The global electron microscope market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for advanced imaging in life sciences, materials research, and semiconductor industries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 4.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% through 2029, fueled by technological advancements and rising R&D investments. As demand escalates, cost remains a critical factor for institutions and manufacturers alike. With prices ranging from hundreds of thousands to several million dollars depending on type and application, understanding the cost structures of leading manufacturers becomes essential for procurement strategy and budget planning. This analysis examines the top nine electron microscope manufacturers—evaluating not just their pricing models but also their value propositions in a competitive, rapidly expanding market.
Top 9 Cost Of Electron Microscope Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Microscope Products
Domain Est. 1993
Website: microscope.healthcare.nikon.com
Key Highlights: Nikon microscope products, including objective lenses, cameras, confocal, multiphoton, super-resolution, and OEM….
#2 Transmission Electron Microscope
Domain Est. 2005
Website: jeolusa.com
Key Highlights: The JEM-2100 Plus Transmission Electron Microscope is a multipurpose 200kV LaB6 TEM that provides solutions for a range of applications. Learn more here….
#3 Scanning Electron Microscopes
Domain Est. 2006
Website: thermofisher.com
Key Highlights: Thermo Scientific floor model scanning electron microscopes offer the flexibility and versatility to meet a wide range of academic and industrial needs….
#4 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Domain Est. 1992
Website: jeol.com
Key Highlights: JEOL can offer a wide range of lineups from general purpose scanning electron microscopes(W-SEM) including a benchtop type that allows operations just to anyone ……
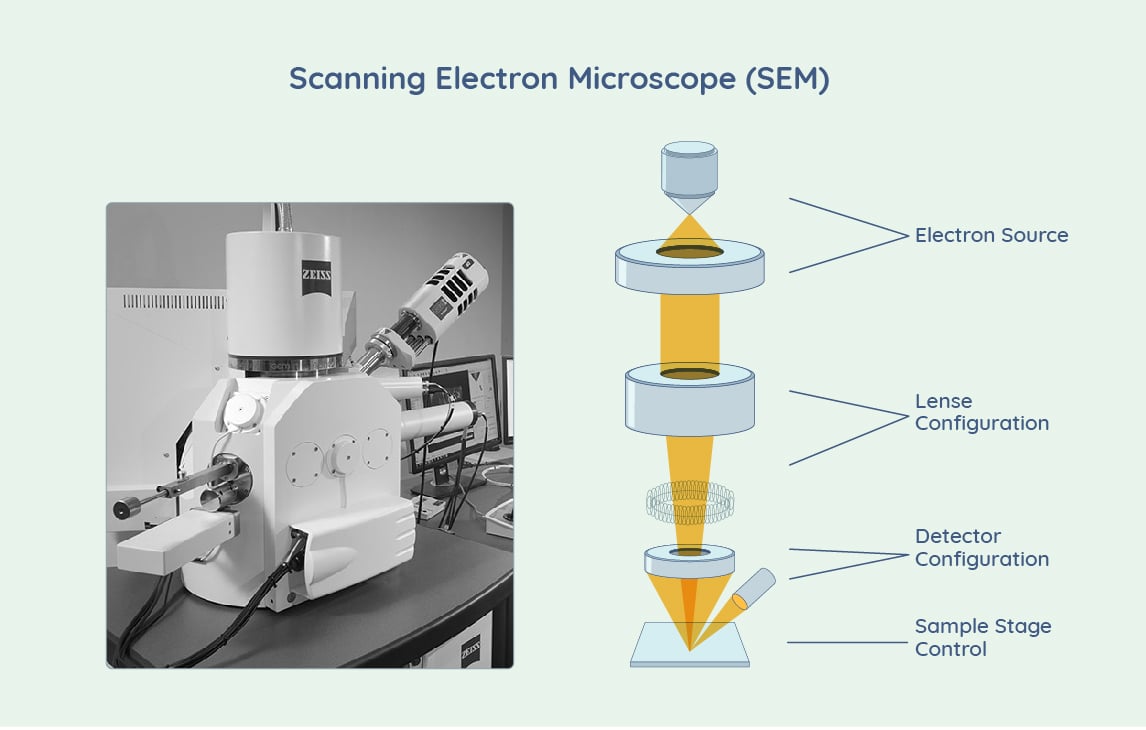
#5 Scanning electron microscopes (SEM)
Domain Est. 1995
Website: zeiss.com
Key Highlights: Scanning Electron Microscopes scan a sample with a focused electron beam and get images with information about the samples’ topography and composition….
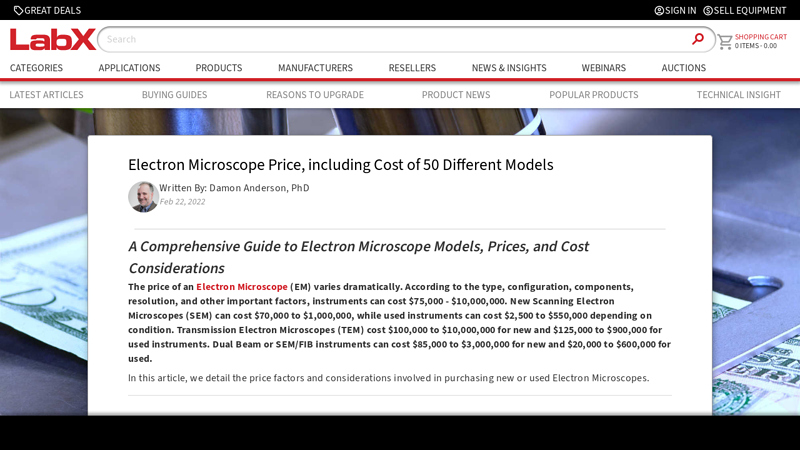
#6 Electron Microscope Price, including Cost of 50 Different Models
Domain Est. 1996
Website: labx.com
Key Highlights: New Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM) can cost $70,000 to $1,000,000, while used instruments can cost $2,500 to $550,000 depending on ……
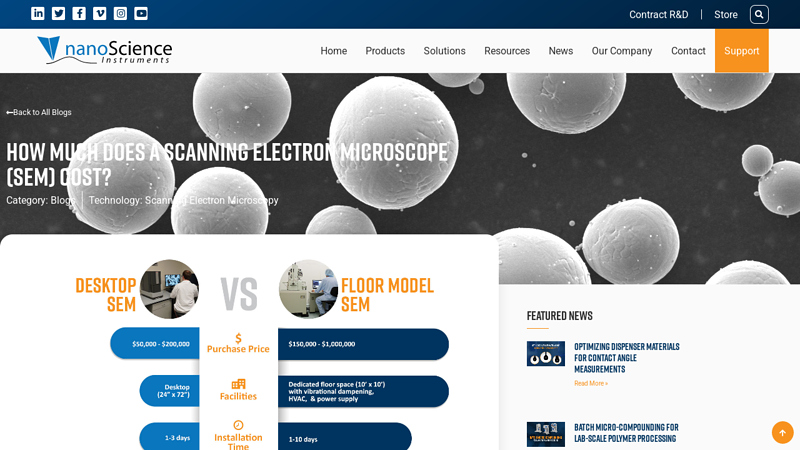
#7 How Much Does a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Cost?
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nanoscience.com
Key Highlights: Typically, new SEMs cost anywhere from $50,000 to over $1,000,000. The cost of scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) can vary significantly depending on several ……
#8 Leica Microsystems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: leica-microsystems.com
Key Highlights: Leica Microscope solutions can give you insights into the smallest sample details as well as analyze, document, and report results fast and reliably….
#9 Electron Microscope Price, including Cost of 50 Different Models
Domain Est. 2001
Website: labmanager.com
Key Highlights: New scanning electron microscopes (SEM) can cost $70,000 to $1,000,000, while used instruments can cost $2,500 to $550,000 depending on condition….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cost Of Electron Microscope
H2: Projected Cost of Electron Microscope in 2026 Market Trends
As the global scientific and industrial sectors advance toward higher precision and nanoscale analysis, electron microscopes remain indispensable tools across research, healthcare, semiconductor development, and materials science. By 2026, the cost of electron microscopes is expected to reflect a complex interplay of technological innovation, supply chain dynamics, regional market expansion, and increasing demand for advanced imaging capabilities.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact on Pricing
One of the primary drivers influencing electron microscope costs in 2026 is the rapid pace of technological innovation. Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEMs) and Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEMs) are becoming more compact, automated, and integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) for image analysis. These enhancements improve resolution, throughput, and ease of use, but they also contribute to higher initial equipment costs. Manufacturers such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, JEOL, and Zeiss are investing heavily in AI-powered automation and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), which supports structural biology research. As these features become standard, the baseline price for high-end systems is expected to rise, with top-tier TEMs potentially exceeding $10 million.
However, mid-range and benchtop SEMs are seeing cost stabilization or even modest declines due to economies of scale and increased competition. Entry-level benchtop models, priced between $70,000 and $150,000 in 2023, are projected to remain in a similar range in 2026, with incremental price increases (3–5% annually) due to inflation and component costs.
Supply Chain and Component Availability
Global supply chain volatility, particularly for high-precision components like electron guns, detectors, and vacuum systems, continues to influence pricing. The semiconductor shortage that began in 2020 has had lingering effects, especially on sensors and control electronics used in electron microscopes. By 2026, while supply chains are expected to stabilize, manufacturers may maintain higher prices to hedge against future disruptions. Additionally, rising costs of rare earth materials and specialized alloys used in electron optics could exert upward pressure on manufacturing expenses.
Regional Market Dynamics
Regional demand patterns will shape pricing strategies. In North America and Western Europe, strong government and private funding for nanotechnology and life sciences support premium pricing. In contrast, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific—especially China, India, and South Korea—are witnessing accelerated adoption of electron microscopy in academia and manufacturing. To capture this growth, vendors are introducing region-specific pricing models and financing options, which could lead to a broader range in effective costs depending on geography. Local manufacturing initiatives in China may also reduce import dependencies and lower costs for regional buyers.
Demand from Key Industries
The semiconductor industry’s push toward sub-3nm node fabrication is increasing the demand for high-resolution imaging and defect analysis, driving investment in advanced electron microscopes. Similarly, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are expanding their use of cryo-EM for drug discovery, boosting demand for specialized TEM systems. These high-value applications justify premium pricing and may insulate the高端 (high-end) segment from price competition.
Conversely, educational institutions and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) are more price-sensitive, favoring refurbished systems or shared facility models. The growing market for reconditioned and pre-owned electron microscopes—often priced at 30–50% of new systems—will remain a cost-effective alternative, contributing to a tiered pricing landscape in 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the cost of electron microscopes will reflect a bifurcated market: high-end systems will see moderate price increases due to advanced features and specialized applications, while mid- and low-end segments benefit from competitive pressures and technological diffusion. Overall, the global average price is expected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4–6% from 2023 to 2026. Buyers should anticipate higher upfront costs for cutting-edge capabilities but will have more options than ever in terms of financing, refurbished equipment, and regional pricing advantages.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Electron Microscopes: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing an electron microscope is a significant investment, and overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to costly setbacks, operational inefficiencies, or legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to watch for in these two areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Performance Verification
One of the most common mistakes is assuming published specifications reflect real-world performance. Vendors may advertise best-case resolution or speed under ideal conditions. Failing to request independent validation, third-party reviews, or on-site demonstrations can result in acquiring a system that underperforms in your specific application environment.
Neglecting Long-Term Reliability and Support
Electron microscopes require stable environmental conditions, regular maintenance, and expert technical support. Sourcing from vendors without a proven service network or with poor response times can lead to extended downtime. Ensure the supplier offers comprehensive service agreements, local technical expertise, and access to spare parts—especially for high-use components like filaments or detectors.
Overlooking Calibration and Traceability Standards
High-precision imaging demands instruments calibrated to recognized international standards (e.g., ISO/IEC 17025). Purchasing a microscope without documented calibration history or traceable standards may compromise data integrity, especially in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or materials certification.
Underestimating Integration and Compatibility Issues
New electron microscopes must often integrate with existing software, sample preparation systems, or data management platforms. Sourcing a system without verifying software compatibility (e.g., with your lab’s image analysis tools) or automation protocols can result in workflow bottlenecks and added costs for custom integration.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Ambiguity in Software Licensing and Data Ownership
Many modern electron microscopes come with proprietary software that governs data acquisition, processing, and storage. A common pitfall is signing licensing agreements that restrict data ownership or prohibit sharing results. Ensure your contract explicitly grants full rights to generated data and allows publication or commercial use without limitation.
Lack of Clarity on IP Infringement Risks
Using certain imaging modes, detectors, or analytical techniques may involve patented technologies. If the vendor hasn’t licensed these underlying technologies appropriately, your organization could face third-party IP infringement claims. Conduct due diligence to confirm that the microscope and its components do not expose you to legal liability.
Hidden Restrictions in Upgrades and Modifications
Some vendors impose contractual or technical restrictions on modifying or upgrading systems, potentially locking users into proprietary upgrade paths. This can limit innovation and increase long-term costs. Review service and licensing agreements to ensure you retain the right to modify, maintain, or enhance the system with third-party components when needed.
Failure to Protect Custom Applications or Methods
If your team develops new imaging protocols or analytical methods using the microscope, unclear agreements may allow the vendor to claim co-ownership or unrestricted use of those innovations. Establish IP ownership terms upfront, particularly if the equipment is used in collaborative or contract research settings.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure they source electron microscopes that deliver reliable performance, align with operational needs, and safeguard their intellectual assets.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cost of Electron Microscope
Purchasing an electron microscope involves significant financial investment and complex logistical and regulatory considerations. Understanding not only the upfront cost but also the associated logistics and compliance requirements is essential for budgeting, planning, and ensuring smooth installation and operation. This guide outlines key aspects to consider when evaluating the total cost of ownership.
Capital and Operational Costs
The cost of an electron microscope extends far beyond the initial purchase price. It includes:
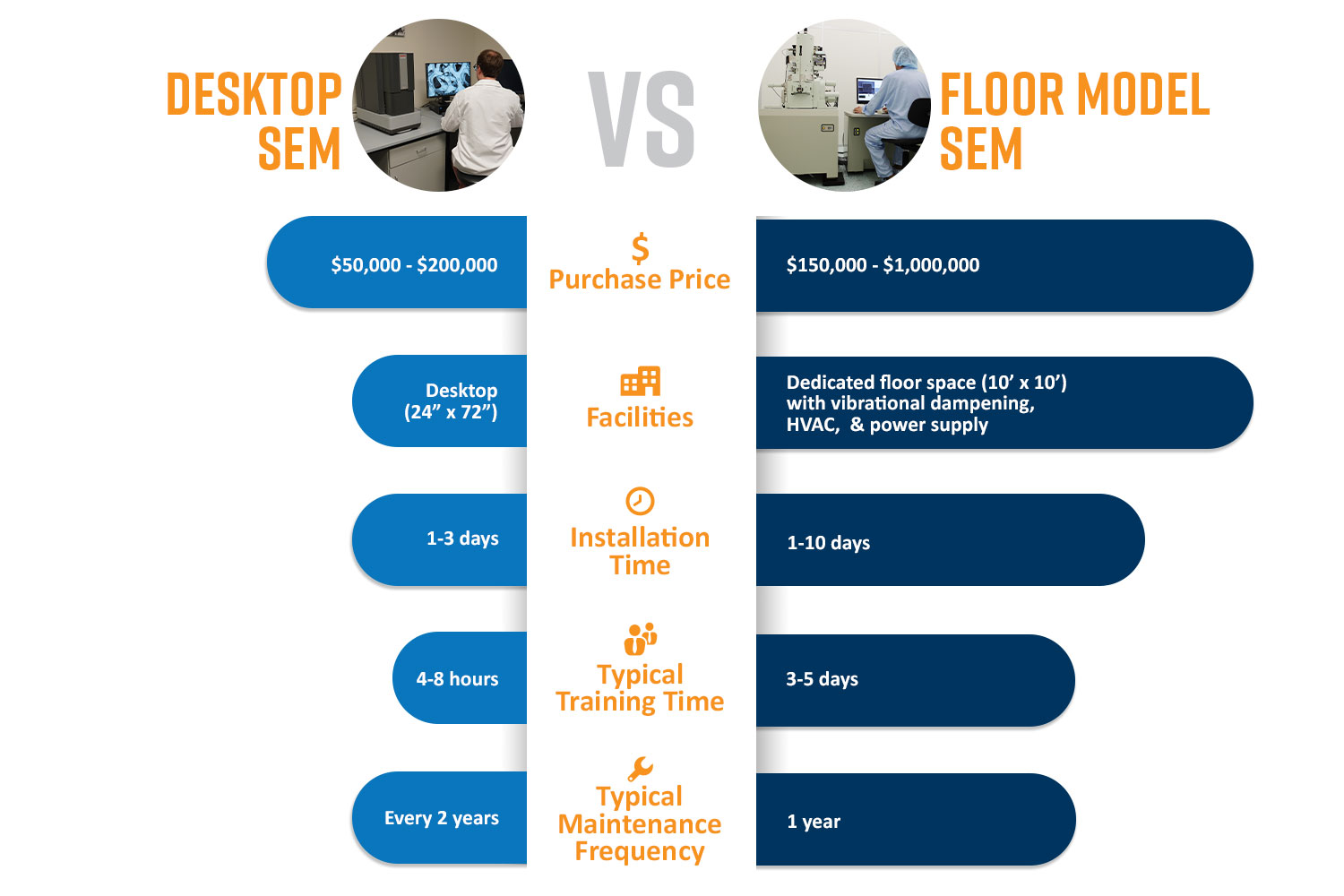
- Instrument Purchase Price: Ranges from $100,000 for basic benchtop models to over $10 million for advanced transmission electron microscopes (TEM) with specialized detectors.
- Installation and Site Preparation: Requires vibration isolation, electromagnetic shielding, stable power supply, cooling systems, and proper flooring. Site prep can add $50,000–$200,000.
- Training and Staffing: Specialized personnel (e.g., microscopists, engineers) are needed for operation and maintenance, impacting long-term labor costs.
- Maintenance and Service Contracts: Annual service agreements typically cost 10–15% of the instrument’s value per year.
- Consumables and Accessories: Includes filaments, detectors, sample holders, cryo-stages, and software licenses.
Import and Export Regulations
Electron microscopes are often manufactured overseas and subject to international trade controls.
- Export Controls: Instruments with high resolution (e.g., sub-nanometer capability) may be classified under dual-use export control regimes such as the Wassenaar Arrangement or U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR).
- Import Duties and Taxes: Subject to customs duties, VAT, or GST depending on the destination country. Duty rates vary; some scientific instruments qualify for exemptions under the International Technological Cooperation (ITC) or similar programs.
- Required Documentation: Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and export license (if applicable) must be prepared accurately.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Operating an electron microscope requires adherence to health, safety, and environmental regulations.
- Radiation Safety: Although electron microscopes are generally shielded, institutions must comply with local radiation safety regulations (e.g., NRC in the U.S., HSE in the UK).
- Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Compliance: High-voltage components generate strong EMFs; installations must meet EMF exposure limits set by bodies like ICNIRP.
- Electrical and Fire Safety: Must comply with national electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC standards internationally) and include proper grounding and circuit protection.
- Hazardous Materials: Use of toxic stains (e.g., uranium acetate in TEM) or cryogens (e.g., liquid nitrogen) requires chemical safety protocols and proper disposal.
Shipping and Handling Logistics
Transporting an electron microscope demands specialized care.
- Fragile and Sensitive Equipment: Must be shipped in climate-controlled, shock-monitored containers with custom crating.
- Freight Forwarding: Engage experienced scientific equipment shippers. Air freight is faster but costly; sea freight is economical but increases transit time and risk.
- Customs Clearance: Ensure timely clearance by providing complete documentation and coordinating with customs brokers.
- On-Site Delivery: Requires crane access, reinforced flooring, and coordination with facility engineers for route planning.
Facility and Infrastructure Requirements
Site readiness impacts both cost and timeline.
- Room Specifications: Controlled temperature (±1°C), low humidity (40–60%), minimal vibration (e.g., on bedrock or isolated slabs), and low ambient electromagnetic interference.
- Power Supply: Stable, clean power with backup systems (e.g., UPS or generator), often requiring 208–480 V three-phase power.
- Ventilation and Exhaust: Some models require exhaust systems for oil diffusion pumps or cryo-pumping units.
- Network and Data Storage: High-speed connectivity and secure data storage for image processing and archiving.
Warranty, Insurance, and Risk Management
Protect your investment from the outset.
- Warranty Coverage: Typically 1–2 years; extended warranties increase long-term cost but reduce downtime risk.
- Transit and Installation Insurance: Covers damage during shipping and setup; essential for high-value equipment.
- Cybersecurity: Ensure software systems comply with institutional IT security policies, especially if connected to networks.
Conclusion
The true cost of an electron microscope encompasses acquisition, logistics, compliance, and lifecycle expenses. Proactive planning for import regulations, site preparation, safety compliance, and operational support ensures a successful deployment and maximizes return on investment. Engaging with suppliers, regulatory experts, and facilities teams early in the process is crucial for accurate budgeting and risk mitigation.
Conclusion: Sourcing Cost of an Electron Microscope
The sourcing cost of an electron microscope involves a comprehensive evaluation of both direct and indirect expenses, extending far beyond the initial purchase price. Key cost factors include the type of microscope (e.g., SEM, TEM), technical specifications, brand reputation, installation, training, maintenance contracts, facility preparation, and ongoing operational costs such as power consumption and consumables.
While high-end models from leading manufacturers offer superior resolution and advanced features, they come with significantly higher acquisition and lifecycle costs. Alternative sourcing strategies—such as purchasing refurbished instruments, leasing, or shared access through research consortia—can provide cost-effective solutions, particularly for academic institutions or small-to-medium enterprises with limited budgets.
A thorough total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis is essential to make an informed sourcing decision. Additionally, considering long-term support, warranty, and technological scalability ensures that the investment remains viable and productive over time. Ultimately, balancing performance requirements with financial constraints through strategic sourcing enables organizations to maximize value and achieve their microscopy objectives efficiently.