The global cranial electrostimulation (CES) device market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising awareness of mental health disorders and increasing demand for non-invasive treatment options. According to Grand View Research, the global neurostimulation devices market, which includes CES, was valued at USD 7.1 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 10% for the neurostimulation devices market through 2028, citing growing adoption of wearable and portable neuromodulation technologies. As anxiety, depression, and insomnia continue to affect millions worldwide, CES devices—offering non-pharmacological intervention through low-level electrical currents—have gained traction among clinicians and consumers alike. This increasing demand has spurred innovation and competition among manufacturers, positioning the CES sector as a pivotal niche within the broader digital mental health landscape. The following analysis identifies the top 8 cranial electrostimulation device manufacturers shaping this evolving market.
Top 8 Cranial Electro Stimulation Device Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
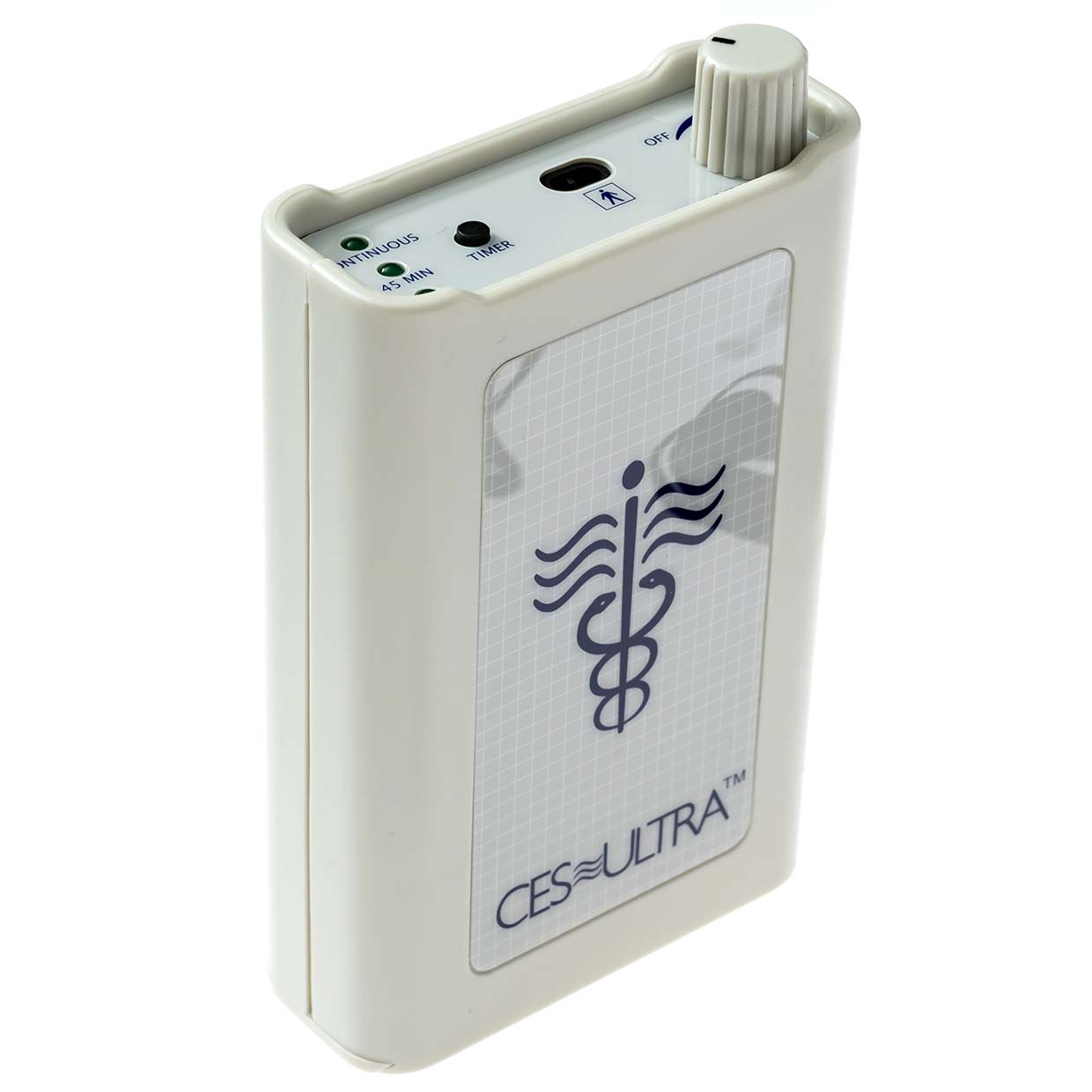
#1 Manufacturers of cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) devices in …
Domain Est. 2004
Website: cesultra.com
Key Highlights: There are currently three major manufacturers of cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) in the United States: 1).The CES Ultra; 2). EPI, Electromedical ……
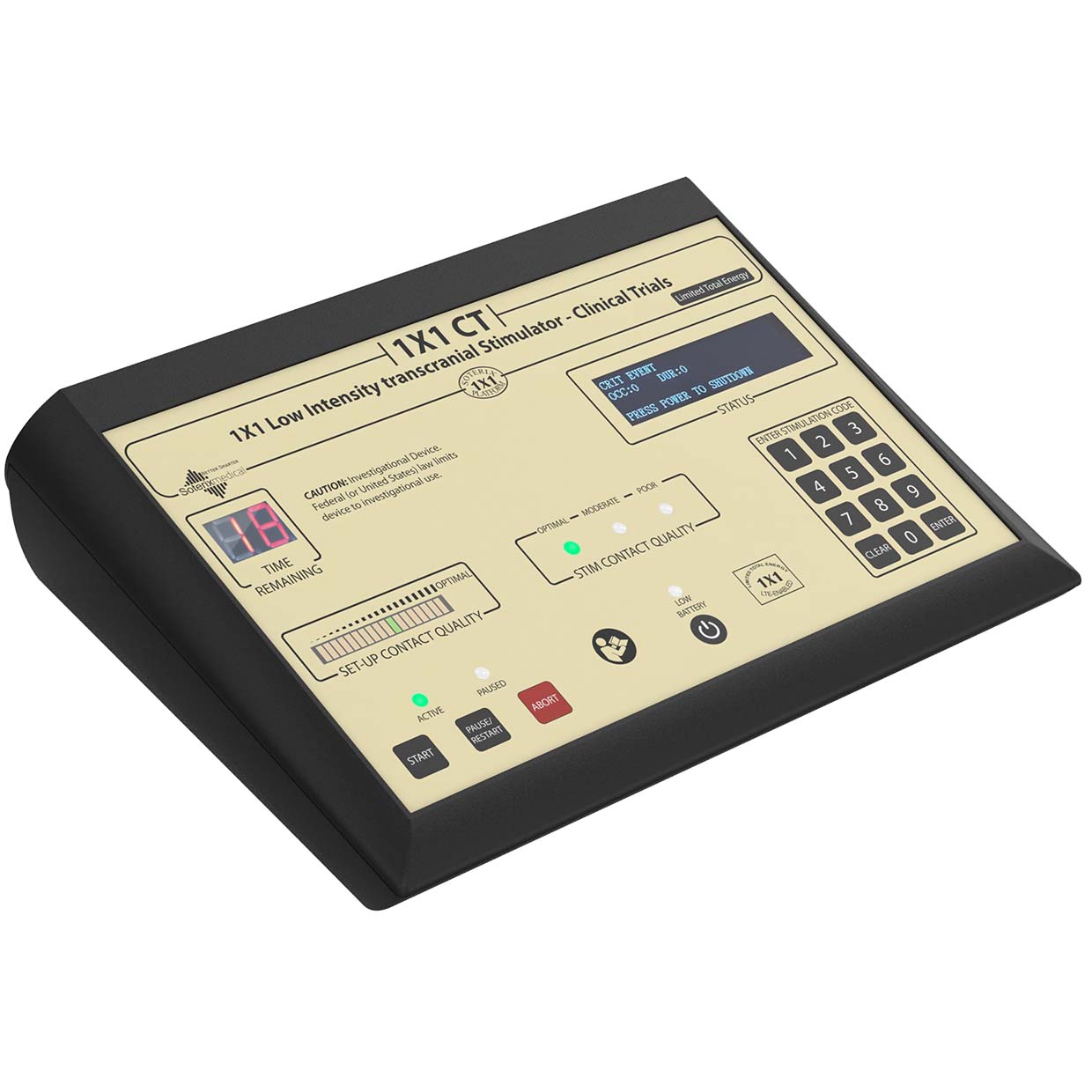
#2 Soterix Medical
Domain Est. 2009
Website: soterixmedical.com
Key Highlights: Soterix Medical is the world leader in non-invasive neuromodulation and brain stimulation technology. Researchers and clinicians choose Soterix Medical ……
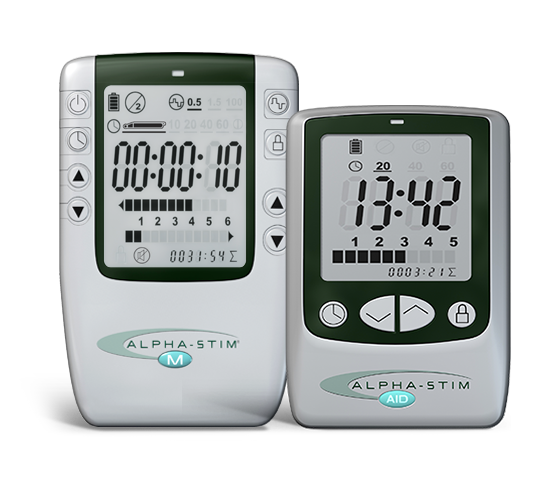
#3 EPII
Domain Est. 1995
Website: epii.com
Key Highlights: EPI is a global medical device company improving lives through unique neuromodulation therapeutics. We develop and manufacture the Alpha-Stim brand….
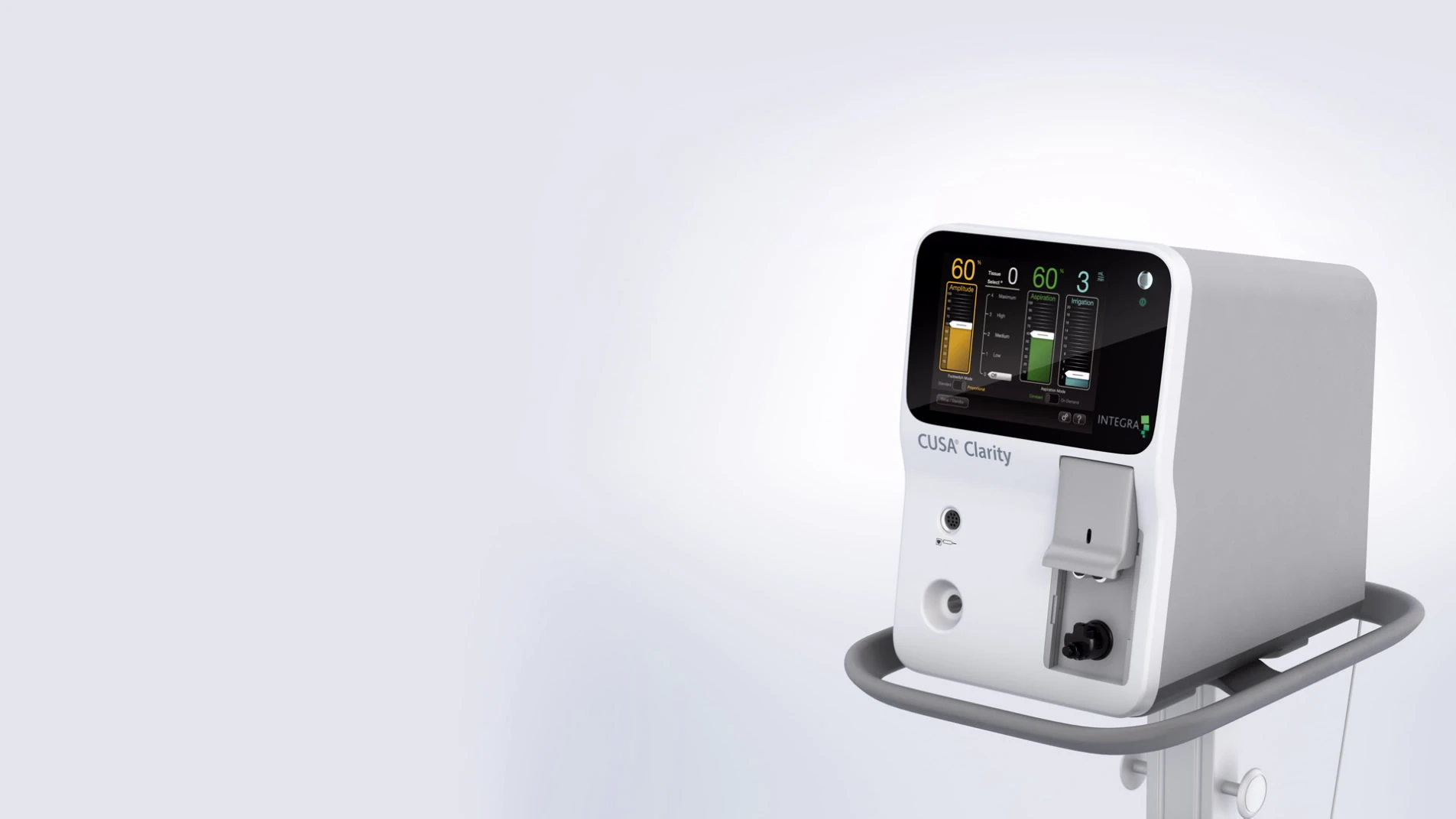
#4 Integra LifeSciences
Domain Est. 1999
Website: integralife.com
Key Highlights: We are the global leader in neurosurgery, offering a broad portfolio of products and solutions for dural access and repair, cerebral spinal fluid management ……
#5 Brain stimulation for depression and chronic pain
Domain Est. 2013
Website: soomamedical.com
Key Highlights: Sooma tDCS is a revolutionary noninvasive brain stimulation treatment that effectively relieves patient symptoms – as well as patient queues at the clinic….
#6 Flow Neuroscience: tDCS Depression Treatment
Domain Est. 2016
Website: flowneuroscience.com
Key Highlights: Flow works with your brain’s natural electrical signals to gently stimulate these regions, helping to relieve depression symptoms….
#7 Cervella Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulator
Domain Est. 2018
Website: cervella.us
Key Highlights: Cervella Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulator is an award-winning, patented, FDA-cleared medical device for non-drug treatment of anxiety and insomnia….
#8 Best CES Device Comparison Table
Domain Est. 2015
Website: caputron.com
Key Highlights: Cranial electrotherapy stimulation, or “CES”, works by gently stimulating various nerves in the brain. It’s a painless, drug-free, and safe way to manage the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cranial Electro Stimulation Device

H2: Emerging Market Trends for Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) Devices in 2026
By 2026, the global market for Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) devices is projected to undergo significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, rising mental health awareness, and evolving regulatory landscapes. Key market trends shaping the industry include:
-
Increased Demand for Non-Invasive Mental Health Solutions
As global awareness of anxiety, depression, and insomnia continues to rise, consumers and healthcare providers are increasingly seeking non-pharmacological treatment alternatives. CES devices, which deliver low-level electrical currents to modulate brain activity, are gaining traction as safe, at-home therapies. The growing preference for self-managed care is accelerating adoption, particularly in North America and Western Europe. -
Technological Integration and Smart Features
CES devices are increasingly incorporating smart technology, including Bluetooth connectivity, mobile app integration, and AI-driven treatment personalization. By 2026, next-generation CES units are expected to offer real-time biofeedback, usage tracking, and adaptive stimulation protocols tailored to individual user responses—enhancing both efficacy and user engagement. -
Regulatory Approvals and Market Expansion
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have granted clearances for several CES devices for conditions like anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Expanded approvals, especially in emerging markets like Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are opening new commercial opportunities. Countries with growing telehealth infrastructures are likely to see faster integration of CES into mental health treatment plans. -
Rising Healthcare Costs and Focus on Cost-Effective Therapies
With escalating healthcare expenditures, payers and providers are emphasizing cost-effective interventions. CES devices, which require a one-time investment and have minimal side effects compared to pharmaceuticals, are being viewed as economically viable long-term solutions. Reimbursement policies in select markets are beginning to reflect this shift, further boosting market penetration. -
Consumer Awareness and Digital Marketing Influence
Online health communities, influencer endorsements, and direct-to-consumer marketing are playing a pivotal role in educating users about CES benefits. E-commerce platforms and telehealth consultations are streamlining access, enabling consumers to purchase FDA-cleared devices with greater confidence. -
Clinical Research and Evidence-Based Growth
Ongoing clinical trials and peer-reviewed studies are strengthening the scientific foundation for CES efficacy. By 2026, increased investment in research is expected to validate CES for additional indications, such as PTSD, cognitive enhancement, and substance withdrawal support—broadening its therapeutic scope. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The CES device market is witnessing entry by both established medical technology firms and innovative startups. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and product differentiation—such as wearable form factors and hybrid neurostimulation platforms—are driving innovation and market consolidation.
In conclusion, the 2026 CES device market is poised for robust growth, fueled by a confluence of mental health demand, technological advancement, and supportive regulatory trends. As CES becomes more integrated into mainstream mental wellness protocols, it is expected to transition from a niche therapy to a cornerstone of non-invasive neuromodulation.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) Device
Quality Concerns in Manufacturing and Components
One of the primary risks when sourcing Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) devices is compromising on product quality. Many suppliers, especially in low-cost manufacturing regions, may use substandard electronic components that fail to meet medical device safety standards. Poorly calibrated current outputs, inconsistent waveform generation, or unreliable electrode materials can lead to ineffective or even unsafe treatments. Additionally, inadequate quality control processes during assembly can result in device malfunctions, short lifespans, or potential harm to end users. It is crucial to verify that suppliers comply with ISO 13485 standards and have a proven track record in medical-grade electronics manufacturing.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Infringement
Sourcing CES devices from third-party manufacturers carries significant intellectual property (IP) risks. There is a danger of unintentionally partnering with suppliers who replicate patented technologies without authorization, exposing the buyer to legal liability. Furthermore, if the design or firmware of the CES device is shared without proper non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or IP assignment clauses, there is a risk of design theft or unauthorized reproduction by the manufacturer. Buyers must conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that the supplier does not infringe on existing patents and that all custom-developed aspects of the device are legally protected through proper contracts and IP ownership agreements.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cranial Electro Stimulation (CES) Devices
This guide outlines key logistics and regulatory compliance considerations for Cranial Electro Stimulation (CES) devices, which are medical devices intended to treat conditions such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia through low-level electrical currents applied to the head. Compliance with international and regional regulations is critical for legal distribution and patient safety.
Regulatory Classification and Approval Pathways
CES devices are classified as medical devices and are subject to regulatory oversight in most markets. Classification typically ranges from Class II (moderate risk) to Class III (high risk), depending on the jurisdiction and specific device claims.
-
United States (FDA):
CES devices are regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under 21 CFR 882.5850. Most CES devices are classified as Class III devices and require Premarket Approval (PMA) unless they are legally marketed via a 510(k) clearance based on a predicate device. As of recent FDA reclassifications, certain CES devices may be eligible for Class II status with special controls, potentially allowing for 510(k) submission instead of PMA. Labeling must include indications for use, contraindications, warnings, and precautions. -
European Union (EU):
Under the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745, CES devices are generally classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on duration of use and risk profile. Compliance requires CE marking through a Notified Body, which involves a conformity assessment, technical documentation review, quality management system audit (ISO 13485), and clinical evaluation. Unique Device Identification (UDI) is mandatory. -
Canada (Health Canada):
CES devices are classified as Class II under the Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282). Licensing requires submission of a Medical Device License (MDL) application, including evidence of safety, effectiveness, and quality. Device registration in the Medical Devices Active Licensing Information Database (MDALID) is required. -
Other Markets (e.g., Australia, Japan, UK):
- Australia (TGA): Class IIa or IIb; inclusion in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) required.
- Japan (PMDA): Class II or III under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act (PMDA); requires certification via a Japanese regulatory certifier (RCB).
- UK (MHRA): Post-Brexit, CE marks are accepted until 2025; thereafter, UKCA marking will be required. Classification follows MDR guidelines.
Quality Management System (QMS) Requirements
Manufacturers must implement a QMS compliant with ISO 13485:2016. Key elements include:
- Document control and record keeping
- Design and development validation
- Risk management per ISO 14971
- Supplier and subcontractor oversight
- Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA)
- Internal audits and management review
Regular audits and ongoing compliance monitoring are essential for maintaining certification and regulatory approval.
Technical Documentation and Clinical Evidence
Regulatory submissions require comprehensive technical documentation, including:
- Device description and specifications
- Risk analysis and mitigation (ISO 14971)
- Design validation and verification reports
- Biocompatibility testing (ISO 10993)
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and electrical safety (IEC 60601-1) testing
- Software validation (if applicable, per IEC 62304)
- Sterilization validation (if applicable)
- Labeling and Instructions for Use (IFU)
- Clinical evaluation report (CER) or clinical trial data
For higher-risk classifications, clinical data from controlled trials may be required to demonstrate safety and effectiveness.
Labeling and Unique Device Identification (UDI)
Labeling must comply with regional requirements and include:
- Device name and model number
- Manufacturer name and address
- Intended use and indications
- Contraindications, warnings, and precautions
- Lot number and expiration date (if applicable)
- UDI carrier (e.g., barcode or Data Matrix)
- Regulatory status (e.g., “Rx Only,” “CE Marked,” “Licensed by Health Canada”)
UDI implementation is required in the U.S. (FDA), EU (MDR), Canada, and other major markets to support traceability and post-market surveillance.
Supply Chain and Logistics Considerations
- Import/Export Controls: Ensure compliance with export regulations (e.g., U.S. Commerce Department, EU dual-use regulations) and import requirements (e.g., import licenses, customs documentation).
- Storage and Distribution: Maintain appropriate storage conditions (temperature, humidity) per device specifications. Use validated shipping methods to prevent damage.
- Cold Chain (if applicable): Not typically required for CES devices unless accessories (e.g., conductive gels) are temperature-sensitive.
- Serialization and Traceability: Implement systems to track devices from manufacturing to end-user, especially for UDI compliance and recall readiness.
- Supplier Qualification: Audit and qualify all suppliers of critical components (e.g., electrodes, cables, power sources) to ensure quality and regulatory compliance.
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance Reporting
Post-market obligations include:
- Establishing a post-market surveillance (PMS) plan per MDR or FDA requirements
- Monitoring adverse events and malfunctions
- Submitting mandatory reports to regulatory authorities (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED, Canada’s MDR)
- Conducting periodic safety update reports (PSURs) for higher-risk devices
- Managing field safety corrective actions (FSCAs), including recalls or safety alerts
A robust complaint handling system and trending analysis are essential for early risk detection.
Cybersecurity and Software Considerations
If the CES device includes software (e.g., mobile app, embedded firmware), compliance with cybersecurity standards is required:
- Follow FDA guidance on cybersecurity for medical devices
- Apply IEC 81001-5-1 for health software security
- Conduct vulnerability testing and patch management planning
- Ensure secure data transmission and storage (if patient data is involved)
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the logistics and compliance landscape for Cranial Electro Stimulation devices requires a proactive, multidisciplinary approach. Manufacturers must adhere to evolving regulatory standards, maintain rigorous quality systems, ensure transparent labeling, and remain vigilant in post-market surveillance. Early engagement with regulatory consultants and Notified Bodies is strongly recommended to streamline approvals and ensure global market access.
Conclusion:
After a thorough evaluation of the market for cranial electrostimulation (CES) devices, it is evident that sourcing a reliable, safe, and effective device requires careful consideration of regulatory compliance, clinical evidence, manufacturer reputation, and intended use. Devices cleared by recognized regulatory bodies such as the FDA or CE-marked demonstrate a higher standard of safety and efficacy, particularly for conditions like anxiety, depression, and insomnia.
Key factors in the sourcing decision include the availability of clinical research supporting the technology, ease of use, device portability, customer support, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, ensuring that the supplier provides proper training, documentation, and post-purchase support is essential for successful implementation.
Based on the analysis, it is recommended to source CES devices from established manufacturers with a proven track record, strong regulatory standing, and transparent reporting of clinical outcomes. Prioritizing quality and compliance over cost alone will ensure long-term effectiveness, user safety, and adherence to medical and ethical standards. Ultimately, integrating a well-vetted cranial electrostimulation device into practice or personal use can offer a non-invasive, well-tolerated option for enhancing mental health and cognitive performance.