The global market for laboratory consumables, including culture flasks, has seen steady expansion driven by rising R&D investments in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and academic research. According to Grand View Research, the global laboratory plastics market was valued at USD 11.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing demand for cell culture applications in vaccine development, cancer research, and regenerative medicine. As bioprocessing and advanced therapeutic development scale globally, the need for high-quality, reliable culture flasks—critical for cell expansion and maintenance—has intensified. Manufacturers that offer sterile, consistent, and scalable solutions are at the forefront of this demand. Based on performance, innovation, and market presence, the following nine culture flask manufacturers have emerged as leaders in meeting the evolving needs of modern life science laboratories.
Top 9 Culture Flask Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Products
Domain Est. 2021
Website: cellcultureflasks.com
Key Highlights: Our products are of high quality and low price. We are the manufacturer and supplier of China Cell Culture Flasks, Tissue culture flask….
#2 Falcon® Cell Culture Flasks
Domain Est. 1991
Website: ecatalog.corning.com
Key Highlights: Falcon® Cell Culture Flasks · Vacuum-gas plasma tissue culture treatment provides consistent cell attachment, spreading, and growth · Choose standard tissue ……
#3 Cell Culture Flasks
Domain Est. 1996
Website: dwk.com
Key Highlights: Manufactured from borosilicate glass, our cell culture flasks offer excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, with select models available with KIMAX ……
#4 Cell Culture Flasks, 75 cm²
Domain Est. 2003
Website: mpbio.com
Key Highlights: 11-day delivery 30-day returnsWe offer cell culture flasks ranging from surface areas of 25 cm² up to 175 cm²….
#5 Cell Culture Flask
Domain Est. 2005
Website: spllifesciences.com
Key Highlights: Culture flasks of SPL Life Sciences are ergonomically designed for easy handling, while achieving minimal contamination during cell culture. Short, wide and ……
#6 Cell Culture Flasks
Domain Est. 2006
Website: thermofisher.com
Key Highlights: Thermo Scientific cell culture flasks are designed for consistency, cell health, and reproducibility. Nunc flasks offer surface and ancillary options for your ……
#7 Tissue Culture Flasks
Domain Est. 2007
Website: celltreat.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryTissue Culture Treated and Suspension Culture Flasks. Larger growth area vs. other brands. Deep Volume Flask available for more media volume….
#8 Cell Culture Flask
Domain Est. 2018
Website: yonyue.com
Key Highlights: Yongyue Medical produces a complete set of cell culture products, welcome to buy. For example, serological pipettes, glass slides, Pasteur pipettes, ……
#9 Tissue Culture Flasks 25
Website: tpp.ch
Key Highlights: Tissue Culture Flasks 25 – 300 cm excellent access of pipettes, tissue scrapers and tissue spatula. marking area with lines on both sides to allow your ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Culture Flask

2026 Market Trends for Culture Flask
Culture Flask, as a platform focused on cultural discovery, experiential learning, and community engagement, is poised to benefit from several converging market trends in 2026. These dynamics will shape user expectations, technological integration, and competitive positioning in the global experience economy.
Rising Demand for Authentic and Immersive Cultural Experiences
By 2026, travelers and learners are increasingly rejecting superficial tourism in favor of deep, meaningful cultural engagement. A post-pandemic shift toward purpose-driven travel, combined with Gen Z and younger Millennial preferences, fuels demand for experiences that offer genuine human connection, local narratives, and participatory activities—such as cooking with artisans, language exchanges, or traditional craft workshops. Culture Flask can capitalize on this by curating hyper-local, community-led experiences that emphasize sustainability and cultural preservation.
Growth of the Digital-Physical Hybrid Experience Economy
The blending of digital access with real-world immersion will define 2026’s experience landscape. Culture Flask can leverage augmented reality (AR), virtual pre-tours, and AI-guided cultural insights to enhance physical experiences. For example, users might preview a Kyoto tea ceremony via VR, then book the in-person session through the platform. This hybrid model extends accessibility while deepening engagement, appealing to both remote learners and on-site explorers.
AI-Personalization and Predictive Curation
Advancements in AI and machine learning enable hyper-personalized recommendations based on user behavior, cultural interests, and learning styles. By 2026, Culture Flask can deploy intelligent algorithms to suggest tailored itineraries, language modules, or local events—anticipating user needs before they search. This level of personalization increases user retention and satisfaction, positioning the platform as a cultural concierge rather than a mere booking tool.
Emphasis on Ethical and Sustainable Cultural Tourism
Consumers in 2026 are more conscious of cultural commodification and the environmental impact of travel. Platforms that prioritize fair compensation for local guides, minimize cultural appropriation, and promote regenerative tourism models will gain trust and market share. Culture Flask can lead by embedding ethical guidelines into its curation process, partnering with certified community cooperatives, and transparently sharing impact metrics with users.
Expansion of the Lifelong Learning and Edutainment Market
The boundary between education and entertainment continues to blur. Adults are investing in self-development through cultural fluency, language acquisition, and historical literacy. Culture Flask can evolve into a micro-learning platform, offering short-form video lessons, interactive timelines, and gamified quizzes tied to real-world experiences—turning cultural exploration into an ongoing, rewarding journey.
Increased Competition from Niche Platforms and Super-Apps
While demand grows, so does competition. In 2026, Culture Flask will face challenges from specialized cultural apps (e.g., language immersion platforms) and super-apps (like WeChat or Grab) expanding into cultural experiences. To differentiate, Culture Flask must double down on its core strengths: authenticity, community curation, and cross-cultural storytelling—building a brand synonymous with trust and depth.
Conclusion
The 2026 market presents significant opportunities for Culture Flask to position itself at the intersection of technology, ethics, and human connection. By embracing immersive tech, AI-driven personalization, and sustainable practices, the platform can become a global leader in meaningful cultural exchange—transforming curiosity into connection.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Culture Flasks (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing culture flasks—especially for specialized bioprocessing, research, or commercial applications—can present several challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for maintaining process integrity, ensuring regulatory compliance, and protecting your organization from legal and operational setbacks.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material Composition
Not all culture flasks are created equal. Low-cost suppliers may use substandard polymers (e.g., polystyrene with inconsistent surface treatments) that affect cell adhesion, growth, or viability. Variability in gamma irradiation or plasma treatment can result in batch-to-batch inconsistency, compromising experimental reproducibility.
2. Poor Surface Treatment and Coating Uniformity
Many flasks rely on surface modifications (e.g., tissue-culture treated or ECM-coated surfaces) for optimal cell attachment. Sourcing from unreliable vendors may result in uneven or ineffective coating, leading to poor cell yield and inconsistent experimental outcomes.
3. Contamination Risks
Flasks that are not manufactured or packaged under sterile conditions—or lack proper endotoxin testing—can introduce microbial or pyrogenic contamination. This is especially critical in GMP or clinical applications where sterility is non-negotiable.
4. Inaccurate Dimensional Specifications
Minor deviations in flask geometry, lid tightness, or venting design can affect gas exchange, evaporation rates, or compatibility with automated systems. Poorly sourced flasks may not fit standard incubators or robotic handlers, disrupting workflows.
5. Lack of Traceability and Certifications
Reputable suppliers provide lot-specific certificates of analysis (CoA), ISO certifications, and regulatory documentation (e.g., USP Class VI, animal-component-free declarations). Overlooking these can expose users to compliance risks, particularly in regulated environments.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Designs
Many advanced flask designs (e.g., vented caps, stackable configurations, or proprietary gas-permeable materials) are protected by patents. Sourcing from third-party manufacturers that replicate patented features without licensing can expose your organization to infringement claims, even if unintentional.
2. Use of Counterfeit or Grey-Market Products
Counterfeit flasks—often reverse-engineered or rebranded—may mimic well-known brands but lack performance validation. Using such products can violate trademark laws and result in supply chain liability, especially if they fail during critical experiments or production.
3. Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
If you collaborate with a supplier to develop a custom flask, failure to define IP ownership in the contract may result in shared or lost rights. This can limit your ability to scale, license, or protect your innovation.
4. Data and Process Exposure Risks
When sourcing custom solutions, disclosing sensitive information about cell lines, media formulations, or process parameters to suppliers without NDAs or IP safeguards can compromise trade secrets or future patentability.
Mitigation Strategies
- Qualify Suppliers Rigorously: Audit manufacturers for quality systems (e.g., ISO 13485), testing protocols, and regulatory compliance.
- Verify Authenticity: Purchase through authorized distributors and request documentation to confirm product legitimacy.
- Conduct Performance Testing: Pilot-test new flask batches for cell growth, sterility, and compatibility before full-scale adoption.
- Review IP Landscape: Conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses before adopting novel flask designs.
- Use Clear Contracts: Define IP ownership, liability, and confidentiality terms when developing or sourcing custom products.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and legal protection when sourcing culture flasks.
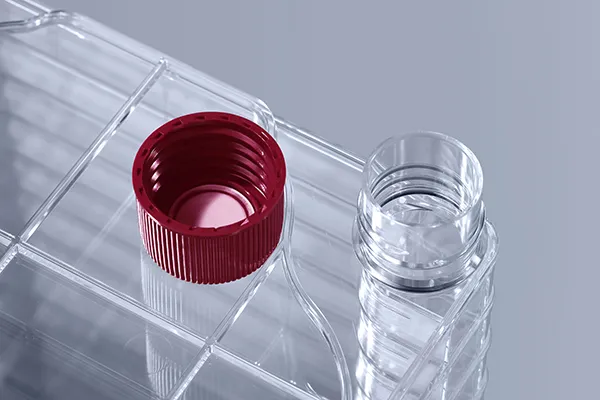

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Culture Flask
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for handling, storing, shipping, and documenting culture flasks in laboratory, biotech, and research environments. Adhering to these protocols ensures biosafety, regulatory compliance, and the integrity of biological materials.
Shipping and Transportation
When shipping culture flasks, compliance with national and international regulations is mandatory. Culture flasks containing biological substances are typically classified as Biological Substance, Category B (UN3373) if they do not meet the criteria for Category A. Use a triple packaging system:
– Primary container: Leak-proof culture flask sealed with parafilm or screw cap.
– Secondary container: Watertight and leak-resistant, with absorbent material if liquid media is present.
– Outer packaging: Rigid, marked with the UN3373 diamond label and proper shipping name: “Biological Substance, Category B.”
Ensure all shipments include completed shipping manifests, sender/recipient details, and emergency contact information. Use only IATA-compliant couriers for air transport.
Storage and Handling
Culture flasks must be stored under appropriate environmental conditions to maintain viability and prevent contamination.
– Store upright in a biosafety cabinet (BSC) or incubator set at the optimal temperature (typically 37°C for mammalian cells).
– Maintain humidity and CO₂ levels as required by the cell line.
– Label each flask with the cell line name, passage number, date, and biosafety level.
– Use personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, lab coat, and eye protection when handling.
Rotate stock using a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to minimize culture aging.
Biosafety and Containment
Culture flasks must be handled according to the designated biosafety level (BSL) of the organism.
– BSL-1 and BSL-2 cultures require work in a certified biosafety cabinet and adherence to standard microbiological practices.
– Decontaminate flasks and work surfaces with 70% ethanol or approved disinfectants after use.
– Autoclave used flasks before disposal in accordance with institutional waste protocols.
Document all incidents involving spills or exposure per institutional biosafety officer (IBO) requirements.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with relevant regulatory bodies, including:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Bloodborne Pathogens and Hazard Communication Standards.
– CDC/NIH Guidelines: Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories (BMBL).
– DOT and IATA: Proper classification, packaging, and documentation for transport.
– Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC): Registration and approval for recombinant or synthetic nucleic acid experiments.
Maintain up-to-date Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), training records, and inventory logs.
Documentation and Traceability
Complete and retain records for accountability and audit readiness. Required documentation includes:
– Cell line origin and authentication reports (e.g., STR profiling).
– Culture maintenance logs (passaging, media changes, observations).
– Shipping manifests and chain-of-custody forms.
– Training and competency records for personnel.
Electronic lab notebooks (ELNs) are recommended for secure, searchable recordkeeping.
Disposal and Decontamination
Dispose of culture flasks only after proper decontamination:
– Liquid cultures: Autoclave at 121°C for a minimum of 30 minutes.
– Empty flasks: Soak in disinfectant (e.g., 10% bleach) for 30 minutes, then autoclave.
– Segregate waste into biohazard containers clearly labeled for regulated medical waste.
Never dispose of culture flasks in regular trash or down the sink without decontamination.
Conclusion for Sourcing Culture Flasks
In conclusion, sourcing culture flasks is a critical step in ensuring the success and reliability of cell culture and microbiological research. The selection process must consider several key factors, including material quality (typically borosilicate glass or polystyrene), sterility, surface treatment (e.g., cell-adherent coatings), compatibility with handling equipment, and adherence to international standards (such as ISO certifications). Additionally, evaluating supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and supply chain consistency is essential to maintain uninterrupted laboratory workflows.
By prioritizing flasks that offer optimal gas exchange, uniform cell growth, and minimal contamination risk, researchers can enhance experimental reproducibility and data integrity. Furthermore, considering sustainable and eco-friendly sourcing options can support long-term laboratory sustainability goals.
Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy for culture flasks not only supports scientific accuracy and efficiency but also contributes to the overall success of research and development initiatives in academic, clinical, and industrial settings.