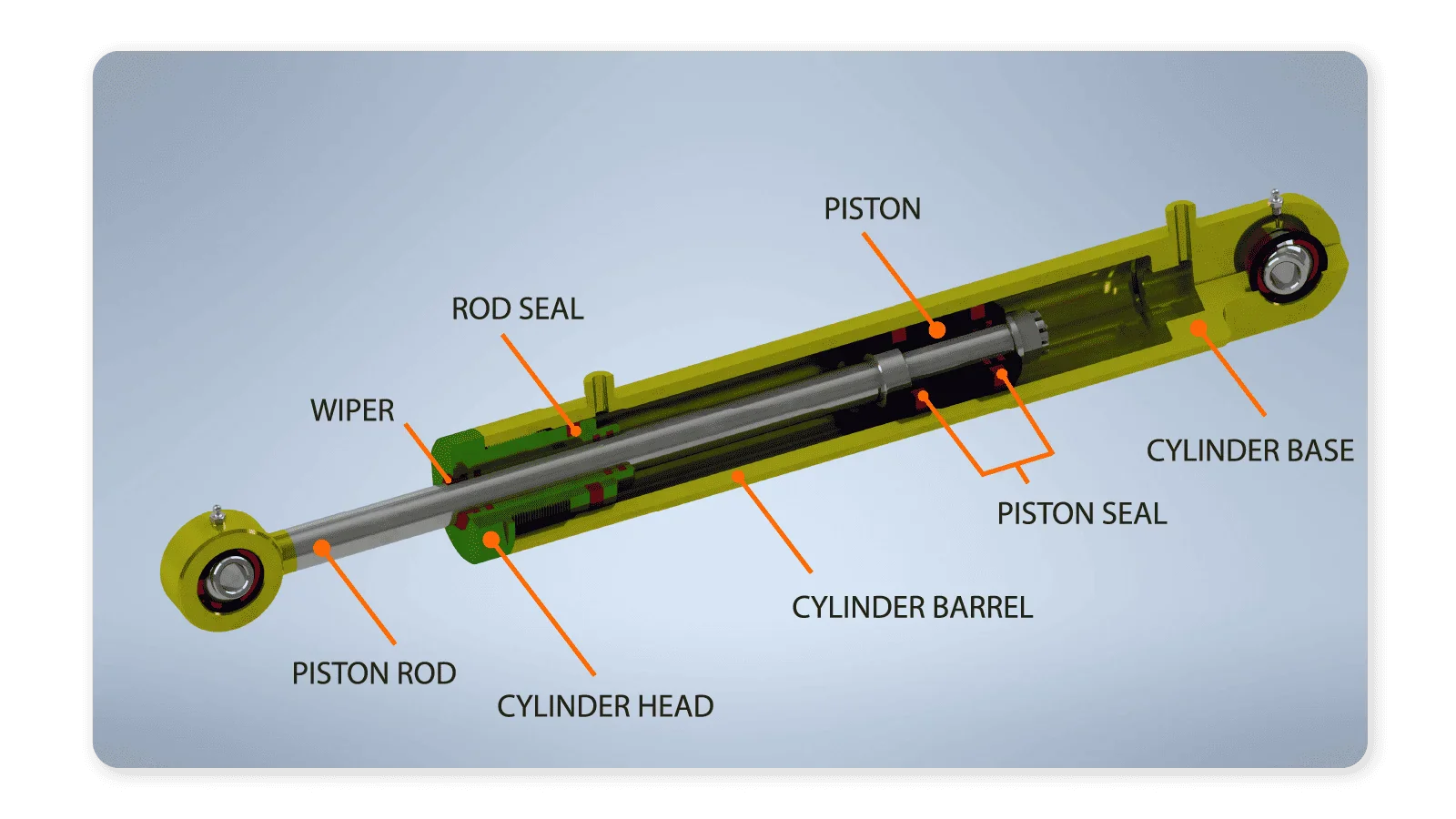
The global cylinder block manufacturing market is undergoing significant expansion, driven by rising automotive production, increasing demand for fuel-efficient engines, and advancements in lightweight materials. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the engine components market—which includes cylinder blocks—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is further supported by Grand View Research, which estimates the global engine block and cylinder head market to expand at a CAGR of approximately 4.2% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by the surge in vehicle electrification and the need for high-performance internal combustion engines in hybrid applications. As OEMs prioritize durability, thermal efficiency, and casting precision, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, scale, and global supply chain integration. Here’s a data-informed look at the top 10 cylinder block manufacturers shaping the future of engine technology.
Top 10 Cyl Block Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hydraulic Cylinders Purpose
Domain Est. 2002
Website: aggressivehydraulics.com
Key Highlights: Custom Hydraulic Cylinders. Our Purpose-Built™ hydraulic cylinders are engineered for high performance in demanding applications….
#2 Hydraulic Cylinders for Molds • Vega Cylinders • Official Shop
Domain Est. 2015
Website: vegacylinders.com
Key Highlights: Vega Cylinders is an international manufacturer of hydraulic cylinders, specifically designed for the plastic injection molding and die-casting industry….
#3 Cylinder Block Manufacturer, Supplier & Exporter
Domain Est. 2017
Website: aecoproducts.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (30) ISO Approved Highly Professional Engine Cylinder Block Air Cooled and Water Cooled Manufacturer. Worldwide Supplier, Exporter and Wholesaler (Estd. 1953)…
#4 Dart Machinery
Domain Est. 1996
Website: dartheads.com
Key Highlights: Dart has become the proven leader in aftermarket cylinder heads, intake manifolds and engine blocks. Learn More…
#5 Brodix
Domain Est. 1998
Website: brodix.com
Key Highlights: For over 50 years Brodix has been the only cylinder head company to perform each stage of the manufacturing process under one roof….
#6 L.A.SLEEVE
Domain Est. 1999
Website: lasleeve.com
Key Highlights: Stop by to see the latest cylinder sleeve models and custom products available from L.A.SLEEVE! L.A.SLEEVE Celebrates 80 Years as a Family Owned Business ……
#7 Cylinder Blocks & Components
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kmpbrand.com
Key Highlights: KMP stock an extensive range of cylinder blocks and associated components suitable for Caterpillar®, Komatsu®, Cummins®, Detroit Diesel®, John Deere®, Case IH® ……
#8
Domain Est. 2012
Website: hpsinternational.com
Key Highlights: HPS production plants can design and manufacture all types of hydraulic cylinders, up to the maximum dimensions of 1 000 mm bore and 11 000 mm stroke….
#9 Cylinder Block, Cylinder Head Custom, Diesel Cylinder Block …
Domain Est. 2016 | Founded: 1977
Website: zhdlen.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1977, our company has developed into a well-known supplier of cylinder blocks, bearing caps, oil pump bodies, gearbox housings and motor casings….
#10 ENGINE BLOCK & CYLINDER HEAD
Domain Est. 2019
Website: hema-usa.com
Key Highlights: A cylinder block, often referred to as an engine block, is used as a bearing for pistons and crankshafts in engines for cars, trucks, and tractors….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cyl Block

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Cylinder Blocks (Cyl Block)
The global cylinder block market is poised for notable transformation in the second half of 2026 (H2 2026), driven by technological innovation, regulatory shifts, and evolving end-market dynamics. Below is a comprehensive analysis of key trends shaping the Cyl Block industry during this period.
1. Accelerated Shift Toward Lightweight Materials
In H2 2026, demand for aluminum and advanced composite cylinder blocks is expected to grow significantly. With automakers striving to meet stricter global emissions standards (e.g., Euro 7, China 7, and updated U.S. CAFE standards), lightweighting remains a core strategy. Aluminum cylinder blocks offer weight reductions of up to 30% compared to traditional cast iron, improving fuel efficiency and reducing CO₂ emissions. Investment in high-pressure die-casting (HPDC) and sand casting with alloy optimization will support mass production of high-integrity aluminum blocks.
2. Integration with Hybrid Powertrains
As hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) reach peak adoption in key markets (Europe, China, and North America), OEMs are redesigning internal combustion engines (ICEs) for hybrid synergy. Cylinder blocks in H2 2026 are increasingly engineered for smaller displacement, higher thermal efficiency, and compatibility with stop-start systems and electric turbocharging. Modular Cyl Block platforms that support both ICE and hybrid configurations are gaining traction, enabling cost-effective scalability across vehicle lineups.
3. Geopolitical Supply Chain Restructuring
Ongoing trade tensions and regionalization of manufacturing are reshaping Cyl Block production. In H2 2026, nearshoring and friend-shoring trends are accelerating, particularly in North America and Eastern Europe. U.S. and EU incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and Green Deal Industrial Plan are driving investments in localized casting facilities and machining centers. This reduces dependency on Asian foundries and mitigates logistics risks, though it may increase short-term production costs.
4. Rise of Electrification Pressuring ICE Volumes
While cylinder blocks remain essential for ICE and hybrid applications, long-term demand is being tempered by the rise of battery electric vehicles (BEVs). In H2 2026, BEV market share is expected to exceed 35% in Western Europe and 25% in China. However, emerging markets (India, Southeast Asia, Latin America) continue to rely on ICEs, supporting stable demand for cost-effective cast iron Cyl Blocks. Global production is expected to plateau, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of +0.8% through 2026, driven by replacement and commercial vehicle demand.
5. Adoption of Smart Manufacturing and AI-Driven Quality Control
Foundries and OEMs are increasingly deploying Industry 4.0 technologies in H2 2026. Real-time monitoring of casting processes using IoT sensors, machine learning for defect prediction, and digital twin modeling are enhancing yield rates and reducing scrap. AI-driven simulation tools optimize coolant jacket and cylinder bore design for improved thermal management—critical for high-performance and downsized engines.
6. Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Environmental regulations are pushing foundries to reduce carbon footprints. In H2 2026, electric melting furnaces powered by renewable energy and closed-loop recycling systems are becoming standard in leading facilities. Aluminum Cyl Block recycling rates exceed 95%, enhancing sustainability profiles. OEMs are also demanding Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) for components, influencing procurement decisions.
7. Commercial Vehicle Segment as a Growth Anchor
While passenger car ICE production declines in mature markets, the commercial vehicle (CV) sector—especially medium- and heavy-duty trucks—remains heavily reliant on robust cast iron cylinder blocks. With global freight demand rising and alternative fuels (e.g., hydrogen ICE, natural gas) still in early adoption, CV OEMs are investing in durable, high-load Cyl Blocks. This segment is expected to account for over 40% of Cyl Block demand in H2 2026.
Conclusion
H2 2026 marks a transitional phase for the cylinder block market: innovation continues to enhance ICE efficiency and manufacturability, but long-term demand faces structural headwinds from electrification. Success will depend on agility—adopting lightweight materials, hybrid compatibility, sustainable processes, and regional supply chains. While the era of ICE dominance is waning, Cyl Blocks will remain a vital component through 2030, particularly in hybrids and commercial applications.
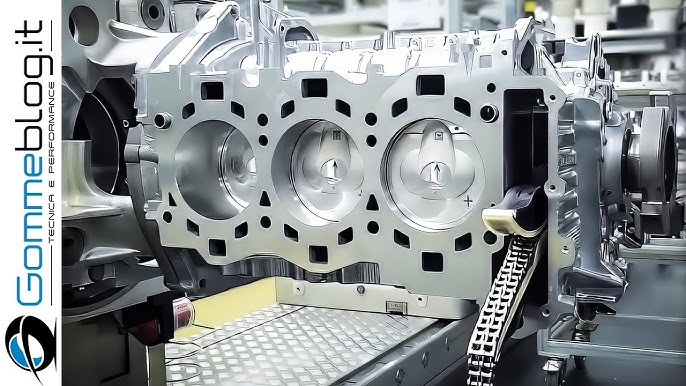
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Cylinder Blocks: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing cylinder blocks, especially from external suppliers or low-cost regions, presents significant challenges related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these risks can lead to costly production delays, product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications and Metallurgy
A major quality concern is receiving cylinder blocks made from substandard materials. Suppliers may use incorrect grades of cast iron or aluminum alloys, or fail to adhere to required heat treatment processes. This can result in reduced strength, poor wear resistance, increased porosity, and susceptibility to cracking under thermal and mechanical stress—ultimately leading to engine failure.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Cylinder blocks require extremely tight tolerances for bore diameters, deck flatness, and alignment of critical features like crankshaft and camshaft bores. Inadequate machining capability or lax quality control at the supplier can result in out-of-spec parts that compromise engine performance, increase oil consumption, or cause assembly line disruptions.
Defects in Casting and Machining
Common casting defects such as porosity, inclusions, cold shuts, and shrinkage cavities may go undetected without rigorous inspection. Similarly, machining errors like improper surface finishes or burrs can interfere with sealing surfaces and component fitment. Without proper non-destructive testing (NDT) and in-process inspections, these defects can pass through to the final product.
Insufficient Process Control and Documentation
Suppliers may lack robust quality management systems (e.g., IATF 16949 certification), resulting in inconsistent production processes. Absence of documented process validation, first-article inspections, and statistical process control (SPC) data makes it difficult to ensure long-term reliability and traceability of components.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Replication and Reverse Engineering
Providing detailed technical drawings and CAD models to suppliers increases the risk of IP theft. Unscrupulous suppliers may reverse engineer the cylinder block design and produce unauthorized copies for resale to competitors or third parties, diluting market exclusivity and eroding competitive advantage.
Lack of Legal Safeguards and Enforcement
In regions with weak IP protection laws or lax enforcement, contractual agreements such as Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and licensing terms may offer limited recourse. Even with strong contracts, pursuing legal action can be time-consuming and costly, particularly across international jurisdictions.
Unauthorized Sub-Tier Sourcing and Diversion
Suppliers may subcontract manufacturing to unapproved facilities without consent, increasing the risk of IP exposure and quality inconsistencies. Parts produced under contract may also be diverted into gray markets or sold to unauthorized customers, undermining pricing strategies and brand integrity.
Inadequate Control Over Design Data and Tools
Failure to restrict access to proprietary tooling (e.g., molds, fixtures) and digital design files heightens the risk of duplication. Suppliers retaining ownership or unrestricted use of tooling after contract completion can manufacture and sell the same parts independently.
Mitigation Strategies
To address these pitfalls, companies should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits, including on-site quality system reviews.
– Require certifications such as IATF 16949 and perform regular quality audits.
– Implement robust IP protection measures, including watermarked drawings, limited data sharing, and secure data transfer protocols.
– Draft comprehensive legal agreements with clear IP ownership, usage rights, and penalties for violations.
– Maintain ownership of tooling and enforce strict controls on sub-tier sourcing.
– Perform independent quality validation through third-party testing and batch sampling.
Proactively managing both quality and IP risks is essential to ensure reliable performance, protect innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in engine manufacturing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cylinder Block
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling, transportation, and documentation of cylinder blocks throughout the supply chain.
Handling and Packaging Requirements
Cylinder blocks are heavy, precision-engineered components that require careful handling to prevent damage and ensure safety. Use secure, reusable pallets or custom crates with protective padding (e.g., foam or corrugated inserts) to prevent scratches, corrosion, and structural deformation. Clearly label all packages with orientation indicators (e.g., “This Side Up”) and weight warnings. Employ mechanical lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts or overhead cranes with appropriate slings) during loading and unloading to reduce manual handling risks.
Transportation Standards
Transport cylinder blocks via temperature-controlled, enclosed vehicles (e.g., dry vans or refrigerated trucks if required) to protect against moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. Secure loads using straps, dunnage, or load-locking systems to prevent shifting during transit. Choose carriers experienced in handling industrial engine components and verify their adherence to safety and delivery protocols. For international shipments, ensure compliance with International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) or IATA regulations if applicable (e.g., residual oils or coatings present).
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure cylinder blocks meet regional and international regulatory standards, including:
– Emissions and Environmental Regulations: Comply with EPA (U.S.), EU Stage V, or equivalent emissions directives if the block is part of a regulated engine system.
– REACH and RoHS: Verify that materials used in the cylinder block (e.g., alloys, coatings) are compliant with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives in the EU.
– Country-Specific Approvals: Confirm compliance with local standards such as CCC (China), PSE (Japan), or BIS (India) when exporting.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain complete and accurate documentation for each shipment, including:
– Commercial invoice with HS code (typically 8409.91 for engine parts)
– Packing list detailing item count, weight, and dimensions
– Certificate of Origin
– Material Compliance Certificate (e.g., RoHS, REACH)
– Test and inspection reports (e.g., pressure testing, dimensional verification)
Implement a traceability system (e.g., barcode or RFID tagging) to track each cylinder block from manufacturing through delivery, supporting warranty claims and recall management if necessary.
Import/Export Controls
Classify cylinder blocks accurately under the Harmonized System (HS) for customs purposes—commonly 8409.91.00 (parts of internal combustion piston engines). Verify export license requirements, especially when shipping to sanctioned countries or if the block contains controlled materials or dual-use technologies. Use Incoterms® 2020 (e.g., FOB, EXW, or DDP) to clearly define responsibilities between buyer and seller.
Storage and Inventory Management
Store cylinder blocks in a dry, climate-controlled warehouse environment to prevent rust and contamination. Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory practices to minimize aging and obsolescence. Elevate pallets off the floor and cover components if not in sealed packaging. Conduct regular audits to ensure stock accuracy and detect potential damage or corrosion.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Dispose of packaging materials in accordance with local recycling and waste regulations. Handle used or rejected cylinder blocks containing residual oils or coolants as hazardous waste where applicable. Provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) if hazardous substances are present. Train personnel in proper handling, emergency procedures, and use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Quality Assurance and Audits
Implement a logistics quality management system aligned with ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 standards. Conduct regular audits of logistics partners and internal procedures to ensure compliance with packaging, handling, and documentation requirements. Address non-conformances promptly and update procedures to prevent recurrence.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cylinder Block:
In conclusion, sourcing a cylinder block requires a comprehensive evaluation of factors such as quality, cost, supplier reliability, lead times, and compatibility with engine specifications. Whether procuring new, remanufactured, or used components, it is essential to partner with trusted suppliers who adhere to industry standards and provide traceable, durable products. A strategic sourcing approach—balancing cost-efficiency with performance and longevity—will ensure optimal engine function and reduce downtime. Ultimately, prioritizing quality and supply chain resilience in cylinder block procurement supports long-term operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.