The global market for penetration testing and cybersecurity solutions has experienced robust growth, driven by escalating cyber threats, increasing digital transformation, and stringent regulatory requirements. According to Grand View Research, the global penetration testing market size was valued at USD 1.48 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.5% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts continued momentum, citing enterprise demand for proactive security assessments and the rising adoption of cloud infrastructure as key growth accelerators. Within this expanding landscape, manufacturers specializing in deeper penetration meaning—referring to advanced tools and methodologies that simulate sophisticated cyberattacks to uncover hidden vulnerabilities—are emerging as critical players. These organizations go beyond surface-level scans, offering intelligent, context-aware solutions that emulate real-world threat actors. As cyber resilience becomes a boardroom priority, the top nine manufacturers in this niche are distinguishing themselves through innovation, depth of analysis, and comprehensive remediation guidance—meeting the evolving needs of industries from finance to healthcare to critical infrastructure.
Top 9 Deeper Penetration Meaning Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 About Company
Website: ghostshield.com
Key Highlights: Smaller particles means deeper penetration and deeper penetration means better protection. With a rich history in underground waterproofing and a direct ……
#2 SoftWave Therapy
Website: softwavetrt.com
Key Highlights: Deeper penetration. Greater comfort. Proven results. SoftWave Gold Li-Series. Start with a spark producing a TRUE shockwave. Orthopedic indications ……
#3 Candela Medical
Website: candelamedical.com
Key Highlights: … deeper penetration and faster treatments. As the only vascular laser FDA-cleared for pediatric treatments, Vbeam Pro delivers the power of 595 nm with the ……
#4 Deep Penetration of a PDT Drug into Tumors by Non
Website: pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Key Highlights: In this paper, a non-covalent PDT cancer drug-gold nanoparticle (Au NP) conjugate system performed a rapid drug release and deep penetration of the drug into ……
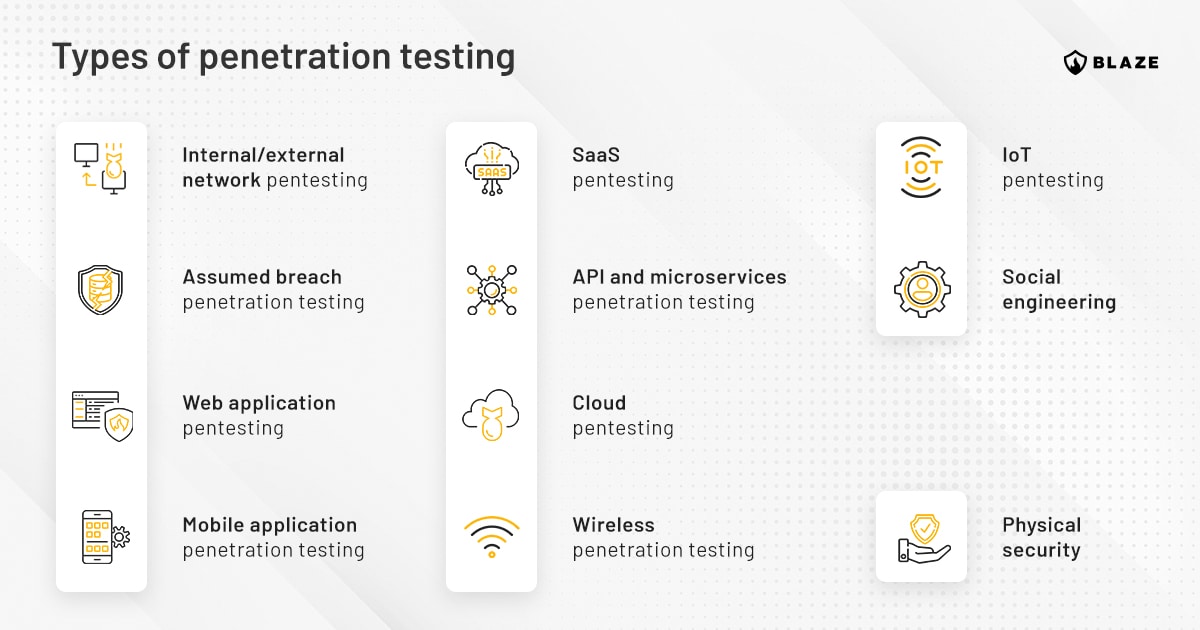
#5 What Are The Different Types Of Penetration Testing?
Website: purplesec.us
Key Highlights: The different types of penetration testing include network services, web application, client side, wireless, social engineering, and physical….
#6 Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
Website: earthdata.nasa.gov
Key Highlights: Background information on synthetic aperture radar, with details on wavelength and frequency, polarization, scattering mechanisms, and interferometry….
#7 Top Penetration Testing Vendors in 2025
Website: deepstrike.io
Key Highlights: A penetration testing vendor or service provider is a company that specializes in probing your IT systems for security weaknesses using ethical ……
#8 PENETRATION definition in American English
Website: collinsdictionary.com
Key Highlights: 1. a. the act, power, or an instance of penetrating b. the act or an instance of inserting the penis into the vagina or anus 2. the depth to which something ……
#9 Nuburu Blue Laser Company
Website: nuburu.net
Key Highlights: For welding that means faster processing speed, deeper weld penetration, or both. You may not need to know the design details, but you need the end result: ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Deeper Penetration Meaning

H2: Emerging Market Trends Shaping Deeper Penetration Meaning by 2026
By 2026, the concept of “deeper penetration” is evolving beyond traditional market share metrics to signify a more holistic, data-driven, and customer-centric approach to business expansion. Across industries, deeper penetration now reflects not just how widely a product or service is adopted, but how deeply it is embedded into customer workflows, behaviors, and ecosystems. Several key trends are driving this transformation:
1. Hyper-Personalization Through AI and Predictive Analytics
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are enabling businesses to deliver hyper-personalized experiences at scale. By analyzing vast datasets—from purchase history to behavioral patterns—companies can anticipate needs and deliver targeted solutions. This predictive engagement fosters deeper emotional and functional integration with consumers, translating into stronger brand loyalty and sustained usage.
2. Ecosystem Integration Over Standalone Products
The focus is shifting from selling discrete products to embedding offerings within broader digital ecosystems. In sectors like fintech, health tech, and smart home devices, deeper penetration means seamless integration with other platforms and services. For example, a fitness app that syncs with wearables, nutrition trackers, and insurance programs achieves far deeper user engagement than a standalone tool.
3. Expansion into Underserved and Rural Markets
Global market strategies are increasingly prioritizing geographic and demographic inclusivity. Enabled by mobile connectivity and localized digital infrastructure, companies are achieving deeper penetration in emerging economies and rural regions. This trend is particularly evident in mobile banking in Africa and agritech in South Asia, where tailored, low-cost models drive widespread adoption.
4. Subscription and Usage-Based Monetization Models
Recurring revenue models are reinforcing deeper customer relationships. By aligning business success with ongoing customer value, subscription and usage-based pricing ensure continuous engagement. This shift is prominent in SaaS, streaming services, and mobility platforms, where retention and usage frequency are key performance indicators.
5. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations Influencing Trust
As businesses strive for deeper market penetration, consumer trust is becoming a critical enabler. Regulations around data privacy (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) and ethical AI use are shaping how companies collect and use customer data. Transparent practices and ethical frameworks are no longer optional—they are essential for achieving sustainable, long-term penetration.
6. Convergence of Physical and Digital Channels
Omnichannel strategies are blurring the lines between online and offline experiences. Retail, healthcare, and education sectors are leveraging digital tools to enhance physical interactions, creating more immersive and seamless customer journeys. This hybrid approach increases touchpoints and deepens user engagement.
In summary, by 2026, deeper penetration will be defined not by reach alone, but by relevance, integration, and resilience in customer relationships. Businesses that prioritize value creation, ethical engagement, and ecosystem synergy will lead in achieving true market depth.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing for Deeper Penetration Meaning (Quality, IP)
When sourcing for deeper penetration—aiming to secure not just cost savings but strategic advantages in quality, innovation, and intellectual property (IP) protection—organizations often encounter critical pitfalls. Overlooking these can undermine long-term competitiveness and value creation.
Overemphasizing Cost Reduction at the Expense of Quality
A primary misstep is prioritizing immediate cost savings over sustained quality. Suppliers offering the lowest bids may cut corners, use substandard materials, or lack robust quality management systems. This can lead to product defects, recalls, and reputational damage, ultimately increasing total cost of ownership.
Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier Capabilities
Many organizations fail to conduct thorough assessments of a supplier’s technical expertise, production processes, and quality control measures. Without verifying certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), process maturity, or track records, firms risk partnering with suppliers unable to deliver consistent, high-quality outputs.
Poorly Defined or Protected Intellectual Property Rights
Sourcing from external partners—especially in innovation-driven industries—introduces significant IP risks. A common pitfall is failing to clearly define IP ownership in contracts. Ambiguities about who owns improvements, designs, or process innovations can lead to disputes, loss of proprietary advantage, or even enable suppliers to leverage your IP for competitors.
Lack of Supplier Collaboration and Transparency
Deep penetration requires trust and collaboration. Treating suppliers as mere vendors rather than strategic partners limits access to their insights and innovation potential. Without open communication and shared goals, opportunities for joint quality improvements or co-development of IP-rich solutions are missed.
Insufficient Monitoring and Performance Management
Once a supplier is onboarded, ongoing oversight is essential. Many organizations neglect continuous quality audits, performance benchmarking, or real-time data sharing. This lack of monitoring can allow quality drift or IP vulnerabilities to go undetected until significant damage occurs.
Underestimating Geopolitical and Regulatory Risks
Global sourcing exposes firms to varying legal standards for quality and IP protection. Partnering with suppliers in jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement or inconsistent regulatory oversight increases the risk of counterfeiting, data leaks, and compliance failures.
Conclusion
To achieve deeper penetration in sourcing, organizations must shift from transactional thinking to strategic partnership models. Avoiding these pitfalls requires a balanced focus on quality assurance, rigorous IP safeguards, continuous collaboration, and proactive risk management across the supply chain.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for “Deeper Penetration” Meaning
When discussing the term “deeper penetration” in a professional context—particularly within logistics, supply chain management, or international trade—it is essential to clarify its meaning to avoid ambiguity, especially since the phrase can be misinterpreted due to its literal or colloquial connotations. In business and logistics, “deeper penetration” typically refers to increased market reach, expanded operational presence, or enhanced integration into a market or system. Below is a guide to ensure proper usage, compliance, and clarity when applying this term in logistics contexts.
Understanding “Deeper Penetration” in Logistics
In logistics and supply chain operations, “deeper penetration” commonly describes:
- Market Penetration: Expanding distribution networks into new geographic regions or customer segments.
- Supply Chain Integration: Strengthening relationships with suppliers, distributors, or partners to improve efficiency and responsiveness.
- Technology Adoption: Implementing advanced systems (e.g., IoT, AI, blockchain) more thoroughly across logistics operations.
- Regulatory Access: Gaining stronger compliance footholds in regulated markets, enabling smoother cross-border operations.
Example:
“By establishing regional hubs in Southeast Asia, the company achieved deeper penetration into emerging markets, reducing delivery times by 30%.”
Compliance and Professional Communication
To maintain professionalism and ensure compliance with corporate communication standards:
- Use Clear, Context-Specific Language
Always define or contextualize “deeper penetration” to prevent misunderstandings. Replace with more precise terms when possible: - Instead of: “We aim for deeper penetration.”
-
Use: “We aim to expand market presence in Tier-2 cities” or “Enhance supply chain integration with local vendors.”
-
Avoid Ambiguity in Documentation
In contracts, reports, or compliance filings, choose unambiguous language. Regulatory bodies and international partners value clarity and transparency. -
Train Teams on Professional Terminology
Conduct training sessions to guide employees on appropriate terminology in logistics reporting, client communications, and internal strategy discussions. -
Review Communications for Cultural Sensitivity
In global logistics operations, certain phrases may carry unintended meanings in different languages or cultures. Use neutral, universally understood business terms.
Best Practices for Logistics Strategy Development
When strategizing for greater market or operational reach:
- Set Measurable Goals: Define penetration in terms of market share, delivery coverage, or partner network size.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Verify that expansion efforts adhere to local trade laws, customs regulations, and data privacy standards.
- Leverage Technology: Use analytics to assess penetration success and identify growth opportunities.
- Monitor Risks: Evaluate geopolitical, logistical, and compliance risks associated with entering new markets.
Conclusion
“Deeper penetration” in logistics signifies strategic growth and integration—not a literal or informal expression. By using precise language, maintaining compliance, and focusing on measurable objectives, logistics professionals can communicate effectively and responsibly. Always prioritize clarity and professionalism to support global operations and stakeholder trust.
A conclusion for “sourcing deeper penetration” would depend on the context—whether it’s in market expansion, research, strategic procurement, or another field. However, assuming the context is business strategy or market sourcing, here’s a well-rounded conclusion:
Conclusion:
Sourcing deeper penetration signifies moving beyond surface-level engagement to establish stronger, more strategic footholds within a market, supply chain, or customer segment. It involves not only acquiring new suppliers or entering new regions but also fostering long-term relationships, enhancing value creation, and unlocking hidden opportunities through detailed analysis and localized insight. Ultimately, deeper penetration in sourcing leads to improved resilience, cost efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage. Organizations that prioritize depth over breadth are better positioned to adapt to disruptions, drive sustainable growth, and achieve long-term success in an increasingly complex global landscape.
Let me know if you’re referring to a different context (e.g., research, military, or technical fields) for a more tailored conclusion.