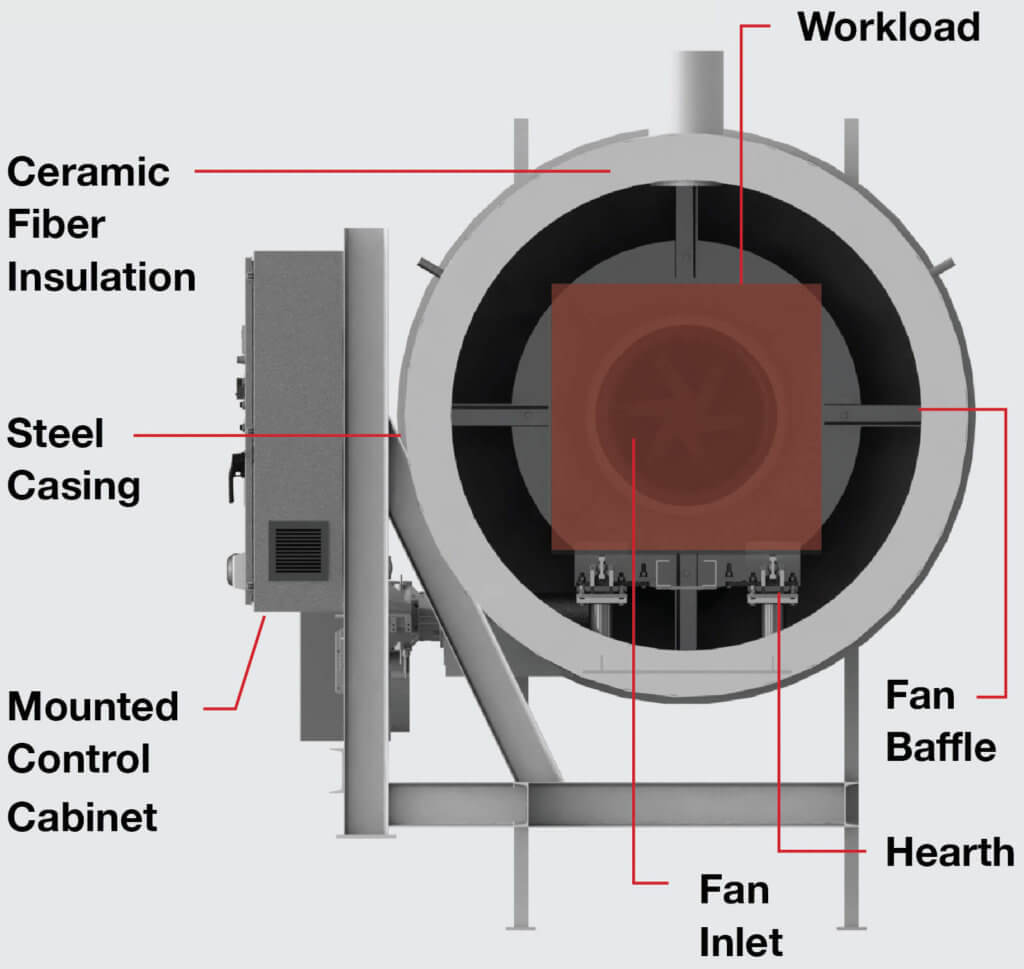
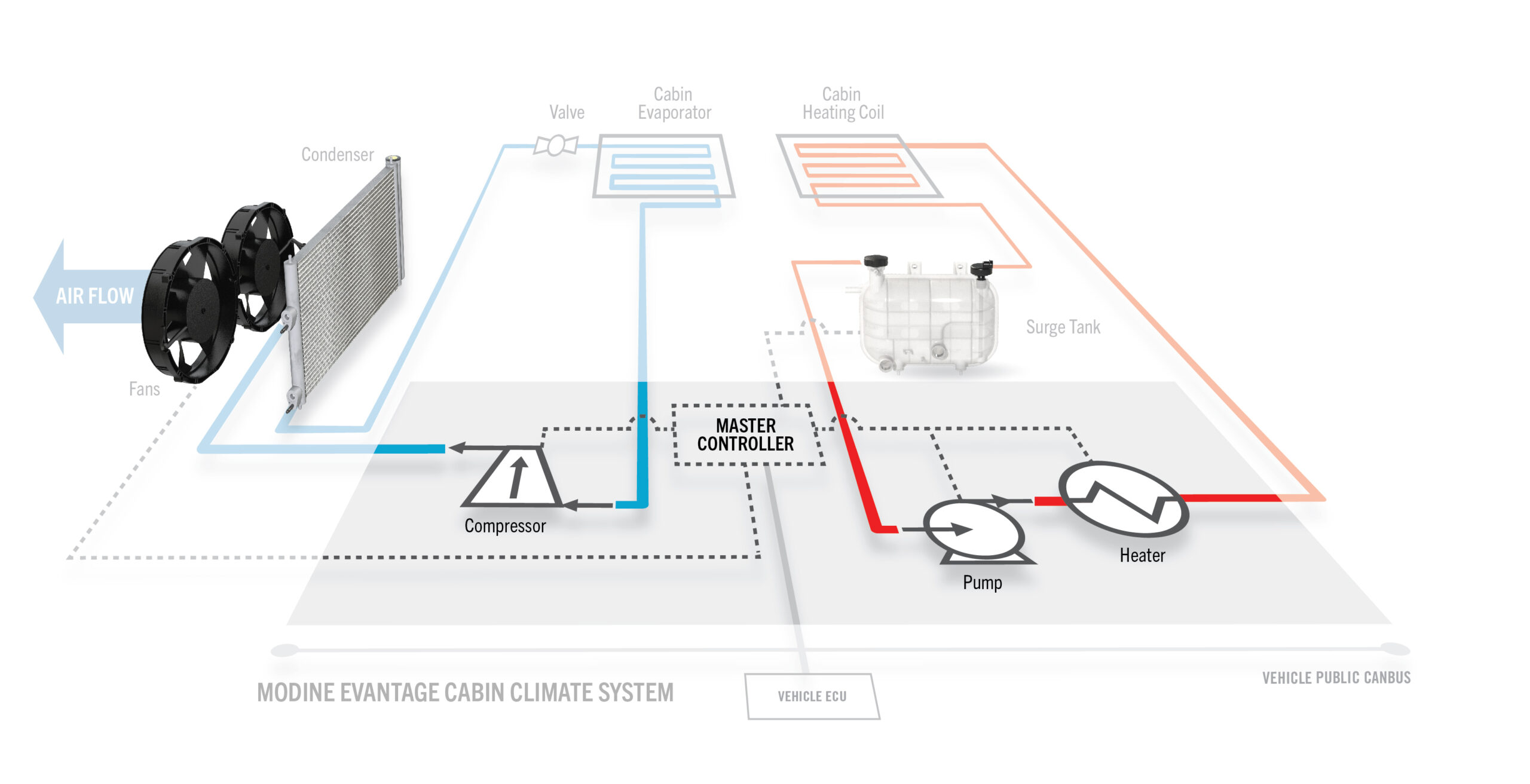
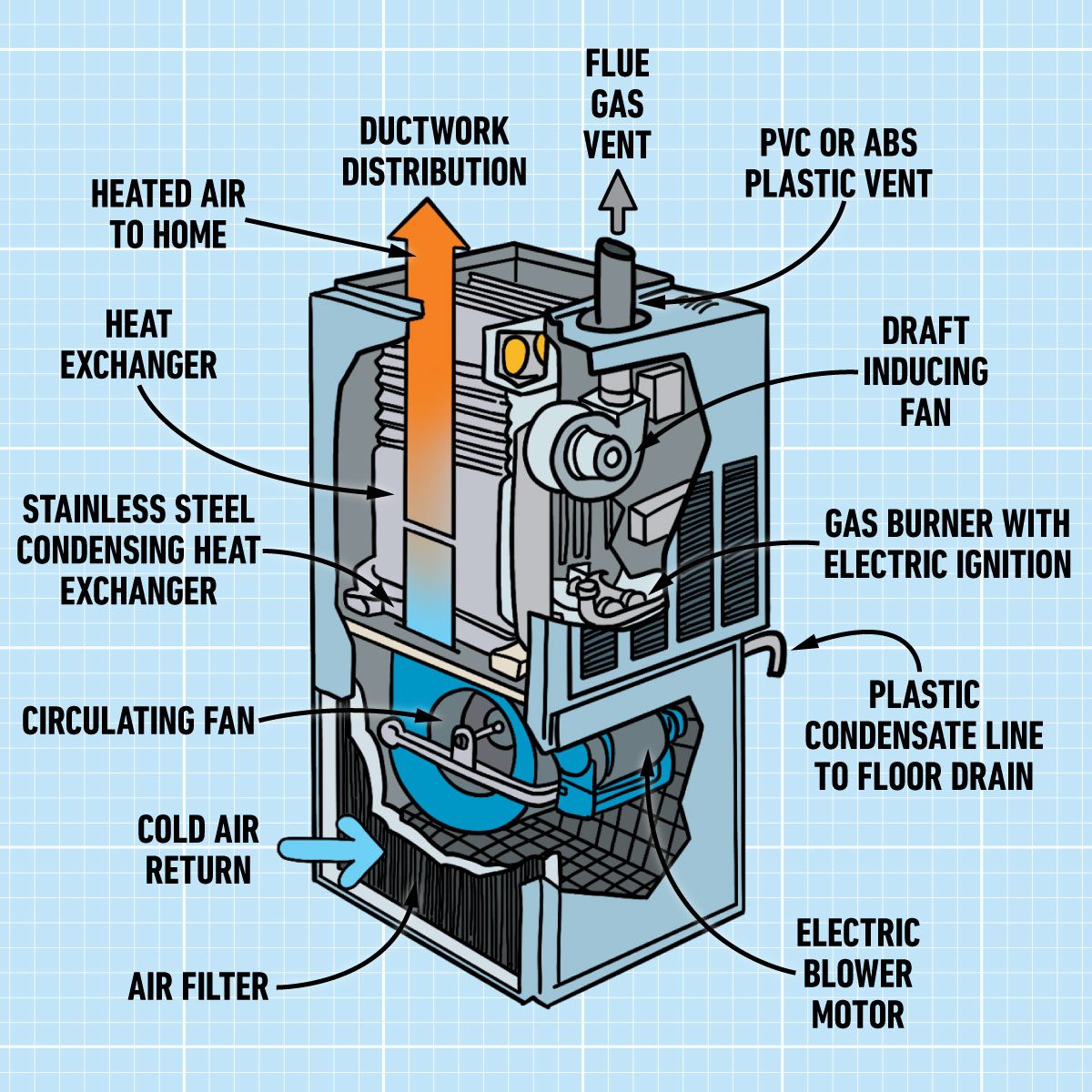
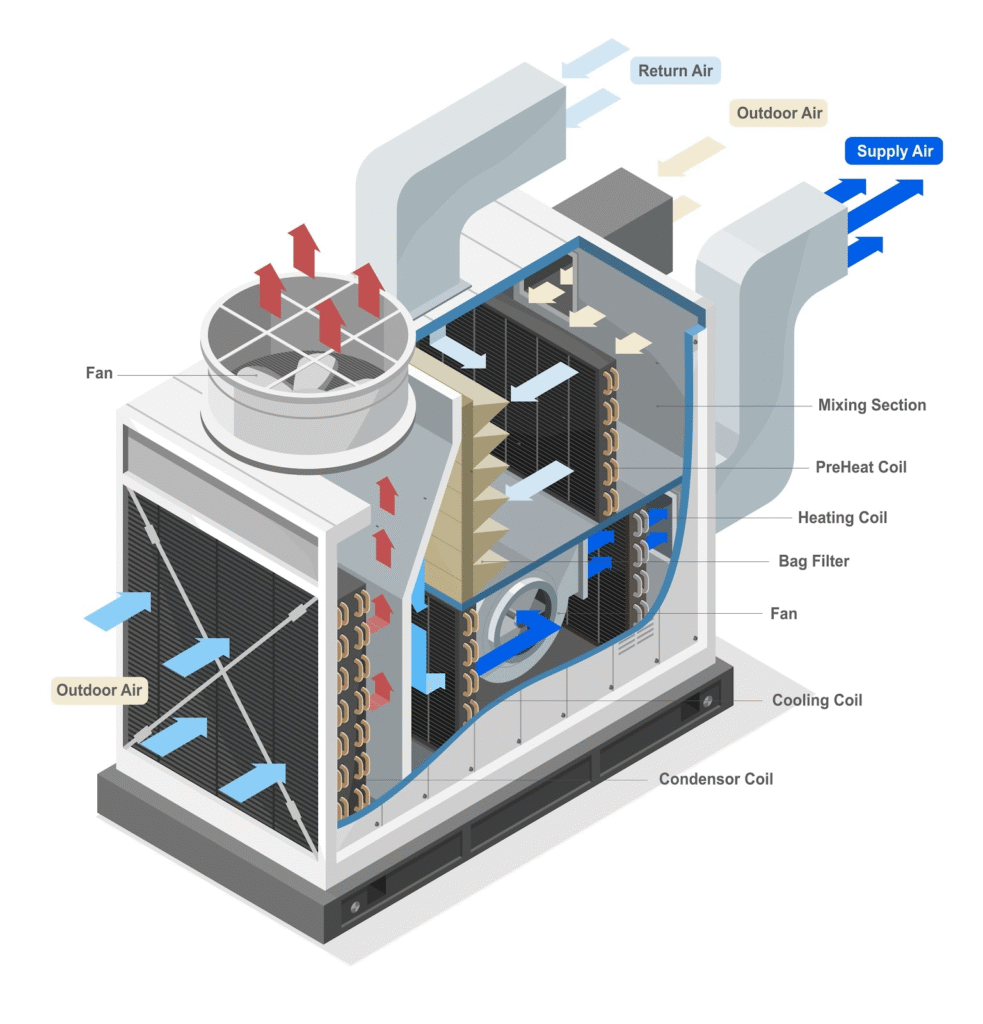
The global furnace manufacturing market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for advanced thermal processing equipment across industries such as steel, cement, glass, and advanced materials. According to Mordor Intelligence, the industrial furnace market was valued at USD 53.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising industrial automation, tighter regulatory standards for energy efficiency, and the adoption of smart manufacturing technologies. In parallel, Grand View Research highlights a growing emphasis on sustainable and low-emission furnace solutions, particularly in North America and Europe, further accelerating innovation among leading manufacturers. As industries prioritize precision, energy efficiency, and scalability, Diagram furnaces—known for their high-performance heating systems and customizable configurations—have emerged as critical assets in modern production environments. Below, we highlight the top 9 Diagram furnace manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape through technological excellence, global reach, and data-backed performance metrics.
Top 9 Diagram Furnace Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Surface Combustion
Domain Est. 1997
Website: surfacecombustion.com
Key Highlights: Surface® Combustion is the leading manufacturer of industrial heat treating furnaces for over 100 years, delivering furnaces that last….
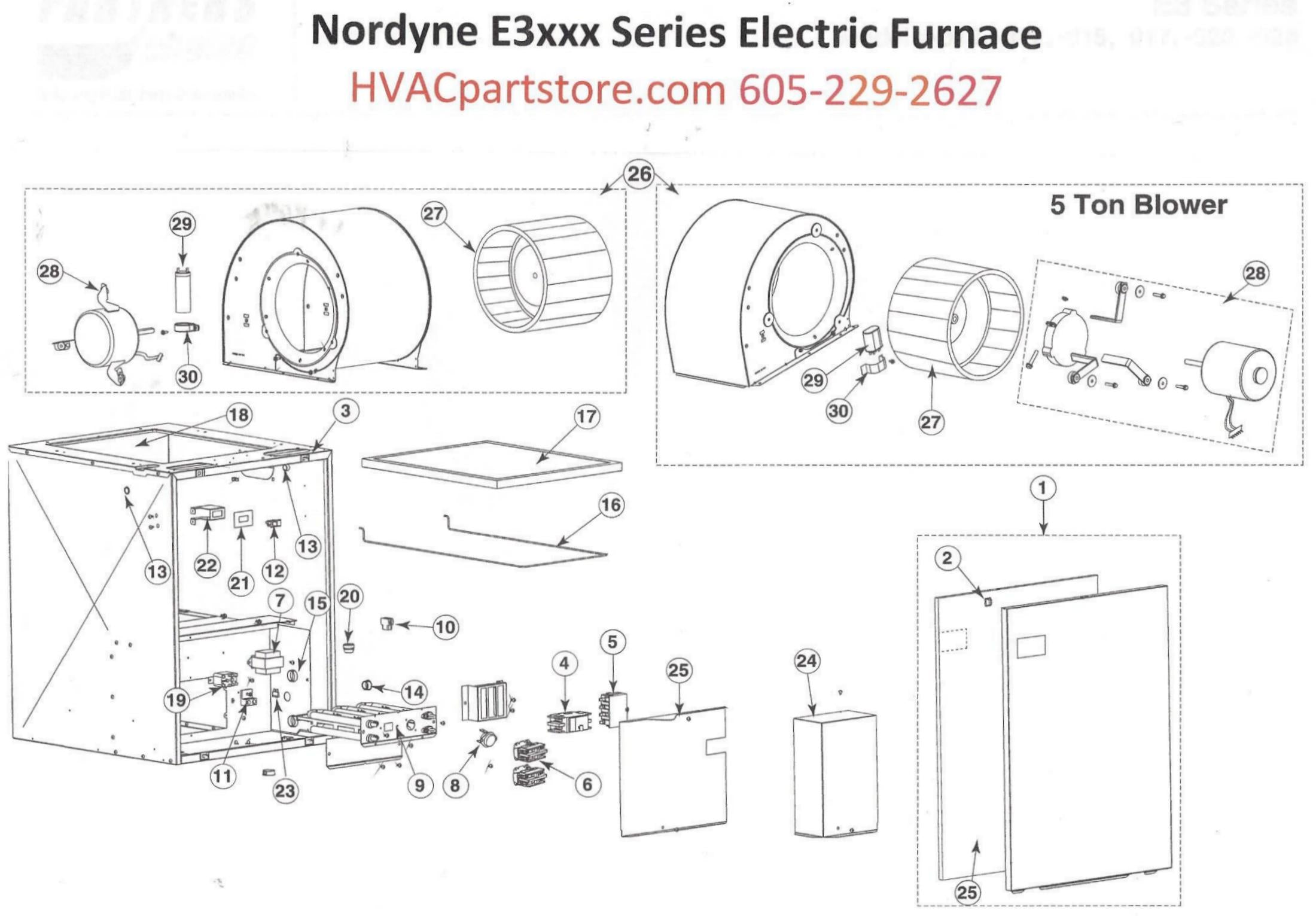
#2 Nordyne
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nordyne.com
Key Highlights: As the most trusted worldwide HVAC manufacturer, Nordyne manufactures top-tier heating and cooling equipment that distributors, contractors, and customers love….
#3 First Co.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: firstco.com
Key Highlights: First Co., an HVAC manufacturer in Dallas, specializes in innovative heating and cooling systems for residential, multi-occupant, and commercial ……
#4 Goodman: Air Conditioning and Heating Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: goodmanmfg.com
Key Highlights: Goodman Manufacturing offers a range of affordable air conditioning, packaged units, heat pumps and gas furnaces for residential heating and cooling needs….
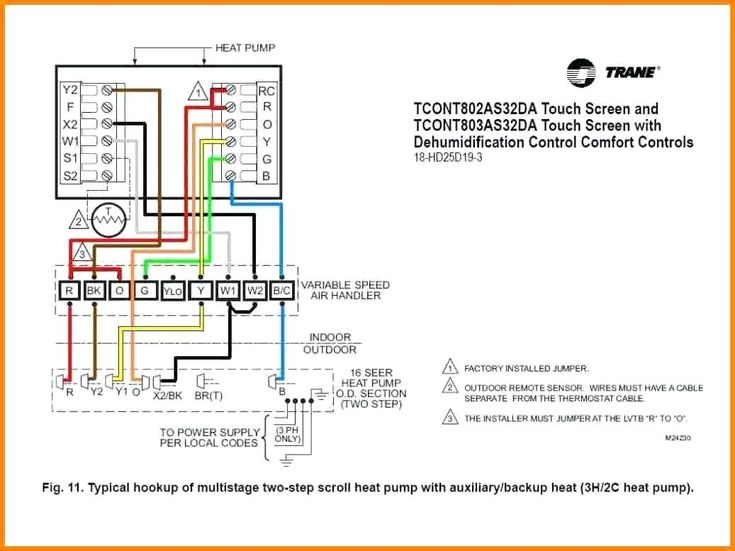
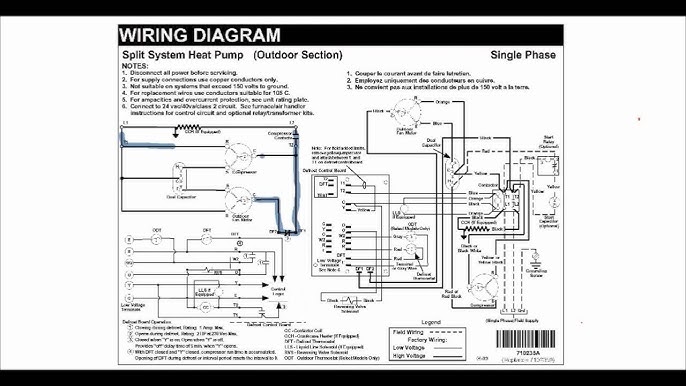
#5 How to Find Wiring Diagrams for HVAC Equipment
Domain Est. 2004
Website: justanswer.com
Key Highlights: To locate wiring diagrams, visit the manufacturer’s official website and navigate to the support or resources section. Use the model number ……
#6 Modine HVAC
Domain Est. 2008
Website: modinehvac.com
Key Highlights: We serve a variety of markets with products such as residential garage and workspace heat, commercial, industrial, classroom HVAC and indoor air quality, ……
#7 Rheem Manufacturing Company
Domain Est. 1995
Website: rheem.com
Key Highlights: Learn about Rheem’s innovative and efficient heating, cooling, and water heating solutions for homes and businesses….
#8 Furnace Parts And Their Functions
Domain Est. 1995
Website: carrier.com
Key Highlights: Furnace parts include the burner (ignites fuel), heat exchanger (transfers heat), blower motor (circulates air), flame sensor (detects the flame), thermostat ( ……
#9 HVAC
Domain Est. 1996
Website: heil-hvac.com
Key Highlights: Find the right heating and cooling solution for your home, backed by trusted local experts. Explore home comfort systems designed for performance, efficiency, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Diagram Furnace
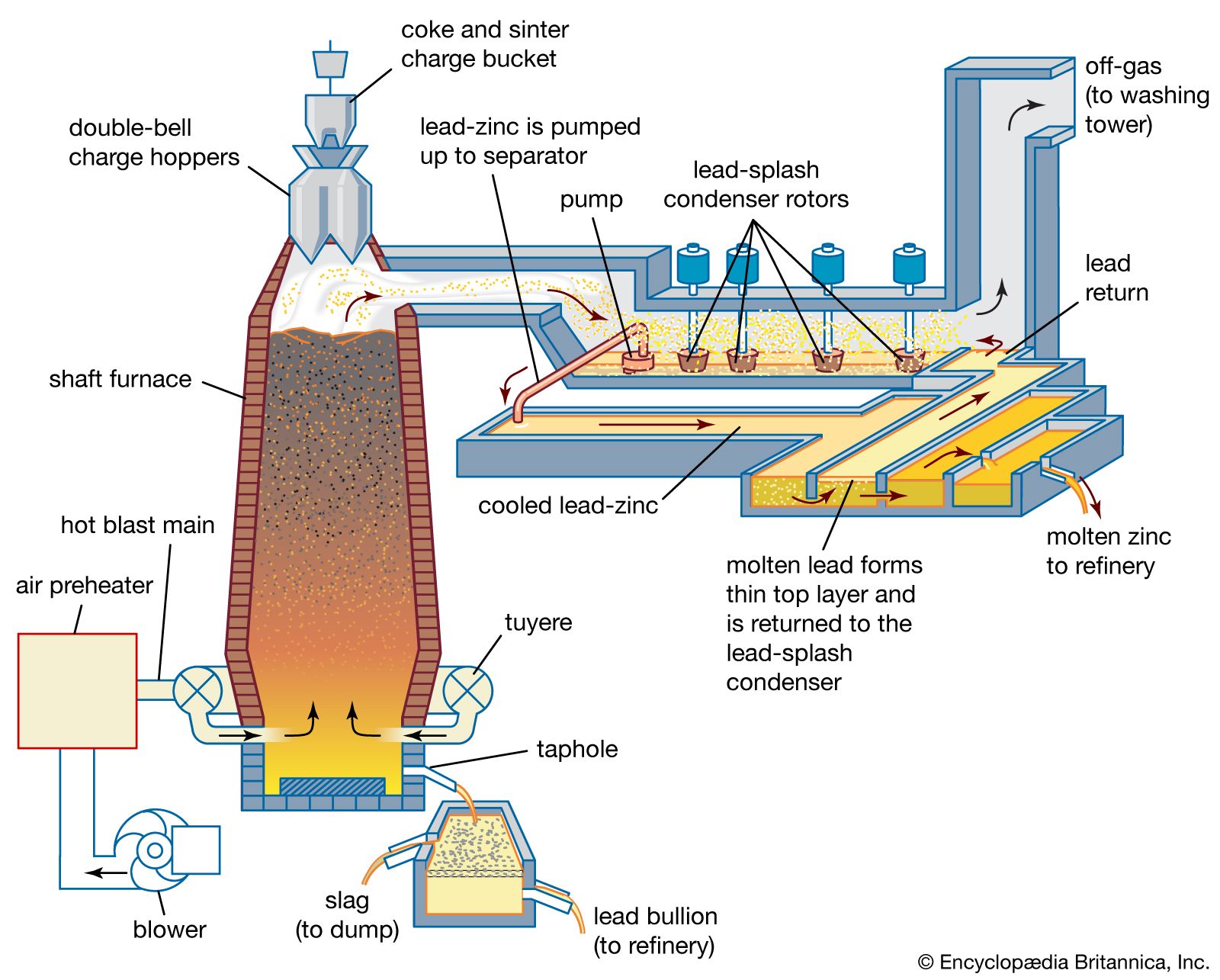
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Diagram Furnace
As we approach 2026, the market for Diagram Furnace—assuming this refers to industrial furnaces used in metallurgy, materials processing, or specialized manufacturing (e.g., in steel, glass, or semiconductor production)—is expected to undergo significant transformation driven by technological innovation, sustainability mandates, and evolving global demand. While “Diagram Furnace” may not be a widely recognized product category, the analysis assumes it represents advanced, data-integrated, or digitally optimized furnace systems that utilize diagrams or digital twins for monitoring and control.
-
Digitalization and Smart Manufacturing Integration
By 2026, industrial furnaces are increasingly embedded with IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and digital twin technology. Diagram Furnaces—those with real-time visual feedback systems and process mapping—will be central to smart factory ecosystems. These systems enable predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and process transparency through interactive diagrams that visualize heat distribution, material flow, and efficiency metrics. The integration with Industry 4.0 platforms is expected to boost adoption, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and high-tech manufacturing sectors. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Regulations
Stricter global carbon emission targets (e.g., EU Green Deal, U.S. Clean Energy Standards) are pushing manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient and low-carbon furnace technologies. Diagram Furnaces with built-in energy mapping capabilities will gain market traction by allowing operators to visualize thermal losses and optimize combustion processes. Hybrid and electric arc furnace systems, often paired with digital monitoring diagrams, are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of over 6% through 2026. -
Rise in Customization and Process-Specific Designs
Demand for specialized materials (e.g., high-purity alloys, advanced ceramics) is driving the need for customizable furnace solutions. Diagram Furnaces that support modular configurations and real-time simulation diagrams will be favored, enabling engineers to model and adjust parameters such as temperature gradients and dwell times before production. This trend is particularly strong in R&D and small-batch production environments. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Industrial growth in Southeast Asia, India, and Africa is fueling demand for cost-effective, reliable furnace systems. While large-scale traditional furnaces dominate, Diagram Furnaces offering remote diagnostics and simplified operational diagrams are becoming more accessible due to cloud-based interfaces and mobile integration. Localization of service and support networks will be key for market penetration. -
Increased Adoption in Renewable Energy and EV Supply Chains
The production of materials for electric vehicles (e.g., lithium-ion battery components, rare-earth magnets) and renewable infrastructure (e.g., silicon for solar panels) requires precise thermal processing. Diagram Furnaces capable of detailed process visualization and compliance reporting are expected to be critical in these high-growth industries, supporting quality control and traceability. -
Cybersecurity and Data Management Challenges
As Diagram Furnaces become more connected, concerns over data integrity and cyber threats will grow. By 2026, market leaders will differentiate themselves through secure, encrypted data pipelines and compliant data-logging features embedded in their diagrammatic interfaces—especially in regulated industries like defense and medical device manufacturing.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Diagram Furnace market will be shaped by the convergence of digital intelligence, sustainability, and industrial modernization. Companies investing in intuitive diagram-based interfaces, AI-enhanced analytics, and energy-efficient designs will lead the market. Success will depend on the ability to provide not just hardware, but integrated, data-rich solutions that enhance operational transparency and regulatory compliance across global supply chains.
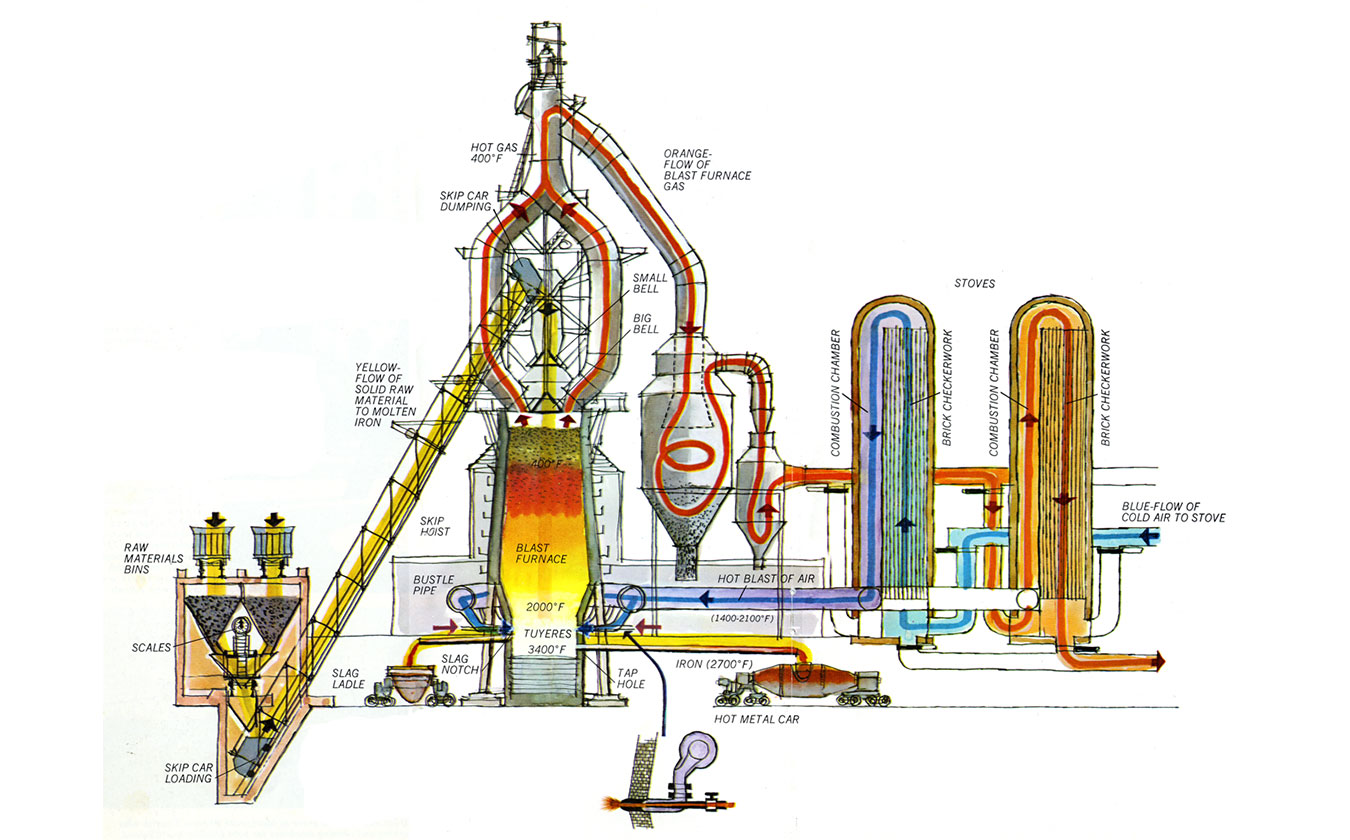
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Diagram Furnace: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a diagram furnace—often referring to a specialized high-temperature furnace used in research or industrial applications such as crystal growth, material synthesis, or thermal processing—can present significant challenges. Among the most critical concerns are ensuring product quality and safeguarding intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational failures, financial losses, or legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Temperature Uniformity and Control
A common issue is selecting a furnace that fails to maintain consistent temperature distribution across the heating zone. Poor temperature uniformity can compromise experimental reproducibility and product quality, especially in sensitive processes like semiconductor or optical crystal growth. Buyers may assume specifications are accurate without requesting third-party validation or test reports.
2. Substandard Materials and Construction
Low-cost suppliers may use inferior heating elements, insulation, or chamber materials that degrade quickly under high temperatures or reactive atmospheres. This compromises furnace lifespan, safety, and performance. For example, using non-vacuum-rated seals or subpar refractory materials can lead to contamination or system failure.
3. Lack of Certification and Compliance
Purchasing from manufacturers without proper certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, UL) increases the risk of receiving non-compliant equipment. This is particularly critical in regulated industries where traceability and safety standards are mandatory. Uncertified systems may also pose safety hazards such as electrical faults or gas leaks.
4. Insufficient After-Sales Support and Documentation
Many suppliers—especially smaller or overseas vendors—fail to provide comprehensive technical documentation, calibration records, or accessible customer support. This makes troubleshooting, maintenance, and validation difficult, leading to extended downtime and increased operational costs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Reverse Engineering and Design Copying
When working with custom-designed diagram furnaces, there is a risk that suppliers—particularly in regions with weaker IP enforcement—may copy or reverse-engineer proprietary furnace designs, control algorithms, or process configurations. This can result in unauthorized replication and loss of competitive advantage.
2. Inadequate Contractual IP Protection
Purchase agreements may lack clear clauses assigning ownership of custom designs or modifications. Without explicit IP transfer or non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), the buyer may inadvertently relinquish rights to their innovations or expose sensitive process parameters to the supplier.
3. Embedded Software and Control Systems
Modern diagram furnaces often include proprietary software for temperature profiling, data logging, or automation. Sourcing from untrusted vendors may introduce software with hidden backdoors, licensing issues, or undocumented features that compromise data integrity or expose process IP.
4. Data and Process Leakage Through Connected Systems
Smart furnaces connected to networks or cloud platforms may transmit operational data. If not properly secured, this data—especially when correlated with unique heating profiles—can reveal sensitive information about material formulations or manufacturing processes.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site audits and reference checks.
- Require performance validation reports and factory acceptance tests (FAT).
- Specify material grades, component origins, and compliance standards in procurement contracts.
- Engage legal counsel to draft robust IP agreements, including NDAs and IP assignment clauses.
- Limit the exposure of proprietary process details during procurement discussions.
- Use secure, isolated control systems and avoid cloud connectivity unless necessary and encrypted.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable furnace performance while protecting their technological investments.
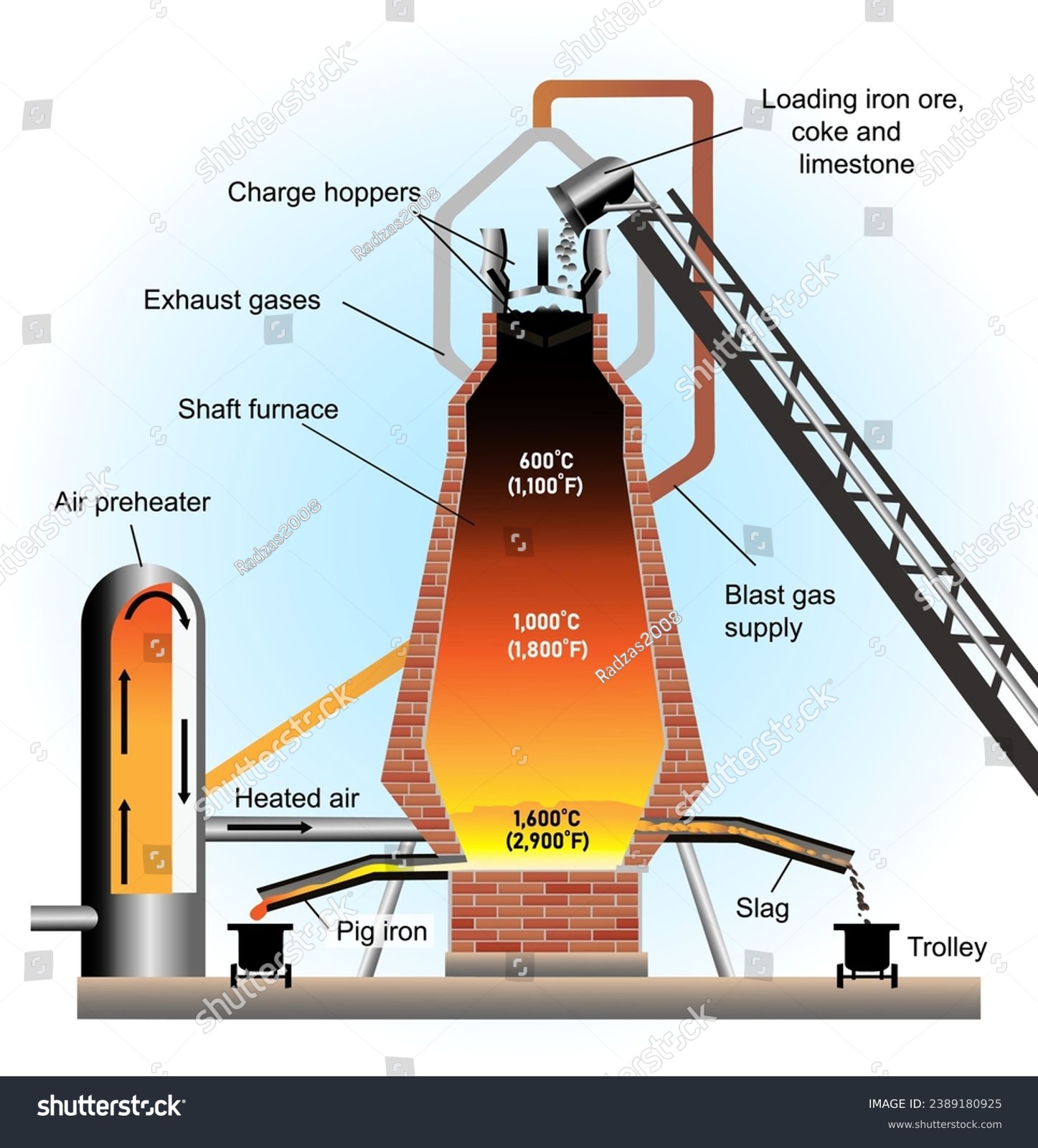
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Diagram Furnace
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and lawful handling, transportation, and operation of the Diagram Furnace. Adherence to these protocols ensures personnel safety, regulatory compliance, environmental protection, and operational continuity.
Regulatory Compliance
All operations involving the Diagram Furnace must comply with applicable local, national, and international regulations. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with emissions standards (e.g., EPA, EU Industrial Emissions Directive) is mandatory. Regular monitoring and reporting of particulate matter, NOx, SOx, and CO₂ emissions are required.
- Workplace Safety Standards: The furnace must adhere to OSHA (or equivalent) safety requirements, including machine guarding, lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, and thermal hazard controls.
- Electrical Codes: Installation and maintenance must follow NEC (National Electrical Code) or IEC standards to prevent electrical hazards.
- Pressure Equipment Directive (if applicable): If the furnace includes pressurized components, compliance with PED 2014/68/EU or ASME Section VIII is required.
- Hazardous Materials Handling: Proper documentation and handling procedures must be maintained for any fuels (e.g., natural gas, hydrogen) or byproducts (e.g., slag, dust).
Transportation & Handling
Proper logistics planning is critical for the safe delivery and installation of the Diagram Furnace.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection: Conduct a full mechanical and electrical inspection prior to shipment. Document integrity of refractory lining, electrical connections, and control systems.
- Packaging & Crating: The furnace must be securely crated with shock-absorbing materials. Critical components (e.g., thermocouples, control panels) should be packed separately and labeled.
- Transportation Mode: Coordinate via flatbed truck or containerized shipping based on size and destination. Ensure route planning avoids low bridges and weight-restricted roads.
- Lifting & Rigging: Use certified lifting equipment and follow manufacturer-specified lifting points. A qualified rigger must supervise all lifting operations.
- Site Receiving Protocol: Verify foundation dimensions, utility connections (gas, power, cooling water), and clear access pathways prior to delivery.
Installation & Commissioning
Installation must follow the manufacturer’s specifications and engineering drawings.
- Foundation Requirements: The furnace must be installed on a vibration-dampened, level foundation capable of supporting its operational weight (including thermal expansion).
- Utility Connections: Connect gas lines with leak-tested fittings; electrical supply must match voltage, phase, and grounding requirements; cooling systems must be flushed and pressure-tested.
- Alignment & Calibration: Perform laser alignment of rotating components (if applicable) and calibrate temperature sensors and control systems.
- Commissioning Checklist: Execute a step-by-step startup procedure, including dry run, low-heat burn-in, and gradual ramp-up to operating temperature. Document all parameters.
Operational Compliance
Ongoing compliance during operation is essential for safety and regulatory adherence.
- Permitting: Maintain valid operating permits, including air quality, wastewater discharge (if applicable), and fire safety certifications.
- Emissions Monitoring: Install continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS) and conduct quarterly third-party audits.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Follow a preventive maintenance program aligned with manufacturer guidelines. Log all refractory repairs, burner servicing, and control system updates.
- Personnel Training: Operators must be trained in emergency shutdown procedures, PPE usage (heat-resistant suits, face shields), and hazard communication (GHS labels).
Waste & Byproduct Management
Address all waste streams generated during furnace operation.
- Slag & Dust Collection: Collect and store furnace slag and particulate matter in sealed, labeled containers. Dispose of through licensed hazardous waste handlers if classified as such.
- Spent Refractories: Recycle or dispose of refractory materials per environmental regulations (e.g., TCLP testing for leachability).
- Recordkeeping: Maintain logs of waste generation, manifests, and disposal certificates for a minimum of five years.
Emergency Preparedness
Implement robust emergency response protocols.
- Fire Suppression: Equip the area with Class D (metal fire) extinguishers and automatic suppression systems.
- Gas Leak Response: Install combustible gas detectors with alarms. Establish evacuation routes and emergency shutoff valves.
- Spill Containment: Provide bunding or containment systems for fuel lines and coolant reservoirs.
- Incident Reporting: All incidents (leaks, overheating, injuries) must be reported immediately and investigated per OSHA or local requirements.
Documentation & Audits
Maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance.
- Required Documents:
- Equipment manuals and CE/UL markings
- Risk assessments and method statements
- Maintenance logs and calibration records
- Training certificates and safety data sheets (SDS)
- Environmental permits and emissions reports
- Internal Audits: Conduct biannual compliance audits to verify adherence to this guide and regulatory standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Schedule annual inspections by certified professionals for pressure systems, electrical safety, and environmental compliance.
Failure to follow this guide may result in safety incidents, regulatory penalties, or operational shutdowns. All personnel must review and acknowledge understanding of these procedures.
Conclusion for Sourcing Diagram: Furnace
In conclusion, the sourcing diagram for the furnace highlights a well-structured and strategic procurement process that ensures the reliable acquisition of critical components and materials necessary for furnace manufacturing or operation. Key elements such as raw material suppliers, equipment manufacturers, logistics partners, and quality control checkpoints are systematically integrated to maintain efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. By identifying and evaluating each stage of the supply chain—from refractory materials and metal alloys to control systems and energy sources—organizations can mitigate risks, enhance supplier relationships, and ensure consistent product performance. Effective sourcing ultimately supports operational excellence, regulatory compliance, and sustainability goals in industrial furnace applications. Continuous monitoring and optimization of the sourcing network will further strengthen resilience and adaptability in a dynamic market environment.