The global digital die cutting machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision, efficiency, and customization in packaging, printing, and industrial manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global digital cutting machines market was valued at USD 1.47 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in automation, increasing adoption of flexible packaging, and the need for rapid prototyping across industries such as automotive, textiles, and consumer goods. Furthermore, Mordor Intelligence projects heightened demand for digital die cutting solutions in the packaging sector, particularly in e-commerce and food & beverage, where intricate designs and short run lengths are becoming the norm. As manufacturers increasingly prioritize agility and scalability, the role of advanced digital die cutting machines has become pivotal. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers lead in innovation, reliability, and technological integration—shaping the future of digital fabrication.
Top 10 Digital Die Cutting Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
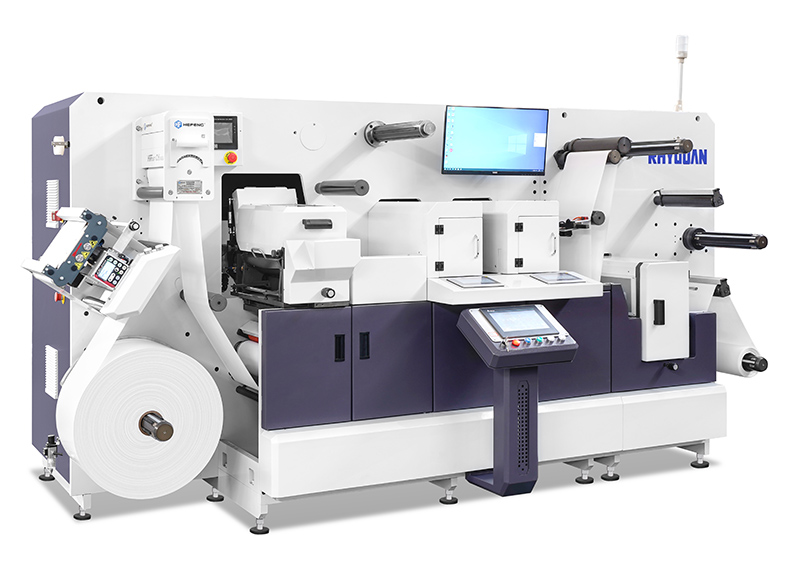
#1 VICUT
Domain Est. 2022
Website: vicutdigitalcutter.com
Key Highlights: VICUT Vulcan series flatbed cutter is ideal for small and medium-sized production and samples of packaging, swing tickets, cards,tags and labels….
#2
Domain Est. 1993
Website: summa.com
Key Highlights: For over four decades, Summa has offered the highest quality in roll-fed cutting plotters and flatbed cutters for the sign making industry, expanding its ……
#3 Die
Domain Est. 1995
#4 Die Cutters
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spiralbinding.com
Key Highlights: These unique die-cutting machines use specialized dies that can be installed to automatically cut various size and shape cuts from large sheets….
#5 Die Cutting Machines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: deltamodtech.com
Key Highlights: Our die cutting machines deliver tight tolerance and clean edges, run after run. Built to handle complexity with confidence….
#6 Digital Die Cutting
Domain Est. 1996
Website: graphicwhizard.com
Key Highlights: Graphic Whizard’s digital die cutters offers interchangeable tools for cutting, creasing, and prototyping on a wide range of materials….
#7 Highcon
Domain Est. 2009
Website: highcon.net
Key Highlights: Highcon develops, markets, sells and supports a portfolio of digital die cutting systems for folding carton and corrugated converters that cover a wide range of ……
#8 Digital Roll & Flatbed Die Cutter VR320F
Domain Est. 2015
Website: cncvicut.com
Key Highlights: High-precision CNC die cutter for label & sticker finishing — roll-to-roll + flatbed, 0.1mm accuracy, cold lamination, automatic matrix removal….
#9 IECHO
Domain Est. 2020
Website: iechocutter.com
Key Highlights: Equipped with various of tools, it can quickly and precisely make through cutting, half cutting, creasing and marking. It is suitable for sample making and ……
#10 Digital die Cutting Machine
Domain Est. 2020
Website: kongsbergsystems.com
Key Highlights: Kongberg digital die cutting machines are the industry benchmark of solidity, performance and quality. There is a Kongsberg digital die cutter for every need….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Digital Die Cutting Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Digital Die Cutting Machines
By 2026, the digital die cutting machine market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer demands, and evolving industry needs. Key trends shaping this market include:
1. Accelerated Adoption of AI and Machine Learning:
Digital die cutting machines will increasingly integrate artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to optimize workflows. These technologies will enable predictive maintenance, real-time error detection, automatic material calibration, and intelligent nesting to minimize waste. AI-driven design suggestions and automated job setup will further reduce operator dependency and boost productivity.
2. Growth in On-Demand and Personalized Printing:
The surge in demand for customized packaging, labels, and promotional materials will drive the adoption of digital die cutting. Brands seeking short-run, high-variability production will favor digital systems for their flexibility and quick turnaround. This trend is particularly strong in e-commerce, luxury goods, and direct-to-consumer marketing.
3. Expansion in Sustainable Manufacturing:
Environmental concerns will push manufacturers toward greener solutions. Digital die cutting supports sustainability by reducing material waste through precision cutting and eliminating the need for physical dies (which often end up in landfills). Expect increased demand for energy-efficient models and compatibility with recyclable and biodegradable substrates.
4. Integration with End-to-End Digital Workflows:
By 2026, seamless integration with digital printing presses, MIS (Management Information Systems), and cloud-based design platforms will become standard. This end-to-end automation will streamline prepress to post-press operations, enabling faster job completion and improved traceability across the production chain.
5. Rising Demand in Emerging Markets:
Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa will experience accelerated growth in digital die cutting adoption. Expanding printing industries, rising e-commerce penetration, and government support for manufacturing modernization will fuel investment in digital finishing technologies.
6. Advancements in Multi-Material and 3D Capabilities:
Next-generation machines will offer enhanced versatility, capable of cutting not only paper and cardboard but also textiles, foils, adhesives, and composites. Some systems will incorporate 3D embossing and creasing functions, blurring the line between cutting and finishing to deliver high-value, tactile packaging.
7. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships:
Market consolidation is expected as major players acquire niche technology firms to enhance their software and automation capabilities. Strategic partnerships between die cutting manufacturers and software developers will become critical to offering comprehensive digital workflow solutions.
In summary, the 2026 digital die cutting machine market will be defined by intelligence, sustainability, and integration. Companies that invest in smart, flexible, and eco-friendly technologies will lead the industry, meeting the evolving demands of modern manufacturing and personalized consumer experiences.
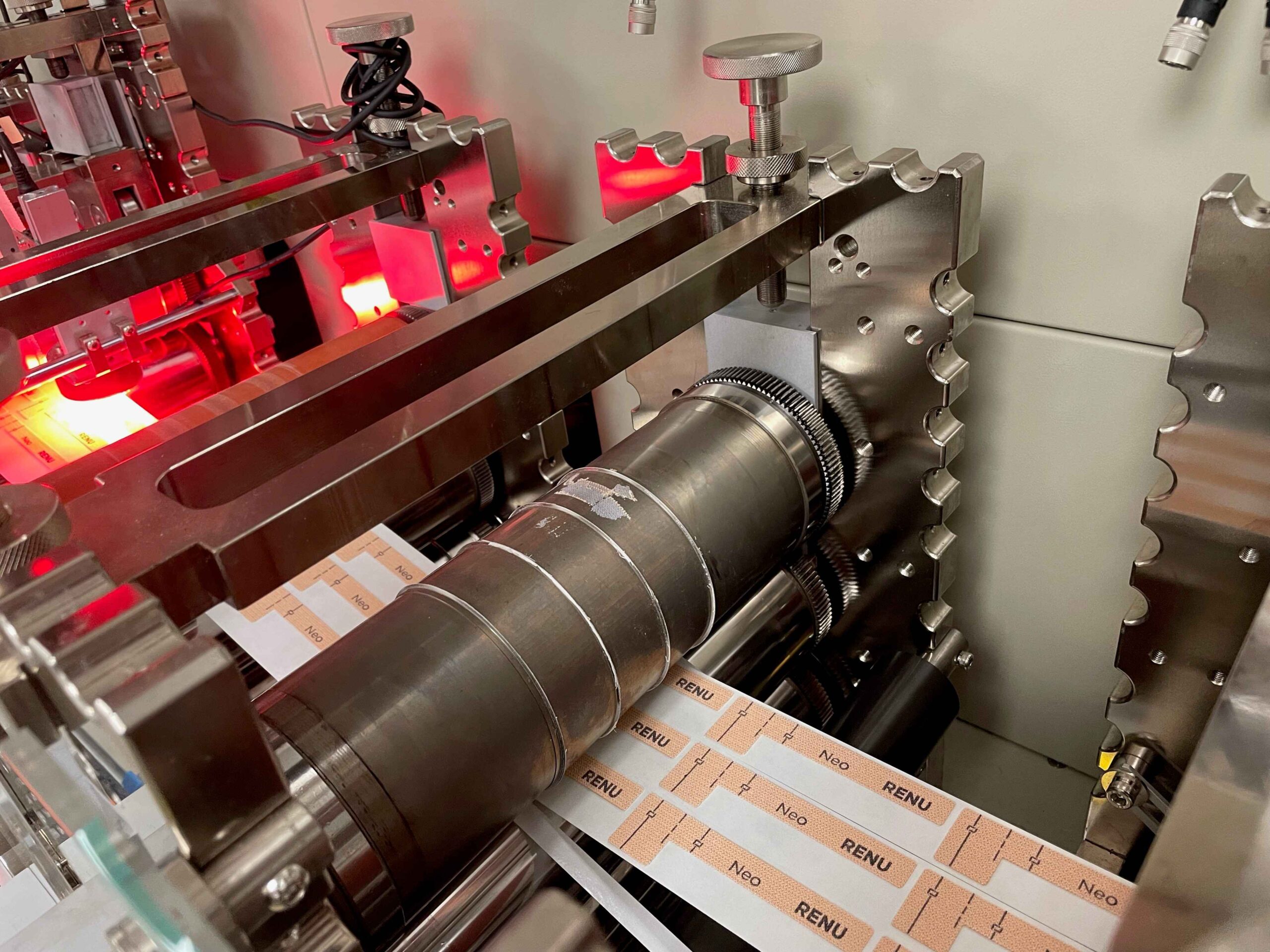
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Digital Die Cutting Machines (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a digital die cutting machine involves significant investment and strategic decision-making. While these machines offer precision and efficiency, buyers often encounter pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these risks helps ensure a successful procurement process.
Poor Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many low-cost digital die cutting machines, especially those from less reputable manufacturers, suffer from substandard materials and inconsistent assembly. This can lead to frequent mechanical failures, reduced cutting accuracy, and shorter machine lifespan. Buyers may overlook certifications, third-party testing, or lack of service history, resulting in high maintenance costs and operational downtime.
Inaccurate or Inconsistent Cutting Performance
A common quality issue is variance in cutting precision due to poor calibration, weak frame rigidity, or low-grade motors and sensors. Machines advertised with high specifications may underperform in real-world conditions, especially when processing diverse materials. Without independent performance validation or on-site testing, buyers risk acquiring equipment that fails to meet production standards.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if a machine initially performs well, poor after-sales support can severely impact long-term usability. Sourcing from manufacturers without regional service centers or adequate technical documentation can lead to extended downtimes. Additionally, limited availability of spare parts—especially for proprietary components—can render the machine obsolete prematurely.
Hidden Software Limitations and Proprietary Lock-In
Many digital die cutters rely on proprietary software that restricts file formats, design tools, or integration with existing workflows. Vendors may lock users into specific design ecosystems or charge high licensing fees for software updates. This reduces flexibility and increases long-term operational costs, posing both a quality-of-use and business continuity risk.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing machines from regions with weak IP enforcement raises concerns about cloned or counterfeit technology. Using a machine that incorporates stolen designs or patented mechanisms can expose the buyer to legal liability, including lawsuits or customs seizures. It’s critical to verify the manufacturer’s IP legitimacy and ensure they hold proper rights to the technology used.
Unauthorized Use of Your Digital Files and Designs
Some machines automatically transmit job data to cloud servers or third parties for “optimization” or “maintenance.” Without clear data usage agreements, this poses a serious IP risk—your proprietary cutting patterns and designs could be stored, copied, or even shared without consent. Always review privacy policies and opt for machines with offline operation and local data control.
Inadequate IP Protection in Contracts
Purchase agreements often lack explicit clauses protecting the buyer’s intellectual property. Without contractual guarantees about data confidentiality, software ownership, and usage rights, companies may lose control over their digital assets. Ensure contracts define IP ownership, restrict data sharing, and include warranties against IP violations.
By carefully evaluating both the physical quality and intellectual property aspects of digital die cutting machines, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and safeguard their operations and creative assets.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Digital Die Cutting Machine
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations when importing, transporting, installing, and operating a digital die cutting machine. Adhering to these guidelines ensures smooth operations, regulatory compliance, and equipment safety.
Import & Customs Compliance
Ensure all import documentation is accurate and complete, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Confirm the machine’s HS (Harmonized System) code—typically 8441.40 or 8477.80 depending on function—to determine applicable tariffs and import duties. Verify compliance with destination country regulations, including product certification requirements (e.g., CE in the EU, FCC in the U.S.).
Shipping & Handling Requirements
Use original packaging or custom crating to protect sensitive components during transit. The machine must be secured on a flatbed or standard shipping container using straps and anti-vibration mounts. Coordinate with a freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial machinery. Notify the carrier of weight, dimensions, and any special handling instructions (e.g., “This Side Up,” “Fragile – Electronics”).
Import Permits & Regulatory Approvals
Check if an import license or special permit is required for industrial automation equipment in the destination country. Ensure the machine meets electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), safety (e.g., UL, CSA), and environmental standards. Provide technical specifications and compliance certificates upon customs inspection to avoid delays.
Installation Site Preparation
Prepare the installation site with adequate floor space, structural support (check machine weight), and environmental controls (temperature: 15–30°C, humidity: 40–60%). Install a dedicated power supply meeting voltage and grounding requirements (e.g., 208–240V, 3-phase). Ensure proper ventilation and minimal dust to protect precision components.
Electrical & Safety Compliance
Verify that electrical installations comply with local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC in Europe). Use licensed electricians for wiring and grounding. Equip the machine with emergency stop buttons and protective enclosures in accordance with ISO 13849-1 (safety of machinery). Conduct an electrical safety inspection before operation.
Operational Certifications
Operators must be trained and certified per manufacturer guidelines. Maintain records of operator training and equipment maintenance. Ensure the machine complies with industry-specific standards if used in regulated sectors (e.g., medical device packaging under FDA 21 CFR Part 820).
Environmental & Waste Management
Dispose of packaging materials (wood, plastic, metal) in accordance with local recycling and waste regulations. If the machine uses consumables (e.g., cutting mats, adhesives), follow proper disposal protocols for hazardous waste, if applicable. Monitor noise emissions to comply with OSHA or EU noise directive limits.
Maintenance & Documentation
Keep detailed logs of maintenance, calibration, and repairs. Retain all compliance documentation, including CE/FCC declarations, safety data sheets (SDS), and warranty information. Update compliance records if modifications are made to the machine.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and adherence to compliance requirements are essential for the safe and efficient deployment of a digital die cutting machine. Partner with certified suppliers, freight handlers, and regulatory consultants to ensure seamless integration into your production environment.
Conclusion:
After a thorough evaluation of various digital die cutting machines and suppliers, it is evident that investing in a high-quality digital die cutting machine offers significant advantages in terms of precision, efficiency, and flexibility for prototyping, short-run production, and customization. The integration of advanced software, user-friendly interfaces, and compatibility with a wide range of materials makes these machines ideal for industries such as packaging, signage, textiles, and craft manufacturing.
Key factors influencing the sourcing decision include machine performance, technical support, after-sales service, initial and operational costs, and scalability to meet future production needs. Among the evaluated suppliers, [insert preferred vendor or type, if applicable] stands out due to its proven reliability, strong reputation, comprehensive training programs, and responsive customer support.
In conclusion, sourcing a digital die cutting machine from a reputable supplier with a balanced combination of technology, cost-effectiveness, and service support will enhance production capabilities, reduce lead times, and provide a competitive edge in the marketplace. This investment aligns strategically with long-term operational goals and positions the organization for growth in an increasingly digital manufacturing environment.