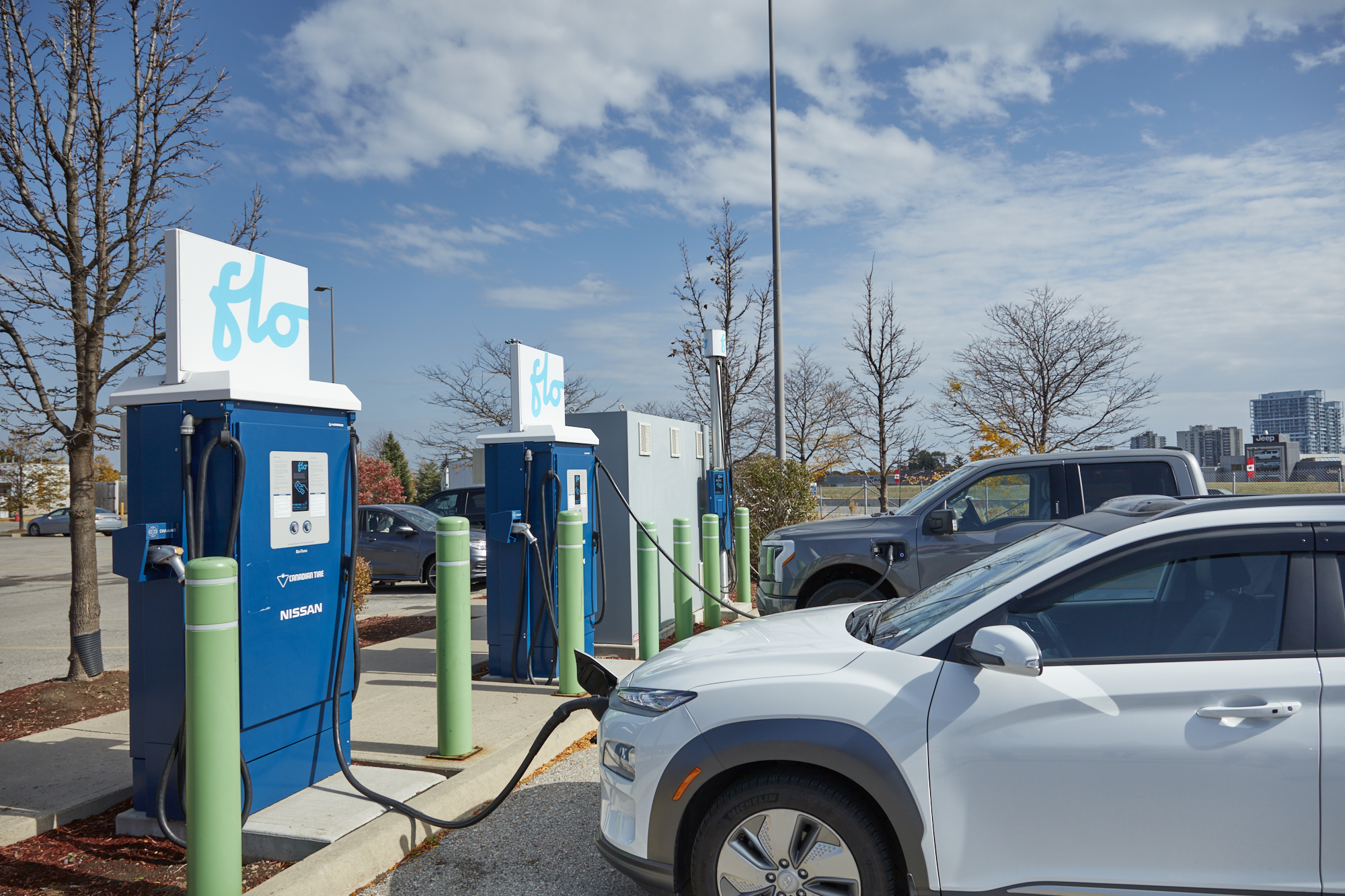
The global DC-DC converter market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and advanced industrial applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 11.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 18.6 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 7.9% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the increasing integration of high-efficiency power conversion solutions in automotive and telecom sectors, along with the global push toward energy efficiency and electrification. As demand intensifies, manufacturers are investing heavily in innovation, miniaturization, and thermal performance. In this competitive landscape, identifying the top DC-DC charger manufacturers becomes critical for OEMs and system integrators seeking reliable, high-performance power solutions. Here’s a data-driven look at the leading players shaping the future of DC-DC conversion technology.
Top 10 Dc Dc Charger Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Alpitronic
Domain Est. 2009 | Founded: 2017
Website: alpitronic.it
Key Highlights: Our DC fast-charging technology. We’ve been leading the charge in developing, producing, and commercializing scalable DC fast chargers since 2017….
#2 Orion
Domain Est. 2000
Website: victronenergy.com
Key Highlights: The Orion-Tr Smart DC-DC charger is an adaptive 3-stage charger (bulk – absorption – float) designed for dual battery systems, such as in vehicles or on boats….
#3 Products
Domain Est. 2001
Website: deltaww.com
Key Highlights: Delta DC chargers have a power output ranging from 25kW to 200kW. With high power efficiency as well as multiple outputs and charging interface options, our DC ……
#4 EVgo
Domain Est. 2002
Website: evgo.com
Key Highlights: As one of the largest and most advanced EV fast charging networks nationwide, EVgo powers the freedom of movement with robust charging for all EV models….
#5 DC Charging Solutions for Fleets & Businesses
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kempower.com
Key Highlights: Kempower offers cutting-edge charging solutions in North America. Contact us for the best EV charging solutions on the market!…
#6 Products
Domain Est. 2008
Website: delta-americas.com
Key Highlights: DC Charger. Delta DC chargers have a power output ranging from 25 to 150 kW. With high power efficiency as well as multiple outputs and charging interface ……
#7 CHAdeMO
Domain Est. 2009
Website: chademo.com
Key Highlights: CHAdeMO provides a fully proven fast charging system that servicesing EV users around the world. Read more…
#8 Fastest EV charging in America
Domain Est. 2011
Website: gravitytechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Extensive product suite. Competitive pricing for full range of DC fast chargers designed for all fleet use cases – 30kW, 200kW, 500kW….
#9 Introducing Charger 1
Domain Est. 2021
Website: community.bluettipower.com
Key Highlights: Quick and safe charging for your power station when driving. Get ready to revolutionize your car charging experience with Charger 1!…
#10 DC EV Chargers: Powerful , Fast and Efficient
Domain Est. 2022
Website: zerovatech.com
Key Highlights: DC chargers offer high-power charging capabilities, enabling quick and convenient EV charging. Experience shorter charging times and get back on the road ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Dc Dc Charger
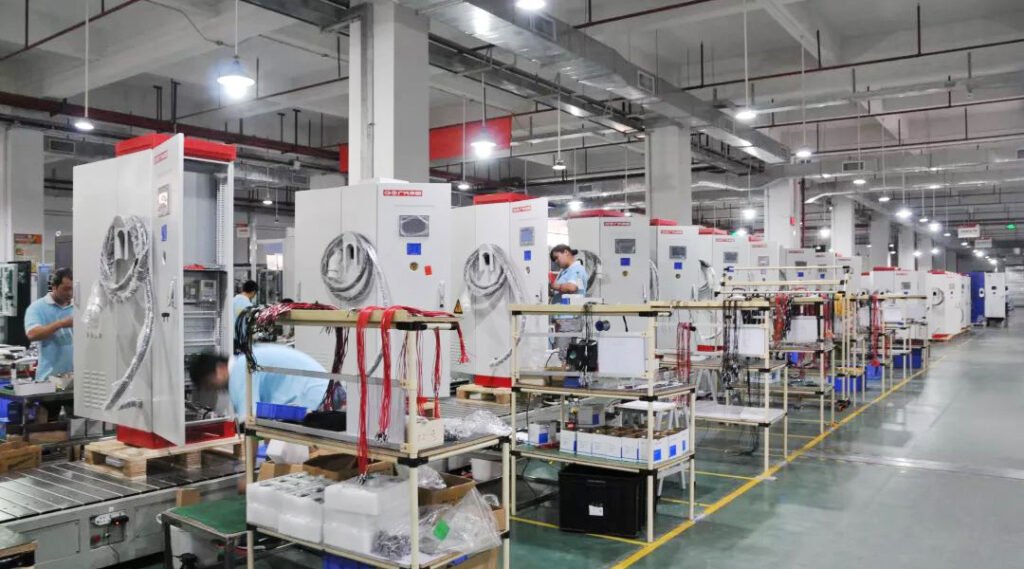

H2: 2026 Market Trends for DC-DC Chargers
The DC-DC charger market in 2026 is poised for robust growth, driven primarily by the accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing complexity of onboard electrical systems. Here are the key trends shaping the market:
1. Surging Demand from the Electric Vehicle (EV) Sector:
The primary driver for DC-DC charger growth in 2026 is the continued expansion of the global EV market. As battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) become more prevalent, the need for efficient DC-DC conversion to step down high-voltage battery power (400V or 800V) to 12V/24V for auxiliary systems (lights, infotainment, ECUs) remains critical. Increasing EV production, especially in regions like China, Europe, and North America, will directly boost DC-DC charger demand.
2. Shift Towards Higher Efficiency and Power Density:
With automakers striving for longer range and reduced energy losses, there is a strong trend toward higher-efficiency DC-DC chargers. Technologies like gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors are enabling designs with improved thermal performance, smaller footprints, and efficiencies exceeding 95%. This supports the integration of more power-hungry onboard electronics without compromising vehicle range.
3. Integration with Vehicle Architecture and 800V Systems:
As 800V vehicle architectures gain traction (e.g., in premium EVs from Porsche, Hyundai, Lucid), DC-DC chargers must evolve to handle higher input voltages efficiently. This requires new topologies and robust thermal management. Additionally, DC-DC chargers are becoming more integrated with the vehicle’s overall power management system, enabling smarter energy distribution and regenerative capabilities.
4. Growth in Commercial and Off-Road Electric Vehicles:
Beyond passenger cars, the electrification of buses, trucks, construction equipment, and agricultural machinery is creating new demand for rugged, high-power DC-DC chargers. These applications often require higher voltage stabilization and durability under harsh conditions, opening opportunities for specialized DC-DC solutions.
5. Expansion in Renewable Energy and Energy Storage Systems (ESS):
Beyond transportation, DC-DC chargers are increasingly used in solar power systems and battery energy storage to manage charge transfer between different voltage levels. In 2026, the growth of distributed energy resources and microgrids will further drive demand for efficient, bidirectional DC-DC converters capable of both charging and discharging.
6. Focus on Bidirectional and Smart Charging Capabilities:
Emerging trends include the development of bidirectional DC-DC chargers that allow energy flow from the main traction battery to the auxiliary battery and vice versa. This supports vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technologies and enables smarter energy management, such as using the auxiliary system to support startup or emergency power.
7. Regional Market Growth and Supply Chain Dynamics:
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, will remain a dominant market due to strong government support for EVs and a mature manufacturing ecosystem. However, North America and Europe are expected to see rapid growth due to regulatory pressures and infrastructure investments. Supply chain resilience, especially for critical semiconductors, will remain a strategic focus for manufacturers.
In summary, the 2026 DC-DC charger market is characterized by technological innovation, strong tailwinds from electrification across multiple sectors, and a shift toward smarter, more efficient power conversion systems. Companies investing in high-efficiency designs, advanced materials, and system integration will be well-positioned to capitalize on these trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing DC-DC Chargers (Quality, IP Protection)
Sourcing DC-DC chargers—especially for critical applications like electric vehicles, industrial systems, or off-grid power—requires careful attention to both quality and ingress protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking key aspects can lead to reliability issues, safety hazards, and costly failures. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Overlooking True Component Quality
Many suppliers offer low-cost DC-DC chargers that appear identical on paper but vary drastically in internal component quality. Common issues include:
– Use of counterfeit or substandard semiconductors and capacitors that degrade quickly under thermal stress.
– Poor PCB layout and thermal management, leading to hotspots and premature failure.
– Inadequate input/output filtering, resulting in electromagnetic interference (EMI) that affects other system components.
Solution: Request detailed BOMs (Bill of Materials), verify component brands, and ask for third-party test reports (e.g., thermal imaging, EMI testing).
2. Misinterpreting IP Ratings
IP (Ingress Protection) ratings indicate resistance to solids and liquids, but suppliers may misrepresent or test under non-realistic conditions:
– “IP67 compliant” without full certification: Some vendors label products IP67 based on design, not verified testing.
– Testing only static conditions: Real-world vibration and thermal cycling can compromise seals over time.
– Focus on enclosure only, ignoring connectors: High IP rating on the main unit but low-IP connectors create weak points.
Solution: Require certified test reports from accredited labs (e.g., IEC 60529), and ensure connectors and cable glands match the overall IP rating.
3. Inadequate Thermal and Load Performance Validation
DC-DC chargers must perform reliably under full load and high ambient temperatures:
– Derating ignored: Some units cannot sustain rated output above 40°C without derating.
– Lack of long-term burn-in testing: Units may pass initial QC but fail after hours of continuous operation.
Solution: Ask for thermal performance curves and confirm operation at maximum ambient temperature with full load.
4. Poor Isolation and Safety Certification
Lack of proper safety certifications increases risk of electric shock or fire:
– Missing or fake certifications (e.g., CE, UL, CB).
– Insufficient isolation voltage between input and output, especially in high-voltage EV systems.
Solution: Verify certification authenticity through official databases and ensure isolation ratings meet or exceed application requirements.
5. Inconsistent Manufacturing and Quality Control
Low-cost manufacturers may lack consistent QC processes:
– Unit-to-unit performance variation due to manual assembly or poor process control.
– No traceability or batch testing, making failure analysis difficult.
Solution: Audit manufacturing facilities if possible, and require sample testing from multiple production batches.
6. Insufficient Protection Features
Reliable DC-DC chargers need comprehensive protection:
– Missing or poorly implemented protections for over-voltage, over-current, over-temperature, and reverse polarity.
– Slow response times that don’t prevent downstream damage.
Solution: Validate protection mechanisms through test reports or functional testing.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—focusing on verified quality, accurate IP ratings, and robust design validation—buyers can avoid costly downtime and ensure long-term reliability of their DC-DC charging systems.
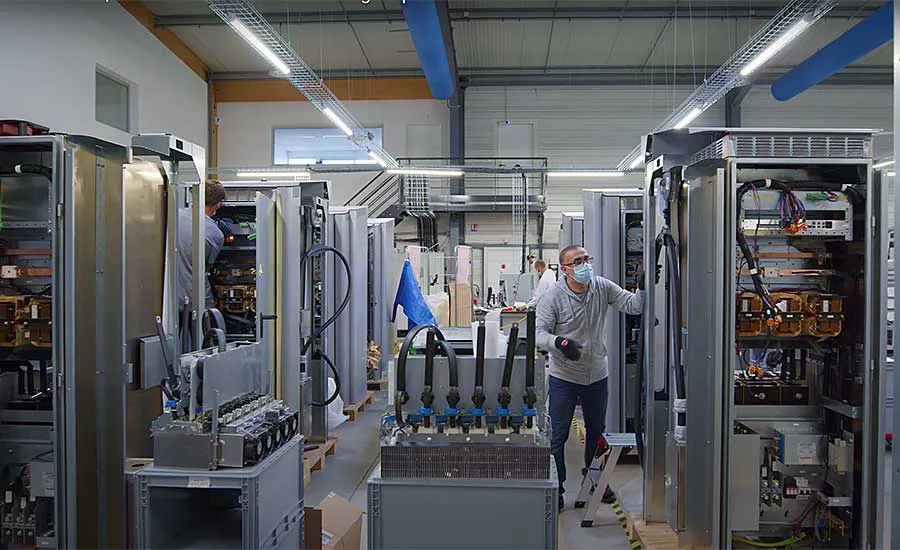

Logistics & Compliance Guide for DC-DC Chargers
Introduction
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for handling, transporting, storing, and certifying DC-DC chargers. These power electronics are commonly used in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and industrial applications. Proper management ensures safety, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Safety & Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
DC-DC chargers must comply with regional and international safety and EMC standards. Key certifications include:
– IEC/EN 62109: Safety standards for power converters in PV systems (applicable to relevant use cases).
– IEC/EN 61000-6-2 & 61000-6-4: EMC standards for industrial environments (emissions and immunity).
– UL 62368-1: North American safety standard for audio/video, information, and communication technology equipment.
– EN 55032 & EN 55035: EMC requirements for multimedia equipment (often applicable to power electronics).
Ensure product labeling includes certification marks (e.g., CE, UKCA, UL, CCC) as required by destination markets.
Environmental & Chemical Regulations
Compliance with hazardous substance restrictions is mandatory:
– RoHS (EU Directive 2011/65/EU): Restricts lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous substances.
– REACH (EC 1907/2006): Requires declaration of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– China RoHS: Similar restrictions with specific labeling requirements for the Chinese market.
Maintain documentation such as Declarations of Conformity (DoC) and material declarations (e.g., IPC-1752) to support audits and customs clearance.
Battery & Transportation Safety (if integrated)
If the DC-DC charger includes battery components or is shipped with batteries:
– Classify under UN 3481 (for lithium-ion batteries contained in equipment) or UN 3091 (lithium metal).
– Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) for air transport and IMDG Code for sea freight.
– Packaging must pass vibration, shock, and thermal tests per UN 38.3.
Even without batteries, DC-DC chargers may contain high-capacity capacitors requiring safe discharge before shipping.
Packaging & Labeling
Protective Packaging
Use anti-static, shock-absorbent materials to protect sensitive electronics. Double-boxing with cushioning (e.g., foam inserts) is recommended for long-distance or international shipments. Ensure packaging prevents moisture ingress with desiccants or vapor barriers when necessary.
Required Labels
Affix the following labels to outer packaging:
– Product name and model number
– Manufacturer/importer contact details
– Weight and dimensions
– “Fragile” and “This Side Up” orientation indicators
– Compliance marks (CE, UL, etc.)
– Handling symbols per ISO 780 (e.g., no stacking, temperature limits)
For hazardous classifications (e.g., if batteries are included), include proper UN labels and hazard class diamonds.
Storage & Handling
Environmental Conditions
Store DC-DC chargers in a dry, temperature-controlled environment:
– Temperature: 5°C to 35°C (41°F to 95°F)
– Relative Humidity: <60%, non-condensing
– Avoid exposure to dust, corrosive gases, or direct sunlight
Monitor storage areas regularly to prevent damage due to environmental stress.
Handling Procedures
- Use ESD-safe practices when unpacking or preparing units for installation.
- Avoid mechanical shocks or vibrations during transfer.
- Do not stack loads beyond the maximum rated weight indicated on packaging.
Transportation Logistics
Mode-Specific Requirements
- Air Freight: Declare technical specifications and confirm non-hazardous status. If batteries are involved, follow IATA DGR Section II or I.
- Sea Freight: Use moisture-resistant packaging; consider container desiccants for long voyages.
- Ground Transport: Secure loads to prevent shifting. Use climate-controlled trucks for extreme climates.
Documentation
Prepare accurate shipping documents, including:
– Commercial invoice with detailed product description
– Packing list (quantity, weight, dimensions per box)
– Certificate of Origin (for tariff classification)
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) if applicable (e.g., for capacitors with electrolytes)
– Export control classification number (ECCN), if subject to dual-use regulations (e.g., under EU Dual-Use Regulation or U.S. EAR)
Import & Customs Clearance
Tariff Classification
Classify DC-DC chargers under the appropriate HS Code:
– 8504.40: DC-DC converters (commonly used in EU, US, and many countries)
Verify local tariff schedules as classifications may vary (e.g., 8504.40.80 in the U.S. HTS).
Import Duties & Taxes
- Determine applicable duties based on origin and trade agreements (e.g., GSP, USMCA).
- In the EU, apply for an Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) certificate to expedite customs.
- Account for VAT, GST, or other local consumption taxes.
Country-Specific Requirements
- China: Requires CCC certification for certain power conversion equipment.
- UK: CE marking accepted until 2025; transition to UKCA marking required for Great Britain.
- India: BIS certification may be required for select electronic power equipment.
- South Korea: KC Mark certification for electrical safety.
Verify requirements with local regulatory authorities or a customs broker.
End-of-Life & Recycling Compliance
WEEE Directive (EU)
If placing DC-DC chargers on the EU market:
– Register with national WEEE authorities.
– Provide take-back and recycling options.
– Label products with the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol.
Global Recycling Programs
Adhere to local e-waste regulations (e.g., Japan’s JIS C 8350, California’s SB 20). Design for disassembly and recyclability to support circular economy goals.
Conclusion
Ensuring compliance and efficient logistics for DC-DC chargers requires coordination across design, manufacturing, shipping, and regulatory domains. Proactive documentation, proper packaging, and adherence to regional standards minimize delays, reduce risk, and support sustainable operations. Regularly review regulatory updates and maintain close communication with logistics partners and compliance experts.
Conclusion for Sourcing DC-DC Charger
Sourcing a DC-DC charger requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, quality standards, and supplier reliability. It is essential to select a charger that matches the input and output voltage/current requirements of the system, ensures high efficiency, and provides necessary protections such as over-voltage, over-current, and thermal shutdown. Additionally, factors like size, thermal performance, and environmental durability must align with the intended operating conditions.
Opting for reputable suppliers with proven manufacturing standards, certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, UL), and strong technical support minimizes risks related to performance and longevity. Cost should not be the sole deciding factor; instead, a balance between cost, reliability, and performance should guide the decision. By carefully assessing these criteria, organizations can source a DC-DC charger that ensures system stability, enhances energy efficiency, and supports long-term operational success in applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, industrial equipment, or telecom infrastructure.