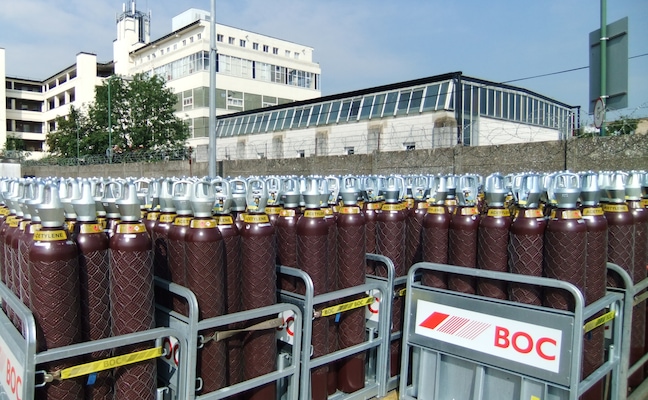
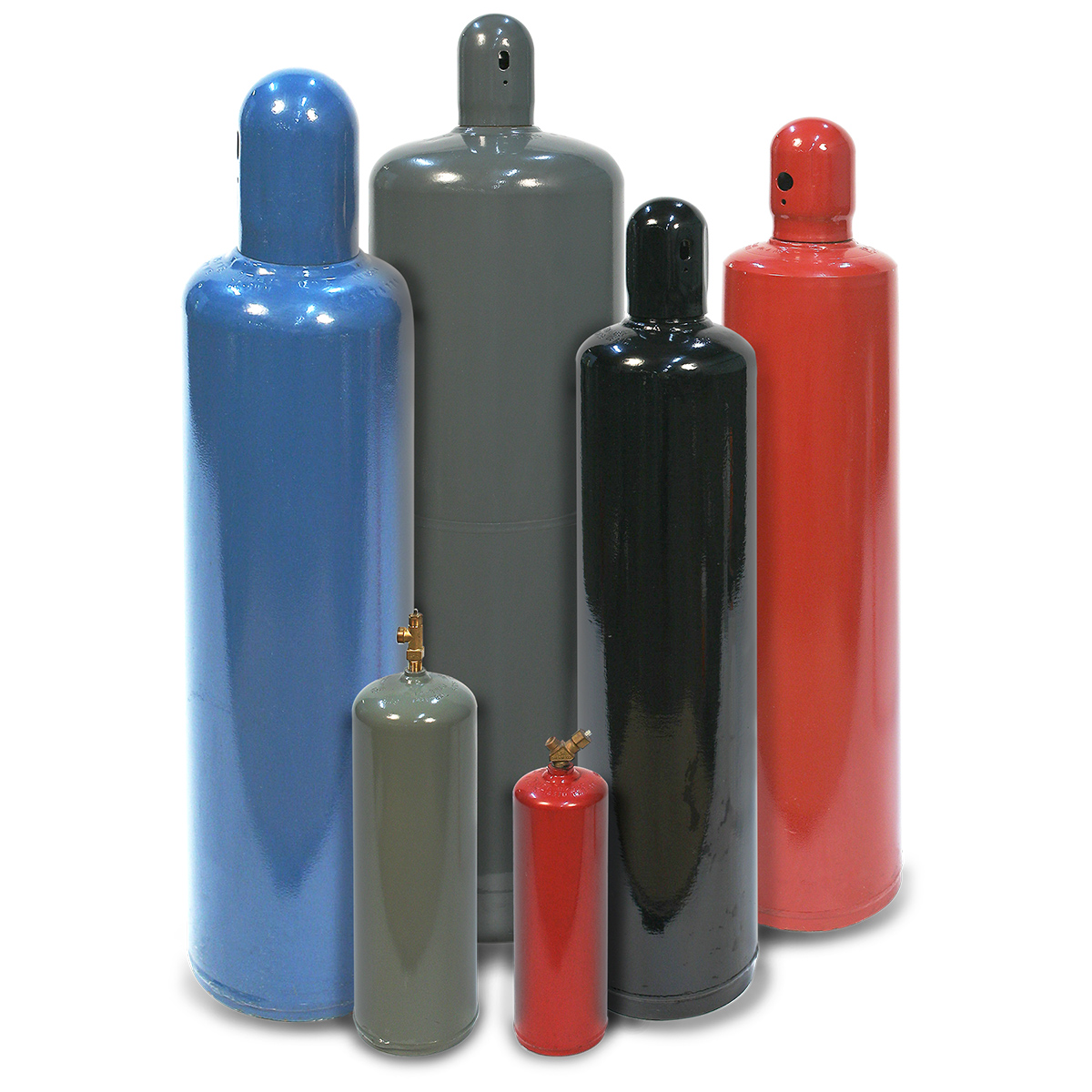
The global acetylene gas market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industrial applications such as metal fabrication, chemical synthesis, and glass manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global acetylene market was valued at USD 6.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing infrastructure development and the expanding manufacturing sector, particularly in Asia-Pacific regions. Acetylene, known for its high flame temperature in oxygen-fuel cutting and welding, remains a critical industrial gas, with cylinder-based supply systems offering portability and reliability. As demand rises, a select group of manufacturers dominate production, ensuring safety, consistency, and scalability in cylinder acetylene supply. Below are the top eight cylinder acetylene manufacturers shaping the industry’s landscape.
Top 8 Cylinder Acetylene Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Acetylene Cylinder
Domain Est. 1995
Website: airgas.com
Key Highlights: Airgas has Acetylene Cylinders for Every Need. Acetylene is one of the most popular industrial gases in use today in the oxyfuel process….
#2 Acetylene
Domain Est. 1997
Website: westernintl.com
Key Highlights: Acetylene produces the highest flame temperature of any fuel gas and is generally more flexible and easier to use in welding and cutting than alternative fuels….
#3 Acetylene Plants Applications and Services
Domain Est. 1997
Website: rexarc.com
Key Highlights: Rexarc produces a wide range of products for acetylene generator applications. Rexarc is the global leader in acetylene plant manufacturing. Visit our website….
#4 ACETYLENE from GCE Group, leading manufacturer of gas flow …
Domain Est. 2004
Website: gcegroup.com
Key Highlights: ACETYLENE. APPLICATION: Acetylene is traditional fuel gas used for oxy-fuel cutting, welding, brazing, heating and related technologies….
#5 Acetylene
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mathesongas.com
Key Highlights: A mainstay in metal fabrication, acetylene is available from MATHESON in a number of cylinder sizes, as well as multi-packs (MicroBulk) and bulk trailers….
#6 Acetylene Cylinders
Domain Est. 1998
Website: norriscylinder.com
Key Highlights: Norris Cylinder manufactures acetylene cylinders with a world renowned asbestos-free, lime-silica porous mass….
#7 Acetylene Cylinders
Domain Est. 2007
Website: rmiorder.com
Key Highlights: Acetylene cylinders equipped with valve and cap, acetone, fuse plugs and specified paint color (except MC and B cylinders). *Specify cylinder color required….
#8 Acetylene Cylinders
Domain Est. 2013
Website: acetylenegasplant.com
Key Highlights: approved tanks and cylinders that fulfill the highest design and manufacturing standards. … Acetylene Plant Manufacturing · Our Customers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cylinder Acetylene
As of now (2024), projecting market trends for cylinder acetylene in 2026 involves analyzing current industry dynamics, technological shifts, regulatory developments, and broader energy trends — particularly those involving hydrogen (H₂), which is increasingly positioned as a clean energy alternative.
Below is a comprehensive analysis of the cylinder acetylene market in 2026, with a focus on how hydrogen (H₂) technologies and market developments may influence or disrupt this sector.
🔹 Overview: Cylinder Acetylene Market (2026 Outlook)
Acetylene (C₂H₂) is primarily used in:
– Oxy-fuel welding and cutting (especially in metal fabrication and construction)
– Chemical synthesis (e.g., vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile)
– Specialty applications in glass and ceramics
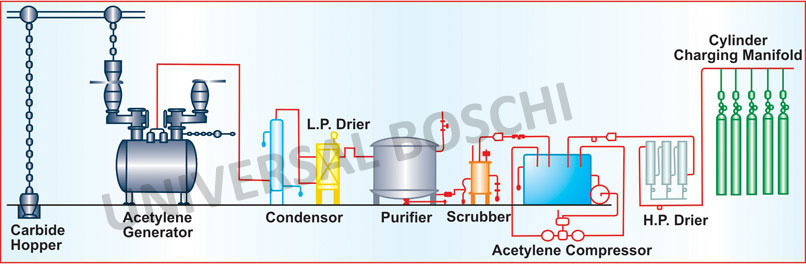
Acetylene is typically stored in cylinders containing a porous mass (like calcium silicate) saturated with acetone, which stabilizes the gas under pressure.
🔹 Key Trends Influencing the Acetylene Market in 2026
1. Declining Demand in Metalworking Due to H₂ and Alternative Technologies
- Hydrogen (H₂) is emerging as a viable alternative in oxy-fuel cutting and welding, especially with the development of hydrogen-oxygen (H₂/O₂) torches.
- Advantages of H₂ over acetylene:
- Higher flame temperature (~2800°C vs. ~3100°C for acetylene — but more controllable)
- Cleaner combustion (only produces water vapor)
- Safer handling (less prone to decomposition/explosion)
- Can be generated on-site via electrolysis, reducing dependency on gas cylinder logistics
✅ Impact on Acetylene (2026):
In industrialized markets (North America, EU, Japan), acetylene demand for welding is expected to decline by 2026 due to substitution by hydrogen-based systems and electric arc technologies.
2. Growth in Green Hydrogen Infrastructure
- Governments and industries are investing heavily in green hydrogen (produced via renewable-powered electrolysis).
- On-site H₂ generation systems are becoming cost-competitive, especially for small- to medium-scale metalworking shops.
📈 Implication:
By 2026, mobile and modular hydrogen generators could replace acetylene cylinder delivery in niche applications, reducing reliance on centralized gas supply chains.
3. Safety and Regulatory Pressures
- Acetylene is highly unstable above 15 psi and requires careful handling.
- Regulatory bodies (e.g., OSHA, EU REACH) are tightening safety standards for high-pressure flammable gases.
- In contrast, H₂, while flammable, is easier to manage with modern sensors and ventilation systems.
⚠️ Market Shift:
Safety concerns are pushing industries toward safer alternatives like hydrogen or plasma cutting, especially in automated or indoor environments.
4. Cost Competitiveness
| Factor | Acetylene | Hydrogen (H₂) |
|——-|———|—————|
| Cylinder cost | High (special handling, acetone replacement) | Lower (standard cylinders or on-site generation) |
| Energy cost | High (production via calcium carbide is energy-intensive) | Falling (especially with renewable electricity) |
| Logistics | Complex (regulated transport) | Simpler or avoidable (on-site production) |
💡 Outlook:
By 2026, on-site H₂ generation could be 20–30% cheaper than acetylene cylinder supply in regions with low-cost renewables.
5. Regional Market Divergence
- Developing Markets (India, Africa, Southeast Asia):
Acetylene demand remains strong due to: - Limited access to H₂ infrastructure
- Lower capital for new welding equipment
-
Established distribution networks for carbide-based acetylene
-
Developed Markets (EU, US, Japan):
Rapid decline in acetylene use due to: - Adoption of H₂ and plasma cutting
- Environmental regulations
- Industry 4.0 automation favoring cleaner processes
🌍 2026 Projection:
Global acetylene market may contract slightly (CAGR: -1.2% from 2024–2026), but remain stable in emerging economies.
6. Chemical Industry Demand (Offsetting Decline)
- Acetylene is still used in vinyl derivatives and specialty chemicals, especially in China.
- However, even here, ethylene-based routes are replacing acetylene due to cost and safety.
- Green H₂ could play a role in decarbonizing chemical processes, further reducing acetylene reliance.
🧪 Note:
Chemical feedstock demand may keep some acetylene production active, but not enough to offset industrial fuel use declines.
🔹 Role of H₂ in Shaping the 2026 Landscape
| H₂ Development | Impact on Acetylene |
|—————-|———————|
| On-site electrolysers | Reduces need for gas cylinder delivery; enables small workshops to adopt H₂/O₂ torches |
| Hydrogen blending in fuel gases | Early adopters may blend H₂ with acetylene to reduce emissions and cost |
| Government hydrogen subsidies | Accelerates adoption in manufacturing; e.g., EU’s Hydrogen Bank, US Inflation Reduction Act |
| H₂ storage innovations (e.g., metal hydrides, ammonia carriers) | May make H₂ safer and more accessible than acetylene cylinders |
🔹 2026 Market Forecast Summary
| Parameter | Projection for 2026 |
|———|———————|
| Global Acetylene Cylinder Market Size | ~$2.1 billion (down from ~$2.3B in 2023) |
| CAGR (2023–2026) | -1.0% to -1.5% |
| Primary Demand Region | Asia-Pacific (India, Indonesia, Vietnam) |
| Largest Decline | North America and Western Europe |
| Key Threat | Hydrogen-oxygen cutting, plasma arc, safety regulations |
| Opportunity for Acetylene | Niche chemical synthesis, legacy equipment base |
🔹 Strategic Recommendations for Industry Players
-
Diversify into H₂ Solutions:
Gas suppliers (e.g., Linde, Air Liquide) should offer H₂ generation systems alongside or instead of acetylene. -
Target Emerging Markets:
Focus cylinder acetylene sales in regions with limited H₂ infrastructure. -
Invest in Hybrid Technologies:
Develop acetylene-H₂ blend systems for transitional markets. -
Emphasize Safety and Training:
Reinforce acetylene’s role in high-precision applications where H₂ is less effective.
✅ Conclusion
By 2026, the cylinder acetylene market will face sustained pressure from hydrogen (H₂), particularly in industrialized nations. While acetylene will persist in chemical manufacturing and developing economies, its role as a fuel gas in welding and cutting will diminish due to the rise of cleaner, safer, and increasingly cost-effective hydrogen technologies.
Hydrogen is not just an alternative — it is a disruptor, and companies in the acetylene space must adapt or risk obsolescence in key sectors.
Sources: IEA Hydrogen Reports 2023, Grand View Research (Acetylene Market, 2023), Air Products, Linde, EU Hydrogen Strategy, OSHA guidelines.
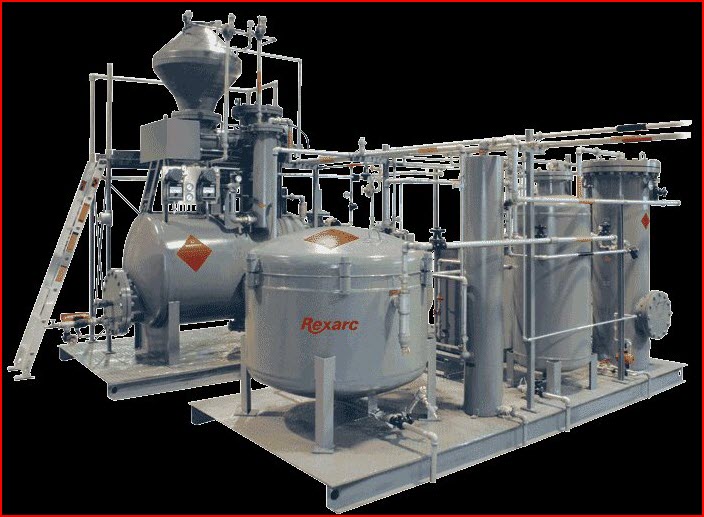

When sourcing acetylene (C₂H₂) in cylinder form, especially where high purity or specific industrial specifications (IP – Industrial Purity) are required, several common pitfalls can compromise safety, performance, and cost-efficiency. However, your note “Use H₂” suggests either a typo or an intent to consider hydrogen (H₂) as an alternative. Below is a breakdown of the common pitfalls in sourcing acetylene, followed by a rationale for why hydrogen might be considered instead, depending on the application.
🔴 Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Acetylene (C₂H₂) in Cylinders
- Poor Gas Purity / Contamination
- Issue: Low-quality acetylene may contain impurities like phosphine (PH₃), sulfur compounds, or air/moisture, leading to unstable combustion, equipment corrosion, or safety hazards.
- Impact: Affects flame quality in welding, risks flashback, and may damage sensitive processes (e.g., chemical synthesis).
-
Mitigation: Specify required purity grade (e.g., ≥99.0% or 99.5%), request COA (Certificate of Analysis), and source from reputable suppliers.
-
Improper Cylinder Fill Weight / Solvent Level
- Issue: Acetylene is dissolved in acetone (or DMF) within a porous mass (e.g., calcium silicate). Under-filling or solvent loss reduces safe withdrawal rate and usable gas volume.
- Impact: Inadequate gas supply duration, pressure fluctuations, potential for cylinder overheating during use.
-
Mitigation: Verify cylinder tare weight and solvent content during inspection; ensure supplier adheres to DOT/ISO standards.
-
Out-of-Date or Poorly Maintained Cylinders
- Issue: Acetylene cylinders require periodic hydrostatic testing (e.g., every 5–10 years depending on region).
- Impact: Risk of cylinder failure, leaks, or explosions under pressure.
-
Mitigation: Check test dates; avoid cylinders past their requalification date.
-
Incorrect Handling & Storage
- Issue: Acetylene is unstable above 15 psi (1 bar) and can decompose explosively if shocked, heated, or mishandled.
- Impact: Fire or explosion risk, especially if cylinders are stored upright, exposed to heat, or near oxidizers.
-
Mitigation: Store and use cylinders upright, in well-ventilated areas, away from heat sources, and never exceed 15 psi withdrawal pressure.
-
Unreliable Supply Chain / Gray Market Suppliers
- Issue: Non-certified or black-market suppliers may refill cylinders improperly or use substandard materials.
- Impact: Safety risks, inconsistent quality, regulatory non-compliance.
-
Mitigation: Use only certified industrial gas suppliers (e.g., Linde, Air Liquide, Praxair).
-
Lack of Traceability & Documentation
- Issue: Missing batch numbers, COAs, or safety data sheets (SDS).
- Impact: Non-compliance in regulated industries (pharma, aerospace), audit failures.
- Mitigation: Require full documentation with each delivery.
⚗️ Why Consider Hydrogen (H₂) Instead? (“Use H₂”)
Depending on your application, hydrogen may be a safer, cleaner, or more efficient alternative to acetylene:
| Application | Acetylene Pitfalls | Why H₂ May Be Better |
|———–|———————|————————|
| Welding & Metal Cutting | High risk of flashback, sooty flame, requires careful pressure control | Hydrogen-oxygen flames (e.g., in oxy-hydrogen torches) are clean, non-carbonizing, and safer in confined spaces |
| Chemical Synthesis | Impurities (e.g., PH₃) can poison catalysts | High-purity H₂ (99.999%) is readily available and critical for processes like hydrogenation |
| Fuel or Energy Carrier | Acetylene is unstable and energy-intensive to store | H₂ has higher energy density per kg and is more suitable for fuel cells or energy storage |
| Safety | Risk of explosive decomposition | H₂ is flammable but does not decompose explosively like acetylene (when handled properly) |
| Environmental Impact | Acetylene production is carbon-intensive | Green H₂ (from electrolysis) can be zero-carbon |
✅ Note: H₂ requires its own safety protocols (e.g., leak detection, ventilation due to wide flammability range), but it avoids the inherent instability of acetylene.
✅ Recommendations
- For high-purity or safety-critical applications: Consider switching from acetylene to high-purity hydrogen (H₂), especially if the process tolerates or benefits from a reducing, clean-burning flame or gas.
- If acetylene is mandatory: Source from certified suppliers, verify cylinder condition and fill quality, and enforce strict handling protocols.
- Always conduct a risk assessment: Compare H₂ vs. C₂H₂ for your specific use case—safety, cost, availability, and environmental impact.
Summary
Pitfalls in sourcing acetylene include poor purity, incorrect cylinder maintenance, safety hazards, and unreliable supply.
“Use H₂” may be sound advice—hydrogen is often a safer, cleaner, and more controllable alternative for many industrial and chemical applications traditionally using acetylene.
Let me know your specific application (e.g., welding, synthesis, calibration), and I can provide a more tailored comparison.
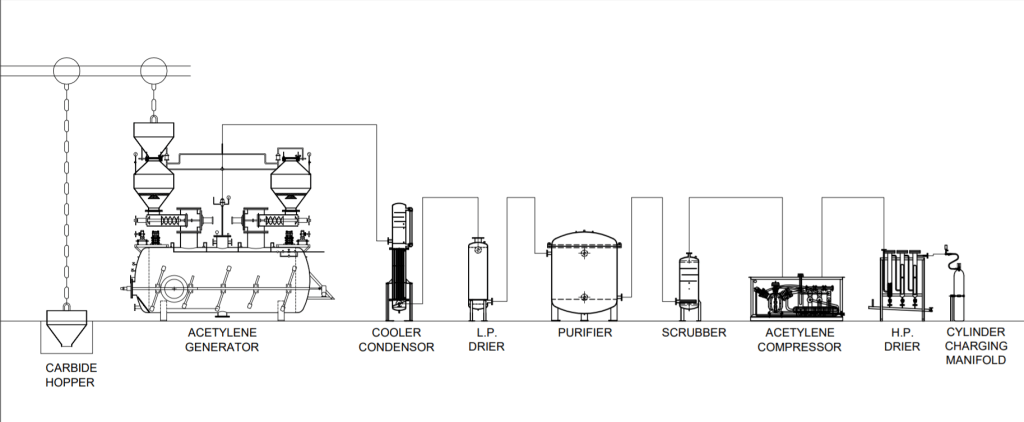
H2: Logistics and Compliance Guide for Acetylene Cylinders
Acetylene is a highly flammable and potentially unstable compressed gas used widely in welding, metal cutting, and industrial applications. Due to its unique chemical properties—particularly its tendency to decompose explosively under pressure—strict logistics and compliance protocols must be followed during handling, storage, transport, and use. This guide outlines key safety, regulatory, and operational considerations for managing acetylene cylinders.
1. Understanding Acetylene and Cylinder Design
- Chemical Properties:
- Formula: C₂H₂
- Flammable range: 2.5% to 100% in air
- Auto-ignition temperature: ~305°C (581°F)
-
Can decompose explosively without oxygen if pressurized above 15 psig (1 bar)
-
Cylinder Construction:
- Acetylene is dissolved in acetone, which is held within a porous mass (usually calcium silicate or similar) inside the cylinder.
- This design prevents the gas from reaching dangerous pressure levels and reduces decomposition risk.
- Never use acetylene cylinders in a horizontal position unless specifically designed for it.
2. Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Compliance with national and international regulations is mandatory. Key standards include:
United States
- DOT (Department of Transportation) – 49 CFR Parts 100–185
- Acetylene is classified as Hazard Class 2.1 (Flammable Gas).
- Cylinders must be:
- DOT-qualified (e.g., DOT 8AL, DOT 3AL)
- Periodically requalified (typically every 5 years)
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.102 – Safety requirements for acetylene use
- Maximum withdrawal rate: 1/7 of cylinder capacity per hour to prevent acetone withdrawal
- Prohibition of copper fittings >65% copper (risk of explosive acetylides)
- NFPA 51: Standard for the Design and Installation of Acetylene Piping Systems
International
- UN Number: 1001
- IMO/IMDG Code – For maritime transport
- ADR – For road transport in Europe
- IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations – For air transport (acetylene is generally prohibited on passenger aircraft; limited exceptions for cargo under special provisions)
3. Handling and Storage
Handling
- Always use proper cylinder caps when moving or storing.
- Transport using cylinder carts; never roll or drag.
- Use correct personal protective equipment (PPE): gloves, safety glasses, flame-resistant clothing.
- Secure cylinders during transport to prevent tipping.
Storage
- Store in a well-ventilated, dry, fire-resistant area away from:
- Oxidizers (e.g., oxygen, chlorine)
- Heat sources, sparks, and direct sunlight
- Keep upright and secured with chains or straps.
- Storage area must:
- Be labeled “Flammable Gas”
- Have fire extinguishers (e.g., CO₂ or dry chemical) nearby
- Be at least 20 feet (6 meters) from combustibles or separated by a fire wall
- Maximum storage temperature: 52°C (125°F)
4. Transport Requirements
- Vehicle Requirements:
- Ventilated cargo area
- “Flammable Gas” placards (Class 2.1) required for loads exceeding threshold quantities
- No smoking policy enforced
- Segregation:
- Separate from oxidizers and ignition sources
- Do not transport with passenger vehicles unless in approved containers
- Documentation:
- Shipping papers must include:
- Proper shipping name: “Acetylene, dissolved”
- UN number: 1001
- Hazard class: 2.1
- Packing group: II
- Emergency contact information
5. Use and Operational Safety
- Pressure Regulation:
- Use acetylene-rated regulators only.
- Never exceed 15 psig (1 bar) outlet pressure.
- Hose and Fittings:
- Use only approved acetylene hoses (typically red).
- Avoid copper or copper-alloy fittings (>65% copper).
- Ventilation:
- Use in well-ventilated areas to prevent accumulation.
- Leak Detection:
- Use soapy water solution (never flame) to check for leaks.
- Decommissioning:
- Return empty cylinders to supplier; do not refill or modify.
6. Emergency Response
- Leak:
- Evacuate area, eliminate ignition sources, ventilate.
- If safe, move cylinder to open area.
- Fire:
- Evacuate and call emergency services.
- Apply water to cool cylinders; do not extinguish flame unless leak can be stopped.
- Decomposition:
- Rare but catastrophic; evacuate immediately if hissing or overheating is observed.
Emergency Contacts:
– Local fire department
– Poison control (if inhalation suspected)
– Supplier or manufacturer emergency line
7. Training and Documentation
- Personnel must be trained in:
- Hazard communication (HazCom)
- DOT/IATA/ADR requirements (as applicable)
- Emergency procedures
- Maintain records of:
- Cylinder inspections and requalifications
- Employee training
- Incident reports
Conclusion
Safe logistics and compliance for acetylene cylinders require adherence to strict technical, regulatory, and operational standards. Due to the inherent hazards of acetylene, proactive risk management, proper training, and continuous vigilance are essential. Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and applicable regulations before handling or transporting acetylene.
Note: Regulations vary by jurisdiction. Always verify compliance with local, state, and federal authorities.
Conclusion for Sourcing Acetylene Cylinders
Sourcing acetylene cylinders requires careful consideration of safety, regulatory compliance, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Acetylene is a highly flammable and unstable gas, making proper handling, storage, and transportation critical. It is essential to partner with certified and reputable suppliers who adhere to national and international safety standards such as those set by OSHA, CGA, and ISO.
Key factors in the sourcing decision include the quality of the cylinder and its internal porous material (typically acetone-soaked), certification and inspection history, cylinder maintenance programs, and the availability of technical support. Additionally, understanding the total cost of ownership—factoring in refill frequency, delivery logistics, rental or purchase options, and safety equipment—is crucial for long-term efficiency.
Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach that balances safety, supply chain reliability, and cost will ensure a consistent and secure acetylene supply for welding, cutting, or other industrial applications. Regular vendor assessments and adherence to safety protocols further mitigate risks and support operational continuity.