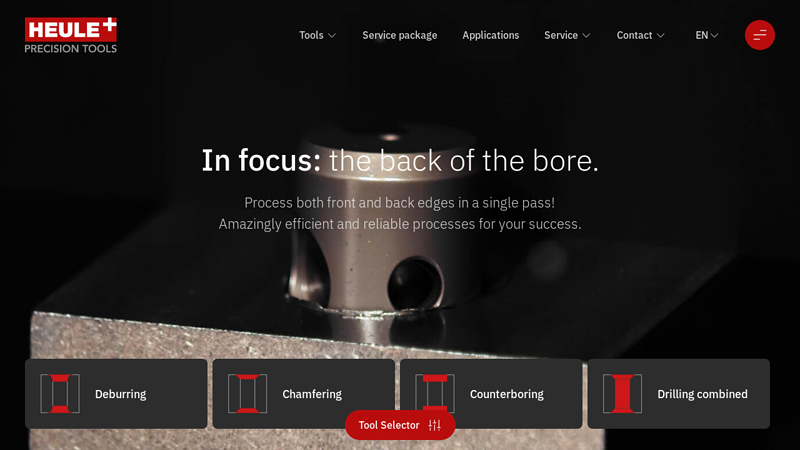
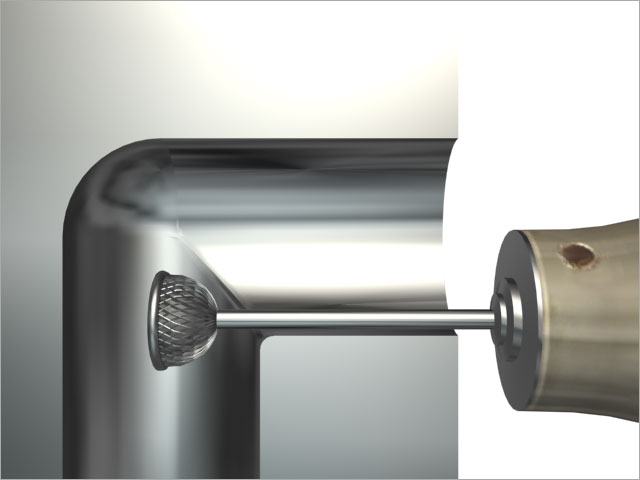
The global deburring tools market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision finishing in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 1.87 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by advancements in automation, rising emphasis on product quality, and tighter regulatory standards requiring burr-free components. As manufacturers seek to improve surface finish efficiency and reduce manual labor, the role of high-performance deburring tools has become increasingly critical. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders through innovation, product reliability, and global reach. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 deburring tool manufacturers shaping the future of precision surface finishing.
Top 10 De Burring Tool Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 EZBurr Tool Company
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ezburr.com
Key Highlights: EZ Burr Tool Company, currently based in Livonia, MI will move all manufacturing operations to its parent company, Cogsdill Tool Products, Inc….
#2 Material Removal Tools
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ati-ia.com
Key Highlights: The Engineers at ATI have developed a family of compliant deburring tools that make automated deburring processes safe, reliable, and affordable. Pneumatic ……
#3 Industrial Deburring Tools
Domain Est. 1999
Website: weilerabrasives.com
Key Highlights: Our guide walks you through the essentials of deburring, from understanding the types of burrs to exploring the best tools for achieving precision….
#4 De‑Burring Tool
Domain Est. 1996
Website: wilsontool.com
Key Highlights: The De-Burring tool accurately and efficiently de-burrs sharp edges on parts. It works by coining a small chamfer on the cut edge of the part with a unique ball ……
#5 Deburring Tools
Domain Est. 1996
Website: toolsforbending.com
Key Highlights: Tools For Bending offers many tools for deburring round tubing and pipe. Deburring and Squaring blades for any tube deburring equipment in the industry….
#6 Deburring Tools
Domain Est. 1997
Website: reedmfgco.com
Key Highlights: DEB0 and DEB3 deburring tools feature a long-lasting, hardened tool steel, deburring blade. Tools deburr aluminum, copper and steel tubing….
#7 Noga Engineering
Domain Est. 1998
Website: noga.com
Key Highlights: Noga program offers a wide comprehensive range of deburring blades. For every type of deburring blades you can see the drawings showing the suitable ……
#8 Precision Deburring & Spotfacing Tools
Domain Est. 2000
Website: heuletool.com
Key Highlights: Discover HEULE’s Swiss-engineered deburring and spotfacing tools for efficient CNC machining. Improve productivity, reduce cycle time, ……
#9 J.W. DONE ORBITOOL
Domain Est. 2000
Website: jwdone.com
Key Highlights: The NEXT TOOL AFTER DRILL, the only deburring tool capable of in-process deburring of cross-drilled holes. Removes burrs only at the hole intersection….
#10 Shaviv USA
Domain Est. 2005
Website: shavivusa.com
Key Highlights: Visit the SHAVIV website: www.shaviv.com. SHAVIV CATALOGS. SHAVIV USA Catalog SHAVIV USA … POPULAR BLADES. The Most Popular Blades Chart AMMO-BURR Series….
Expert Sourcing Insights for De Burring Tool

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Deburring Tools
The global deburring tools market is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by evolving manufacturing demands, technological advancements, and shifting industrial priorities. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Rising Demand for Automation and Robotics Integration:
With manufacturers focusing on efficiency, consistency, and reducing reliance on skilled manual labor, the integration of deburring tools into automated systems and robotic cells will accelerate. Expect increased demand for robotic deburring arms, CNC-compatible tools, and smart end-effectors capable of adaptive force control. This trend is particularly strong in automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering sectors.
2. Growth in Advanced Materials Processing:
The proliferation of high-strength alloys, composites, and hardened materials in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and electric vehicles (EVs) necessitates specialized deburring solutions. Tools designed for non-traditional materials—offering precision, minimal heat generation, and reduced tool wear—will see heightened demand. Electrochemical (ECM) and thermal energy (TEM) deburring methods may gain traction for complex internal geometries.
3. Emphasis on Precision and Miniaturization:
As components become smaller and more complex (e.g., in electronics, medical implants, and micro-machining), the need for ultra-precise, micro-deburring tools will grow. Manufacturers will prioritize tools with micron-level accuracy, minimal burr reformation, and compatibility with tight tolerances, driving innovation in tool geometry and coating technologies.
4. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Solutions:
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will push the market toward greener deburring methods. Dry deburring, water-based coolants, and recyclable abrasive media will gain favor over solvent-based or waste-intensive processes. Tool longevity and reduced consumable waste will become competitive advantages.
5. Digitalization and Smart Tooling:
The integration of IoT sensors and data analytics into deburring tools will enable predictive maintenance, real-time process monitoring, and quality assurance. Smart tools that provide feedback on wear, force applied, and burr removal effectiveness will enhance process control and reduce downtime.
6. Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience:
Asia-Pacific, especially China and India, will remain key growth markets due to expanding manufacturing bases. However, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions will encourage nearshoring and regional production, benefiting local tool suppliers and increasing demand for cost-effective, reliable solutions.
7. Consolidation and Innovation in Product Offerings:
Market players will likely consolidate to offer comprehensive deburring solutions—combining mechanical, abrasive, and non-traditional methods—under one platform. Innovation will focus on multi-functional tools, improved ergonomics for handheld devices, and modular systems for greater flexibility.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the deburring tools market will be characterized by smarter, more automated, and material-specific solutions. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate in response to precision demands, sustainability imperatives, and the growing integration of digital technologies within advanced manufacturing ecosystems.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing De-Burring Tools (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing de-burring tools—especially from international or third-party suppliers—can present significant challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these risks can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety concerns, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to watch for.
Quality Inconsistencies and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing de-burring tools is inconsistent product quality. Suppliers may use inferior materials or cut corners in manufacturing to reduce costs, leading to tools that wear out quickly, fail under stress, or produce poor surface finishes. This can result in higher long-term costs due to frequent replacements and rework, and may compromise the integrity of finished parts.
Lack of Standardization and Dimensional Accuracy
Many low-cost suppliers fail to adhere to strict dimensional tolerances and industry standards (e.g., ISO, DIN). De-burring tools that are not precisely manufactured can cause damage to workpieces, lead to inconsistent edge finishing, or fail to fit into automated systems. Without proper quality control documentation or certifications, verifying consistency across batches becomes difficult.
Inadequate Performance Testing and Validation
Reputable de-burring tools undergo rigorous performance testing for hardness, durability, and cutting efficiency. When sourcing from unverified suppliers, there is often no evidence of such testing. Tools may perform adequately in initial trials but degrade rapidly in real-world applications, disrupting production schedules and increasing maintenance costs.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from suppliers who replicate patented or proprietary de-burring tool designs exposes your company to IP infringement claims. Even if your organization did not design the tool, importing or using counterfeit or cloned tools can lead to legal liability, shipment seizures, and reputational damage. This is particularly prevalent when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement.
Lack of Transparency in Manufacturing Origin
Some suppliers may obscure the true origin of their tools by relabeling products or using intermediary distributors. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to assess manufacturing practices, verify compliance with IP laws, and ensure traceability—especially critical in regulated industries such as aerospace or medical devices.
Absence of Technical Support and Documentation
Low-cost suppliers often provide minimal technical documentation, usage guidelines, or after-sales support. Without proper specifications, maintenance instructions, or material certifications, integrating the tools into production processes becomes risky and may void equipment warranties.
Failure to Protect Your Own IP When Customizing Tools
When commissioning custom de-burring tools, organizations risk exposing proprietary designs or processes to suppliers without proper contractual safeguards. Without clear non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and IP ownership clauses, suppliers may replicate or sell your designs to competitors.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, request quality certifications, perform sample testing, and ensure robust legal agreements are in place. Prioritizing reputable suppliers with transparent manufacturing practices helps safeguard both tool performance and your organization’s intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for De-Burring Tool
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and lawful handling, transportation, and use of de-burring tools. Adherence ensures operational safety, regulatory compliance, and product integrity.
Product Classification & Regulatory Compliance
De-burring tools are typically classified as industrial hand or power tools. Compliance depends on design (manual, pneumatic, electric, or battery-powered). Key regulations include:
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Mandates safe workplace practices. Tools must comply with guarding, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and worker protection standards (e.g., 29 CFR 1910 Subpart P for hand and portable powered tools).
- ANSI B107 Series: Applies to portable power tools. Relevant standards include ANSI B107.16 (for rotary tools) and ANSI B107.23 (for die grinders), covering safety, performance, and labeling.
- CE Marking (EU): Required for tools sold in the European Economic Area. Compliance with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive is essential.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Restrict hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in electrical components and materials.
- EPA Regulations (USA): May apply if tool usage generates hazardous particulates (e.g., metal dust). Dust control and disposal must comply with local air quality and waste regulations.
Ensure all tools come with a Declaration of Conformity and technical documentation.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging protects the tool during transit and supports compliance with international shipping standards.
- Internal Packaging: Use anti-static or protective wrapping for electronic components. Include foam inserts to prevent movement.
- Outer Packaging: Use durable corrugated cardboard or wooden crates for heavy or multiple units. Clearly label with:
- Product name and model number
- Net weight and dimensions
- “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators
- Manufacturer and importer information
- Hazardous Materials: Most de-burring tools are non-hazardous. However, lithium-ion batteries (if included) must comply with IATA/IMDG regulations for air and sea transport, including proper packaging, labeling (UN3480), and documentation.
- Export Controls: Verify if tools contain components subject to export restrictions (e.g., advanced motors or controllers). Tools may require an ECCN (Export Control Classification Number).
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure all international shipments include accurate and complete documentation:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Import/Export Licenses (if applicable)
- CE Certificate or Test Reports (for EU)
- FCC Declaration (for electric tools with electronic circuits, USA)
Verify destination country-specific requirements; some nations require additional conformity assessments or registration.
Storage & Handling Guidelines
Proper storage maintains tool performance and safety.
- Environment: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled area (10–30°C / 50–86°F), away from direct sunlight and corrosive chemicals.
- Humidity: Keep relative humidity below 60% to prevent rust and electrical damage.
- Shelving: Use sturdy racks. Store tools in original packaging or protective cases to avoid physical damage.
- Battery-Powered Tools: Store batteries at 40–60% charge. Remove from tools during long-term storage.
- Handling: Use appropriate lifting equipment for bulk shipments. Avoid dropping or impact.
Safety & Operational Compliance
End-user compliance is critical to prevent accidents and ensure regulatory adherence.
- Training: Operators must be trained on proper use, PPE requirements, and emergency procedures.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Required use of safety glasses, hearing protection, gloves, and dust masks/respirators when generating particulates.
- Maintenance Logs: Maintain records of inspections, servicing, and blade/burr replacements per manufacturer guidelines.
- Dust Control: Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems or dust extractors to comply with OSHA PELs (Permissible Exposure Limits) for metal dust.
Disposal & End-of-Life
Dispose of tools and components responsibly.
- Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE): In the EU, de-burring tools must be recycled under WEEE Directive. Use certified e-waste recyclers.
- Batteries: Recycle lithium-ion or NiCd batteries through approved programs (e.g., Call2Recycle in North America).
- Metal Components: Recycle steel, aluminum, and other metals through certified scrap facilities.
- Hazardous Parts: Tools with PCBs or hazardous coatings must be processed as hazardous waste per local regulations.
Following this guide ensures compliance across the lifecycle of de-burring tools, from shipment to disposal, minimizing risk and supporting sustainable operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Deburring Tool:
After thorough evaluation of available options, it is concluded that sourcing a deburring tool should be guided by specific operational requirements, including material type, production volume, precision needs, and ergonomics. Automated or CNC-integrated deburring tools are recommended for high-volume, consistent applications to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs. For low-volume or custom work, handheld or bench-mounted tools offer greater flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Critical factors such as tool durability, ease of maintenance, safety features, and compatibility with existing machinery must also be considered. Supplier reliability, after-sales support, and total cost of ownership further influence the final decision.
Ultimately, selecting the appropriate deburring tool enhances product quality, ensures compliance with surface finish standards, and contributes to overall process optimization. A well-informed sourcing decision will deliver long-term operational benefits and a strong return on investment.