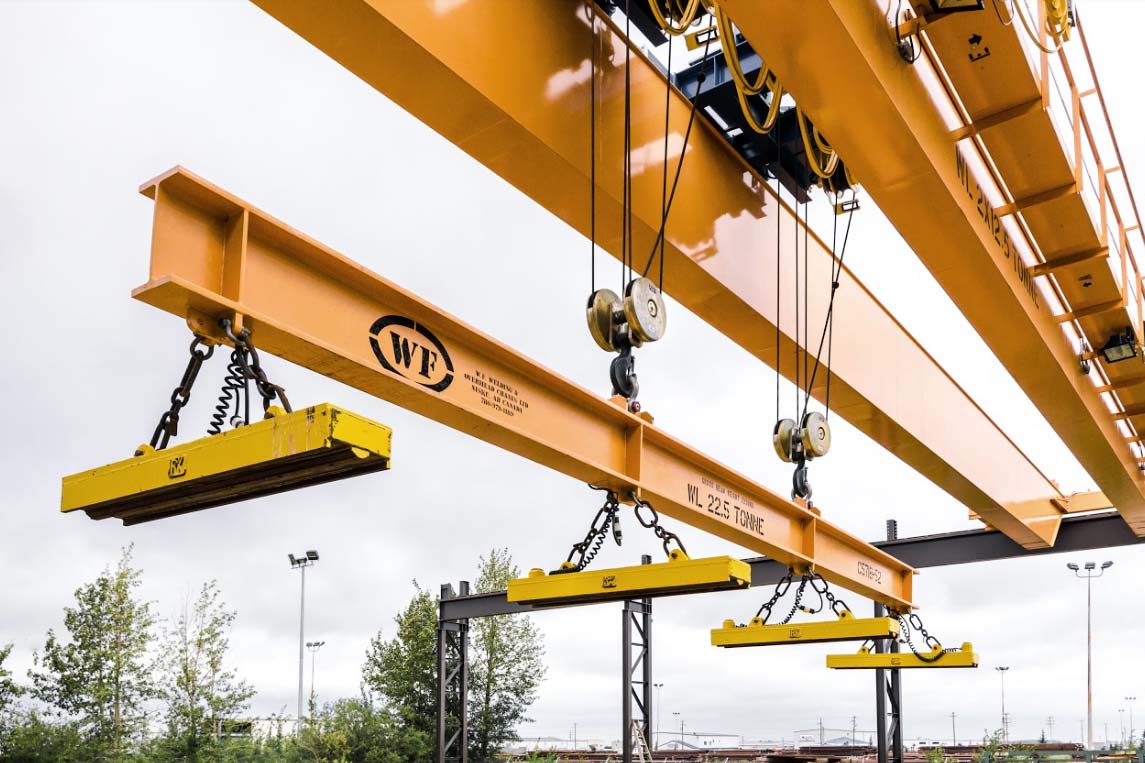
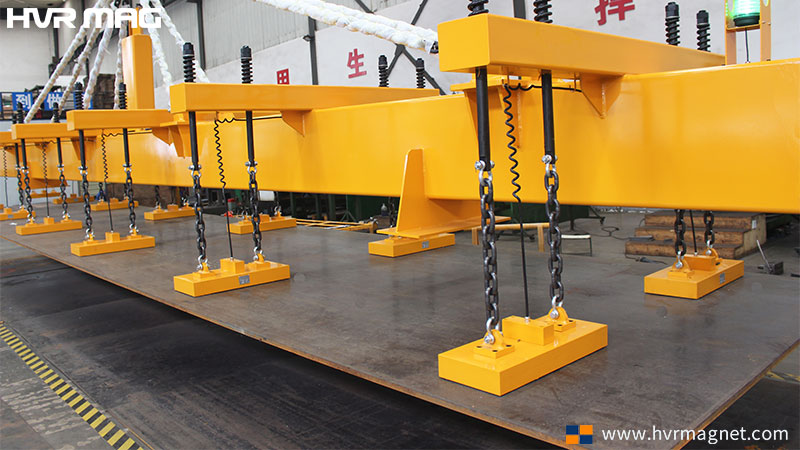
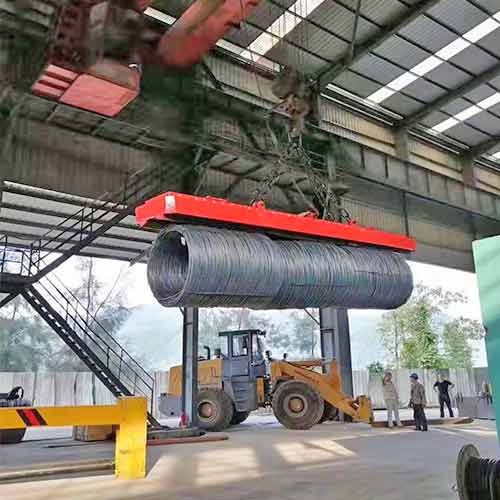
The global crane magnet market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions across heavy industries such as scrap recycling, steel manufacturing, and port logistics. According to Mordor Intelligence, the Industrial Magnets Market — a key segment encompassing crane magnets — is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global lifting magnet market size was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by automation trends and rising industrial output. With innovation in electromagnetic technology and improved safety standards, the demand for high-performance crane magnets is on an upward trajectory. As a result, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in delivering durable, energy-efficient, and intelligent magnetic lifting solutions. Below are the top 10 crane magnet manufacturers shaping the future of industrial material handling.
Top 10 Crane Magnet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Magnetics, Inc.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: magnetics.com
Key Highlights: We design, engineer, and manufacture magnetic solutions to help improve productivity, purify products, protect processing equipment, increase profits….
#2 Walker Magnetics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: walkermagnet.com
Key Highlights: We design and manufacture a wide range of permanent, electromagnetic, electro-permanent magnet products and systems for industrial applications….
#3 Cranes, hoists and drives
Domain Est. 1998
Website: demagcranes.com
Key Highlights: Powerful reliable light crane systems, crane components, hoists and drives are our core competence. As one of the world’s leading manufacturers, we have been ……
#4 Magnets
Domain Est. 2008
Website: crane1.com
Key Highlights: MLTUS, a CRANE 1 Services company, is your one-stop shop for all of your industrial lifting magnet inspections, services and repairs….
#5 Industrial Magnetics Lifting Magnets
Domain Est. 2009
Website: hhilifting.com
Key Highlights: 2–5 day delivery 10-day returnsHolloway Houston provides a selection of industrial lifting magnets designed to assist with material handling tasks across different industries….
#6 Magnet Crane Manufacturers and Suppliers
Domain Est. 2017
Website: chinacranemanufacturer.com
Key Highlights: Kino Cranes is one of the world’s largest magnet crane manufacturers and suppliers in China … Official Website: www.kinocranes.com. Copyright © Henan Kino ……
#7 Magnetek
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cmco.com
Key Highlights: Magnetek specializes in the development & manufacturing of digital power & motion control systems for material handling, people-moving & mining ……
#8 Electro Magnets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: evertz-group.com
Key Highlights: Our magnets run across the complete range of round and rectangular lifting magnets for light, normal and heavy design to special one-off designs….
#9 Our magnetic lifting products
Domain Est. 2008
Website: sgmmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: SGM Magnetics designs and manufactures control panels for all its lifting magnet solutions, ensuring compliance with the latest regulations and industry ……
#10 Magnet Cranes
Domain Est. 2017
Website: wfsteelandcrane.com
Key Highlights: WF Steel & Crane offers a range of magnet cranes, customized to suit client application, with a range of magnets to lift flats, radius sections, beam sections ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Crane Magnet

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Crane Magnet
As we move into the second half of 2026, Crane Magnet—presumably a manufacturer or supplier of magnetic lifting, separation, or industrial magnetic solutions—operates within a dynamic industrial landscape shaped by technological advancements, evolving regulatory standards, and shifting global demand. The following analysis outlines key market trends influencing Crane Magnet’s business environment during H2 2026:
1. Growth in Renewable Energy and Electrification
The rapid expansion of renewable energy infrastructure—particularly offshore wind farms, solar power installations, and high-voltage transmission systems—continues to drive demand for heavy-duty lifting and material handling equipment. Crane Magnet’s electromagnetic lifting systems are increasingly being integrated into wind turbine assembly and maintenance operations. The surge in electric vehicle (EV) production also boosts demand for magnetic separators and lifting equipment in battery recycling and rare earth material processing.
Implication: Crane Magnet should focus on developing lightweight, energy-efficient electromagnets tailored for clean energy applications and circular economy processes.
2. Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Manufacturing facilities are increasingly adopting Industry 4.0 principles, emphasizing connectivity, predictive maintenance, and automation. Magnetic lifting systems are being upgraded with IoT-enabled sensors, real-time load monitoring, and remote diagnostics.
Implication: Crane Magnet can differentiate itself by offering “smart magnets” with integrated digital controls and compatibility with industrial automation platforms (e.g., Siemens MindSphere, Rockwell Automation). Partnerships with automation integrators will enhance market positioning.
3. Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Global environmental regulations, particularly in the EU and North America, are pushing industries to reduce energy consumption and improve material recovery. Magnetic separation technologies play a vital role in recycling operations (e.g., ferrous metal recovery from e-waste, construction debris). Stricter emissions standards are also prompting steel mills and foundries to optimize scrap handling, increasing reliance on efficient magnetic lifting systems.
Implication: Crane Magnet should emphasize energy-efficient designs (e.g., permanent-electro hybrid magnets) and promote compliance benefits in marketing and sales outreach. ESG reporting on product lifecycle and recyclability will enhance brand credibility.
4. Reshoring and Supply Chain Reconfiguration
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have accelerated reshoring initiatives in North America and Europe. As manufacturing returns to these regions, there is increased investment in industrial infrastructure, including cranes, hoists, and material handling systems.
Implication: Crane Magnet is well-positioned to serve domestic manufacturers upgrading facilities. Localized service networks and faster delivery timelines will be competitive advantages.
5. Advancements in Rare Earth and Permanent Magnet Technologies
Innovations in neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) and other rare earth magnets are enabling stronger, more compact lifting and separation systems. Alternative materials and magnet recycling methods are reducing dependency on imported rare earth elements, lowering costs and supply risk.
Implication: R&D investments in next-generation permanent magnets and partnerships with material science firms can open new product lines and reduce production costs.
6. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The industrial magnet sector is experiencing consolidation, with larger players acquiring niche innovators. Crane Magnet faces competition from global brands (e.g., Walker Magnetics, Eriez, Gauss) as well as emerging Asian manufacturers offering lower-cost alternatives.
Implication: Differentiation through innovation, quality, and service will be critical. Strategic M&A or partnerships could enhance capabilities and market reach.
Conclusion:
In H2 2026, Crane Magnet operates in a favorable but competitive environment marked by strong demand from sustainable industries, digital transformation, and regional manufacturing growth. To capitalize on these trends, Crane Magnet should prioritize innovation in smart, energy-efficient magnetic systems, expand into clean tech and recycling markets, and strengthen its digital and service offerings. By aligning with global sustainability goals and industrial modernization, Crane Magnet can solidify its position as a leader in advanced magnetic solutions.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Crane Magnets (Quality, IP)
Sourcing crane magnets involves significant risks if due diligence is not performed, particularly concerning quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, legal disputes, and long-term cost overruns. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Quality Control and Substandard Materials
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing crane magnets—especially from low-cost suppliers—is inconsistent or inadequate quality control. Many manufacturers cut corners by using inferior materials such as low-grade steel, subpar insulation, or undersized copper windings. This compromises the magnet’s lifting capacity, durability, and thermal performance, increasing the risk of coil burnout or mechanical failure. Without proper testing (e.g., load testing, insulation resistance checks, or thermal cycling), buyers may receive magnets that fail prematurely under real-world conditions.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
Crane magnets used in industrial environments must meet strict safety and performance standards such as ISO, CE, or OSHA regulations. A common pitfall is sourcing magnets without valid third-party certifications. Non-compliant magnets may not have undergone proper safety testing, posing serious risks in lifting operations. Additionally, using uncertified equipment can void insurance coverage and expose the buyer to liability in the event of an accident.
Inadequate Thermal Management Design
Overheating is a leading cause of crane magnet failure. Some suppliers provide magnets with poor thermal design, such as insufficient cooling fins or inadequate duty cycle specifications. Without proper heat dissipation, the coil insulation degrades rapidly, leading to short circuits or complete magnet failure. Buyers often overlook thermal performance data, assuming all magnets with the same lifting capacity are equivalent, which is not the case.
Misrepresentation of Lifting Capacity and Performance
Suppliers may exaggerate lifting capacity under ideal conditions (e.g., clean, flat steel surfaces) without clarifying real-world performance. In practice, factors like surface rust, paint, or uneven materials drastically reduce effective lifting power. Failure to account for these variables can result in dropped loads and safety incidents. Always verify performance data with realistic test conditions and request detailed de-rating curves.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing crane magnets from unverified suppliers, particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement, can expose buyers to intellectual property violations. Some manufacturers replicate patented designs, coil configurations, or control systems without authorization. If these infringing products are imported or used, the end-user may face legal action, customs seizures, or reputational damage. Always conduct supplier audits and request proof of IP ownership or licensing.
Incomplete or Inaccurate Documentation
Lack of comprehensive technical documentation—including electrical schematics, maintenance manuals, and material certifications—hinders installation, troubleshooting, and compliance. Poor documentation is often a red flag for overall product quality and can delay commissioning or violate regulatory requirements.
Hidden Costs from Poor Reliability
While some crane magnets appear cost-effective upfront, frequent breakdowns, high maintenance, and short lifespans lead to significant hidden costs. Downtime in material handling operations can be extremely expensive. Prioritizing initial price over proven reliability and service support results in higher total cost of ownership.
Failure to Verify Supplier Authenticity
Counterfeit or “white label” suppliers may rebrand generic magnets without the engineering expertise or quality systems of reputable manufacturers. Without on-site audits or references, buyers risk working with intermediaries who lack accountability. Always verify the actual manufacturer and conduct factory assessments when possible.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, insistence on certifications, clear performance specifications, and attention to both technical and legal details. Investing time upfront ensures safe, reliable, and legally compliant crane magnet operations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Crane Magnet
Crane magnets are powerful industrial lifting devices used primarily in scrap yards, steel mills, and recycling centers. Due to their specialized nature, transporting and operating crane magnets requires strict adherence to logistics and regulatory compliance standards to ensure safety, efficiency, and legal conformity. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, shipping, documentation, and regulatory compliance related to crane magnets.
Transportation & Handling
Proper transportation and handling are critical for crane magnets due to their weight, magnetic properties, and potential safety risks.
-
Secure Packaging and Crating: Always transport crane magnets in sturdy, custom-fitted crates that prevent movement during transit. Use non-magnetic materials for internal bracing to avoid unintended magnetic attraction to packaging components.
-
Magnetic Shielding: When not in use, deactivate or shield the magnet’s magnetic field during transport. For electromagnets, ensure power is disconnected and residual magnetism is minimized. Permanent magnets should be stored with magnetic keepers or shielding plates to prevent accidental attraction to ferrous materials.
-
Load Securing: Secure crane magnets to transport vehicles using heavy-duty chains, straps, or specialized fixtures. Ensure the load is balanced and complies with weight distribution regulations for trucks, railcars, or shipping containers.
-
Hazardous Material Considerations: While crane magnets are not classified as hazardous materials per se, their strong magnetic fields can interfere with navigation and communication equipment. Label shipments with “Strong Magnetic Field” warnings in accordance with IATA/IMDG regulations if air or sea freight is used.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to international, national, and local regulations is essential when shipping and operating crane magnets.
-
International Air Transport Association (IATA): For air freight, crane magnets must undergo magnetic field strength testing. If the magnetic field exceeds 0.00525 gauss at 15 feet (4.6 meters), the shipment is classified as a “Magnetized Material” (UN2807) and requires special documentation, labeling, and packaging.
-
International Maritime Organization (IMO) / IMDG Code: For ocean freight, magnets are subject to IMDG classification. Testing must confirm field strength, and packages must display the “Magnetized Material” label along with proper shipping name and UN number.
-
Department of Transportation (DOT) – USA: Comply with 49 CFR regulations for domestic ground transport. Strong magnets may require placarding and documentation if they meet hazardous material criteria based on magnetic field strength.
-
CE Marking & EU Machinery Directive: For sale or operation within the European Union, crane magnets must meet the requirements of the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), including safety, electrical, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
-
OSHA and Local Safety Regulations: Operators must comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.179 (Overhead and Gantry Cranes) and other local workplace safety standards. This includes operator training, routine inspections, and safe operating procedures.
Documentation Requirements
Accurate and complete documentation ensures smooth customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
-
Technical Specifications Sheet: Include details such as model number, lifting capacity, weight, dimensions, voltage, and magnetic field strength.
-
Test Reports: Provide recent magnetic field test reports from an accredited lab, especially for air or sea shipments.
-
Safety Data Sheet (SDS): While not always required, an SDS can be prepared to outline handling, storage, and emergency procedures.
-
Commercial Invoice and Packing List: Clearly describe the item as “Industrial Crane Magnet” and specify if it’s an electromagnet or permanent magnet.
-
Certificate of Conformity (CoC): Required for exports to certain regions (e.g., CE, GOST, or KC Mark), confirming compliance with regional safety and technical standards.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Once delivered, proper installation and operation are vital for safety and regulatory adherence.
-
Qualified Personnel: Installation and maintenance should only be performed by trained and certified technicians familiar with electrical and mechanical systems.
-
Electrical Compliance: Electromagnetic crane magnets must be connected to properly grounded power sources that meet local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC in Europe).
-
Routine Inspections: Implement a maintenance schedule that includes visual checks, cable integrity testing, and performance verification to comply with safety standards.
-
Operator Training: All crane and magnet operators must be trained in safe lifting practices, emergency shutdown procedures, and hazard awareness (e.g., flying debris, pinch points).
Environmental and End-of-Life Considerations
-
Recycling and Disposal: Crane magnets, especially those containing rare-earth materials or copper windings, should be recycled through certified e-waste or metal recycling facilities.
-
Environmental Regulations: Comply with local and international environmental laws (e.g., RoHS, WEEE) regarding hazardous substances in electrical components.
By following this logistics and compliance guide, businesses can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient handling of crane magnets throughout their lifecycle—from shipment and installation to operation and disposal.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Crane Magnet:
Sourcing a crane magnet requires a thorough evaluation of operational needs, material handling requirements, and technical specifications. It is essential to select a magnet that matches the lifting capacity, duty cycle, and type of material (e.g., scrap steel, billets, plates) to ensure safety, efficiency, and longevity. Key factors such as electromagnetic vs. permanent magnet type, power supply availability, environmental conditions, and compliance with safety standards must be carefully considered.
Partnering with reputable suppliers who offer quality certifications, technical support, spare parts, and after-sales service is crucial for reliable performance and minimal downtime. Additionally, conducting a cost-benefit analysis—including initial investment, maintenance, and energy consumption—helps in making a cost-effective decision.
In conclusion, a well-researched and strategic sourcing approach to crane magnets enhances operational productivity, ensures workplace safety, and contributes to long-term cost savings in material handling operations.