The global crank position sensor market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising vehicle production and the increasing complexity of engine management systems. According to Mordor Intelligence, the automotive sensors market—which includes crank position sensors—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7% from 2023 to 2028, with crank position sensors playing a critical role in fuel efficiency and emissions control. As demand escalates, cost-effectiveness in manufacturing has become a key differentiator among suppliers. With production hubs concentrated in Asia-Pacific—where labor and operational costs are lower—several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in providing high-quality yet competitively priced crank position sensors. Drawing on industry data and supply chain analysis, here are the top five cost-efficient crank position sensor manufacturers shaping the market landscape.
Top 5 Crank Position Sensor Cost Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 OEM & Aftermarket Crankshaft Sensor Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2018
Website: cowtotal.com
Key Highlights: COWTOTAL is a top OEM & aftermarket Crankshaft Sensors manufacturer, offering high-quality engine position detection components and factory-direct wholesale ……
#2 Camshaft and Crankshaft Position Sensors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: walkerproducts.com
Key Highlights: Walker Products is a premier manufacturer of Camshaft and Crankshaft Position Sensors, offering precision-engineered, OE replacement solutions for nearly all ……
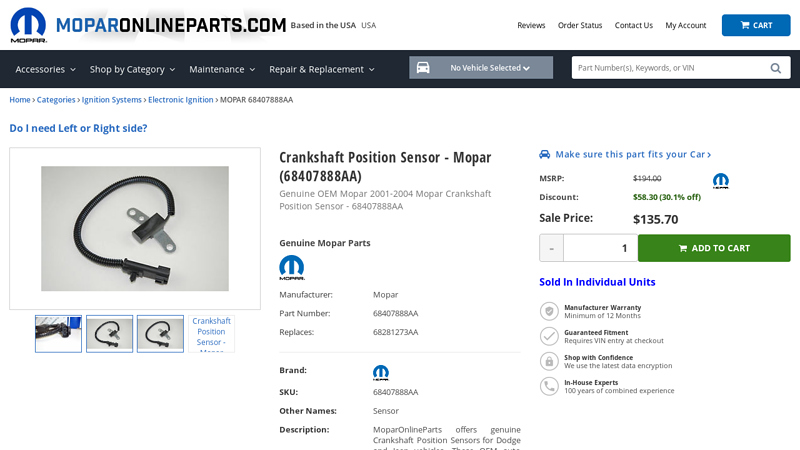
#3 Crankshaft Position Sensor – 68407888AA
Domain Est. 2007
Website: parts.moparonlineparts.com
Key Highlights: 5-day delivery 30-day returnsMoparOnlineParts offers genuine Crankshaft Position Sensors for Dodge and Jeep vehicles. These OEM auto accessories are available at low prices in our …
#4 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Domain Est. 1996
#5 Replacement Crank Position Sensor Information
Domain Est. 2004
Website: partsgeek.com
Key Highlights: 2–3 day delivery · 30-day returnsReplacement crank position sensors cost between $15-200, on average. If you don’t want to keep installing new sensors, check to see if you have an…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Crank Position Sensor Cost

2026 Market Trends for Crank Position Sensor Cost
The global crank position sensor (CKP) market is poised for notable shifts in cost dynamics by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving vehicle manufacturing trends, and supply chain developments. While precise cost figures are proprietary and vary by region, OEM vs. aftermarket channels, and volume, the following trends are expected to shape pricing:
1. Modest Cost Reduction Amid Rising Complexity
Despite increasing technical demands—such as higher accuracy, thermal stability, and integration with advanced engine management systems—overall CKP sensor costs are projected to decline slightly by 2026. This will be primarily driven by economies of scale, especially in high-volume automotive markets like China and India, and the maturation of sensor manufacturing processes. However, the shift toward more sophisticated sensor types (e.g., magnetoresistive and Hall-effect sensors over traditional variable reluctance types) may offset some savings, particularly in premium and performance vehicles.
2. Impact of Electrification and Powertrain Diversification
As the automotive industry transitions toward electrification, the demand for traditional CKP sensors in internal combustion engines (ICE) may plateau or decline in mature markets. However, hybrid vehicles still require CKPs, sustaining partial demand. By 2026, manufacturers may consolidate production lines and repurpose sensor technologies for hybrid applications, leading to cost efficiencies. Nonetheless, the shrinking ICE market could reduce competition among suppliers, potentially stabilizing or even increasing prices in niche segments.
3. Supply Chain Optimization and Regional Manufacturing
Ongoing efforts to localize supply chains and reduce dependency on single-source regions (e.g., post-pandemic and geopolitical disruptions) will influence costs. Increased regional production in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe is expected to lower logistics and tariff-related expenses, contributing to a downward pressure on CKP sensor prices. Additionally, automation in sensor assembly and testing is anticipated to improve yield rates and reduce labor costs.
4. Growth in Aftermarket and Replacement Demand
With the global vehicle parc aging and average vehicle lifespans increasing, the aftermarket segment for CKP sensors will remain strong through 2026. Intense competition among aftermarket suppliers is likely to keep replacement sensor prices low, with commoditization driving cost reductions. However, rising demand for OEM-equivalent performance may support premium pricing for high-reliability sensors.
5. Material and Semiconductor Price Volatility
Fluctuations in raw material costs—particularly rare earth elements used in magnets and semiconductor components—could impact CKP sensor pricing. While long-term contracts and material substitution strategies may mitigate risks, unforeseen shortages or trade restrictions could temporarily increase costs, especially in the first half of 2026.
In summary, the crank position sensor market in 2026 is expected to experience a slight net decrease in average unit cost, supported by manufacturing efficiencies and regional production growth. However, this trend will be counterbalanced by technological advancements and material cost volatility, resulting in a stable-to-slightly-declining price environment across most segments.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Crank Position Sensors: Cost vs. Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing crank position sensors (CPS) at the lowest possible cost can lead to significant downstream issues, particularly concerning component quality and intellectual property (IP) exposure. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for maintaining product reliability, regulatory compliance, and long-term business integrity.
Overlooking Quality for Short-Term Cost Savings
One of the most prevalent mistakes is prioritizing upfront cost reduction without evaluating long-term reliability. Low-cost sensors from unverified suppliers may use substandard materials (e.g., inferior magnets, poor-grade plastics), leading to premature failure due to heat, vibration, or moisture exposure. This can result in increased warranty claims, vehicle downtime, and reputational damage. Additionally, inconsistent manufacturing processes may lead to variable performance, affecting engine timing accuracy and emissions compliance.
Compromising on Environmental and Performance Specifications
Cost-driven sourcing decisions often neglect compliance with critical environmental standards such as IP (Ingress Protection) ratings. A sensor lacking adequate IP67 or IP68 certification may fail in harsh automotive environments, allowing dust or water ingress that disrupts signal integrity. Similarly, sensors that do not meet required temperature ranges (e.g., -40°C to +150°C) or electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards can malfunction, leading to engine stalling or diagnostic errors.
Ignoring Intellectual Property and Counterfeit Risks
Sourcing from suppliers in regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of inadvertently procuring counterfeit or cloned sensors. These components may mimic OEM designs but lack proper licensing, exposing the buyer to legal liability and IP infringement claims. Furthermore, counterfeit sensors often have unreliable calibration and durability, posing serious safety and performance risks. Lack of traceability and documentation also makes it difficult to validate authenticity and ensure regulatory compliance.
Supply Chain Vulnerability and Lack of Support
Low-cost suppliers may offer limited technical support, poor documentation, or inconsistent availability. This can delay production, complicate integration, and hinder troubleshooting. In the event of a field failure, the absence of engineering collaboration or root cause analysis from the supplier can prolong resolution times and increase recall risks.
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough supplier audits, request sample testing under real-world conditions, verify certifications (AEC-Q100, ISO/TS 16949), and ensure contractual IP protections. A total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis—factoring in failure rates, warranty costs, and downtime—often reveals that higher-quality sensors offer better value over time.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Crank Position Sensor Cost
Understanding the total cost of acquiring and deploying crank position sensors involves more than just the unit price. Logistics and compliance factors significantly influence the final landed cost and supply chain efficiency. This guide outlines key considerations to help manage and optimize costs effectively.
Procurement and Sourcing Strategy
Selecting the right suppliers and negotiating favorable terms are critical to controlling costs. Consider sourcing from regions with competitive manufacturing costs, but ensure suppliers meet quality and delivery standards. Utilize long-term contracts or volume purchasing agreements to secure pricing stability and potential discounts. Evaluating multiple suppliers helps mitigate supply chain risks and supports competitive pricing.
International Shipping and Freight Costs
Freight expenses can vary widely based on shipping method (air, sea, or land), origin, destination, and sensor volume. Air freight offers speed but at a higher cost, suitable for urgent or low-volume shipments. Sea freight is more economical for bulk orders but involves longer lead times. Accurate freight classification, packaging optimization, and route planning can reduce transportation expenses. Include Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) clarity in contracts to define cost responsibilities.
Import Duties and Tariffs
Crank position sensors may be subject to import duties and tariffs depending on the destination country and product classification (e.g., HS Code 8543.20 for electrical sensors in many jurisdictions). Duty rates vary by trade agreements and country-specific regulations. Conduct a tariff analysis before importing and explore duty reduction programs such as Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) or Duty Drawback schemes. Accurate product classification helps avoid unexpected costs and customs delays.
Customs Clearance and Documentation
Proper documentation is essential to avoid delays and penalties that increase landed cost. Required documents typically include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and bill of lading/airway bill. Ensure product descriptions and values are accurately declared to prevent customs audits or valuation disputes. Compliance with destination country labeling and language requirements (e.g., bilingual labeling) is also necessary.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Crank position sensors must meet regulatory standards to enter and be sold in target markets. Key certifications include:
- CE Marking (Europe): Required for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and safety under the RED and LVD directives.
- FCC Certification (USA): Applicable if the sensor emits radio frequencies.
- E-Mark (ECE Regulations): Mandatory for automotive components sold in many European markets.
- RoHS and REACH (EU): Restrict hazardous substances and require chemical compliance.
Non-compliant products may be rejected at customs or recalled, incurring significant costs. Budget for testing, certification, and periodic audits.
Inventory and Warehousing Management
Holding costs, including warehousing, insurance, and inventory obsolescence, contribute to total cost. Implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices to reduce stock levels while ensuring supply continuity. Use demand forecasting to align procurement with production schedules and avoid overstocking or stockouts.
Reverse Logistics and Returns
Plan for handling defective or non-conforming sensors. Return shipping, inspection, repair, and disposal processes add to the cost structure. Clear return policies and supplier agreements (e.g., RMA processes) help manage these expenses efficiently. Recycling or disposal must comply with environmental regulations such as WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment).
Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Supply chain disruptions (e.g., port delays, geopolitical issues, natural disasters) can impact cost and availability. Diversify suppliers, maintain safety stock for critical sensors, and monitor global trade developments. Include force majeure clauses in contracts to address unforeseen events.
Total Landed Cost Calculation
To determine the true cost of a crank position sensor, sum all components:
- Unit price
- Packaging and handling
- Freight and insurance
- Import duties and taxes
- Customs clearance fees
- Compliance certification costs
- Inventory carrying costs
- Risk and contingency reserves
Tracking and analyzing these elements enables better decision-making and cost optimization across the logistics and compliance lifecycle.
Conclusion: Crank Position Sensor Sourcing Cost
After evaluating various sourcing options for the crank position sensor, it is evident that cost-efficiency can be achieved through a strategic balance of quality, supplier reliability, and volume purchasing. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) sensors offer superior reliability and performance but come at a higher price point. Aftermarket alternatives provide significant cost savings, particularly when sourced from reputable manufacturers, though careful vetting is required to ensure durability and compatibility.
Global suppliers, especially from regions with lower manufacturing costs, present competitive pricing; however, logistics, import duties, and lead times must be factored into the total cost of ownership. Establishing long-term partnerships with pre-qualified suppliers and leveraging bulk procurement can further drive down per-unit costs while maintaining acceptable quality standards.
In conclusion, the optimal sourcing strategy involves a blended approach—utilizing cost-effective aftermarket sensors for non-critical applications and OEM parts where performance and warranty are paramount—resulting in an overall reduction in procurement expenses without compromising operational reliability. Regular market reviews and supplier performance assessments should be conducted to ensure continued cost efficiency and supply chain resilience.