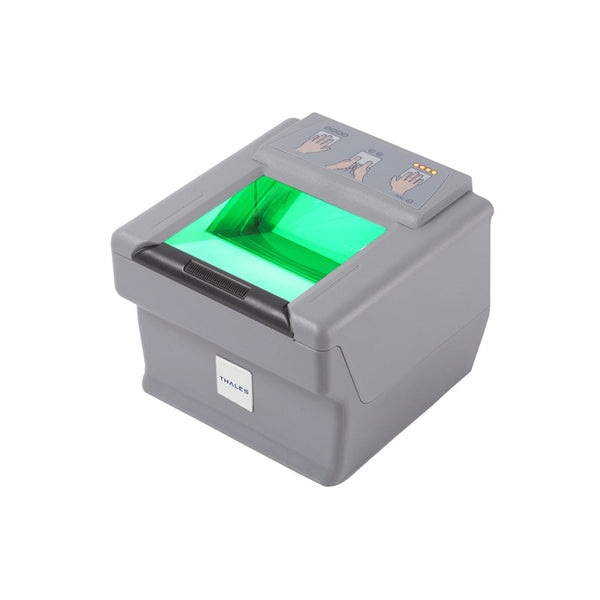
#5 Thales biometric LiveScan
Domain Est. 2000
Website: thalesgroup.com
Key Highlights: A multibiometric system delivering fast, customizable, forensic-grade quality for secure and compliant civil and criminal enrolment….
#6 Integrated Biometrics
Domain Est. 2002
Website: integratedbiometrics.com
Key Highlights: Integrated Biometrics creates the lightest, fastest, most reliable FBI-Certified fingerprint scanners with durable, patented light emitting sensor film….
#7 Biometrics4ALL
Domain Est. 2004
Website: biometrics4all.com
Key Highlights: Biometrics4ALL is a leading biometrics company specializing in FBI-certified Live Scan systems for background checks, criminal booking, and identity management….
#8 Fingerprint Biometric Authentication and Verification
Domain Est. 2005
Website: hidglobal.com
Key Highlights: HID offers a variety of fingerprint technologies featuring varying image capture methods, security features, form factors and industry certifications….
#9 Live Scan Fingerprinting and Print on FD
Domain Est. 2006
Website: bayometric.com
Key Highlights: Bayometric is industry-leading supplier of fingerprint scanner devices specializing in unrivalled fingerprint readers. To supply top quality fingerprint devices ……
#10 Live Scan System
Domain Est. 2007
Website: certifixlivescan.com
Key Highlights: Complete Live Scan system with certified hardware for fast, accurate fingerprint capture and fingerprint card printing….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Digital Fingerprinting Equipment

2026 Market Trends for Digital Fingerprinting Equipment
The digital fingerprinting equipment market is poised for substantial transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in biometric technologies, increasing demand for secure authentication, and expanding applications across public and private sectors. As global concerns over identity theft, cybersecurity, and national security intensify, digital fingerprinting solutions are becoming integral to identity verification systems. This analysis explores key market trends expected to shape the digital fingerprinting equipment landscape in 2026.
Growing Adoption Across Law Enforcement and Government Agencies
Law enforcement and government institutions remain the largest adopters of digital fingerprinting equipment. By 2026, many countries are expected to modernize their criminal identification systems, incorporating high-resolution live-scan devices and automated fingerprint identification systems (AFIS). The integration of digital fingerprinting into national ID programs, border control, and visa processing will accelerate deployment. Governments are investing in centralized biometric databases, fueling demand for reliable, fast, and interoperable fingerprint scanners.
Expansion in Commercial and Civil Applications
Beyond traditional security uses, digital fingerprinting is gaining traction in commercial sectors. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and educational organizations are adopting biometric authentication to enhance data security and streamline user verification. In banking, fingerprint-enabled ATMs and mobile banking apps are becoming more prevalent. Similarly, hospitals are using fingerprint scanners for secure access to patient records and to prevent medical identity fraud. This diversification is expected to significantly expand the market size by 2026.
Technological Advancements and Miniaturization
Rapid innovation in sensor technology is a key driver of market growth. By 2026, expect widespread availability of compact, high-accuracy fingerprint scanners utilizing optical, capacitive, and ultrasonic sensing methods. Ultrasonic sensors, in particular, offer enhanced security by capturing 3D fingerprint data and are resistant to spoofing. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms will improve matching accuracy, reduce false rejections, and enable real-time processing. Portable and mobile-compatible fingerprint devices will also become more common, supporting field operations and remote identity verification.
Rising Emphasis on Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
As digital fingerprinting collects sensitive biometric data, concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity are intensifying. In response, manufacturers are incorporating end-to-end encryption, on-device processing, and compliance with global data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. The trend toward decentralized storage—where biometric templates are stored locally on secure chips rather than centralized servers—will gain momentum by 2026, reducing the risk of large-scale data breaches.
Regional Market Dynamics
Growth in the Asia-Pacific region is expected to outpace other markets due to large-scale government biometric initiatives in countries like India, China, and Indonesia. India’s Aadhaar program, for instance, has already demonstrated the scalability of digital fingerprinting, and similar projects are emerging across Southeast Asia. Meanwhile, North America will maintain strong demand driven by homeland security needs and private-sector adoption. Europe’s market will grow steadily, influenced by EU-wide digital identity frameworks and stricter privacy norms.
Integration with Multi-Modal Biometric Systems
By 2026, digital fingerprinting equipment will increasingly be part of multi-modal biometric systems that combine fingerprints with facial recognition, iris scanning, or voice authentication. This layered approach enhances security and reliability, particularly in high-risk environments such as airports, financial institutions, and critical infrastructure. Vendors are developing unified platforms that support seamless integration of multiple biometric modalities, offering improved user experience and fraud prevention.
Conclusion
The digital fingerprinting equipment market in 2026 will be characterized by technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and expanding applications across sectors. As the need for secure, efficient, and scalable identity verification grows, digital fingerprinting will remain a cornerstone of modern biometric systems. Stakeholders—ranging from technology providers to policymakers—must navigate evolving privacy standards and interoperability requirements to capitalize on this dynamic growth trajectory.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Digital Fingerprinting Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing digital fingerprinting equipment involves significant technical and legal considerations. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to operational failures, legal disputes, and financial losses. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Equipment Quality and Performance
One of the most frequent issues when procuring digital fingerprinting systems is underestimating the importance of equipment quality. Low-quality devices may fail to meet accuracy, speed, or durability requirements.
- Inaccurate Scanning Results: Substandard sensors may produce poor image quality, leading to failed matches or false positives. This undermines the reliability of the entire identification process.
- Durability and Reliability Issues: Equipment not built for high-volume or rugged environments may break down frequently, increasing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Lack of Compliance with Standards: Some devices do not meet international biometric standards (e.g., ISO/IEC 19794), which can prevent interoperability with national databases or law enforcement systems.
- Insufficient Technical Support and Calibration: Vendors may offer limited post-purchase support, making it difficult to maintain or troubleshoot devices, especially in remote locations.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Digital fingerprinting technology often involves proprietary algorithms, software, and hardware designs. Sourcing equipment without proper IP due diligence can expose organizations to legal liabilities.
- Use of Unlicensed Biometric Algorithms: Some vendors incorporate third-party fingerprint matching algorithms without valid licensing. Purchasers may unknowingly use infringing technology, leading to lawsuits or forced system decommissioning.
- Counterfeit or Clone Devices: The market includes imitation equipment that replicates genuine products. These clones often violate patents and trademarks and may lack security updates or certifications.
- Ambiguous Software Licensing Terms: Vendors may impose restrictive or unclear software licenses that limit usage, integration, or data ownership, potentially disrupting operations or limiting scalability.
- Failure to Verify IP Ownership: Without proper vetting, buyers risk purchasing from vendors who do not own the IP they claim to offer, increasing the chance of legal challenges from true rights holders.
Inadequate Vendor Due Diligence
Organizations often rush procurement without thoroughly evaluating the vendor’s track record, certifications, and IP portfolio.
- Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain: Some vendors source components from unverified suppliers, increasing the risk of compromised hardware or IP violations.
- No Proof of IP Registration or Licenses: Reputable vendors should provide documentation proving ownership or legal rights to use patented technologies. Absence of such proof is a red flag.
- Overreliance on Resellers or Distributors: Intermediaries may lack detailed knowledge of the equipment’s IP status or quality control, leading to misrepresentation.
Conclusion
To mitigate risks, organizations must prioritize thorough technical evaluation and legal review during procurement. Conduct independent quality testing, verify all IP rights, and choose vendors with transparent, auditable practices. Ensuring compliance with both performance standards and intellectual property laws is essential for secure and sustainable deployment of digital fingerprinting systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Digital Fingerprinting Equipment
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the procurement, transportation, storage, deployment, and maintenance of digital fingerprinting equipment. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational efficiency, data security, and regulatory compliance.
Equipment Procurement & Vendor Selection
Selecting the right digital fingerprinting equipment and vendor is critical. Ensure all devices meet FBI’s Criminal Justice Information Services (CJIS) Security Policy requirements and are listed on the FBI’s Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System (IAFIS) Certified Devices List. Evaluate vendors based on compliance certifications (e.g., FIPS 140-2, CJIS compliance), technical support availability, warranty terms, and data privacy policies. Verify that equipment includes tamper-evident features and secure data encryption both at rest and in transit.
Shipping & Transportation Protocols
Secure all digital fingerprinting devices during shipment using tamper-evident packaging and tracked courier services with chain-of-custody documentation. Devices must be encrypted and powered off before transport. For international shipping, comply with export control regulations such as the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR), if applicable. Maintain detailed shipping logs including dates, personnel involved, tracking numbers, and delivery confirmations.
Secure Storage & Inventory Management
Store unused or inactive fingerprinting equipment in access-controlled environments (e.g., locked cabinets within secured facilities) with environmental controls to prevent damage. Implement an inventory management system to track serial numbers, location, deployment status, and maintenance history. Conduct regular audits (at least quarterly) to verify physical presence and condition of all devices, ensuring accountability and loss prevention.
Deployment & On-Site Security
Deploy equipment only in approved, secure locations with restricted physical access. Ensure devices are connected to secure, password-protected networks compliant with CJIS requirements—avoid public or unsecured Wi-Fi. Use strong authentication (multi-factor authentication where possible) for access to the device and associated software. Log all usage, including operator ID, time stamps, and purpose of use, to maintain an audit trail.
Data Handling & Privacy Compliance
All fingerprint data must be encrypted end-to-end and transmitted via secure protocols (e.g., TLS 1.2 or higher). Data should be stored only on CJIS-compliant servers or approved cloud platforms with appropriate safeguards. Adhere strictly to data retention policies; delete biometric data when no longer required by law or regulation. Comply with privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), or state-specific biometric privacy laws (e.g., BIPA in Illinois).
Maintenance & Servicing Procedures
Schedule regular preventive maintenance as per manufacturer guidelines. All servicing must be conducted by authorized personnel with documented clearance. Before sending equipment for repair, securely wipe all stored data using NIST 800-88 compliant sanitization methods. Maintain service records, including dates, technician details, and actions performed, for audit purposes.
Incident Response & Breach Reporting
Establish a clear incident response plan for equipment loss, theft, or data breaches. In the event of a compromised device, immediately deactivate remote access, report to relevant authorities (e.g., FBI CJIS, local law enforcement), and notify affected individuals if required by law. Document all incident details and conduct a post-incident review to strengthen protocols.
Training & Personnel Compliance
Ensure all personnel using or managing digital fingerprinting equipment complete CJIS Security Awareness Training and role-specific operational training. Maintain training records and re-certify staff annually. Enforce strict user access controls—grant permissions based on the principle of least privilege.
Regulatory Audits & Documentation
Prepare for periodic compliance audits by maintaining comprehensive documentation, including equipment logs, training records, maintenance reports, data handling policies, and incident reports. Ensure all policies align with current CJIS, NIST, and organizational regulatory requirements. Update documentation promptly to reflect changes in laws, equipment, or operational procedures.
Conclusion: Sourcing Digital Fingerprinting Equipment
In conclusion, sourcing digital fingerprinting equipment requires a comprehensive evaluation of technological capabilities, vendor reliability, compliance with regulatory standards, and long-term operational needs. The transition from traditional ink-based methods to digital systems offers significant advantages, including enhanced accuracy, faster processing times, improved data integration, and greater user convenience. When selecting equipment, it is essential to prioritize solutions that are FBI-certified (such as under the FBI’s Electronic Biometric Transmission Specification – EBTSTM), interoperable with existing identification systems, and supported by robust service and maintenance agreements.
Cost-effectiveness should be balanced with quality and durability, recognizing that initial investment in high-performance scanners and software can yield substantial returns through improved efficiency and reduced error rates. Additionally, scalability and future-proofing should be considered to accommodate evolving security and identification demands.
Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach—grounded in thorough market research, stakeholder consultation, and pilot testing—ensures the selection of digital fingerprinting equipment that meets both current requirements and future growth objectives, thereby strengthening identity management, security, and operational effectiveness across law enforcement, border control, and civil identification applications.