The global demand for precision in cash handling and coin processing has driven significant growth in the counting machine market, with businesses across banking, retail, and logistics increasingly adopting automated solutions to enhance efficiency and reduce errors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the Automatic Counting Machines Market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by rising cash transaction volumes in emerging economies, stringent anti-counterfeit measures, and the integration of smart technologies such as AI and IoT in modern counting systems. As operational accuracy becomes a priority, manufacturers are focusing on innovation, durability, and compliance with global standards. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top players who combine technological advancement with market reach is crucial for businesses seeking reliable, high-performance solutions. Here, we examine the top 10 counting machine manufacturers leading the charge in this growing industry.
Top 10 Counting Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ChemoMetec
Domain Est. 2000
Website: chemometec.com
Key Highlights: ChemoMetec is a worldwide leading manufacturer of automated cell counters and analysis equipment. Born in Scandinavia, operating globally….
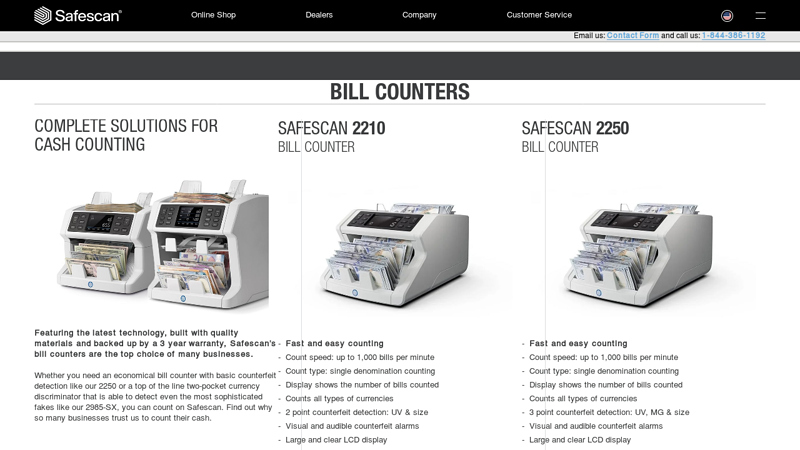
#2 Bill Counters
Domain Est. 2001
Website: safescan.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsCOMPLETE SOLUTIONS FOR CASH COUNTING. Featuring the latest technology, built with quality materials and backed up by a 3 year warranty, Safescan’s bill …
#3 Insight Sign Up
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tellermate.com
Key Highlights: Tellermate are known worldwide for our Money Counting Machines and intelligent cash drawers. We’re people you can count on….
#4 Cashmaster: Cash Management
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cashmaster.com
Key Highlights: Discover accurate, easy-to-use cash counting machines and expert cash management solutions designed to save time, reduce errors, and boost efficiency….
#5 Cummins Allison Money Counters, Coin Sorters, Currency Scanners
Domain Est. 1996
Website: prod.cumminsallison.com
Key Highlights: Cummins Allison is a leading innovator of technologies and equipment for counting coins, counting money, sorting money, sorting coins, imaging checks, ……
#6 vacuumatic.global: Vacuumatic
Domain Est. 1997
Website: vacuumatic.com
Key Highlights: We supply state of the art paper, card and bank note counting, batch marking and tabbing machines to the security and commercial print sectors….
#7 Semacon Currency Counter and Coin Counter Money Handling …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: semacon.com
Key Highlights: Every Semacon machine undergoes extensive burn-in, rigorous quality assurance testing and precision calibration at our US manufacturing facility….
#8 Banknote processing systems: reliable and efficient
Domain Est. 2000
Website: gi-de.com
Key Highlights: G+D offers scalable solutions for cash centers of any size, for reliable and efficient banknote processing. High-precision sensor technologies form the core of ……
#9 Note Counters & Sorters
Domain Est. 2010
Website: glory-global.com
Key Highlights: Achieving a counting speed of 1,800 notes per minute, the GFB-830 is an advanced and configurable banknote counter delivering exceptional speed and efficiency….
#10 Julong
Domain Est. 2020
Website: julong-global.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture powerful machines and offer responsive solutions for smoother transactions and cash processing. Work with us today!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Counting Machine

2026 Market Trends for Counting Machines
The global counting machine market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industry needs, and growing demands for efficiency and accuracy. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
H2: Integration of Advanced Automation and AI
Counting machines are increasingly incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance functionality. By 2026, AI-powered systems will be standard in high-end models, enabling features such as real-time anomaly detection, predictive maintenance, and adaptive learning for handling irregular or damaged items. Automated decision-making will reduce human intervention, improving throughput in industries like pharmaceuticals, banking, and manufacturing.
H2: Rising Demand in E-Commerce and Logistics
The explosive growth of e-commerce continues to drive demand for high-speed, accurate counting solutions in warehousing and fulfillment centers. By 2026, compact, scalable counting machines capable of integrating with warehouse management systems (WMS) will be in high demand. These machines will support rapid inventory turnover, reduce errors in order fulfillment, and streamline returns processing.
H2: Emphasis on Hygiene and Contactless Operation
Post-pandemic hygiene standards are influencing design, especially in food, pharmaceutical, and healthcare sectors. Counting machines with touchless interfaces, antimicrobial surfaces, and easy-to-clean components will gain traction. In 2026, expect to see more models featuring voice control, motion sensors, and remote monitoring to minimize physical contact.
H2: Expansion of IoT and Cloud Connectivity
Internet of Things (IoT) integration will allow counting machines to transmit data in real time to cloud platforms for analytics and reporting. By 2026, manufacturers will offer cloud-based dashboards that track machine performance, count accuracy, and maintenance alerts. This connectivity supports Industry 4.0 initiatives and enables centralized management across multiple facilities.
H2: Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental concerns are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient counting machines with reduced carbon footprints. By 2026, regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals will favor machines built with recyclable materials and low-power components. Energy-saving modes and longer operational lifespans will be key selling points.
H2: Customization for Niche Applications
As industries diversify, there is growing demand for specialized counting machines tailored to specific products—such as irregular tablets, small electronics, or agricultural seeds. By 2026, modular and reconfigurable designs will allow businesses to adapt machines for multiple use cases, improving ROI and reducing the need for multiple devices.
H2: Competitive Pricing and Market Expansion in Emerging Economies
With manufacturing costs decreasing and local production rising, especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, counting machines will become more affordable. By 2026, emerging markets will see increased adoption in SMEs and retail sectors, driven by digitization and government support for automation.
In summary, the 2026 counting machine market will be defined by smarter, faster, and more connected solutions that cater to evolving industrial demands while prioritizing hygiene, sustainability, and cost-efficiency.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Counting Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing counting machines—especially from overseas suppliers—can present significant challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these issues can lead to financial losses, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to watch for in both areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Many suppliers, particularly in low-cost regions, may not adhere to internationally recognized quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001). This can result in inconsistent build quality, inaccurate counting mechanisms, or frequent mechanical failures. Always verify certifications and conduct third-party quality audits.
2. Use of Substandard Components
To cut costs, some manufacturers use inferior materials or outdated electronics, leading to reduced durability and reliability. Request detailed component lists and perform sample testing under real-world conditions before placing bulk orders.
3. Lack of Calibration and Testing Documentation
Counting machines require precise calibration. Suppliers may skip or falsify testing reports, resulting in machines that underperform. Insist on factory acceptance tests (FAT) with verifiable documentation and consider on-site inspections.
4. Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Poor supplier support can render machines unusable when maintenance is needed. Confirm the availability of spare parts, technical documentation, and responsive customer service before signing contracts.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Risk of IP Infringement
Sourcing from suppliers with weak IP compliance can expose your business to legal liability. Machines may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., sensor designs, software algorithms) without proper licensing. Conduct due diligence to ensure the product does not infringe on third-party IP.
2. Lack of IP Ownership Clarity
If you customize the machine design or software, unclear contracts may leave ownership ambiguous. Always define IP rights in writing, specifying that custom developments are assigned to your company.
3. Supplier Copying or Reselling Your Design
Once a supplier has your specifications or prototypes, they may replicate and sell the machine to your competitors. Use strong non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and consider working with trusted partners under controlled IP frameworks.
4. Weak Enforcement in Certain Jurisdictions
Even with contracts in place, enforcing IP rights can be difficult in countries with underdeveloped legal systems. Choose suppliers in jurisdictions with stronger IP protections or use escrow arrangements for design files.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier vetting, use independent quality inspections, consult IP legal counsel, and include clear terms in procurement contracts. Proactive risk management ensures reliable performance and protects your business interests.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Counting Machine
Proper handling, transportation, import/export, and regulatory compliance are essential when shipping or operating a counting machine. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure smooth logistics and adherence to applicable regulations.
Product Classification and Documentation
Accurate classification and documentation are critical for customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
- HS Code Classification: Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the counting machine (e.g., 9031.49 for electronic counting or sorting equipment). This determines import duties and regulatory requirements in the destination country.
- Commercial Invoice: Include detailed product description, value, quantity, HS code, country of origin, and terms of sale (e.g., EXW, FOB, DDP).
- Packing List: Provide a comprehensive list of contents, weights, dimensions, and serial numbers (if applicable) for each package.
- Certificate of Origin: Required by some countries to determine tariff eligibility; may qualify for preferential treatment under trade agreements.
- Technical Specifications Sheet: Include voltage, power requirements, materials used, and compliance certifications to support customs and safety evaluations.
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Secure packaging ensures the counting machine arrives undamaged and meets carrier standards.
- Protective Packaging: Use anti-static materials, foam inserts, and sturdy corrugated boxes to protect sensitive electronic components and mechanical parts.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with handling instructions (“Fragile,” “This Side Up”), model and serial number, and shipping address. Include barcodes or RFID tags if required.
- Weight and Dimensions: Confirm compliance with carrier size and weight limits to avoid additional fees or shipment rejection.
- Shipping Method: Choose appropriate transport (air, sea, or ground) based on urgency, cost, and destination. Air freight is recommended for time-sensitive or high-value units.
Import and Export Compliance
Ensure all international trade regulations are followed to prevent delays or penalties.
- Export Controls: Verify if the counting machine is subject to export restrictions (e.g., under EAR or ITAR in the U.S.), especially if it includes advanced sensors or encryption.
- Import Licenses: Check if the destination country requires an import license or special permit for electronic or industrial equipment.
- Duties and Taxes: Calculate applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on declared value and HS code. Use Incoterms to clarify responsibility.
- Customs Broker: Engage a licensed customs broker in the destination country to facilitate clearance and manage documentation.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Meet regional safety and environmental standards to legally operate the machine.
- Electrical Safety: Ensure compliance with IEC, UL, CE, or other regional standards for electrical equipment (e.g., CE marking for EU, FCC for U.S.).
- EMC Compliance: Confirm electromagnetic compatibility to avoid interference with other devices (required under EU EMC Directive, FCC Part 15).
- RoHS and REACH: Comply with restrictions on hazardous substances (RoHS) and chemical registration (REACH) in applicable markets.
- WEEE Compliance: In the EU and other regions, provide information on proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Follow guidelines to ensure safe and legal operation upon delivery.
- Voltage Compatibility: Verify that the machine operates at the local voltage and frequency (e.g., 110V/60Hz in North America, 230V/50Hz in Europe). Use a transformer if necessary.
- Site Readiness: Ensure the installation site meets environmental requirements (temperature, humidity, dust levels) and has adequate power supply.
- User Training and Manuals: Provide operation and safety manuals in the local language. Include maintenance schedules and compliance declarations.
- Regulatory Registration: In some industries (e.g., banking, pharmaceuticals), counting machines may require registration or certification by a national standards body.
Maintenance and Servicing Logistics
Plan for ongoing support and compliance throughout the machine’s lifecycle.
- Spare Parts Supply Chain: Maintain inventory of critical components and ensure availability in the region.
- Service Technician Access: Confirm that service personnel are trained and authorized, especially for warranty or regulated environments.
- Recall and Compliance Updates: Monitor for regulatory changes or product recalls and communicate updates to customers promptly.
By following this guide, businesses can ensure the efficient, compliant, and safe global movement and operation of counting machines. Always consult local authorities or legal experts for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Counting Machine:
After thorough evaluation of market options, technical specifications, and operational requirements, sourcing a counting machine proves to be a strategic investment that enhances efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in inventory and cash management processes. The selected counting machine offers advanced features such as high-speed counting, error detection, compatibility with various item types (coins, bills, or small parts), and integration capabilities with existing software systems.
Additionally, considerations such as reliability, ease of use, maintenance support, and total cost of ownership were key factors in the decision-making process. By implementing the chosen counting machine, the organization can minimize human errors, reduce processing time, and improve overall operational transparency.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate counting machine aligns with organizational goals of automation and accuracy, delivering both short-term gains and long-term value. Future scalability and technological advancements should be monitored to ensure continued optimization of counting processes.