Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
The efficient transfer and pressurization of liquefied gases—LNG, liquid nitrogen, oxygen, and other cryogenic fluids—depends on one critical component: the cryogenic centrifugal pump. For procurement teams and engineering leaders across the marine, energy, and industrial gas sectors, selecting the right pump directly impacts operational efficiency, safety compliance, and total cost of ownership.
The challenge is clear: The global cryogenic pump market presents buyers with a complex landscape of specifications, supplier capabilities, and application-specific requirements. From air separation units (ASUs) to LNG bunkering operations and gas transportation systems, each use case demands precise performance parameters that generic pump solutions cannot meet.
What This Guide Covers
This B2B guide provides decision-makers with the technical and commercial intelligence needed to navigate cryogenic centrifugal pump procurement:
| Section | Focus Area |
|———|————|
| Technology Overview | Operating principles, design configurations (electric, hydraulic, submerged) |
| Application Matching | Industry-specific requirements for marine, energy, and process applications |
| Supplier Evaluation | Key criteria for assessing manufacturers and distributors |
| Specification Guidance | Critical parameters for RFQ development |
| Total Cost Analysis | Lifecycle considerations beyond purchase price |
Whether you’re sourcing pumps for tanker unloading operations, process transfer applications, or integrated cryogenic systems, this guide delivers actionable insights to reduce procurement risk and optimize equipment selection.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The following sections break down what buyers in the USA and European markets need to know before engaging suppliers.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Cryogenic Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cryogenic centrifugal pump
- Understanding cryogenic centrifugal pump Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of cryogenic centrifugal pump
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cryogenic centrifugal pump’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for cryogenic centrifugal pump
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cryogenic centrifugal pump
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cryogenic centrifugal pump’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cryogenic centrifugal pump Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cryogenic centrifugal pump With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cryogenic centrifugal pump
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cryogenic centrifugal pump Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cryogenic centrifugal pump
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cryogenic centrifugal pump
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Cryogenic Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cryogenic Pumps Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Cryogenic Pumps Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and Canada ; Mass-Vac, Inc. North Billerica, MA 01862 ; Taricco Corporation. Long Beach, CA 90813 ; Coker ……
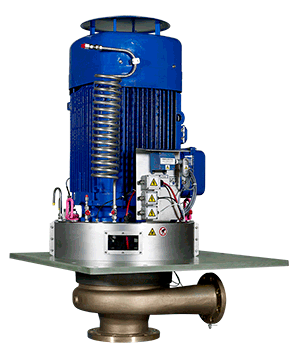
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Top 10 Cryogenic Pump Manufacturers in the World 2025 – Cryo Tech
Domain: cryogenictank.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Leading cryogenic pump manufacturers, including Barber-Nichols, Nikkiso, Fives, Ruhrpumpen, and CryoTech, are at the forefront of delivering innovative, high- ……
3. CRYOMEC – Cryogenic pumps
Domain: cryomade.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: We coordinate a global experience in cryogenic pumps for over three decades. Improve the reliability and efficiency of your cryogenic pumps, with our help….
4. CRYO-MACH Series Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps | Blackmer
Domain: psgdover.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Every pump is designed, manufactured and inspected in North Hollywood, CA, USA, under the industry’s most rigorous quality standards. Max. Flow Rate 1,150 gpm ( ……
5. Centrifugal Pumps Cryogenic Pumps – GlobalSpec
Domain: globalspec.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: List of Centrifugal Pumps Cryogenic Pumps Product Specs, Datasheets, Manufacturers & Suppliers….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
6. Cryogenic Pumps | Barber-Nichols
Domain: barber-nichols.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Barber-Nichols’ specializes in three types of Cryogenic Pumps: Submersible Motor Pumps, Vacuum Housing Pumps, and Long-Shaft Pumps….
7. Cryogenic Pumps | Maintenance-Free Operating Period | PBS
Domain: pbs.cz
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The cryopumps are supplied to various industries and leading manufacturers in the world, including CERN research centre and LINDE, a leading global industrial ……
8. Cryogenic Pump Companies – Market Research Future
Domain: marketresearchfuture.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Tri-Star Industries, for example, specializes in high-flow cryogenic pumps, while Inoxcva excels in custom-engineered solutions for demanding applications….
Understanding cryogenic centrifugal pump Types and Variations
Understanding Cryogenic Centrifugal Pump Types and Variations
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps serve as critical components in liquefied gas transfer and pressurization operations across multiple industries. Selecting the appropriate pump type directly impacts operational efficiency, safety, and total cost of ownership. This section examines the primary variations available to industrial buyers.
Cryogenic Centrifugal Pump Types: Comparison Overview
| Type | Key Features | Primary Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Centrifugal Pumps | Motor-driven, variable speed control, high flow rates | Air separation units, large-scale LNG facilities, industrial gas plants | ✓ Precise flow control, high efficiency ✗ Requires electrical infrastructure |
| Hydraulic Centrifugal Pumps | Hydraulic power transmission, robust construction | Offshore platforms, remote installations, hazardous environments | ✓ No electrical ignition risk, reliable in harsh conditions ✗ Higher maintenance requirements |
| Submerged Centrifugal Pumps | Motor submerged in cryogenic liquid, compact design | Storage tank applications, tanker unloading, bunkering operations | ✓ Eliminates shaft seal issues, reduced NPSH requirements ✗ Limited accessibility for maintenance |
| Vertical Centrifugal Pumps | Vertical shaft orientation, small footprint | Space-constrained installations, process applications | ✓ Minimal floor space, self-priming capability ✗ Height limitations |
| Multi-stage Centrifugal Pumps | Multiple impellers in series, high-pressure output | Gas transportation, high-head applications, pipeline injection | ✓ Achieves higher discharge pressures ✗ Increased complexity and cost |
Detailed Analysis by Pump Type
Electric Centrifugal Pumps
Electric centrifugal pumps represent the most widely deployed configuration in fixed industrial installations. These units utilize electric motors—typically induction or permanent magnet designs—to drive the impeller assembly.
Technical characteristics:
– Flow rates ranging from 50 to 5,000+ m³/h
– Variable frequency drive (VFD) compatibility for precise process control
– Operating temperatures down to -196°C for liquid nitrogen applications

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Optimal use cases:
– Air separation units (ASU) requiring continuous, high-volume operation
– LNG regasification terminals
– Industrial gas production facilities
Electric centrifugal pumps deliver superior energy efficiency when connected to stable power infrastructure, making them the preferred choice for permanent installations where electrical supply is reliable.
Hydraulic Centrifugal Pumps
Hydraulic centrifugal pumps transmit power through hydraulic fluid rather than direct electrical connection. This design eliminates electrical components from the pump head area—a significant advantage in potentially explosive atmospheres.
Technical characteristics:
– Intrinsically safe operation in hazardous zones
– Power transmission via hydraulic lines from remote power units
– Suitable for ATEX and IECEx compliance requirements

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Optimal use cases:
– Offshore LNG platforms and FPSOs
– Remote or mobile cryogenic transfer operations
– Installations requiring Zone 0/1 compliance
The trade-off involves additional hydraulic system maintenance and slightly reduced overall efficiency compared to direct electric drive configurations.
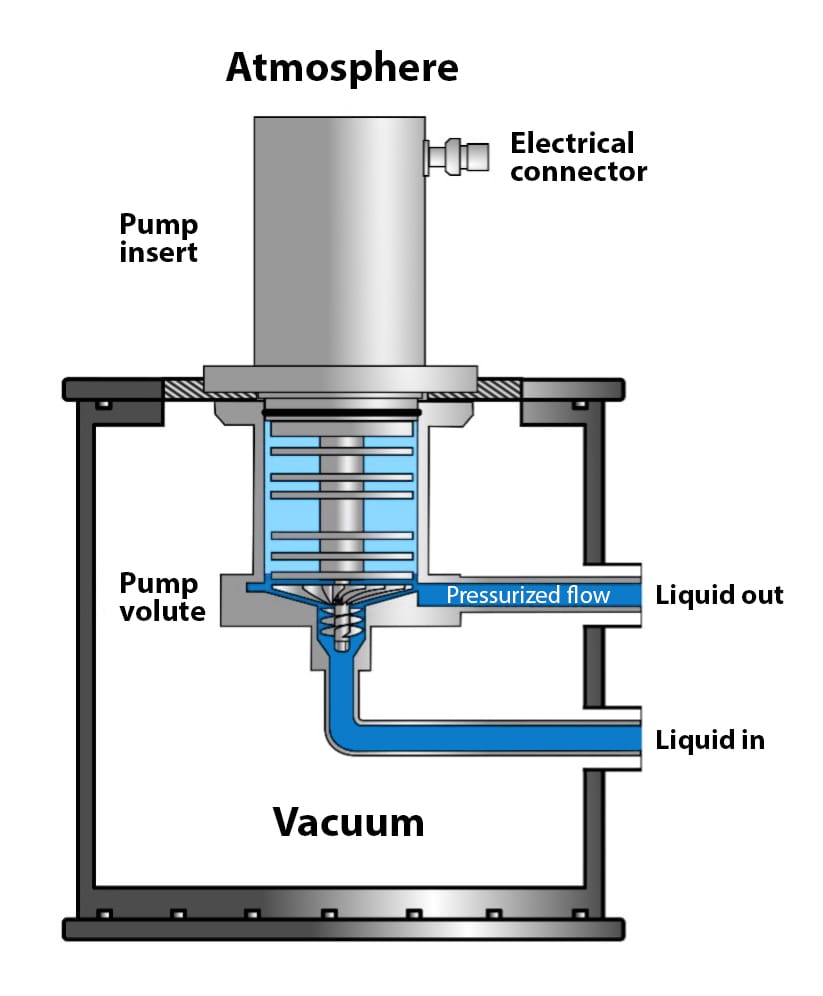
Submerged Centrifugal Pumps
Submerged (or submersible) centrifugal pumps position the entire pump assembly—including the motor—within the cryogenic liquid. This configuration, offered by manufacturers such as Cryostar, eliminates the mechanical shaft seal that traditionally represents the most maintenance-intensive component.
Technical characteristics:
– Motor cooled directly by cryogenic fluid
– No external shaft seal required
– Reduced net positive suction head (NPSH) requirements
– Compact vertical installation within storage vessels

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Optimal use cases:
– LNG storage tank pump-out operations
– Ship-to-shore and ship-to-ship transfer (bunkering)
– Tanker unloading operations
– Marine industry applications
Submerged pumps significantly reduce vapor generation during transfer operations, improving both safety and product retention.
Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Vertical centrifugal pumps orient the shaft perpendicular to the ground, with the motor mounted above the pump casing. This arrangement minimizes the installation footprint while maintaining accessibility to drive components.
Technical characteristics:
– Reduced floor space requirements
– Gravity-assisted priming in many configurations
– Simplified foundation requirements

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Optimal use cases:
– Process applications with space constraints
– Cryogenic fluid circulation systems
– Installations where horizontal space is limited
Vertical configurations suit facilities where plant layout optimization is critical, though maximum achievable head may be lower than horizontal equivalents.
Multi-stage Centrifugal Pumps
Multi-stage centrifugal pumps incorporate two or more impellers arranged in series within a single casing. Each stage incrementally increases discharge pressure, enabling these units to achieve heads that single-stage designs cannot match.
Technical characteristics:
– Discharge pressures exceeding 100 bar in some configurations
– Sequential pressure building through multiple impeller stages
– Available in both horizontal and vertical orientations
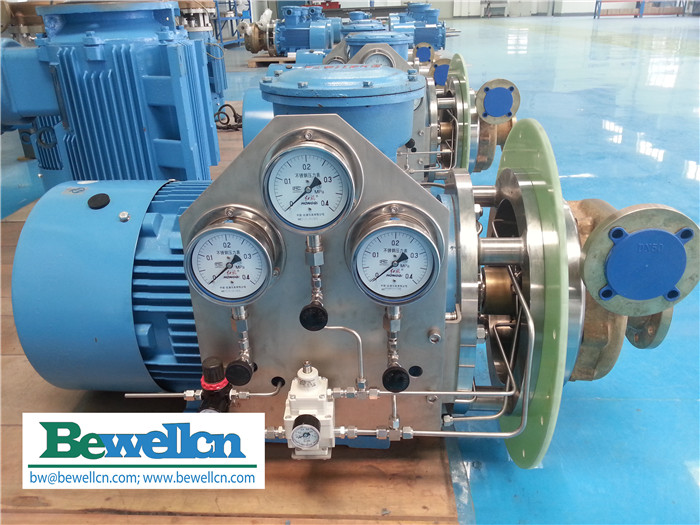

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Optimal use cases:
– LNG pipeline injection
– High-pressure gas transportation systems
– Applications requiring significant elevation changes
– Cryogenic fluid transfer over long distances
Multi-stage pumps command higher capital costs but prove essential where process requirements demand elevated discharge pressures.
Selection Considerations for B2B Buyers
When evaluating cryogenic centrifugal pump types, procurement teams should assess:
- Operating environment — Fixed installation vs. mobile/offshore deployment
- Hazardous area classification — ATEX, IECEx, or NEC requirements
- Flow and pressure requirements — Match pump curves to process demands
- Maintenance accessibility — Submerged designs limit in-situ service options
- Total cost of ownership — Factor energy efficiency, spare parts availability, and service intervals
Engaging directly with established cryogenic pump suppliers ensures proper sizing and configuration for specific application parameters.
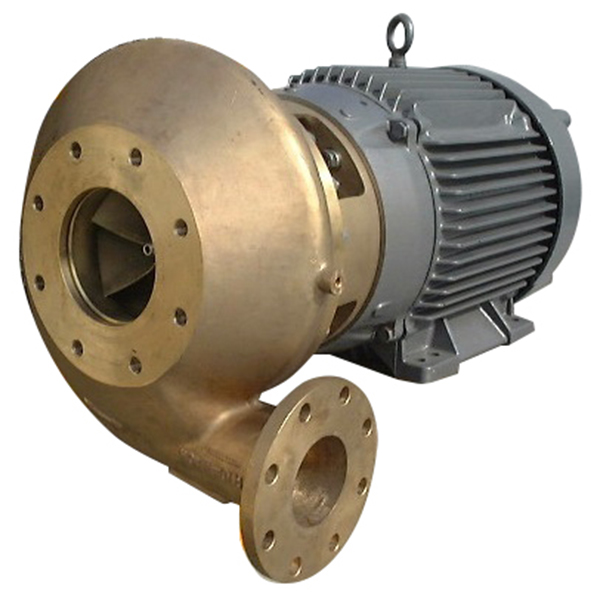

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Industrial Applications of cryogenic centrifugal pump
Key Industrial Applications of Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps serve as critical infrastructure components across multiple industries requiring reliable transfer and pressurization of liquefied gases at extremely low temperatures. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of primary applications and their specific operational benefits.
Industry Applications Overview
| Industry | Primary Applications | Cryogenic Fluids Handled |
|---|---|---|
| Marine & LNG Shipping | Cargo transfer, bunkering operations, tank pressure control | LNG, LPG |
| Energy & Gas Processing | Gas transportation, storage facility operations, fuel supply systems | LNG, methane, ethane, propane, butane |
| Industrial Gas Production | Air separation units (ASU), process transfer operations | Liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen, liquid argon |
| Petrochemical | Feedstock transfer, process cooling applications | Ethylene, propylene, mixed refrigerants |
| Aerospace & Research | Propellant handling, cryogenic testing facilities | Liquid hydrogen, liquid helium |
Detailed Benefits by Application
LNG and Gas Transportation Operations
- High-volume transfer capability for tanker unloading and ship-to-ship bunkering
- Consistent flow rates essential for meeting tight operational schedules
- Pressure control functionality for LNG carrier tank management
- Reduced boil-off losses through efficient fluid handling
Air Separation Units (ASU)
- Continuous operation reliability for 24/7 production environments
- Precise flow control for maintaining separation column efficiency
- Low maintenance requirements minimizing production downtime
- Compatibility with multiple cryogenic outputs (nitrogen, oxygen, argon)
Process and Transfer Applications
- Hermetic sealing options preventing product contamination
- Variable speed configurations (electric, hydraulic, submerged designs) matching specific process requirements
- Scalable capacity from small-scale research to industrial throughput
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cryogenic centrifugal pump’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Maintaining Seal Integrity at Extreme Low Temperatures
Scenario:
A European LNG terminal operator experiences repeated seal failures on their cryogenic centrifugal pumps during unloading operations from tankers. The thermal cycling between ambient and cryogenic temperatures (-160°C) causes conventional sealing materials to contract, crack, and leak—resulting in unplanned downtime and safety concerns.
Problem:
Standard elastomers and seal materials become brittle at cryogenic temperatures, losing elasticity and failing to maintain proper compression. This leads to:
– Product loss through leakage
– Increased maintenance frequency
– Potential safety hazards from gas release
– Regulatory compliance issues
Solution:
| Action | Implementation |
|——–|—————-|
| Specify cryogenic-rated seal materials | Select PTFE, expanded graphite, or specialized polymers designed for temperatures below -150°C |
| Implement double mechanical seals | Provides redundancy and allows for seal condition monitoring |
| Install thermal barriers | Reduces heat transfer to seals, minimizing thermal shock |
| Establish predictive maintenance protocols | Use vibration analysis and leak detection to replace seals before failure |
Pain Point 2: Cavitation and Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) Challenges
Scenario:
A U.S.-based air separation unit (ASU) facility notices reduced flow rates and increased noise from their liquid nitrogen transfer pumps. Inspection reveals impeller damage consistent with cavitation—the pump is operating with insufficient NPSH margin due to low tank levels and inadequate system design.
Problem:
Cryogenic fluids have low boiling points and high vapor pressures relative to their operating temperatures. This makes cryogenic centrifugal pumps particularly susceptible to:
– Cavitation damage to impellers and volutes
– Reduced pump efficiency and flow capacity
– Premature bearing and component wear
– Process interruptions during critical transfer operations
Solution:
| Action | Implementation |
|——–|—————-|
| Optimize suction system design | Minimize suction line length and elevation changes; use larger diameter piping |
| Maintain adequate liquid head | Ensure storage tank levels provide sufficient static head above NPSH required |
| Select inducer-equipped pumps | Inducers improve suction performance and lower NPSH requirements |
| Implement subcooling systems | Reduce fluid temperature below saturation to increase NPSH available |
| Install real-time monitoring | Deploy pressure and flow sensors to detect early cavitation indicators |
Pain Point 3: Thermal Shock During Cooldown and Startup
Scenario:
A gas transportation company operating submerged cryogenic centrifugal pumps experiences frequent bearing failures and shaft misalignment. Root cause analysis reveals that rapid cooldown procedures are subjecting pump components to thermal gradients exceeding 100°C within minutes, causing differential contraction and mechanical stress.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem:
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps require careful thermal management during startup. Improper cooldown creates:
– Uneven contraction between pump components (shaft, bearings, casing)
– Temporary loss of clearances leading to contact and wear
– Thermal stress fractures in castings and welds
– Extended commissioning times and startup delays
Solution:
| Action | Implementation |
|——–|—————-|
| Develop standardized cooldown procedures | Follow manufacturer-specified temperature ramp rates (typically 1-2°C per minute) |
| Use recirculation loops for gradual cooling | Circulate small quantities of cryogenic fluid to achieve uniform temperature reduction |
| Specify compatible material pairings | Select components with similar thermal expansion coefficients |
| Install temperature monitoring | Place RTDs or thermocouples at critical locations to verify even cooldown |
| Train operations personnel | Ensure all operators understand thermal management requirements and consequences of deviation |
Key Takeaways
| Pain Point | Root Cause | Primary Solution Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Seal integrity failures | Material incompatibility with cryogenic temperatures | Cryogenic-rated materials + predictive maintenance |
| Cavitation damage | Insufficient NPSH margin | System design optimization + inducer selection |
| Thermal shock damage | Rapid temperature changes during startup | Controlled cooldown procedures + monitoring |
Addressing these challenges proactively during pump specification, system design, and operational planning significantly reduces total cost of ownership and maximizes uptime for cryogenic centrifugal pump installations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cryogenic centrifugal pump
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
Selecting appropriate materials for cryogenic centrifugal pumps is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts operational reliability, safety, and total cost of ownership. At cryogenic temperatures—typically below -150°C (-238°F)—conventional materials undergo significant property changes that can lead to catastrophic failures if not properly addressed.
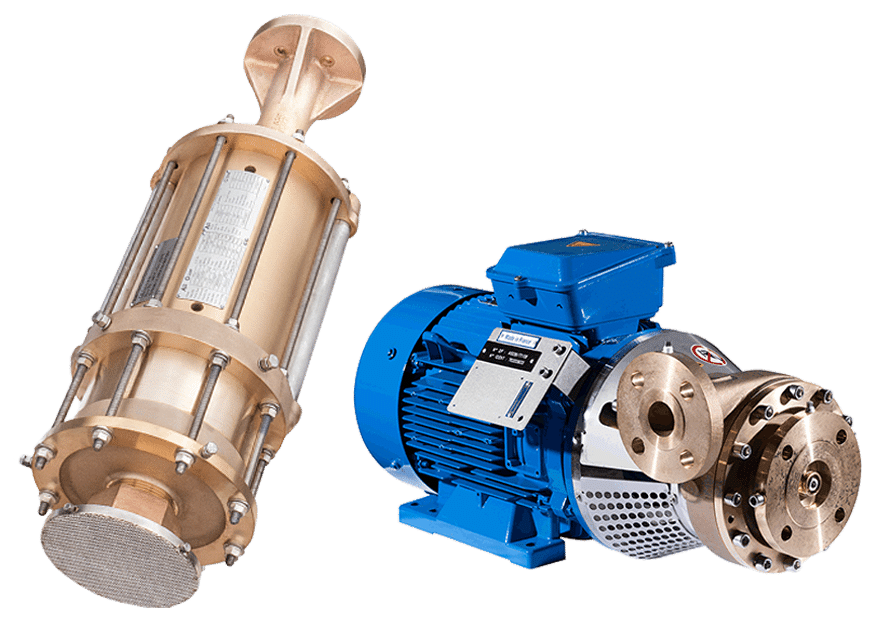
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Material Selection Criteria
When specifying materials for cryogenic centrifugal pump components, engineers must evaluate:
- Low-temperature ductility: Materials must maintain adequate toughness and resist brittle fracture at operating temperatures
- Thermal contraction compatibility: Components must accommodate differential contraction rates during cooldown cycles
- Corrosion resistance: Exposure to liquefied gases (LNG, nitrogen, oxygen, argon) demands chemical stability
- Mechanical strength retention: Yield and tensile strength characteristics at cryogenic temperatures
- Thermal conductivity: Heat transfer properties affecting pump efficiency and boil-off rates
Critical Component Material Requirements
Impellers and Rotating Elements
Impellers face the most demanding conditions—combining cryogenic exposure with high rotational stresses and potential cavitation. Materials must exhibit:
- Excellent fatigue resistance at low temperatures
- High strength-to-weight ratio for dynamic balance
- Resistance to erosion from two-phase flow conditions
Pump Casings and Pressure-Containing Parts
Casings require materials that maintain structural integrity under thermal shock during cooldown and warmup cycles. Weldability is essential for fabrication and field repairs.
Shafts and Bearings
Shaft materials must balance stiffness for rotor dynamics with cryogenic toughness. Bearing materials—particularly in submerged pump designs—must function without conventional lubricants.
Seals and Gaskets
Sealing elements require materials that maintain elasticity and sealing force at cryogenic temperatures while resisting thermal cycling degradation.
Primary Material Options
Austenitic Stainless Steels
Austenitic stainless steels remain the workhorse materials for cryogenic pump applications. Their face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure prevents the ductile-to-brittle transition that affects ferritic and martensitic steels.
304/304L Stainless Steel: Cost-effective choice for non-critical components and moderate cryogenic service. The low-carbon “L” grade improves weldability and reduces sensitization risk.
316/316L Stainless Steel: Enhanced corrosion resistance from molybdenum addition. Preferred for marine and offshore applications where chloride exposure is a concern.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
321 Stainless Steel: Titanium-stabilized grade offering superior performance in high-temperature service and thermal cycling applications.
High-Nickel Alloys
For the most demanding cryogenic applications, nickel-based alloys provide superior performance:
Inconel 625: Exceptional strength retention at cryogenic temperatures combined with outstanding corrosion resistance. Commonly specified for LNG pump impellers and critical rotating components.
Inconel 718: Age-hardenable alloy achieving high strength levels while maintaining cryogenic toughness. Used in high-pressure pump applications.
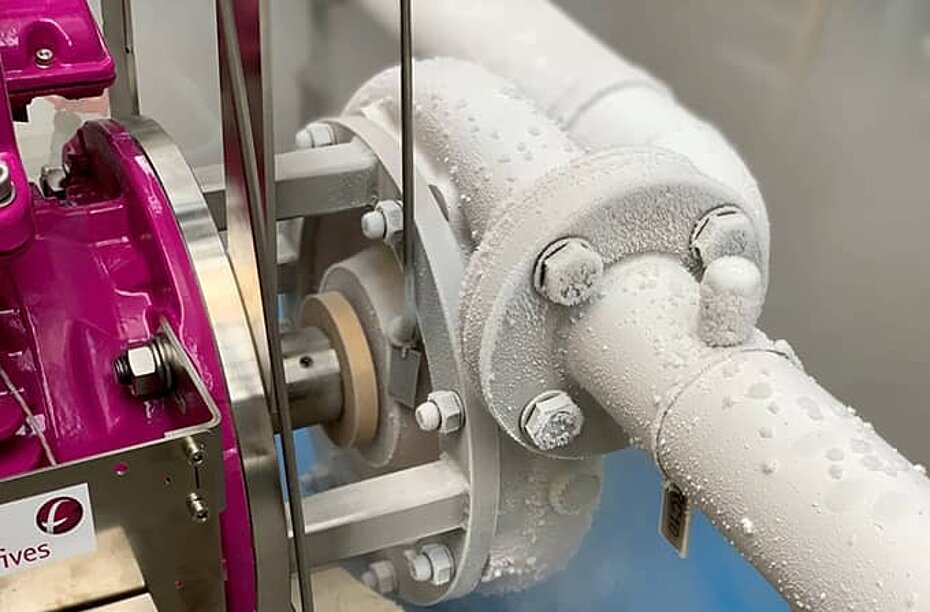

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Monel 400: Nickel-copper alloy with excellent resistance to hydrofluoric acid and seawater. Suitable for specialty gas applications.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys offer weight advantages and good cryogenic properties for specific applications:
5083-H321: Marine-grade aluminum with excellent weldability and corrosion resistance. Used in large-scale LNG pump components where weight reduction is beneficial.
6061-T6: Heat-treatable alloy suitable for machined components in less demanding cryogenic service.
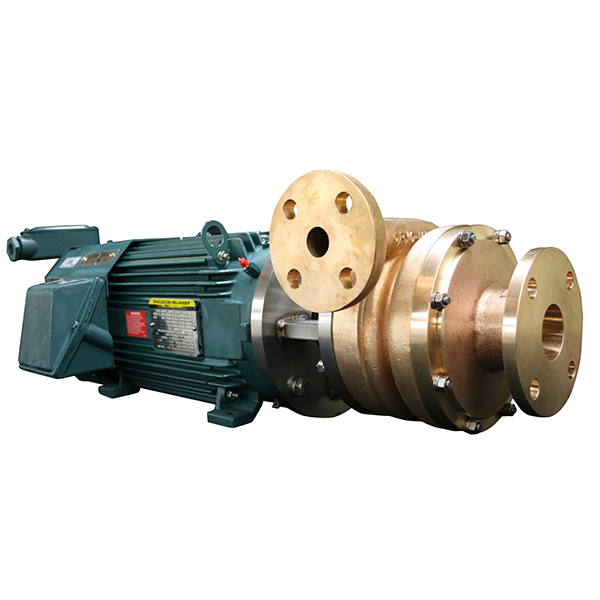

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Specialty Materials
9% Nickel Steel: Specifically developed for cryogenic service, offering excellent toughness at LNG temperatures (-162°C). Commonly used for pump baseplates and structural components.
Copper Alloys (Aluminum Bronze): Used for wear rings and bushings where galling resistance is required.
PTFE and Modified PTFE Compounds: Primary sealing materials for gaskets and packing, maintaining flexibility at cryogenic temperatures.
Carbon/Graphite Composites: Used for dry-running bearings in submerged pump designs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Material Selection by Pump Type
Electric Centrifugal Pumps
External motor-driven pumps typically employ:
– 316L stainless steel casings
– Inconel 625 or 718 impellers for high-performance applications
– Mechanical seals with silicon carbide faces and Inconel hardware
Submerged Motor Pumps
Submerged designs—where the motor operates within the cryogenic liquid—require:
– All-stainless construction (typically 304L or 316L)
– Carbon/graphite bearings for process-lubricated operation
– Specialized motor winding insulation materials
Hydraulic-Driven Pumps
Hydraulic pump designs separate the drive system from cryogenic exposure, allowing:
– Standard materials for hydraulic components
– Cryogenic-grade materials only for wetted parts
– Simplified material specifications and reduced costs
Application-Specific Considerations
LNG Service
Liquefied natural gas applications at -162°C (-260°F) demand:
– Full cryogenic material certification per ASTM A370 impact testing
– Charpy V-notch testing at design temperature
– Compliance with IGC Code for marine applications
Liquid Nitrogen and Oxygen Service
Air separation unit (ASU) applications require:
– Oxygen-clean materials with proper surface preparation
– Elimination of hydrocarbon contamination
– Specific material restrictions for oxygen service (no titanium in rotating components)
Liquid Hydrogen Service
The most demanding cryogenic application (-253°C/-423°F) requires:
– Hydrogen embrittlement-resistant materials
– Austenitic stainless steels with controlled ferrite content
– Special welding procedures to prevent hydrogen cracking
Quality and Certification Requirements
Material procurement for cryogenic pump applications should specify:
- Mill test reports (MTRs) with full chemical analysis
- Cryogenic impact testing per ASTM A370 at design temperature
- Positive material identification (PMI) verification
- Traceability documentation for critical components
- Compliance with applicable codes (ASME, API, EN standards)
Material Comparison Table
| Material | Temperature Range | Relative Cost | Key Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304L SS | To -269°C | Low | Casings, piping, general components | Cost-effective, weldable, good availability | Lower strength than alternatives |
| 316L SS | To -269°C | Low-Medium | Marine/offshore pumps, chloride environments | Enhanced corrosion resistance, weldable | Slightly higher cost than 304L |
| 321 SS | To -269°C | Medium | Thermal cycling applications | Stabilized for high-temp service | Limited availability in some forms |
| Inconel 625 | To -269°C | High | Impellers, critical rotating parts | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | High cost, difficult machining |
| Inconel 718 | To -269°C | High | High-pressure pump components | Age-hardenable, highest strength | Complex heat treatment required |
| Monel 400 | To -240°C | Medium-High | Specialty gas applications | HF acid resistance | Lower strength than Inconel grades |
| 5083-H321 Al | To -269°C | Low | Large structural components | Lightweight, weldable | Lower strength, limited pressure capability |
| 9% Nickel Steel | To -196°C | Medium | Baseplates, structural elements | Excellent LNG service properties | Not suitable for liquid hydrogen |
| Aluminum Bronze | To -196°C | Medium | Wear rings, bushings | Galling resistance, self-lubricating | Temperature limitations |
| PTFE/Modified PTFE | To -269°C | Low | Seals, gaskets | Chemical inertness, flexibility retention | Creep under load, permeation |
| Carbon/Graphite | To -269°C | Medium | Bearings, bushings | Dry-running capability | Brittleness, limited load capacity |
Economic Considerations
Material selection involves balancing performance requirements against lifecycle costs:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Initial cost: Premium alloys increase upfront investment but may reduce maintenance frequency
- Availability: Standard grades offer shorter lead times and easier replacement part sourcing
- Fabrication costs: Difficult-to-machine materials (Inconel) significantly increase manufacturing expenses
- Spare parts inventory: Standardizing on fewer material grades reduces inventory carrying costs
- Repair considerations: Weldable materials enable field repairs versus component replacement
Conclusion
Strategic material selection for cryogenic centrifugal pumps requires balancing technical performance, regulatory compliance, and economic factors. For most industrial applications, austenitic stainless steels (304L, 316L) provide the optimal combination of cryogenic performance, availability, and cost-effectiveness. High-nickel alloys should be reserved for critical rotating components and demanding service conditions where their superior properties justify the cost premium.
Engaging with qualified cryogenic pump suppliers early in the specification process ensures material selections align with application requirements, manufacturing capabilities, and long-term operational objectives.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cryogenic centrifugal pump
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps operate under extreme conditions—handling liquefied gases at temperatures as low as -196°C (-320°F) while maintaining precise flow rates and pressures. This demanding operational environment requires manufacturing processes that deliver exceptional material integrity, dimensional precision, and long-term reliability. Understanding how these pumps are manufactured helps procurement teams and engineers evaluate supplier capabilities and make informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The production of cryogenic centrifugal pumps follows a rigorous, multi-stage workflow designed to ensure each component can withstand thermal shock, maintain structural integrity at cryogenic temperatures, and deliver consistent hydraulic performance.
Stage 1: Material Preparation and Selection
Material selection is the foundation of cryogenic pump manufacturing. Standard carbon steels become brittle at cryogenic temperatures, making specialized materials essential.
| Component | Typical Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Impeller | 316L/304L Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloys | Ductility retention at low temperatures, corrosion resistance |
| Casing | Austenitic Stainless Steel (304L, 316L) | Thermal expansion compatibility, weldability |
| Shaft | 17-4 PH Stainless Steel, Inconel | High strength, fatigue resistance |
| Bearings | PTFE composites, Ceramic | Low friction, self-lubrication at cryogenic temps |
| Seals | PTFE, Expanded Graphite | Chemical inertness, temperature stability |
Material preparation steps include:
- Chemical composition verification through spectrometric analysis
- Impact testing (Charpy V-notch) at operating temperatures to confirm ductility
- Ultrasonic inspection of raw stock for internal defects
- Heat treatment documentation and traceability establishment
- Surface preparation including cleaning and degreasing to remove contaminants
Stage 2: Component Forming and Machining
Precision forming operations transform raw materials into pump components with the tight tolerances required for cryogenic service.
Impeller Manufacturing:
– Investment casting or 5-axis CNC machining from solid billets for complex hydraulic geometries
– Surface finish requirements typically 1.6 µm Ra or finer on flow passages
– Dynamic balancing to ISO 1940 G2.5 or better
– Dimensional tolerances of ±0.025mm on critical surfaces
Casing Production:
– Precision casting followed by CNC machining of sealing surfaces and mounting interfaces
– Hydrostatic pressure testing at 1.5x design pressure
– Controlled welding procedures with pre-heat and post-weld heat treatment where applicable
Shaft Fabrication:
– CNC turning and grinding to achieve concentricity within 0.01mm TIR (Total Indicator Runout)
– Surface hardening treatments for bearing journals
– Non-destructive examination (NDE) including magnetic particle or dye penetrant inspection
Stage 3: Assembly and Integration
Assembly of cryogenic centrifugal pumps requires cleanroom or controlled environment conditions to prevent contamination that could compromise seal integrity or hydraulic performance.
Assembly sequence:
- Pre-assembly inspection — All components verified against drawings and specifications
- Bearing installation — Precision fitting with controlled interference or clearance fits
- Seal system integration — Mechanical seals or hermetic seal assemblies installed per manufacturer specifications
- Impeller mounting — Torque-controlled fastening with thread-locking compounds rated for cryogenic service
- Casing closure — Controlled bolt tensioning sequences to ensure uniform gasket compression
- Motor coupling or integration — Alignment verification using laser alignment tools (typical tolerance: 0.05mm offset, 0.05mm/100mm angularity)
Critical assembly considerations:
- Cleanliness protocols — All wetted surfaces cleaned to remove particulates, oils, and moisture
- Torque documentation — All fastener torques recorded for traceability
- Clearance verification — Running clearances checked against design specifications
- Lubrication — Cryogenic-compatible lubricants applied where required
Stage 4: Quality Control and Testing
Quality assurance for cryogenic centrifugal pumps extends beyond standard pump testing protocols to address the unique challenges of low-temperature operation.
Dimensional and Material Verification:
| Inspection Type | Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional accuracy | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) | Per engineering drawings |
| Surface finish | Profilometer | ≤1.6 µm Ra on flow surfaces |
| Material composition | PMI (Positive Material Identification) | Match certified MTRs |
| Weld integrity | Radiographic or ultrasonic testing | Per ASME Section V |
| Surface defects | Dye penetrant or magnetic particle | No linear indications |
Functional Testing:
- Hydrostatic testing — Pressure testing at 1.5x maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP)
- Performance testing — Flow, head, and efficiency verification against design curves
- NPSH testing — Net Positive Suction Head verification for cavitation resistance
- Vibration analysis — Baseline vibration signatures recorded per ISO 10816
- Leak testing — Helium leak detection for hermetically sealed units (sensitivity to 10⁻⁹ mbar·L/s)
Cryogenic-Specific Testing:
For critical applications, manufacturers may perform:
– Thermal shock testing — Rapid cooling to operating temperature to verify material and seal integrity
– Cryogenic performance verification — Testing with actual process fluids (LN2, LNG) at operating temperatures
– Endurance testing — Extended run testing to verify bearing and seal life
Quality Standards and Certifications
Cryogenic centrifugal pump manufacturers serving industrial markets in the USA and Europe typically maintain certifications and comply with standards across multiple regulatory frameworks.
ISO Quality Management Standards
| Standard | Scope | Relevance to Cryogenic Pumps |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Foundation for consistent manufacturing processes |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Addresses emissions, waste handling in production |
| ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational Health & Safety | Critical given hazardous material handling |
Industry-Specific Standards
Pump Design and Performance:
– API 610 — Centrifugal pumps for petroleum, petrochemical, and natural gas industries
– ISO 13709 — International equivalent to API 610
– ISO 5199 — Technical specifications for centrifugal pumps (Class II)
– ASME B73.1/B73.2 — Horizontal and vertical end suction pumps
Pressure Equipment:
– ASME BPVC — Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (USA)
– PED 2014/68/EU — Pressure Equipment Directive (Europe)
– ATEX 2014/34/EU — Equipment for explosive atmospheres (Europe)
Cryogenic-Specific Standards:
– EN 13480 — Metallic industrial piping (includes cryogenic service requirements)
– CGA (Compressed Gas Association) standards — Guidelines for cryogenic equipment
– NFPA 59A — Standard for LNG production, storage, and handling
Material Standards:
– ASTM A240/A312/A351 — Stainless steel specifications
– ASME Section II — Material specifications for pressure equipment
– EN 10028/10088 — European flat and stainless steel product standards
Documentation and Traceability
Quality-focused manufacturers provide comprehensive documentation packages including:
- Material Test Reports (MTRs) — EN 10204 Type 3.1 or 3.2 certification
- Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) and Procedure Qualification Records (PQR)
- NDE reports — Radiographic, ultrasonic, and penetrant test results
- Hydrostatic test certificates
- Performance test curves — Actual vs. predicted performance
- Dimensional inspection reports
- Assembly and torque records
- Certificate of Conformance (CoC)
Supplier Evaluation Criteria
When evaluating cryogenic centrifugal pump manufacturers, consider the following quality-related factors:
Manufacturing Capabilities:
– In-house machining, casting, and assembly capabilities vs. outsourced operations
– Cleanroom or controlled environment assembly facilities
– Cryogenic test loop availability for cold testing
Quality System Maturity:
– Third-party certification status (ISO 9001, API Q1)
– Internal audit programs and corrective action processes
– Supplier quality management for critical sub-components
Engineering Expertise:
– Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) capabilities for hydraulic optimization
– Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for thermal and structural analysis
– Application engineering support for system integration
Track Record:
– Reference installations in similar applications (LNG, ASU, industrial gas)
– Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) data
– Warranty terms and field service capabilities
Key Takeaways
Manufacturing cryogenic centrifugal pumps demands specialized expertise in materials, precision machining, and quality control protocols that go beyond standard pump production. Buyers should verify that suppliers:
- Use appropriate cryogenic-grade materials with documented low-temperature impact testing
- Maintain robust quality management systems with ISO 9001 certification as a minimum
- Comply with relevant industry standards (API 610, PED, ATEX) based on application requirements
- Provide comprehensive documentation including MTRs, NDE reports, and test certificates
- Offer cryogenic-specific testing capabilities for critical applications
Thorough evaluation of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices helps ensure procurement of pumps that deliver reliable, long-term performance in demanding cryogenic service conditions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cryogenic centrifugal pump’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
Sourcing cryogenic centrifugal pumps requires systematic evaluation of technical specifications, supplier capabilities, and compliance requirements. This checklist guides procurement teams through each critical phase.
Phase 1: Define Technical Requirements
Before contacting suppliers, document your operational parameters:
| Parameter | Details to Specify |
|---|---|
| Fluid Type | LNG, liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen, argon, ethane, propane, or mixed gases |
| Flow Rate | Required GPM/m³/h at operating conditions |
| Head/Pressure | Discharge pressure requirements (bar/psi) |
| Temperature Range | Operating temperature (typically -196°C to -160°C for most cryogenic applications) |
| NPSH Available | Net Positive Suction Head at installation site |
| Mounting Configuration | Submerged, electric, or hydraulic drive |
| Duty Cycle | Continuous, intermittent, or standby service |
Checklist:
– [ ] Document process flow diagrams with pump placement
– [ ] Calculate system curve and required operating point
– [ ] Identify fluid properties (density, viscosity at operating temperature)
– [ ] Determine installation constraints (space, orientation, access)
– [ ] Specify redundancy requirements (N+1 configurations)
Phase 2: Identify Application-Specific Requirements
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps serve distinct applications. Match your use case:
Primary Applications:
– [ ] Air separation units (ASU)
– [ ] LNG transfer and bunkering operations
– [ ] Tanker unloading operations
– [ ] Gas transportation systems
– [ ] Process and transfer at cryogenic temperatures
– [ ] Industrial gas production
Application-Specific Considerations:
– [ ] Marine applications: Verify classification society approvals (DNV, Lloyd’s, ABS)
– [ ] ASU installations: Confirm oxygen-compatible materials and cleaning
– [ ] LNG bunkering: Check hazardous area certifications
Phase 3: Evaluate Supplier Qualifications
Technical Capability Assessment:
– [ ] Request engineering references for similar applications
– [ ] Verify in-house hydraulic design and testing capabilities
– [ ] Confirm cryogenic testing facilities availability
– [ ] Review material certifications for cryogenic service (stainless steel grades, special alloys)
Quality and Compliance:
– [ ] ISO 9001 certification
– [ ] API 610/ISO 13709 compliance (where applicable)
– [ ] ATEX/IECEx certification for hazardous areas
– [ ] PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) compliance for European installations
– [ ] ASME compliance for USA installations
Supplier Evaluation Matrix:
| Criteria | Weight | Supplier A | Supplier B | Supplier C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical capability | 25% | |||
| Cryogenic experience | 20% | |||
| Lead time | 15% | |||
| After-sales support | 15% | |||
| Price competitiveness | 15% | |||
| Geographic presence | 10% |
Phase 4: Request for Quotation (RFQ) Preparation
Essential RFQ Documentation:
– [ ] Process data sheet with all operating conditions
– [ ] Piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&ID)
– [ ] Site conditions (ambient temperature, altitude, hazardous area classification)
– [ ] Preferred materials of construction
– [ ] Required documentation packages (ITP, MDR, test certificates)
– [ ] Spare parts requirements (commissioning, 2-year operation)
– [ ] Training and installation supervision needs
Commercial Terms to Define:
– [ ] Delivery terms (Incoterms 2020)
– [ ] Payment milestones
– [ ] Warranty period and conditions
– [ ] Performance guarantees and penalties
– [ ] Liquidated damages for late delivery
Phase 5: Technical Bid Evaluation
Performance Verification:
– [ ] Compare quoted performance curves against system requirements
– [ ] Verify NPSH required vs. NPSH available (minimum 0.5m margin)
– [ ] Check efficiency at rated and off-design conditions
– [ ] Evaluate power consumption and motor sizing
– [ ] Review bearing and seal life expectations
Design Review:
– [ ] Material selection for cryogenic compatibility
– [ ] Seal type and configuration (mechanical seals, gas seals)
– [ ] Bearing system (product-lubricated, external lubrication)
– [ ] Thermal contraction allowances
– [ ] Instrumentation and control interfaces
Phase 6: Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT)
Pre-Shipment Test Requirements:
– [ ] Hydrostatic pressure test
– [ ] Performance test (flow, head, efficiency, NPSH)
– [ ] Mechanical running test
– [ ] Vibration analysis
– [ ] Cryogenic performance test (if specified)
– [ ] Documentation review and approval
Witness Points:
– [ ] Define hold points requiring customer presence
– [ ] Establish remote witnessing options if travel is restricted
– [ ] Agree on test procedure review timeline
Phase 7: Logistics and Installation Planning
Shipping Considerations:
– [ ] Cryogenic pump preservation requirements during transit
– [ ] Lifting and handling specifications
– [ ] Storage conditions at destination
– [ ] Import/export documentation (certificates of origin, compliance declarations)
Installation Preparation:
– [ ] Foundation and grouting specifications
– [ ] Alignment tolerances
– [ ] Piping connection requirements
– [ ] Electrical and instrumentation hookup details
– [ ] Pre-commissioning checklist from manufacturer
Phase 8: After-Sales and Lifecycle Support
Service Agreement Evaluation:
– [ ] Local service center availability (USA/Europe)
– [ ] Emergency response time commitments
– [ ] Spare parts lead times and stocking agreements
– [ ] Remote monitoring and diagnostics capabilities
– [ ] Planned maintenance intervals and costs
Long-Term Considerations:
– [ ] Spare parts interchangeability and obsolescence management
– [ ] Training programs for operations and maintenance personnel
– [ ] Performance monitoring and optimization services
– [ ] Upgrade and retrofit options
Key Supplier Questions Checklist
Use these questions during supplier discussions:
- What is your installed base for cryogenic centrifugal pumps in similar applications?
- Can you provide references from comparable installations in USA/Europe?
- What is the standard lead time from order to delivery?
- Do you offer submerged, electric, and hydraulic configurations?
- What cryogenic testing capabilities do you have in-house?
- How do you address thermal shock during startup and shutdown?
- What is your warranty coverage for cryogenic service?
- Where are your nearest service centers located?
Red Flags to Watch
Avoid suppliers who:
– Cannot provide cryogenic-specific performance data
– Lack references in your specific application
– Offer no local service support in your region
– Cannot demonstrate material traceability for cryogenic components
– Have unclear or evasive responses about testing capabilities
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cryogenic centrifugal pump Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Cryogenic Centrifugal Pump Sourcing
Sourcing cryogenic centrifugal pumps represents a significant capital investment for industrial operations across the USA and Europe. Understanding the complete cost structure enables procurement teams to make informed decisions and negotiate effectively with suppliers like Cryostar and other specialized manufacturers.
Total Cost Breakdown
Materials Cost (40-55% of Total Unit Cost)
| Component | Cost Driver | Typical % of Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Cryogenic-grade stainless steel (304L/316L) | Raw material pricing, grade specifications | 35-45% |
| Impeller assembly | Precision machining, balancing requirements | 15-20% |
| Shaft seals (mechanical/hermetic) | Seal type, cryogenic compatibility | 10-15% |
| Bearings (ceramic/hybrid) | Temperature rating, load capacity | 8-12% |
| Motor/drive system | Electric, hydraulic, or submerged configuration | 15-25% |
| Insulation materials | Vacuum jacket, MLI requirements | 5-8% |
Key pricing factors:
– Pump type selection (electric centrifugal, hydraulic, or submerged configurations)
– Flow rate and head requirements
– Operating temperature range (LNG, nitrogen, oxygen applications)
– Wetted materials certification (ASME, PED, API standards)
Labor and Manufacturing (25-35% of Total Unit Cost)
| Labor Category | Description | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Precision machining | Tight tolerances for cryogenic service | High |
| Welding/fabrication | Certified welders, X-ray inspection | Medium-High |
| Assembly and balancing | Clean room assembly, dynamic balancing | Medium |
| Testing and QA | Cryogenic performance testing, certification | Medium |
| Engineering/customization | Application-specific modifications | Variable |
Regional labor cost considerations:
– USA manufacturing: Higher labor rates ($45-85/hour), shorter lead times for domestic buyers
– European manufacturing (Germany, France, Italy): Comparable rates (€40-75/hour), established cryogenic expertise
– Asian manufacturing: Lower labor costs but increased logistics and QC requirements
Logistics and Delivery (10-20% of Total Landed Cost)
| Cost Element | USA Destination | Europe Destination |
|---|---|---|
| Crating/specialized packaging | $2,000-8,000 | €1,800-7,000 |
| Ocean freight (from Europe) | $3,500-12,000 | N/A (domestic) |
| Ocean freight (from Asia) | $4,000-15,000 | $4,500-16,000 |
| Customs duties | 0-5.5% (HTS dependent) | 0-4.5% (CN code dependent) |
| Insurance (marine/transit) | 0.3-0.8% of value | 0.3-0.8% of value |
| Last-mile delivery | $500-3,000 | €400-2,500 |
Critical logistics considerations:
– Oversized/overweight shipment surcharges for large-capacity pumps
– Temperature-controlled transport requirements for pre-cooled units
– Port handling fees and terminal charges
– Import documentation (certificates of conformity, test reports)
Indicative Price Ranges by Application
| Pump Category | Capacity Range | Price Range (USD) | Price Range (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small centrifugal (ASU service) | 10-50 m³/h | $25,000-75,000 | €22,000-68,000 |
| Medium centrifugal (process transfer) | 50-200 m³/h | $75,000-200,000 | €68,000-180,000 |
| Large centrifugal (LNG/bunkering) | 200-1,000+ m³/h | $200,000-800,000+ | €180,000-720,000+ |
| Submerged motor pumps | Variable | +15-30% premium | +15-30% premium |
Cost-Saving Strategies for Procurement Teams
1. Specification Optimization
- Right-size the pump: Avoid over-specifying flow rates and head requirements
- Standardize materials: Use 304L stainless where 316L isn’t required
- Evaluate seal options: Mechanical seals vs. hermetic designs based on actual service conditions
- Review certification requirements: Specify only necessary certifications (ATEX, API, PED)
2. Procurement Tactics
- Bundle orders: Combine multiple pump purchases for volume discounts (typically 5-15%)
- Long-term agreements: Negotiate framework contracts with preferred suppliers
- Competitive bidding: Obtain quotes from multiple qualified manufacturers (Cryostar, Nikkiso, Ebara, etc.)
- Consider refurbished units: For non-critical applications, certified rebuilt pumps offer 30-50% savings
3. Logistics Optimization
- Consolidate shipments: Combine with other cryogenic equipment orders
- Negotiate Incoterms: DDP terms shift logistics burden to supplier but may include markup
- Regional sourcing: European buyers benefit from EU-manufactured pumps (no duties, shorter transit)
- Plan lead times: Rush orders incur 15-25% expediting premiums
4. Total Cost of Ownership Considerations
- Energy efficiency: Higher-efficiency pumps justify premium pricing through operational savings
- Maintenance requirements: Factor in spare parts availability and service contracts
- Warranty terms: Extended warranties (2-3 years) reduce early-life failure costs
- Lifecycle support: Evaluate supplier’s service network in your operating region
Hidden Costs to Budget For
| Cost Category | Typical Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Installation and commissioning | 5-12% of pump cost | May require OEM technicians |
| Spare parts inventory | 8-15% of pump cost | Critical spares for continuous operation |
| Training | $2,000-10,000 | Operator and maintenance personnel |
| Foundation/piping modifications | Variable | Site-specific requirements |
| Commissioning fluids (LN2, etc.) | $1,000-5,000 | Initial cool-down and testing |
Negotiation Leverage Points
- Payment terms: Request 30-60 day terms vs. standard progress payments
- Spare parts pricing: Lock in spare parts pricing at time of pump purchase
- Performance guarantees: Include efficiency and NPSH guarantees with penalties
- Service agreements: Bundle commissioning support into purchase price
- Documentation packages: Ensure comprehensive O&M manuals and test certificates are included
By conducting thorough cost analysis across materials, labor, and logistics components, procurement professionals can optimize cryogenic centrifugal pump sourcing while maintaining the quality and reliability standards essential for air separation, LNG, and industrial gas applications.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cryogenic centrifugal pump With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps With Other Solutions
When selecting pumping technology for cryogenic fluid transfer, engineers must evaluate multiple options based on operational requirements, total cost of ownership, and application-specific demands. This analysis compares cryogenic centrifugal pumps against two primary alternatives: reciprocating pumps and submerged motor pumps.
Comparison Overview
| Feature | Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps | Reciprocating Pumps | Submerged Motor Pumps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate Capacity | High (continuous flow) | Low to moderate (pulsating) | Moderate to high |
| Pressure Generation | Moderate | Very high | Moderate |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low | High (valves, seals, pistons) | Very low |
| Initial Capital Cost | Moderate | Lower | Higher |
| Energy Efficiency | 70-85% | 60-75% | 75-90% |
| Footprint | Compact | Larger | Compact (in-tank) |
| Pulsation | Minimal | Significant | Minimal |
| NPSH Requirements | Moderate | Lower | Minimal |
| Ideal Applications | Continuous transfer, bunkering, ASU | High-pressure injection, small volumes | LNG storage, marine applications |
Detailed Analysis
Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps dominate cryogenic applications requiring continuous, high-volume flow. Their simple rotating design minimizes wear components, reducing maintenance intervals and operational downtime. Available in electric, hydraulic, and submerged configurations (as offered by manufacturers like Cryostar), these pumps adapt to diverse installation requirements across air separation units, gas transportation, and tanker unloading operations.
Reciprocating Pumps
Reciprocating pumps excel in applications demanding extremely high discharge pressures—particularly cylinder filling and high-pressure gas injection. However, their pulsating flow characteristics require dampening systems, and frequent valve and seal replacements increase lifecycle costs. For continuous transfer applications, they represent a less efficient choice.
Submerged Motor Pumps
Submerged configurations eliminate external shaft seals entirely, virtually eliminating fugitive emissions and reducing NPSH concerns. While capital costs run higher, their placement within cryogenic tanks suits marine LNG carriers and storage facilities where reliability and space constraints are paramount.
Selection Recommendation
For most industrial cryogenic transfer operations—including LNG bunkering, process applications, and air separation—centrifugal pumps deliver the optimal balance of reliability, efficiency, and operational flexibility. Reserve reciprocating technology for high-pressure, low-volume requirements, and consider submerged options where seal-less operation and space efficiency justify premium investment.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cryogenic centrifugal pump
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
Key Technical Properties
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps operate under extreme conditions, requiring precise specifications to ensure safe and efficient performance. Understanding these properties is critical for procurement decisions.
Performance Specifications
| Property | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate (Q) | Volume of cryogenic fluid pumped per unit time | 5–5,000 m³/h |
| Head (H) | Pressure differential the pump generates | 50–3,000 m |
| NPSH Required (NPSHr) | Minimum suction head to prevent cavitation | 0.5–5 m |
| Operating Temperature | Temperature range for cryogenic service | -196°C to -50°C |
| Discharge Pressure | Maximum outlet pressure rating | Up to 100 bar |
| Efficiency (η) | Hydraulic efficiency at rated conditions | 60–85% |
Material and Design Considerations
- Wetted Materials: Austenitic stainless steels (304L, 316L), aluminum alloys, or Inconel for cryogenic compatibility
- Seal Configuration: Mechanical seals, labyrinth seals, or hermetically sealed designs to minimize leakage
- Insulation Type: Vacuum-jacketed or foam-insulated housings to reduce heat ingress
- Bearing Systems: Product-lubricated or dry gas bearings rated for cryogenic temperatures
Pump Configurations
| Type | Application |
|---|---|
| Submerged (In-Tank) | LNG storage tanks, air separation units |
| Electric Centrifugal | Process transfer, high-flow applications |
| Hydraulic Drive | Hazardous areas, explosion-proof requirements |
Trade Terminology for B2B Procurement
Commercial Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Lowest unit count per order; typically 1–5 units for specialized cryogenic pumps |
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Supplier providing pumps for integration into third-party systems |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Supplier offering custom-designed pump solutions |
| Lead Time | Production-to-delivery timeframe; standard 12–24 weeks for cryogenic pumps |
| EXW / FOB / CIF | Incoterms defining shipping responsibility and cost allocation |
Technical and Compliance Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| API 610 | American Petroleum Institute standard for centrifugal pumps in petroleum and heavy-duty chemical service |
| ATEX Certification | EU directive compliance for equipment in explosive atmospheres |
| PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) | European regulation for pressure-bearing equipment |
| ASME B73 | Dimensional standard for horizontal end-suction centrifugal pumps |
| MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) | Reliability metric indicating expected operational lifespan |
| FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) | Pre-shipment testing to verify performance against specifications |
Service and Support Terms
- Spare Parts Availability: Critical for minimizing downtime; confirm stock levels for wear components (impellers, seals, bearings)
- Warranty Terms: Standard 12–24 months; extended warranties available for high-value contracts
- Aftermarket Support: Field service, remote diagnostics, and refurbishment programs
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Comprehensive cost analysis including acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal
Specification Checklist for RFQ Preparation
- Required flow rate and head at operating temperature
- Cryogenic fluid type (LNG, LN2, LOX, LAr)
- Suction conditions and available NPSH
- Drive type preference (electric, hydraulic, submerged motor)
- Certification requirements (ATEX, PED, API)
- Installation environment (indoor/outdoor, hazardous zone classification)
- Spare parts and service support requirements
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cryogenic centrifugal pump Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Cryogenic Centrifugal Pump Sector
Market Overview and Growth Drivers
The global cryogenic centrifugal pump market continues to expand, driven primarily by increasing demand across LNG infrastructure, air separation units (ASUs), and marine applications. As liquefied natural gas trade volumes grow and industrial gas applications proliferate, procurement teams face evolving sourcing challenges and opportunities.
Key Market Drivers:
– Expansion of LNG bunkering infrastructure globally
– Growth in air separation unit installations for industrial gas production
– Increasing demand for hydrogen and helium handling capabilities
– Stricter emissions regulations pushing adoption of cleaner fuel alternatives
Regional Sourcing Landscape
| Region | Market Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Mature market with established supplier base; strong LNG export infrastructure | Focus on compliance with API and ASME standards; lead times affected by domestic demand |
| Europe | Emphasis on sustainability and energy transition; growing hydrogen economy | EU regulatory alignment; preference for suppliers with documented environmental credentials |
| Asia-Pacific | Fastest-growing demand center; manufacturing hub | Competitive pricing; verify quality certifications and after-sales support capabilities |
Current Sourcing Trends
1. Supplier Consolidation and Specialization
Leading manufacturers like Cryostar offer comprehensive portfolios spanning electric centrifugal pumps, hydraulic variants, and submerged configurations. Buyers increasingly prefer suppliers capable of delivering integrated solutions rather than component-only offerings.
2. Application-Specific Configuration Demands
Procurement specifications now routinely address:
– Marine applications: Compatibility with LNG carrier systems, including tank pressure control
– Industrial gas processing: Integration with ASU operations and transfer applications
– Bunkering operations: High-flow capacity with rapid cycling capabilities
3. Extended Service and Lifecycle Agreements
Total cost of ownership calculations now dominate purchasing decisions. Buyers prioritize suppliers offering:
– Predictive maintenance programs
– Regional service center coverage
– Spare parts availability guarantees
– Remote monitoring capabilities
Sustainability Considerations in Procurement
Environmental performance has become a non-negotiable evaluation criterion for European and increasingly North American buyers.
Sustainability Evaluation Criteria:
– Energy efficiency ratings across operating ranges
– Leak prevention and emissions control features
– Material sourcing transparency
– End-of-life recyclability documentation
– Supplier carbon footprint reporting
The shift toward hydrogen as an energy carrier creates additional procurement complexity, as cryogenic centrifugal pumps must accommodate liquid hydrogen’s unique properties—including its extremely low boiling point and high diffusivity.
Historical Context and Technology Evolution
Cryogenic centrifugal pump technology has evolved significantly from early industrial gas applications to today’s sophisticated systems. Key developmental milestones include:
- 1950s-1970s: Initial deployment in air separation and aerospace applications
- 1980s-1990s: LNG trade expansion drove capacity and reliability improvements
- 2000s-2010s: Submerged pump designs gained prominence for marine applications
- 2020s-Present: Digital integration, hydrogen-ready designs, and sustainability optimization
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
For Procurement Teams:
- Qualify multiple suppliers across geographic regions to mitigate supply chain disruptions
- Prioritize technical collaboration with manufacturers during specification development
- Evaluate total lifecycle costs including energy consumption, maintenance, and downtime
- Verify certifications relevant to your application (API 610, ISO 13709, marine classification societies)
- Assess supplier financial stability given long equipment lifecycles and service dependencies
Due Diligence Checklist:
– [ ] Documented performance in comparable applications
– [ ] Reference installations accessible for site visits
– [ ] Clear warranty terms and service level agreements
– [ ] Compliance documentation for target operating jurisdictions
– [ ] Sustainability metrics and improvement commitments
Market Outlook
The cryogenic centrifugal pump sector faces continued transformation as energy transition initiatives reshape demand patterns. Buyers who establish strategic supplier relationships now—emphasizing flexibility, sustainability, and technical partnership—will be better positioned to navigate evolving requirements in LNG, hydrogen, and industrial gas applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cryogenic centrifugal pump
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
1. What is a cryogenic centrifugal pump and how does it differ from standard centrifugal pumps?
A cryogenic centrifugal pump is specifically engineered for the transfer and pressurization of liquefied gases at extremely low temperatures (typically below -150°C/-238°F). Unlike standard centrifugal pumps, these units feature:
- Specialized materials resistant to thermal contraction and embrittlement
- Extended shaft designs to isolate bearings and seals from cryogenic temperatures
- Unique sealing systems designed for low-temperature operation
- Thermal management features to handle temperature gradients
2. What are the primary industrial applications for cryogenic centrifugal pumps?
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| LNG/Gas Processing | LNG transfer, bunkering, tanker unloading |
| Air Separation | Liquid oxygen, nitrogen, and argon handling in ASUs |
| Marine | Fuel gas supply systems on LNG carriers |
| Petrochemical | Ethane, propane, and butane processing |
| Aerospace | Liquid hydrogen and oxygen for rocket propulsion |
| Industrial Gas | Distribution and storage operations |
3. What configuration options are available for cryogenic centrifugal pumps?
Leading manufacturers offer three primary configurations:
- Electric centrifugal pumps – Standard motor-driven units for fixed installations
- Hydraulic-driven pumps – Suitable for hazardous environments or where electric power is limited
- Submerged pumps – Installed directly in cryogenic tanks, eliminating suction lift concerns and reducing NPSH requirements
4. What factors should we consider when specifying a cryogenic centrifugal pump?
Key specification parameters include:
- Flow rate requirements (m³/h or GPM)
- Discharge pressure (bar or PSI)
- Fluid type (LNG, LOX, LIN, LAR, etc.)
- Operating temperature range
- Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSHa)
- Installation type (vertical, horizontal, submerged)
- Hazardous area classification (ATEX, IECEx)
- Material compatibility with process fluid
5. What certifications and standards should cryogenic centrifugal pumps meet for B2B procurement?
Ensure pumps comply with:
- API 610 – Centrifugal pumps for petroleum, petrochemical, and natural gas industries
- EN 12162 – Liquid pumps safety requirements
- ATEX/IECEx – Explosion protection for hazardous atmospheres
- PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) – For European markets
- ASME – Pressure vessel and component standards
- ISO 9001 – Quality management certification
6. What is the typical lead time and total cost of ownership considerations?
Lead times vary based on configuration:
– Standard models: 12-20 weeks
– Custom-engineered solutions: 24-40 weeks
Total cost of ownership factors:
– Initial capital expenditure
– Installation and commissioning costs
– Energy consumption (efficiency ratings)
– Maintenance intervals and spare parts availability
– Seal replacement frequency
– Downtime costs during service
7. What maintenance requirements should we anticipate?
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps require:
| Maintenance Item | Typical Interval |
|---|---|
| Seal inspection/replacement | 8,000-15,000 operating hours |
| Bearing inspection | Annual |
| Vibration monitoring | Continuous or quarterly |
| Performance testing | Semi-annual |
| Complete overhaul | 5-7 years |
Note: Submerged pump designs typically offer reduced maintenance due to fewer external sealing points.
8. What technical support and after-sales services should we expect from suppliers?
Qualified cryogenic centrifugal pump suppliers should provide:
- Engineering consultation during specification and selection
- Installation supervision and commissioning support
- Operator training programs
- 24/7 technical support hotlines
- Spare parts inventory with guaranteed availability
- Field service teams in your operating region
- Performance optimization services
- Extended warranty options
Request supplier references from similar installations and verify their regional service capabilities before procurement.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cryogenic centrifugal pump
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion: Cryogenic Centrifugal Pumps
Cryogenic centrifugal pumps represent a critical infrastructure investment for operations handling liquefied gases across LNG, marine, industrial gas, and air separation applications. The strategic value of proper sourcing extends beyond initial procurement costs to encompass operational efficiency, safety compliance, and total cost of ownership.
Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers
| Factor | Strategic Impact |
|---|---|
| Supplier expertise | Directly affects system reliability and technical support quality |
| Application matching | Ensures optimal performance for specific cryogenic fluids (LNG, nitrogen, oxygen) |
| Regional support | Critical for maintenance response times in USA and European operations |
| Technology roadmap | Positions operations for evolving efficiency and environmental standards |
Market Outlook
The cryogenic pump sector continues expanding alongside LNG infrastructure growth, bunkering operations, and industrial gas demand. Buyers should anticipate:
- Increased automation integration in pump monitoring systems
- Enhanced efficiency requirements driven by energy cost pressures
- Stricter regulatory compliance for safety and emissions
Final Recommendation
Prioritize suppliers demonstrating proven cryogenic expertise, comprehensive after-sales support networks, and technology alignment with your operational requirements. Evaluate total lifecycle costs rather than upfront pricing alone to maximize long-term ROI on these mission-critical assets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.