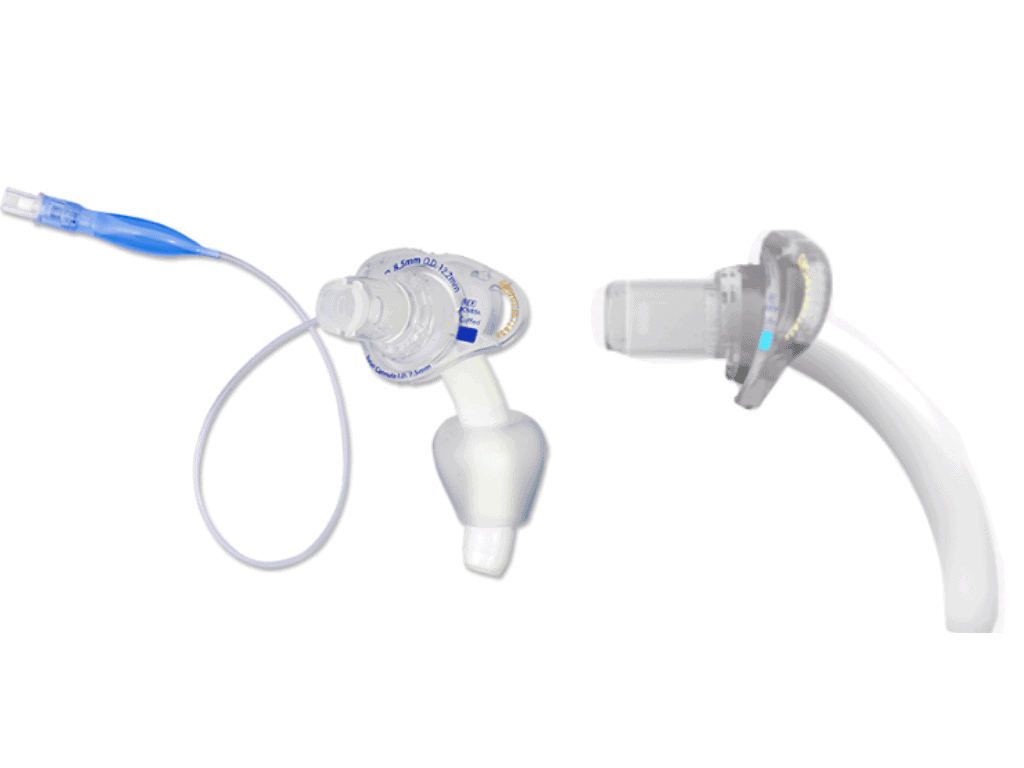
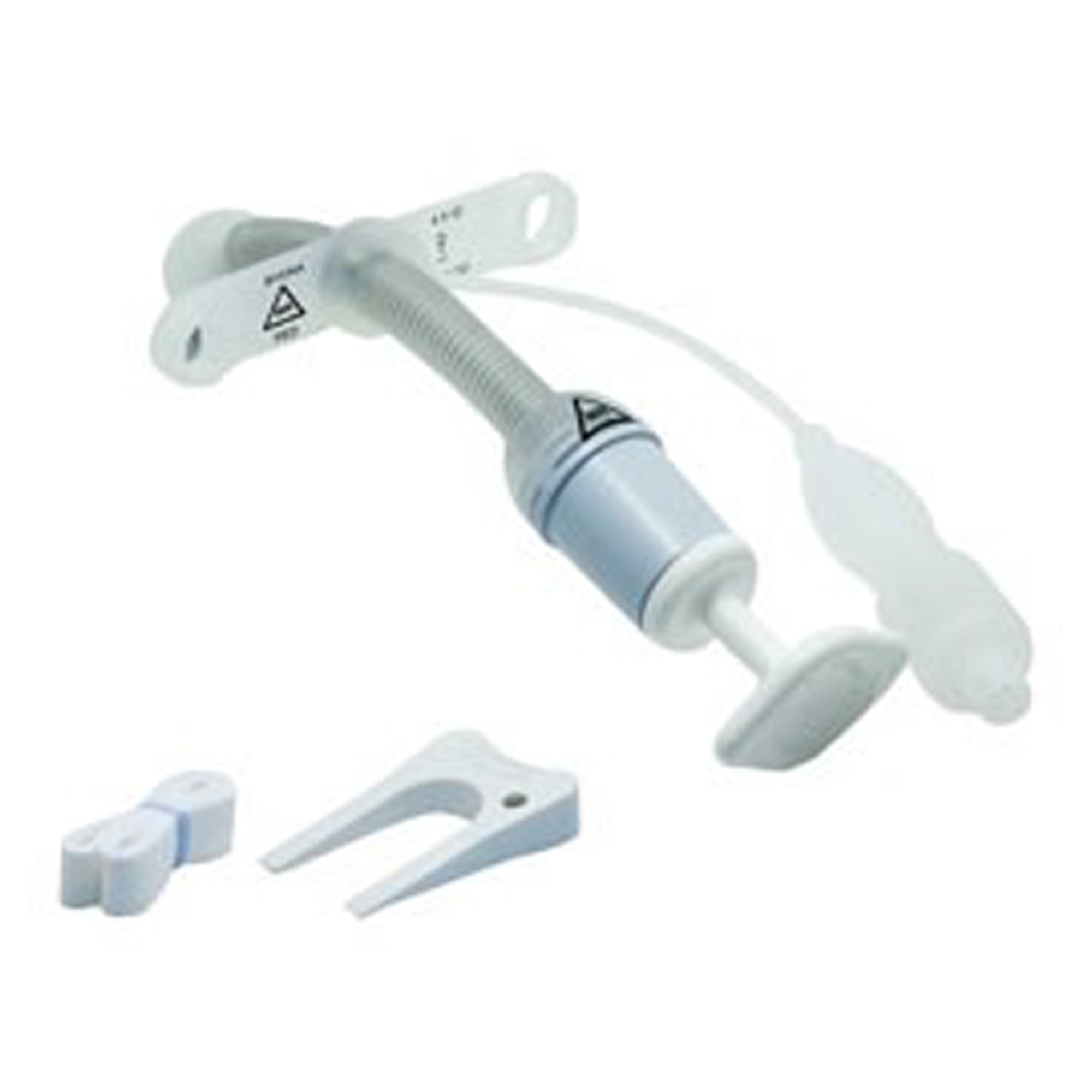
The global tracheostomy tubes market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising incidences of respiratory disorders, increasing ICU admissions, and a growing elderly population. According to Mordor Intelligence, the tracheostomy tubes market was valued at approximately USD 380 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This expansion reflects heightened demand for specialized tracheostomy devices, including both cuffed and uncuffed variants, tailored to diverse clinical needs ranging from long-term ventilation support to airway management in spontaneously breathing patients. As healthcare facilities prioritize patient safety and airway efficacy, innovation in tube design, biocompatibility, and ease of use has become a key competitive differentiator among manufacturers. In this evolving landscape, six leading companies have emerged as prominent players in the development and supply of high-quality cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tubes, combining clinical reliability with technological advancement to meet global healthcare demands.
Top 6 Cuffed Uncuffed Tracheostomy Tube Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tracheostomy Products
Domain Est. 1990
Website: medtronic.com
Key Highlights: Shiley™ flexible tracheostomy tube with disposable or reusable inner cannula options are available in cuffed and cuffless configurations….
#2 InTube™ tracheal tube uncuffed
Domain Est. 1996
Website: intersurgical.com
Key Highlights: InTube tracheal tubes are single use, sterile, available in three varieties: cuffed, uncuffed and reinforced, in a comprehensive range of sizes from paediatric ……
#3 Understanding my Tracheostomy Tube
Domain Est. 1996
Website: atosmedical.com
Key Highlights: Some tracheostomy tubes have a cuff, which is an inflatable balloon around the outer cannula that seals your airway to prevent air from escaping around the tube ……
#4 Bivona™ Uncuffed Adult Tracheostomy Tubes
Domain Est. 1997
Website: icumed.com
Key Highlights: The silicone uncuffed tube is for patients who do not require a cuff. The soft neck flange helps the tube to be secured with minimal stoma irritation….
#5 Tracheostomy Tubes
Domain Est. 2015
Website: medis-medical.com
Key Highlights: Tracheostomy Tubes are supplied cuffed and uncuffed with optional AccuCuff™ cuff pressure indicator to suit a variety of clinical situations and patient needs….
#6 Cuffed Tracheostomy Tube Bivona FlexTend TTS Various Sizes
Domain Est. 2020
Website: rapiroy.com
Key Highlights: Constructed from soft, biocompatible silicone with a Straight Neck Flange, these tubes provide exceptional patient comfort and adaptability, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cuffed Uncuffed Tracheostomy Tube
H2: Market Trends for Cuffed and Uncuffed Tracheostomy Tubes in 2026
The global market for cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tubes is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by rising critical care needs, advancements in respiratory care, and an increasing prevalence of respiratory disorders. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Growing Demand in Critical Care Settings
With the continued emphasis on intensive care unit (ICU) preparedness post-pandemic, demand for tracheostomy tubes—especially cuffed variants—has surged. Cuffed tubes are preferred in mechanically ventilated patients for airway protection and effective ventilation, making them essential in prolonged ICU stays. The expansion of critical care infrastructure in emerging economies is expected to further boost market growth. -
Preference Shift Toward Cuffed Tracheostomy Tubes
Cuffed tracheostomy tubes are witnessing higher adoption due to their ability to prevent aspiration and allow for positive-pressure ventilation. Technological innovations, such as high-volume low-pressure (HVLP) cuffs that reduce tracheal injury, are enhancing patient safety and driving preference in hospital settings. -
Rising Use of Uncuffed Tubes in Long-Term and Pediatric Care
Uncuffed tracheostomy tubes remain vital in pediatric patients and for long-term tracheostomy management where spontaneous breathing is preserved. Their use is expanding in home healthcare settings and rehabilitation centers, supported by growing awareness of tracheostomy care and improved patient mobility. -
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Manufacturers are focusing on developing anti-microbial coated tubes, adjustable flange designs, and improved biocompatible materials to reduce infection risks and enhance patient comfort. Smart tracheostomy tubes with integrated monitoring capabilities are also in early development stages, signaling future innovation potential. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa are experiencing increased healthcare investments and hospital capacity expansions. This growth, coupled with rising awareness of respiratory care, is creating new opportunities for both cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tube providers. -
Impact of Regulatory Standards and Safety Guidelines
Stringent regulatory requirements from agencies such as the FDA and EU MDR are pushing manufacturers to adhere to higher quality and safety standards. This is encouraging product standardization and boosting trust among healthcare providers, positively influencing market dynamics. -
Influence of Home Healthcare Trends
The shift toward home-based care for chronic respiratory conditions is driving demand for user-friendly, low-maintenance tracheostomy solutions. Uncuffed tubes, in particular, are benefiting from this trend due to their suitability for stable patients requiring long-term airway access.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tubes reflects a balance between acute care needs and long-term patient management. With innovation, expanded access, and evolving clinical practices, the sector is set for sustained growth, with cuffed tubes dominating hospital use and uncuffed variants gaining traction in outpatient and pediatric applications.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Cuffed and Uncuffed Tracheostomy Tubes (Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns)
Sourcing cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tubes involves navigating a complex landscape of medical device regulations, quality standards, and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Organizations and procurement teams often encounter several pitfalls that can compromise patient safety, lead to regulatory non-compliance, or expose them to legal risks. Below are key challenges related to quality and IP:
1. Compromised Product Quality Due to Unverified Suppliers
A major risk when sourcing tracheostomy tubes—especially from low-cost or unfamiliar suppliers—is receiving substandard products. Poor-quality tubes may have inconsistent cuff inflation, material brittleness, or incorrect sizing, increasing the risk of airway complications. Many suppliers, particularly in unregulated markets, may lack ISO 13485 certification or fail to meet FDA/CE marking requirements, leading to unreliable product performance.
2. Use of Non-Compliant or Counterfeit Materials
Some manufacturers use medical-grade plastics or silicone that do not comply with biocompatibility standards (e.g., ISO 10993). This can lead to patient irritation, allergic reactions, or device failure. Counterfeit products may mimic well-known brands but fail to undergo proper sterilization or performance testing, posing significant clinical risks.
3. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable tracheostomy tubes must come with full traceability, including lot numbers, expiration dates, and certificates of conformity. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide verifiable documentation increases the risk of using expired, recalled, or unapproved devices.
4. Intellectual Property Infringement
Many leading tracheostomy tube designs are protected by patents and trademarks (e.g., Shiley™, Portex™). Sourcing generic or “compatible” tubes that replicate patented features—such as specific cuff shapes, connector designs, or insertion aids—can result in IP infringement. This exposes buyers and distributors to legal action, product seizures, or import bans, particularly in regions with strong IP enforcement like the US and EU.
5. Mislabeling and Design Copying
Some suppliers produce devices that closely resemble branded products in appearance, packaging, or labeling, creating confusion and potentially misleading clinicians. This not only raises IP concerns but may also violate FDA or EU MDR regulations on device labeling and transparency.
6. Inadequate Regulatory Approvals
Tracheostomy tubes are Class II medical devices in most jurisdictions, requiring rigorous pre-market notification (e.g., 510(k) in the US) or conformity assessment (e.g., under EU MDR). Sourcing from manufacturers without valid regulatory clearance increases liability and may prevent legal distribution or clinical use.
7. Poor Post-Market Surveillance Support
High-quality suppliers offer robust post-market surveillance, including recall management and adverse event reporting. Sourcing from manufacturers with weak support systems limits the ability to respond quickly to safety issues, increasing patient and institutional risk.
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, verify regulatory certifications, audit supplier quality management systems, and consult legal experts when evaluating devices with potential IP conflicts. Prioritizing patient safety and regulatory compliance over cost savings is essential when sourcing life-sustaining devices like tracheostomy tubes.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cuffed and Uncuffed Tracheostomy Tubes
Product Overview and Classification
Cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tubes are medical devices used to establish and maintain a patent airway in patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation or airway support. Cuffed tubes feature an inflatable balloon (cuff) near the distal end to seal the trachea, preventing aspiration and enabling positive-pressure ventilation. Uncuffed tubes lack this feature and are typically used in patients who can protect their airway or require minimal ventilatory support. These devices are classified as Class II medical devices under regulatory frameworks such as the U.S. FDA 510(k) and EU MDR, requiring adherence to specific quality, safety, and performance standards.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Manufacturers and distributors must comply with regional and international regulations to market tracheostomy tubes. In the United States, devices require FDA 510(k) clearance demonstrating substantial equivalence to a predicate device. Under the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR 2017/745), tracheostomy tubes must undergo conformity assessment by a Notified Body and carry the CE mark. Key compliance elements include adherence to ISO 10651-4:2009 (Lung ventilators – Part 4: Particular requirements for mandatory ventilators used in anaesthetic and respiratory applications), ISO 8536-4 (Infusion equipment for medical use – Part 4: Infusion sets for single use gravity feed), and biocompatibility standards per ISO 10993. Technical documentation, post-market surveillance, and Unique Device Identification (UDI) are mandatory.
Labeling and Packaging Standards
Labels on cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tubes must include critical information: device name, size (inner diameter, length), lot number, expiration date, single-use designation, sterile status, and manufacturer details. The U.S. FDA and EU MDR require UDI placement on both the device label and packaging. Symbols must conform to ISO 15223-1 for medical device labeling (e.g., sterile, single use, latex-free if applicable). Packaging must maintain sterility through validated methods (e.g., ethylene oxide or gamma irradiation) and include instructions for use (IFU) in all relevant languages for the target market. All labeling must be clear, legible, and not misleading.
Storage and Handling Procedures
Tracheostomy tubes should be stored in a clean, dry environment at temperatures between 15°C and 30°C, away from direct sunlight and chemical vapors. Products must remain sealed in their original sterile packaging until point of use. Handling personnel should wear clean gloves to prevent contamination. Do not use devices if the packaging is damaged, tampered with, or past the expiration date. Rotating stock using a first-expired, first-out (FEFO) system ensures product efficacy and compliance with shelf-life requirements.
Distribution and Supply Chain Controls
Distribution of tracheostomy tubes must maintain the integrity of sterile packaging and environmental conditions. Transport vehicles should be enclosed and temperature-monitored where required. Distributors must be authorized and comply with Good Distribution Practice (GDP) guidelines per FDA and EU regulations. Temperature excursions during transit must be documented and assessed for impact on product sterility and material integrity. Chain of custody records, including shipping and receiving logs, should be maintained for traceability and recall readiness.
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance Reporting
Manufacturers are required to establish a post-market surveillance (PMS) system to monitor device performance and detect adverse events. Under EU MDR, a Post-Market Surveillance Plan (PMSP) and Periodic Safety Update Report (PSUR) are mandatory. In the U.S., manufacturers must comply with FDA Medical Device Reporting (MDR) regulations (21 CFR Part 803), reporting device-related deaths, serious injuries, or malfunctions within specified timeframes. Complaint handling procedures must be documented, and root cause analysis conducted for any non-conformities.
Training and Documentation for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare facilities receiving tracheostomy tubes should ensure staff are trained in proper insertion, maintenance, and emergency management of tracheostomies. Training materials and IFUs must be readily accessible. Facilities must document training completion and maintain records of device usage, adverse events, and inventory management. Accurate documentation supports patient safety and regulatory audits.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Used tracheostomy tubes are considered biohazardous medical waste and must be disposed of according to local, national, and international regulations (e.g., OSHA, EPA, and EU directives on waste management). Single-use devices must never be reprocessed or reused. Facilities must follow approved biohazard disposal protocols, including segregation, containment, and incineration or autoclaving as appropriate. Manufacturers should provide disposal recommendations in the IFU.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cuffed and Uncuffed Tracheostomy Tubes
In conclusion, sourcing cuffed and uncuffed tracheostomy tubes requires careful consideration of clinical requirements, patient needs, product quality, regulatory compliance, and supply chain reliability. Cuffed tubes are essential for patients requiring mechanical ventilation or those at risk of aspiration, providing airway security and positive pressure ventilation. In contrast, uncuffed tubes are preferable for patients who are spontaneously breathing and need airway patency with the ability to speak and clear secretions more easily.
Effective sourcing involves partnering with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA/CE regulations. Factors such as tube material (e.g., silicone, PVC), size range, cuff design (high-volume low-pressure), and the availability of customized options should be evaluated to ensure clinical compatibility and patient safety.
Additionally, establishing a diversified supplier base helps mitigate risks related to supply disruptions, while ongoing engagement with healthcare providers ensures that the selected products meet practical clinical demands. A strategic, patient-centered approach to sourcing ensures the availability of appropriate tracheostomy tubes, supports optimal patient outcomes, and enhances overall respiratory care delivery in both hospital and home care settings.