The global deep penetration welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-strength, precision welding in industries such as automotive, heavy machinery, shipbuilding, and energy. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial welding equipment market was valued at USD 27.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030, with deep penetration techniques like laser and plasma arc welding gaining traction due to their superior weld quality and efficiency. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a CAGR of over 5.5% for the welding equipment market through 2028, citing automation and advancements in high-power density welding technologies as key growth enablers. As manufacturers strive for greater throughput and structural integrity, the adoption of deep penetration welding systems—capable of achieving full-thickness fusion in a single pass—has become a strategic priority. In this competitive landscape, a select group of innovators are leading the charge in technology, reliability, and global reach. Here’s a data-informed look at the top 10 deep penetration welding manufacturers shaping the future of advanced manufacturing.
Top 10 Deep Penetration Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
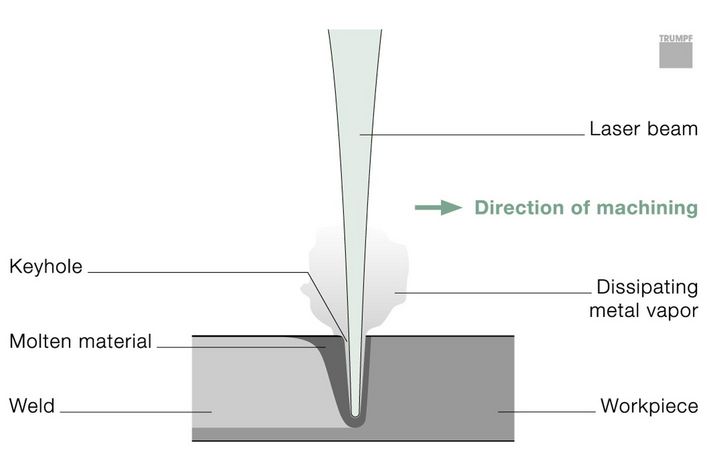
#1 Deep penetration welding
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: This process is used in applications requiring deeper welds or where several layers of material have to be welded simultaneously….
#2 Fronius welding machines and welding equipment
Website: fronius.com
Key Highlights: Optimally equipped: with Fronius welding machines for MIG/MAG, TIG, and MMA welding as well as welding torches, welding accessories, and much more….
#3 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#4 American Friction Welding
Website: teamafw.com
Key Highlights: We are experts at welding dissimilar metals and near-net-shape parts using direct-drive rotary friction welding to deliver full-strength, deep-penetration welds ……
#5 Faster Deep Penetration Welding
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Combining a new fiber laser and process head enables deep penetration copper welding over large working areas….
#6 Welding
Website: forneyind.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $300 60-day returns31115 Deep Penetration Rust Resolv. Deep Penetration Rust Resolver 1/8″ x 14″ Electrode – 1/2 lb. $6.99. Add to Cart. 31114 Deep Penetration R…
#7 Microtech Welding Corp.
Website: microtechwelding.com
Key Highlights: Quality Precision Welding. Your reliable partner for American-made welding solutions with unmatched speed, service, and proven expertise….
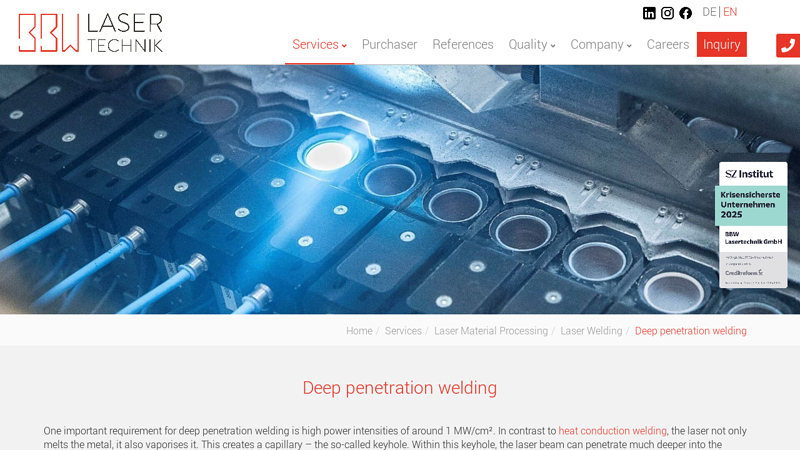
#8 Deep penetration welding
Website: bbw-lasertechnik.de
Key Highlights: In deep penetration welding, the laser radiation penetrates much deeper into the material. The welding depth is therefore greater than the weld seam width….
#9 Solutions
Website: connect.panasonic.com
Key Highlights: Low spatter even when welding thick plates. Yahata Seiko could achieve deep penetration and beautiful bead appearance with high power TAWERS HD pulse welding….
#10 Powerful Fronius Welding Machine Solutions
Website: hornetcs.com
Key Highlights: Exceptionally high welding speed and deep penetration · Consistent wire feed for uniform welds · Full mechanization and robotic integration possible · High ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Deep Penetration Welding

H2: Market Trends in Deep Penetration Welding for 2026
The global deep penetration welding market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising industrial automation, and increased demand in high-performance sectors such as automotive, aerospace, energy, and heavy manufacturing. Deep penetration welding—encompassing processes like laser beam welding (LBW), electron beam welding (EBW), and advanced gas metal arc welding (GMAW)—offers superior joint strength, reduced distortion, and high productivity, positioning it as a critical technology in modern fabrication.
1. Technological Innovation and Automation Integration
By 2026, the integration of deep penetration welding with Industry 4.0 technologies—such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT)—is expected to accelerate. Smart welding systems equipped with real-time monitoring and adaptive control will enhance precision, reduce defects, and improve repeatability. Robotic welding cells utilizing deep penetration techniques are being increasingly deployed in high-volume manufacturing, especially in electric vehicle (EV) production, where consistent, high-strength welds are essential for battery enclosures and structural components.
2. Growth in the Automotive and EV Sectors
The automotive industry remains a dominant driver of deep penetration welding demand. As automakers shift toward lightweight materials (e.g., high-strength steels and aluminum alloys) to improve fuel efficiency and meet emission standards, deep penetration methods like laser welding provide the required precision and strength. The burgeoning EV market further amplifies this trend, with battery pack manufacturing relying heavily on laser deep penetration welding for joining dissimilar metals and ensuring electrical conductivity and thermal stability.
3. Expansion in Renewable Energy and Infrastructure
The renewable energy sector—particularly wind and solar—is expected to boost demand for deep penetration welding. Offshore wind turbine installations require robust, corrosion-resistant welds in thick-section materials, where electron beam and hybrid laser-arc welding excel. Additionally, infrastructure projects involving bridges, pipelines, and pressure vessels will continue to rely on deep penetration techniques for long-term durability and safety compliance.
4. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to lead the market growth by 2026, fueled by industrial expansion in China, India, and South Korea. These regions are investing heavily in advanced manufacturing and smart factories, increasing the adoption of automated deep penetration welding solutions. Europe and North America will maintain strong demand due to aerospace and defense applications, stringent safety regulations, and a focus on sustainable manufacturing practices.
5. Sustainability and Material Efficiency
Environmental concerns are shaping welding technology development. By 2026, manufacturers will prioritize energy-efficient welding systems with lower emissions and reduced material waste. Innovations in beam delivery systems, hybrid welding processes, and closed-loop feedback mechanisms will improve energy utilization and weld quality, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion
The 2026 market landscape for deep penetration welding will be defined by digitalization, sector-specific customization, and a strong emphasis on quality and efficiency. As industries pursue higher performance and automation, deep penetration welding technologies will play a pivotal role in enabling next-generation manufacturing capabilities. Companies investing in R&D and integrated smart welding solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving market.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Deep Penetration Welding (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing deep penetration welding—such as laser beam welding, electron beam welding, or advanced pulsed MIG/MAG processes—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failure to address these aspects can lead to significant technical, financial, and legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Process Qualification and Certification
Sourcing from vendors without proper certification (e.g., ISO 3834, AWS D1.1, ASME IX) or without documented welding procedure specifications (WPS) and procedure qualification records (PQR) is a major risk. Deep penetration processes demand high precision; unqualified procedures can result in inconsistent weld quality, lack of penetration control, or defects like porosity and cracking.
2. Poor Material Traceability and Compatibility
Using materials without full traceability (e.g., mill test certificates) or mismatched base/filler metals can compromise weld integrity. Deep penetration techniques are sensitive to material composition; even minor impurities or variations can lead to brittle microstructures or hot cracking.
3. Insufficient Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Protocols
Relying on basic visual inspections or inadequate NDT methods (e.g., skipping ultrasonic or radiographic testing) can miss subsurface defects typical in deep welds, such as root porosity or lack of fusion. Ensure sourcing agreements mandate appropriate NDT coverage based on application criticality.
4. Inconsistent Process Control and Monitoring
Deep penetration processes require tight control of parameters (e.g., power density, travel speed, shielding gas). Vendors without real-time monitoring systems (e.g., weld seam tracking, plasma monitoring) may deliver inconsistent results, especially on complex geometries.
5. Lack of Skilled Personnel and Training Records
Even with advanced equipment, welder/operator expertise is crucial. Overlooking verification of operator certifications and ongoing training programs can result in poor execution, especially when handling high-value or safety-critical components.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Absence of Clear IP Ownership Agreements
When custom welding procedures or joint designs are developed during sourcing, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Suppliers may claim rights to process innovations, limiting your freedom to use or modify the technology.
2. Inadequate Protection of Proprietary Designs and Fixtures
Sharing detailed CAD models or specialized tooling for deep penetration welds without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or IP clauses exposes your designs to misuse or reverse engineering. Ensure all technical documentation is shared under controlled terms.
3. Unrestricted Use of Supplier-Developed Processes
Some vendors may use proprietary techniques (e.g., hybrid laser-arc methods) without licensing clarity. Sourcing without understanding usage rights can lead to legal exposure or dependency on a single supplier for future production.
4. Failure to Audit Supplier IP Compliance
Suppliers might inadvertently use third-party patented technologies (e.g., specific beam oscillation patterns or control algorithms). Without audit rights or warranties, your organization could face infringement claims downstream.
5. Insufficient Documentation for IP Enforcement
Lack of detailed records—such as process development logs, design iterations, and supplier communications—can weaken your position in enforcing or defending IP rights. Maintain thorough documentation throughout the sourcing lifecycle.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Require full compliance with international welding standards and independent third-party audits.
- Conduct on-site process validation and witness test welds before full-scale production.
- Draft comprehensive sourcing contracts that specify IP ownership, confidentiality, and usage rights.
- Include indemnification clauses for IP infringement.
- Establish joint development agreements when co-creating new welding solutions.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable performance, protect competitive advantages, and avoid costly disputes in deep penetration welding applications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Deep Penetration Welding
Overview of Deep Penetration Welding
Deep Penetration Welding refers to advanced welding techniques—such as Laser Beam Welding (LBW), Electron Beam Welding (EBW), and Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)—that produce welds with high depth-to-width ratios. These methods are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and heavy industrial applications where structural integrity and precision are critical. Ensuring safe, compliant, and efficient logistics for these processes is essential.
Equipment and Material Logistics
Transportation of Welding Equipment
- High-precision welding systems (e.g., laser or electron beam units) must be transported using shock-absorbent packaging and climate-controlled vehicles to prevent damage.
- Secure all optical components, vacuum chambers (for EBW), and power supplies with protective covers and anti-vibration mounts.
- Follow manufacturer handling guidelines and conduct pre- and post-shipment inspections.
Handling of Consumables and Gases
- Shielding gases (e.g., argon, helium) must be stored and transported in accordance with local compressed gas regulations (e.g., OSHA, CGA standards).
- Gas cylinders should be secured upright, labeled properly, and stored in well-ventilated, fire-safe areas.
- Use only compatible fittings and regulators; inspect for leaks before use.
Raw Material Supply Chain
- Incoming base metals (e.g., high-strength steels, titanium alloys) must be traceable with certified material test reports (MTRs).
- Store materials in dry, clean environments to prevent contamination that could compromise weld integrity.
- Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize material aging issues.
Regulatory Compliance
Occupational Safety and Health (OSHA)
- Ensure all welding areas are equipped with proper ventilation systems to control fumes and gases, especially when welding coated or galvanized metals.
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE), including auto-darkening helmets, flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection.
- Post warning signs for high-energy radiation (laser/EB) zones and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
Environmental Regulations (EPA, Local Authorities)
- Capture and filter welding fumes using certified fume extraction systems to meet air quality standards.
- Dispose of welding slag, grinding dust, and contaminated consumables as hazardous waste where applicable.
- Maintain records of emissions monitoring and waste disposal manifests.
International Standards
- Comply with ISO 3834 (welding quality requirements) and ISO 15614 (welding procedure qualification).
- Adhere to ASME Section IX (for pressure-containing applications) or AWS D1.1 (structural welding code) as applicable.
- Maintain documentation for welding procedure specifications (WPS), procedure qualification records (PQR), and welder certifications.
Radiation and High-Energy Safety (Laser/EBW)
Laser Safety (ANSI Z136.1)
- Classify lasers per ANSI standards and install interlocks, beam enclosures, and emergency stops.
- Conduct regular beam alignment checks and use appropriate laser safety eyewear.
- Train personnel on laser operation, hazard zones, and emergency response.
Electron Beam Safety
- Ensure vacuum chambers are equipped with radiation shielding (e.g., lead-lined enclosures).
- Perform routine checks on X-ray emissions and maintain logs.
- Only trained and certified operators should conduct EBW operations.
Documentation and Traceability
Welding Records
- Maintain detailed logs of each weld, including date, operator, WPS number, material batch, and inspection results.
- Store digital records securely with backup protocols to prevent data loss.
Material Traceability
- Use barcoding or RFID tagging to track materials from receipt through final weld.
- Ensure traceability extends to subcomponents in regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, nuclear).
Compliance Audits
- Conduct internal audits quarterly to verify adherence to safety, quality, and environmental standards.
- Prepare for external audits (e.g., NADCAP, ISO certification) with complete, up-to-date documentation.
Training and Personnel Qualifications
Certification Requirements
- Welders and operators must be certified per AWS, ASME, or equivalent standards.
- Retraining and re-certification should occur at defined intervals or after equipment/process changes.
Safety Training
- Provide annual training on hazard communication (HazCom), emergency procedures, and PPE use.
- Include specific modules on laser/EB safety for relevant personnel.
Emergency Preparedness
Fire Prevention and Response
- Equip welding areas with Class D fire extinguishers suitable for metal fires.
- Prohibit flammable materials near welding zones and enforce hot work permit systems.
Radiation Exposure Protocols
- Establish emergency shutdown procedures for laser/EB systems.
- Designate assembly points and decontamination zones in case of radiation incidents.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance in Deep Penetration Welding require meticulous planning, strict adherence to regulations, and ongoing training. By integrating robust safety protocols, maintaining complete documentation, and ensuring equipment and material integrity, organizations can achieve high-quality welds while meeting all legal and operational standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing Deep Penetration Welding
Sourcing deep penetration welding services is a strategic decision that significantly impacts the quality, durability, and efficiency of high-integrity metal fabrications. This advanced welding technique, characterized by its ability to achieve greater weld depth with fewer passes, offers substantial benefits in terms of structural strength, reduced distortion, and improved productivity—particularly in industries such as shipbuilding, heavy machinery, pressure vessels, and aerospace.
When sourcing deep penetration welding, it is essential to partner with certified, experienced providers equipped with advanced technologies such as submerged arc welding (SAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), or laser and plasma welding systems. Key considerations include the vendor’s compliance with international welding standards (e.g., ISO 3834, ASME, AWS), metallurgical expertise, quality control protocols, and track record in handling similar materials and joint configurations.
Ultimately, investing in a reliable deep penetration welding supplier not only ensures superior weld integrity and performance but also reduces long-term maintenance and operational costs. As manufacturing demands continue to evolve, strategic sourcing of this specialized capability will remain critical for achieving competitive advantage and meeting stringent engineering requirements.