The global cotton fabric laminate market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for durable, versatile textiles in industries ranging from automotive and construction to apparel and healthcare. According to Grand View Research, the global technical textiles market — which includes laminated fabrics — was valued at USD 207.6 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. Cotton fabric laminates, known for their breathability, strength, and compatibility with performance coatings, are increasingly favored in applications requiring both comfort and enhanced functionality. Mordor Intelligence projects similar momentum, noting that innovation in sustainable and hybrid textile solutions is accelerating adoption across emerging economies. As demand for high-performance, eco-friendly materials rises, manufacturers specializing in cotton-based laminates are positioned at the forefront of this evolution — setting the stage for the top 10 companies leading the charge in quality, scale, and technological advancement.
Top 10 Cotton Fabric Laminate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 8681 Cotton Cloth
Domain Est. 1997
Website: formica.com
Key Highlights: A high gloss texture ideal for applications that require maximum smoothness and reflectance. Recommended for horizontal or vertical interior application.Missing: fabric manufactur…
#2 Fabric and Composite Material Solutions
Domain Est. 1995
Website: xamax.com
Key Highlights: Xamax has expanded globally by inventing, manufacturing and distributing material layers consisting of non-woven fabrics, thermoplastic laminates, technical ……
#3 Cotton fabric laminate SRBF Material
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tufnol.com
Key Highlights: A low-cost general-purpose cotton fabric laminate sheet grade for mechanical applications. Crow Brand Tufnol is a coarse weave grade of phenolic cotton sheet ……
#4 Laminated Sheet Final
Domain Est. 1996
Website: currentcomposites.com
Key Highlights: Our Laminated Sheets are made out of thermosetting resins including Phenolic, Melamine and Epoxy. We also manufacture Carbon Fiber Laminated Sheets….
#5 laminated fabric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: isovolta.com
Key Highlights: A thermosetting laminate based on cotton fabric sheets as a carrier material and modified phenol/formaldehyde resins as a binder….
#6 Laminated Fabrics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: textechindustries.com
Key Highlights: Tex Tech creates laminated fabrics using woven, non-woven, and knit textiles, with TPU, PVC, aluminized, PVDC and many other films….
#7 High-Quality Woven Fabrics
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1900
Website: hamrickmills.com
Key Highlights: Since 1900, Hamrick Mills has taken pride in producing high-quality woven fabrics in both poly/cotton blends as well as 100% cotton….
#8 Laminated Cotton – Fabric: Splash Fabric
Domain Est. 1999
Website: eeschenck.com
Key Highlights: Wash-n-wipe, family friendly, durable and long-lasting laminated fabric. Great for aprons, bags, tablecloths, cushion covers, kids and more!…
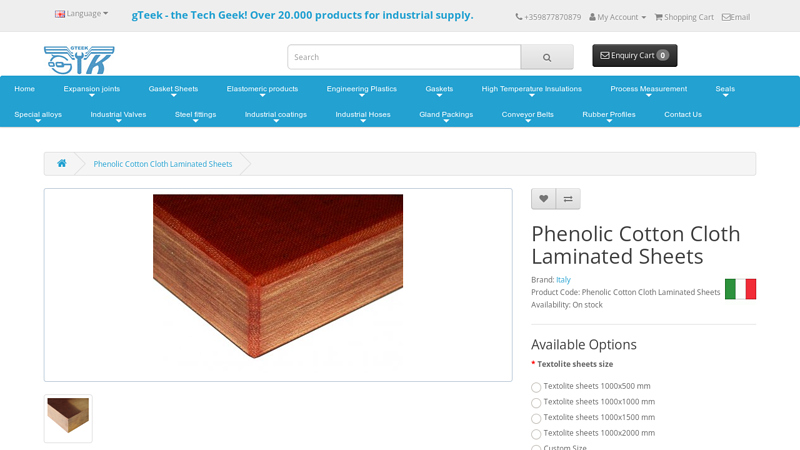
#9 Phenolic Cotton Cloth Laminated Sheets
Domain Est. 2017
Website: gteek.com
Key Highlights: Phenolic Cotton Cloth Laminated Sheets is a laminated material made by hot pressing of cotton cloths impregnated with a thermosetting phenol-formaldehyde-based ……
#10 Laminated Fabric Shop
Domain Est. 2023
Website: laminatedfabricshop.com
Key Highlights: We carry over 400 prints from Riley Blake, Robert Kaufman, Alexander Henry, and Westminster – you’ll be sure to find the perfect laminated fabric for your ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cotton Fabric Laminate

2026 Market Trends for Cotton Fabric Laminate
The global cotton fabric laminate market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability imperatives. This analysis examines key market dynamics, growth drivers, regional outlooks, and emerging applications shaping the industry landscape.
Rising Demand in Apparel and Performance Wear
Cotton fabric laminates are gaining traction in the apparel sector, particularly in activewear, outerwear, and technical garments. The integration of cotton with performance membranes (e.g., polyurethane or TPU) enhances moisture management, breathability, and durability while maintaining comfort. By 2026, the growing emphasis on functional fashion and athleisure is expected to boost demand, especially in North America and Europe. Innovations such as biodegradable laminating adhesives and lightweight composites are further expanding cotton laminate applications in sportswear and protective clothing.
Sustainability as a Key Growth Driver
Sustainability continues to be a dominant trend influencing the textile industry. Cotton, being a renewable and biodegradable fiber, aligns well with eco-conscious consumer values. In 2026, brands are increasingly adopting cotton fabric laminates made with recycled or organic cotton and eco-friendly lamination processes. Regulatory pressures and certifications such as GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) and OEKO-TEX are pushing manufacturers to adopt cleaner production methods. Water-based and solvent-free lamination technologies are expected to gain market share, reducing environmental impact.
Expansion in Technical and Industrial Applications
Beyond fashion, cotton fabric laminates are seeing increased use in technical textiles, including automotive interiors, medical textiles, and protective gear. The inherent softness and hypoallergenic properties of cotton make it suitable for healthcare applications, such as wound dressings and reusable medical gowns. In the automotive sector, laminated cotton fabrics are being used for seat covers and sound insulation due to their acoustic and thermal properties. These niche applications are projected to grow steadily by 2026, supported by R&D investments and material innovation.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific remains the largest producer and consumer of cotton fabric laminates, led by China, India, and Bangladesh. These countries benefit from established textile manufacturing infrastructure and access to raw cotton. However, increasing labor costs and environmental regulations are prompting a shift toward automation and sustainable practices. Meanwhile, North America and Western Europe are witnessing growth driven by premium and eco-labeled products. Emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Latin America are also expected to contribute to demand expansion due to rising disposable incomes and urbanization.
Technological Advancements and Smart Textiles
The integration of smart technologies into cotton laminates is an emerging frontier. By 2026, developments in conductive coatings and laminated sensor-embedded fabrics could enable applications in wearable health monitoring and responsive clothing. Research into antimicrobial, UV-protective, and self-cleaning cotton laminates is accelerating, opening new opportunities in high-performance and specialty textiles.
Challenges and Outlook
Despite positive trends, the market faces challenges such as fluctuating cotton prices, competition from synthetic alternatives, and supply chain disruptions. However, the long-term outlook remains favorable due to the irreplaceable comfort and environmental profile of cotton. By 2026, the global cotton fabric laminate market is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5–7%, with innovation and sustainability at the core of future competitiveness.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cotton Fabric Laminate (Quality, IP)
Sourcing cotton fabric laminate involves unique challenges, particularly concerning both material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to production delays, legal risks, reputational damage, and compromised product performance. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing cotton fabric laminate is receiving materials that fail to meet required quality standards. This often stems from inconsistent manufacturing processes or the use of substandard raw materials. Buyers may encounter variations in lamination adhesion, fabric weight, color fastness, or breathability, especially when sourcing from suppliers with inadequate quality control systems. Such inconsistencies can lead to product defects, high rejection rates, and increased costs during production.
Lack of Transparency in Material Composition and Sourcing
Many suppliers do not fully disclose the composition of the laminate layers—such as the type of adhesive, coating material (e.g., PU, PVC), or treatment chemicals used. This lack of transparency can result in non-compliance with environmental regulations (e.g., REACH, OEKO-TEX) or sustainability claims. Additionally, undisclosed synthetic layers can mislead buyers aiming for natural or biodegradable products, affecting brand integrity and customer trust.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Some suppliers provide limited or falsified test reports for critical performance metrics like tear strength, wash durability, water resistance, or pilling resistance. Relying solely on supplier-provided certifications without third-party verification can expose buyers to liability if the fabric fails in end-use applications. Ensuring access to up-to-date, independent lab reports is essential for quality assurance.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Cotton fabric laminates often incorporate patented lamination techniques, embossing patterns, or functional treatments (e.g., antimicrobial coatings). Sourcing from suppliers who use protected technologies without proper licensing exposes the buyer to IP infringement claims. This is especially critical when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement, where unauthorized replication of proprietary processes is common.
Unsecured Design and Pattern Ownership
If you provide custom designs, textures, or patterns for the laminate surface, failing to establish clear contractual ownership and usage rights can lead to misuse. Suppliers might replicate and sell your designs to competitors unless protected by a robust Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) and IP assignment clauses in the procurement contract.
Supply Chain Traceability Gaps
Without full traceability from cotton farm to finished laminate, brands risk exposure to unethical practices such as forced labor or environmentally harmful production. This is increasingly important for companies committed to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards. Lack of documentation or certification (e.g., GOTS, BCI) can undermine marketing claims and lead to consumer backlash.
Overlooking Long-Term Supplier Reliability
Choosing suppliers based solely on low cost or fast turnaround often leads to instability in supply and quality. Smaller or unproven laminators may lack the capacity for consistent large-volume production or fail to protect your IP adequately. Conducting due diligence on the supplier’s operational history, client base, and compliance records is essential to mitigate long-term risks.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—implementing rigorous quality audits, securing IP rights through legal agreements, and demanding full material transparency—buyers can ensure reliable, compliant, and innovative sourcing of cotton fabric laminate.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cotton Fabric Laminate
Overview
Cotton fabric laminate is a composite textile material consisting of cotton fabric bonded with another layer—commonly polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or another fabric—using heat, adhesives, or pressure. Due to its hybrid composition, the logistics and compliance considerations for cotton fabric laminate differ from those of pure cotton fabric. This guide outlines key aspects of transporting, storing, and ensuring regulatory compliance for this material.
Classification & Tariff Codes
Accurate product classification is essential for international shipping and customs clearance. Cotton fabric laminate is typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) based on the dominant material by weight or function.
- HS Code Examples:
- If cotton is the predominant component by weight: 5407.94 or 5516.41 (depending on weave, coating, and use).
- If synthetic coating (e.g., PU/PVC) dominates: 5903.20 or 5903.90 (impregnated, coated, covered, or laminated textile fabrics).
- Recommendation: Obtain a binding tariff classification from the destination country’s customs authority to avoid misdeclaration and delays.
International Shipping & Documentation
Transporting cotton fabric laminate internationally requires thorough documentation to ensure compliance and smooth customs processing.
- Required Documents:
- Commercial Invoice (itemizing material composition, weight, value)
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin (preferably Form A for GSP or regional agreements)
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheet (SDS), if applicable (e.g., with chemical adhesives)
- Special Considerations:
- Declare both cotton and synthetic components clearly to avoid customs scrutiny.
- Some countries require proof of sustainable or organic cotton sourcing if marketed as such (e.g., GOTS certification).
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with environmental, safety, and textile standards varies by region and end-use application.
- REACH (EU):
- Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., phthalates in PVC coatings, certain azo dyes) exceed allowable limits.
- Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) applies to chemical components used in lamination.
- RoHS (for electronic applications):
- If used in electronics or automotive interiors, ensure compliance with restrictions on hazardous substances.
- Proposition 65 (California, USA):
- Disclose if the laminate contains chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm (e.g., certain flame retardants).
- Textile Labeling Laws:
- U.S. (FTC): Fiber content must be accurately labeled (e.g., “60% Cotton, 40% Polyurethane Laminate”).
- EU (Textile Regulation (EU) No 1007/2011): Precise fiber composition labeling required.
Packaging & Storage
Proper handling preserves material quality during transit and warehousing.
- Packaging Requirements:
- Use moisture-resistant wrapping (e.g., polyethylene film) to prevent mildew.
- Roll packaging on sturdy cardboard cores; avoid folding to prevent creasing.
- Palletize securely and wrap with stretch film to prevent shifting.
- Storage Conditions:
- Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area.
- Ideal temperature: 15–25°C; relative humidity: 45–65%.
- Keep away from direct sunlight and heat sources to prevent adhesive degradation or discoloration.
Import Restrictions & Duties
Certain countries impose specific restrictions on laminated textiles.
- Quotas & Safeguards:
- Monitor for quotas on cotton textiles under agreements like the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) or Multi-Fiber Arrangement successors.
- Anti-Dumping Measures:
- Some regions may impose duties on laminated fabrics from specific countries if deemed unfairly priced.
- Eco-Labeling Requirements:
- EU Ecolabel or Oeko-Tex Standard 100 certification may be required for sustainable or baby product applications.
Sustainability & Traceability
Increasingly important for brand compliance and market access.
- Certifications to Consider:
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard): For organic cotton content.
- Oeko-Tex Standard 100: Ensures absence of harmful substances.
- ** bluesign®**: Focuses on sustainable and safe textile production.
- Supply Chain Transparency:
- Maintain documentation of raw material sourcing, lamination process, and chemical usage for audits.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of cotton fabric laminate requires attention to its dual-nature composition. Proper classification, accurate labeling, adherence to chemical regulations, and secure packaging are critical. Staying informed about evolving international standards and maintaining robust documentation will ensure smooth global trade operations and minimize compliance risks.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cotton Fabric Lamination:
Sourcing cotton fabric laminate requires a strategic approach that balances quality, sustainability, cost-efficiency, and reliability. Cotton, known for its breathability, comfort, and natural fiber content, becomes even more functional when laminated with films or membranes, enhancing properties such as water resistance, durability, and thermal insulation. When sourcing, it is essential to identify suppliers who not only offer consistent quality and technical specifications matching your product requirements but also adhere to ethical and environmental standards.
Key considerations include the lamination method (e.g., adhesive, flame, or thermal bonding), the type of laminate material (e.g., PU, TPU, or PTFE), and the end-use application—whether for apparel, outdoor gear, medical textiles, or industrial uses. Sustainability is increasingly important; therefore, prioritizing suppliers who offer eco-friendly lamination processes and certifications (such as OEKO-TEX®, GOTS, or bluesign®) can support responsible sourcing practices.
Additionally, building strong relationships with vetted manufacturers, conducting sample testing, and ensuring compliance with international regulations contribute to a successful supply chain. In conclusion, effective sourcing of cotton fabric laminate involves a comprehensive evaluation of technical, environmental, and commercial factors to ensure performance, durability, and alignment with brand values in the final product.