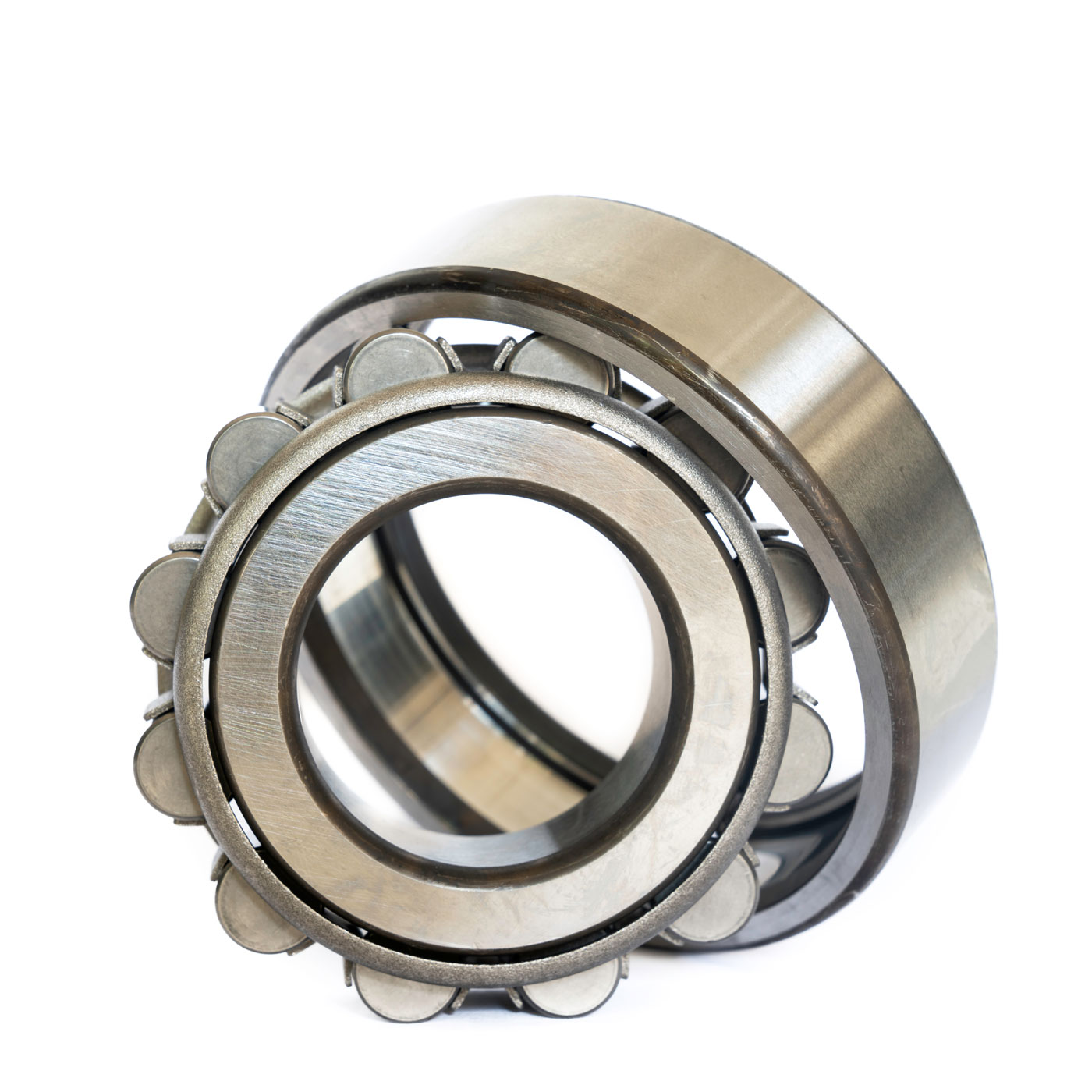
The global cylinder roller bearing market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industrial, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global roller bearing market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029, with cylindrical roller bearings representing a significant segment due to their high radial load capacity and efficiency in high-speed applications. Similarly, Grand View Research estimated the overall bearing market to reach USD 128.5 billion by 2030, fueled by advancements in automation and growing infrastructure investments, particularly in Asia-Pacific. As industries prioritize durability and performance, leading manufacturers are innovating in materials, precision engineering, and smart monitoring integration. In this competitive landscape, identifying the top cylinder roller bearing manufacturers becomes critical for procurement teams and engineers seeking reliable, high-performance components aligned with global quality standards.
Top 10 Cylinder Roller Bearing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 NKE FERSA
Domain Est. 1998
Website: industry.fersa.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture high-precision, custom-made bearing solutions for industrial OEMs, and a wide range of top-performance bearings for the industrial aftermarket….
#2 Precision Roller Bearings Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1919
Website: rbcbearings.com
Key Highlights: About Us. Founded in 1919, RBC Bearings Incorporated is an international manufacturer and marketer of highly engineered precision bearings and products, which ……
#3 American Roller Bearing: Roller Bearings Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: amroll.com
Key Highlights: American Roller Bearing is a leading manufacturer of anti-friction bearings for the heavy lifting industry. Visit us today to learn more about our bearings!…
#4 Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Domain Est. 2006
Website: schaeffler.us
Key Highlights: Schaeffler offers classic and single-row cylindrical roller bearings, designed for extremely high radial load-carrying capacity and high rigidity….
#5 RKB Bearing Industries – Swiss Technological Bearings
Domain Est. 2008
Website: rkbbearings.com
Key Highlights: RKB spherical roller bearings for a cement producer in Peru. Through our official Peruvian partner Rodasur, we secured the order to supply two spherical ……
#6 Timken Cylindrical Bearings
Domain Est. 1994
Website: timken.com
Key Highlights: Our comprehensive line of single-, double- and multi-row Timken cylindrical roller bearings helps extend equipment life and lower maintenance costs….
#7 Cylindrical roller bearings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: skf.com
Key Highlights: SKF Cylindrical roller bearings are available in a wide range of designs, series, variants and sizes. The main design differences are the number of roller rows ……
#8 Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: Check out NSK cylindrical roller bearings. With high speed applications, high strength, and high radial load capacity, this product will get the job done….
#9 Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rexnord.com
Key Highlights: Link-Belt cylindrical roller bearings are ready to meet your needs. We offer standard cylindrical roller bearing sizes and styles, as well as custom bearings….
#10 Rollway Open Ball and Roller Bearings
Domain Est. 2021
Website: regalrexnord.com
Key Highlights: Rollway bearings have played a significant role in the open ball and roller bearing industry, providing high quality standard and metric bearings….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cylinder Roller Bearing

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cylinder Roller Bearings
The global cylinder roller bearing market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing industrial automation, advancements in manufacturing technologies, and rising demand from key end-use sectors such as automotive, aerospace, heavy machinery, and renewable energy. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency, durability, and energy savings, cylinder roller bearings—known for their high radial load capacity and performance under heavy-duty conditions—are gaining broader adoption.
Rising Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
By 2026, the expansion of Industry 4.0 initiatives across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific is expected to significantly influence demand for high-performance bearings. Smart factories require reliable and maintenance-efficient components, and cylinder roller bearings are increasingly being integrated with condition monitoring systems and IoT-enabled sensors. This shift supports predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and enhances operational efficiency, making smart cylinder roller bearings a growing segment within the market.
Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Automotive Innovation
The automotive sector remains a major consumer of cylinder roller bearings, particularly in transmissions, gearboxes, and electric drivetrains. With the global push toward electric mobility, manufacturers are redesigning powertrain systems that demand bearings capable of handling high speeds and variable loads. By 2026, demand for lightweight, high-efficiency cylinder roller bearings in EVs is projected to rise, supported by investments in EV infrastructure and government emission regulations.
Expansion in Renewable Energy Applications
Wind energy is a key growth driver for cylinder roller bearings. These bearings are extensively used in wind turbine gearboxes and main shafts due to their ability to withstand high radial loads and variable operational conditions. As countries accelerate their transition to renewable energy, investments in wind farm projects—especially offshore installations—are expected to boost demand. The trend toward larger, more efficient turbines further emphasizes the need for durable and high-capacity bearings, reinforcing market growth.
Advancements in Material Science and Bearing Design
Innovation in materials—such as high-purity steel, ceramic hybrids, and advanced coatings—is enhancing the performance and lifespan of cylinder roller bearings. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to focus on developing corrosion-resistant, low-friction bearings suitable for extreme environments. Additionally, improved sealing technologies and lubrication systems will support longer service intervals, particularly in mining, construction, and rail applications.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to dominate the cylinder roller bearing market by 2026, led by industrial growth in China, India, and Southeast Asia. The region’s expanding manufacturing base, coupled with infrastructure development, will fuel demand. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see steady growth, driven by modernization of industrial equipment and strict regulatory standards promoting energy efficiency.
Supply Chain and Sustainability Trends
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in bearing manufacturing. By 2026, leading producers are expected to adopt greener production processes, including energy-efficient machining and recycling of raw materials. Additionally, localized supply chains and nearshoring strategies—accelerated by geopolitical and logistical considerations—may reshape sourcing patterns, reducing dependency on single regional suppliers.
Conclusion
The cylinder roller bearing market in 2026 will be characterized by technological innovation, sector-specific customization, and a strong emphasis on reliability and sustainability. As industries evolve toward smarter, cleaner, and more efficient operations, cylinder roller bearings will play a pivotal role in enabling these transitions, ensuring sustained market expansion and competitive differentiation among key players.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cylinder Roller Bearings: Quality and IP Concerns
Sourcing cylinder roller bearings is a critical task that demands attention to both quality standards and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Buyers, especially in manufacturing, automotive, and industrial sectors, often encounter several pitfalls that can compromise performance, safety, and legal compliance. Below are the most common issues related to quality and IP when sourcing these components.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material and Manufacturing Standards
One of the most frequent issues is receiving bearings made from substandard materials or produced using inconsistent manufacturing processes. Low-quality steel or improper heat treatment can lead to premature wear, reduced load capacity, and bearing failure. Buyers may unknowingly source from suppliers who cut corners to lower costs, resulting in non-compliance with international standards such as ISO 15 or DIN 6195.
2. Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Cylinder roller bearings require tight tolerances to ensure smooth operation and longevity. Inferior bearings often exhibit deviations in inner/outer diameter, roller diameter, or raceway geometry. These inconsistencies can cause increased friction, vibration, and system downtime, especially in high-precision applications.
3. Inadequate Heat Treatment and Surface Finish
Proper heat treatment enhances hardness and fatigue resistance. Poorly processed bearings are more susceptible to spalling, cracking, and deformation under load. Additionally, rough surface finishes accelerate wear and reduce lubrication efficiency, further degrading performance.
4. Misrepresentation of Load and Speed Ratings
Some suppliers exaggerate dynamic and static load ratings or maximum speed capabilities. This misrepresentation can lead to bearing selection errors, resulting in mechanical failure under operational stress. Always verify ratings through independent testing or trusted certification.
5. Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable bearings come with documentation such as material test reports (MTRs), ISO certifications, or inspection certificates. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide traceability increases the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant products entering the supply chain.
Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
1. Counterfeit or Replica Bearings
A major IP risk is the proliferation of counterfeit bearings that mimic well-known brands (e.g., SKF, FAG, NSK). These replicas often use similar logos, packaging, and part numbers but lack the engineering and quality control of genuine products. Using counterfeit bearings not only violates IP rights but also poses safety and reliability hazards.
2. Unauthorized Manufacturing and Brand Imitation
Some manufacturers produce bearings that closely resemble patented designs or registered trademarks without licensing. Even if the product functions acceptably, purchasing such items may expose the buyer to legal liability for facilitating IP infringement.
3. Grey Market Imports
Bearings sourced through unofficial distribution channels—often at lower prices—may be diverted goods or reconditioned units passed off as new. These products may not meet regional safety standards and could be involved in IP violations, especially if branded without authorization.
4. Lack of IP Due Diligence in Supplier Vetting
Buyers often focus on price and delivery timelines while overlooking IP compliance. Failing to audit suppliers for legitimate licensing, production rights, or brand authorization increases exposure to legal risk and reputational damage.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should work with certified suppliers, demand full documentation, conduct third-party inspections when necessary, and perform due diligence on IP compliance. Investing in genuine, high-quality cylinder roller bearings not only ensures operational reliability but also protects against legal and safety risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cylinder Roller Bearings
Product Overview
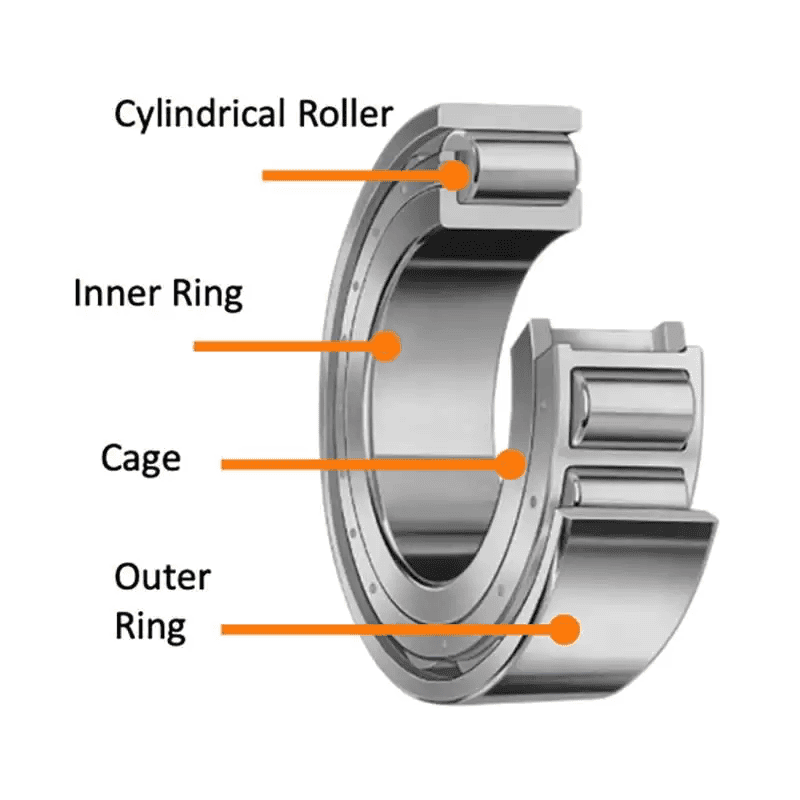
Cylinder roller bearings are precision mechanical components designed to support high radial loads with minimal friction. They consist of cylindrical rolling elements held in place by inner and outer rings and, in some designs, a cage. Due to their load capacity and performance, they are widely used in industrial machinery, automotive systems, power generation, and construction equipment. Proper logistics and compliance handling is essential to maintain performance integrity and meet regulatory requirements.
International Shipping Classification
Cylinder roller bearings are typically classified under the following Harmonized System (HS) code:
– HS Code: 8482.10 – Ball or roller bearings
This classification applies globally under the Harmonized System and is critical for accurate customs declarations, duty assessment, and import/export compliance. Always verify local customs regulations, as some countries may have sub-classifications or additional requirements.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
To ensure bearings arrive undamaged and contamination-free:
– Use original manufacturer packaging whenever possible, which includes sealed plastic wrapping and protective cartons.
– For bulk shipments, employ rigid, double-walled corrugated boxes with internal dividers to prevent movement.
– Protect against moisture with desiccants and vapor barrier materials, especially for ocean freight.
– Avoid stacking excessive weight on bearing packages; label with “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack,” and “This Side Up” indicators.
– Handle with clean gloves to prevent corrosion from skin oils.
Storage Conditions
Store cylinder roller bearings in a controlled environment to maintain performance:
– Temperature: Maintain between 15°C and 25°C (59°F–77°F).
– Humidity: Keep relative humidity below 60% to prevent rust and corrosion.
– Location: Store on shelves indoors, away from direct sunlight, dust, chemicals, and vibration sources.
– Orientation: Keep in original packaging until use; avoid horizontal stacking of large bearings to prevent deformation.
Transportation Modes and Considerations
Choose transportation methods based on urgency, cost, and destination:
– Air Freight: Recommended for high-value or time-sensitive shipments; ensures faster delivery with reduced handling.
– Ocean Freight: Cost-effective for large volumes; use containerized shipping with moisture control and secure lashing.
– Ground Transport: Suitable for regional distribution; ensure shock absorption and weather protection.
– Use tracking and insurance for all shipments exceeding standard value thresholds.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to international and regional regulations:
– REACH (EU): Confirm no restricted substances (e.g., certain lubricants or coatings) are present in bearing materials.
– RoHS (EU): Applies if bearings are part of electrical equipment; verify compliance for associated components.
– Export Controls: Bearings may fall under dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation 2021/821) if intended for military or aerospace applications. Obtain necessary export licenses when required.
– Country-Specific Regulations: Some countries impose import permits, certification (e.g., SIRIM in Malaysia, INMETRO in Brazil), or labeling requirements. Verify prior to shipment.
Documentation Requirements
Accurate documentation is critical for customs clearance and traceability:
– Commercial Invoice (with HS code, value, and country of origin)
– Packing List (detailing quantities, weights, and dimensions)
– Certificate of Origin (for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Export Declaration (as required by exporting country)
– Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), if lubricants are present
– Compliance Certificates (e.g., ISO 9001, if applicable)
Quality and Inspection Protocols
Implement checks before dispatch and upon receipt:
– Perform visual inspections for dents, corrosion, or packaging damage.
– Verify lot numbers and traceability documentation.
– Use calibrated instruments to check critical dimensions if required.
– Retain inspection records for audit and compliance purposes.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Address end-of-life considerations:
– Bearings are typically made of steel and recyclable. Dispose of through certified metal recycling programs.
– Used lubricants must be handled as hazardous waste in accordance with local regulations (e.g., EPA rules in the U.S.).
– Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive if bearings are part of electronic assemblies in the EU.
Best Practices Summary
- Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with precision components.
- Label all packages with UN-approved markings when shipping hazardous lubricants.
- Maintain a documented logistics and compliance procedure aligned with ISO standards.
- Regularly audit supply chain partners for compliance with packaging, handling, and regulatory requirements.
Adhering to this guide ensures the safe, legal, and efficient movement of cylinder roller bearings across global supply chains while minimizing risk and maximizing product reliability.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cylinder Roller Bearings
In conclusion, sourcing cylindrical roller bearings requires a careful evaluation of several critical factors including load capacity, speed requirements, precision, environmental conditions, and application-specific demands. Selecting the right supplier is equally important, with considerations such as product quality, certification (e.g., ISO standards), technical support, lead times, and cost-effectiveness playing a significant role in the decision-making process.
By partnering with reputable manufacturers or distributors and leveraging competitive sourcing strategies—such as consolidating suppliers, negotiating long-term contracts, and conducting regular performance assessments—organizations can ensure reliable supply, optimal bearing performance, and improved operational efficiency. Additionally, ongoing monitoring of market trends and advancements in bearing technology can provide opportunities for innovation and cost savings.
Ultimately, a strategic and informed approach to sourcing cylindrical roller bearings not only enhances equipment reliability and service life but also contributes to reduced maintenance costs and unplanned downtime, supporting overall productivity and competitiveness in industrial operations.