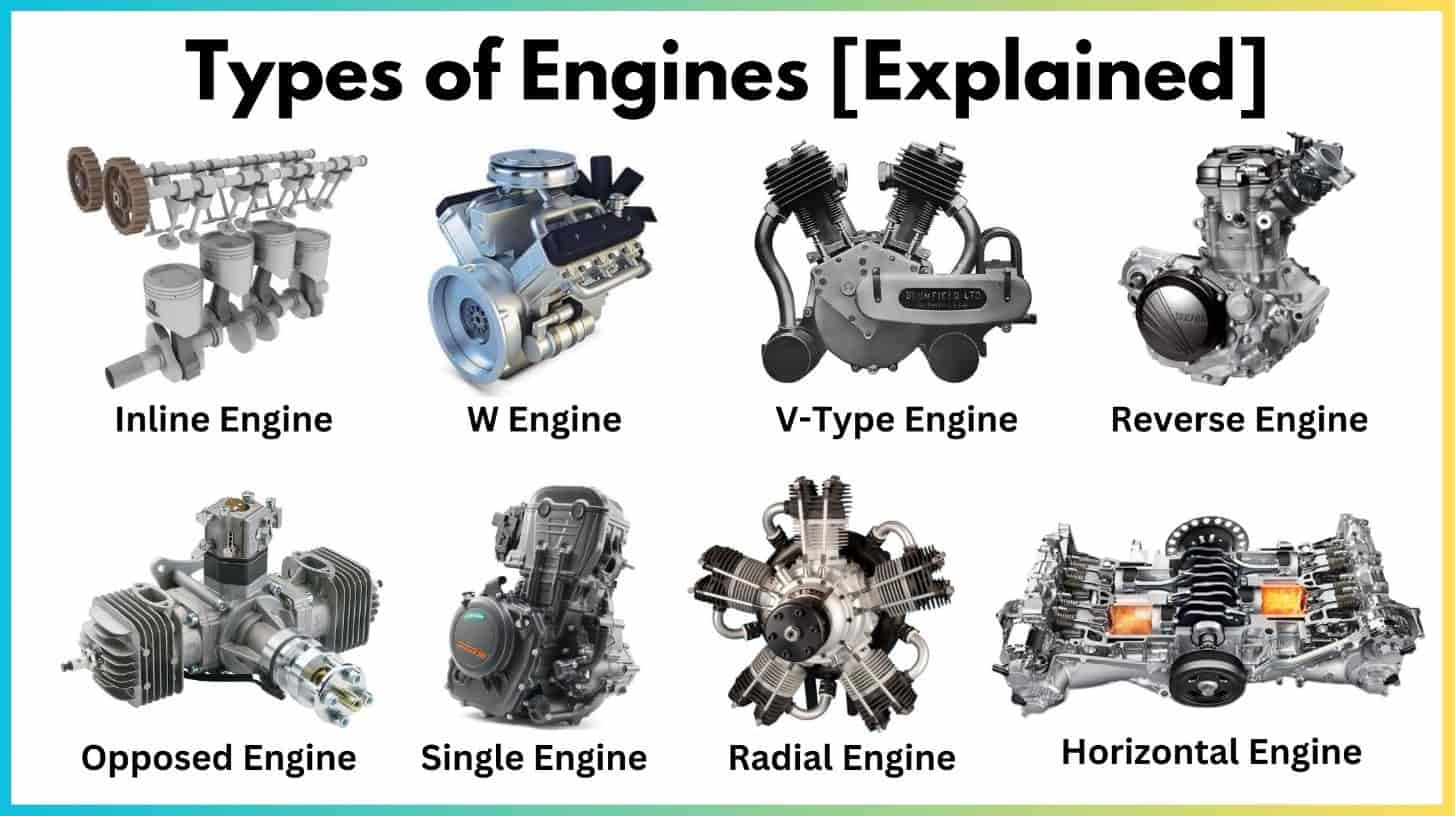
The global motors market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising automation, advancements in industrial technology, and expanding applications across automotive, manufacturing, and HVAC sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global electric motors market was valued at approximately USD 110 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028. Complementing this, Grand View Research reported that the global electric motor market size reached USD 131.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This accelerating demand is fueled by energy efficiency regulations, the proliferation of electric vehicles, and the integration of smart technologies in motor systems. As the industry evolves, a diverse range of motor types—including AC, DC, servo, stepper, and BLDC motors—has emerged to meet specialized performance requirements across applications. In this dynamic landscape, leading manufacturers are not only innovating in design and efficiency but also scaling production to cater to global industrial and consumer needs. Below is a data-driven look at the top 10 different kinds of motors and the key manufacturers shaping the future of motion control and electromechanical systems.
Top 10 Different Kinds Of Motors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Engines
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cummins.com
Key Highlights: We offer an expansive lineup of engine technologies, including diesel, natural gas, and alternative fuel engines….
#2 YASA Limited
Domain Est. 2000
Website: yasa.com
Key Highlights: YASA is at the forefront of eMotor innovation. Our axial flux technology motors are up to 4x more powerful than those used in most Electric Vehicles on the ……
#3 ABB Motors and Generators
Domain Est. 1990
Website: new.abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB offers a wide range of low voltage motors for the US market, designed to boost reliability, energy efficiency, and productivity across various industries….
#4 General Motors
Domain Est. 1992
Website: gm.com
Key Highlights: GM is home to Chevrolet, Buick, GMC & Cadillac and has been leading the auto industry for over a century. See how we create a vehicle for every drive….
#5 Baldor.com
Domain Est. 1995
Website: baldor.com
Key Highlights: Product Offering ; AC Motors · Brake Motors · Definite Purpose ; Servo Motors · AC Brushless Servo HDS Motors · Servo Gearboxes ; Large AC Motors · Large Induction ……
#6 NIDEC CORPORATION
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nidec.com
Key Highlights: This list contains a wide variety of products, ranging from ultra-small to ultra-large motors to mechatronics, optics, and electronics products….
#7 Commercial Trucks, Buses, Engines & Parts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: international.com
Key Highlights: Proud makers of trucks, buses, engines, parts, and history….
#8 DeLorean Motor Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: delorean.com
Key Highlights: DeLorean is a legacy mobility company focused on redefining human connections through creative technologies….
#9 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
#10 Maxon Motor
Domain Est. 2012
Expert Sourcing Insights for Different Kinds Of Motors

2026 Market Trends for Different Kinds of Motors
As technological advancements accelerate and global demand for energy efficiency grows, the electric motor market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Various types of motors—including AC motors, DC motors, stepper motors, servo motors, and emerging technologies like brushless DC (BLDC) and synchronous reluctance motors—are experiencing distinct shifts in demand, innovation, and application. This analysis explores the key market trends shaping the future of these motors across industries such as automotive, industrial automation, HVAC, robotics, and consumer electronics.
AC Motors: Continued Dominance with a Shift Toward Efficiency
Alternating Current (AC) motors, particularly induction and synchronous types, remain the backbone of industrial applications due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. By 2026, the AC motor market is expected to grow steadily, driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) IE4 and upcoming IE5 efficiency standards.
Induction motors will continue to dominate sectors like pumps, compressors, and conveyors, especially in emerging economies. However, there is a notable shift toward permanent magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance motors (PMa-SynRM) in high-efficiency applications. These hybrid designs offer the robustness of AC motors with improved power density and efficiency, aligning with global carbon reduction targets.
Regional growth in Asia-Pacific, particularly in China and India, will fuel demand due to expanding manufacturing and infrastructure development. Smart motor systems integrated with IoT and predictive maintenance capabilities are also becoming standard, enhancing operational efficiency and lifecycle management.
DC Motors: Niche Applications and Gradual Replacement
Direct Current (DC) motors, especially brushed types, are witnessing a gradual decline in many traditional applications due to maintenance requirements and lower efficiency compared to newer technologies. However, they remain relevant in niche markets such as automotive accessories (e.g., window lifts, wipers), toys, and low-cost industrial tools.
By 2026, the DC motor market will likely see modest growth, primarily sustained by legacy systems and cost-sensitive applications in developing regions. However, their share is expected to erode further as brushless alternatives become more affordable. The real shift lies in the transition from brushed DC to brushless DC (BLDC) motors, which offer superior efficiency, longer life, and quieter operation.
Brushless DC (BLDC) Motors: Rapid Growth Across Sectors
BLDC motors are one of the fastest-growing segments in the motor market. Their rise is fueled by demand for energy-efficient, compact, and controllable solutions in electric vehicles (EVs), drones, home appliances, and HVAC systems.
In the automotive sector, BLDC motors are increasingly used in electric power steering, cooling fans, and cabin air compressors. The global push toward electrification means that BLDC adoption in EVs and hybrid vehicles will surge by 2026. Similarly, in consumer electronics, BLDC motors are becoming standard in high-end appliances like refrigerators and washing machines due to variable speed control and reduced energy consumption.
Advancements in power electronics, such as integrated motor drivers and sensorless control algorithms, are reducing system costs and complexity, making BLDC motors more accessible across price-sensitive markets.
Stepper Motors: Precision in Automation and 3D Printing
Stepper motors maintain a strong presence in applications requiring precise position control, such as CNC machines, 3D printers, medical devices, and robotics. While their efficiency is lower than servo or BLDC motors, their open-loop control simplicity and cost-effectiveness keep them competitive in mid-precision tasks.
By 2026, the stepper motor market will benefit from growth in additive manufacturing and automation. Innovations such as closed-loop stepper systems (hybrid servo-steppers) are blurring the line between steppers and servos, offering better torque control and reduced overheating. These improvements will expand their use in industrial automation and robotics, particularly in small-scale and collaborative robots (cobots).
Servo Motors: High Performance in Advanced Automation
Servo motors—especially AC servo systems—are critical in high-precision, high-dynamic applications like robotics, semiconductor manufacturing, and automated assembly lines. The market for servo motors is expected to expand significantly by 2026, driven by the Industry 4.0 revolution and the increasing deployment of smart factories.
Advancements in digital communication protocols (e.g., EtherCAT, PROFINET) enable faster response times and tighter integration with control systems. Additionally, miniaturization and improved thermal management are allowing servo motors to be used in more compact and mobile robotic platforms. The integration of AI-driven motion control algorithms will further enhance their adaptability and precision.
Regional demand in North America and Europe will be strong due to advanced manufacturing ecosystems, while Asia-Pacific will remain the largest market, led by Japan, South Korea, and China’s robotics industries.
Emerging Motor Technologies: Synchronous Reluctance and Axial Flux Motors
Beyond conventional types, emerging motor technologies are gaining traction. Synchronous reluctance motors (SynRM) are being adopted in industrial and HVAC applications due to their high efficiency and lack of permanent magnets, which reduces dependency on rare-earth materials. By 2026, SynRM adoption will increase, especially as motor manufacturers seek to meet IE4/IE5 standards without the cost volatility of rare-earth magnets.
Axial flux motors, known for their high power density and compact design, are emerging in electric vehicles and aerospace. Companies like YASA and Magnax are commercializing axial flux technology, and by 2026, these motors are expected to capture a notable share in premium EVs and high-performance applications where space and weight are critical.
Conclusion: Convergence of Efficiency, Intelligence, and Electrification
By 2026, the motor market will be shaped by three overarching trends: the global push for energy efficiency, the integration of intelligence and connectivity, and the acceleration of electrification across transportation and industry. While traditional AC and DC motors will persist, the momentum is clearly shifting toward BLDC, servo, and emerging high-efficiency designs.
Manufacturers who invest in smart motor systems, predictive maintenance, and sustainable materials will lead the market. Meanwhile, regional dynamics and regulatory landscapes will continue to influence adoption rates, with Europe and North America focusing on sustainability, and Asia driving volume through industrial and consumer growth. Overall, the motor industry in 2026 will be smarter, cleaner, and more integrated than ever before.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Different Kinds of Motors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing electric motors—whether AC, DC, stepper, servo, or specialty types—can be fraught with challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps mitigate supply chain disruptions, legal exposure, and performance failures.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, lack robust quality management systems. This can result in motors with inconsistent torque, efficiency, or lifespan. Variability in materials (e.g., substandard copper windings or bearings) directly impacts motor reliability. Without third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, UL, CE), buyers risk receiving motors that fail prematurely or don’t meet performance specifications.
Misrepresentation of IP and Counterfeit Components
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or cloned motors. Some suppliers may falsely claim original design or patent ownership, when in fact they are replicating proprietary technology. This exposes the buyer to legal liability, especially if the motors are integrated into end products sold in IP-sensitive markets like the EU or North America.
Inadequate Protection Ratings (IP Ratings) Misleading Buyers
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating is critical for motors used in harsh environments. A common pitfall is suppliers inflating IP ratings (e.g., claiming IP67 when the motor only meets IP54). Without independent testing or verifiable documentation, buyers may deploy motors in applications where dust or moisture leads to rapid failure.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reliable motor sourcing requires full traceability of components and manufacturing processes. Many suppliers fail to provide essential documentation such as material certifications, test reports, or compliance records. This absence complicates quality audits, regulatory compliance, and root cause analysis in case of field failures.
Overlooking Long-Term Support and Spare Parts Availability
Some suppliers offer competitive pricing but lack the infrastructure for long-term support. This becomes a critical issue when maintenance, repairs, or spare parts are needed years after purchase. Motors with custom designs are especially vulnerable if the supplier discontinues production or goes out of business.
Insufficient Due Diligence on Supplier Capabilities
Buyers often focus on price and delivery time while neglecting to verify a supplier’s technical expertise, R&D capabilities, or production capacity. This can lead to sourcing motors that are not optimized for the intended application, resulting in inefficiencies or integration challenges.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, third-party inspections, clear contractual IP clauses, and performance validation through testing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Different Kinds of Motors
When transporting and managing motors across international or domestic supply chains, understanding the specific logistics and compliance requirements for each motor type is essential. This guide outlines key considerations for various motor categories to ensure safe, legal, and efficient handling.
AC Motors
Logistics Considerations:
AC motors, especially large industrial models, are heavy and often require specialized packaging and handling equipment. Secure crating and palletization are critical to prevent internal damage during transit. Climate-controlled environments may be necessary for sensitive components, particularly in humid or extreme temperature conditions.
Compliance Requirements:
AC motors must comply with energy efficiency regulations such as the IE (International Efficiency) classification under IEC 60034-30. In the U.S., DOE (Department of Energy) efficiency standards apply. CE marking is required for the European market, and motors may need to meet RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regulations. Documentation must include technical files, test reports, and declarations of conformity.
DC Motors
Logistics Considerations:
Smaller DC motors (e.g., brushed or brushless types used in electronics) are less bulky but sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD) and vibration. Anti-static packaging and cushioning materials are recommended. Lithium-powered DC motors (e.g., in electric vehicles or drones) may fall under dangerous goods regulations when shipped.
Compliance Requirements:
DC motors must meet electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) directives (e.g., EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU). For motors integrated into devices, compliance with end-product regulations (such as medical, automotive, or consumer electronics standards) may apply. Export controls may restrict certain high-performance or military-grade DC motors under ITAR or EAR regulations.
Servo Motors
Logistics Considerations:
Servo motors are precision instruments with delicate encoders and feedback systems. They require shock-resistant packaging and protection from moisture and dust. Transport should avoid extreme temperatures that could affect calibration. Air freight is often preferred for time-sensitive deliveries.
Compliance Requirements:
In addition to EMC and safety standards (e.g., IEC 61800 series), servo systems may need to comply with functional safety standards such as IEC 61508 or ISO 13849 for industrial automation applications. Export classification under ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) may apply due to high accuracy and control capabilities.
Stepper Motors
Logistics Considerations:
Stepper motors are generally less sensitive than servos but still require protection from physical shock and magnetic interference. Packaging should prevent shaft rotation during transport to avoid internal damage. Suitable for standard parcel shipping when properly packed.
Compliance Requirements:
Must comply with general electrical safety standards (e.g., UL, CSA, or CE). If used in medical or aerospace applications, additional sector-specific certifications are required. RoHS and REACH compliance is mandatory in the EU. No special export controls typically apply unless integrated into controlled systems.
Linear Motors
Logistics Considerations:
Linear motors often have long, fragile stator or forcer components that are prone to bending or misalignment. Custom wooden crates with internal bracing are recommended. Flatbed trucking or air cargo with careful loading procedures may be necessary. Avoid exposure to dust and debris.
Compliance Requirements:
Subject to industrial machinery directives (e.g., EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC) when integrated into systems. Must meet EMC and low-voltage directives. High-power models may require specific electrical installation certifications. Export controls may apply due to precision and performance characteristics.
Gear Motors
Logistics Considerations:
Gear motors combine motors with gearboxes, increasing weight and complexity. Oil leakage from gearbox units must be prevented; units should be stored and shipped in specified orientations. Use of absorbent materials and sealed containers is advised.
Compliance Requirements:
Compliance includes motor efficiency standards plus mechanical safety considerations. Gear lubricants may be subject to environmental regulations (e.g., EPA or EU chemical regulations). Complete units must meet regional safety certifications (e.g., UL, TÜV). Noise level standards (e.g., EU Noise Directive) may also apply.
Universal Motors
Logistics Considerations:
Commonly used in power tools and home appliances, these motors are compact but generate heat and require ventilation during operation. Transport in original packaging with impact protection is recommended. Avoid stacking heavy items on top.
Compliance Requirements:
Must comply with appliance-specific safety standards (e.g., UL 1012 for power tools). RoHS and WEEE compliance is required in Europe. EMC regulations apply due to high electrical noise generation. Energy labeling may be required depending on the end-use device.
General Compliance & Logistics Best Practices
- Packaging: Use ESD-safe, moisture-resistant, and shock-absorbent materials appropriate to motor size and sensitivity.
- Documentation: Maintain up-to-date technical documentation, test certificates, and compliance declarations (DoC).
- Labeling: Clearly mark motors with voltage, power rating, efficiency class, and compliance marks (CE, UL, etc.).
- Shipping: Classify motors correctly under HS codes for customs; declare any hazardous components (e.g., lubricants, batteries).
- Regulatory Monitoring: Stay updated with evolving regulations such as EU Ecodesign Directive, U.S. DOE rules, and international trade controls.
By aligning logistics strategies with compliance obligations for each motor type, businesses can minimize delays, avoid penalties, and ensure product reliability in global markets.
In conclusion, sourcing different kinds of motors requires a thorough understanding of the specific application requirements, performance specifications, and operational environment. Whether selecting AC motors, DC motors, stepper motors, servo motors, or specialized variants like brushless or gear motors, each type offers distinct advantages and limitations in terms of efficiency, control precision, power output, and cost. A successful sourcing strategy involves evaluating suppliers based on quality, reliability, technical support, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, considering factors such as energy efficiency, maintenance needs, scalability, and future compatibility ensures long-term performance and cost-effectiveness. By aligning motor selection with both technical demands and business objectives, organizations can optimize system performance, reduce downtime, and achieve sustainable operational success.