The global fuel injectors market is poised for steady expansion, driven by increasing vehicle production, stringent emission regulations, and the ongoing demand for fuel-efficient engines. According to Grand View Research, the global fuel injectors market size was valued at USD 13.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in direct injection technologies and rising adoption of gasoline direct injection (GDI) systems across passenger and commercial vehicles. As automakers strive to meet global efficiency and emissions standards, the need for high-performance, cost-effective fuel injectors has never been greater. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, scale, and competitive pricing to capture significant market share. Based on market presence, technological capability, and cost-efficiency, the following nine companies represent the top cost-competitive fuel injector manufacturers shaping the future of automotive propulsion.
Top 9 Cost Fuel Injectors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Aftermarket Fuel Injection Systems, EFI Systems, Kits, and Accessories
Domain Est. 1995
Website: holley.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $149From GM’s factory COPO Camaro to NASCAR to your car, get the new standard in fuel injection with Holley’s fuel injection kits and EFI ……
#2 Fuel Injector
Domain Est. 2001
Website: buyautoparts.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $99 · 60-day returns…
#3 FiTech Fuel Injection
Domain Est. 2013
Website: fitechefi.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $150 · 365-day returns…
#4 Fuel Injector Clinic: FIC
Domain Est. 2000
Website: fuelinjectorclinic.com
Key Highlights: Fuel Injector Clinic offers high performance fuel injector Data Matching for both High impedance and Low impedance injectors. Dynamic Cleaning and injector ……
#5 Fuel Injectors
Domain Est. 2003
Website: fueltech.net
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsFuelTech high performance racing fuel injector 170 lb/hr. with EV1 connectors. FT Injector 170 lb/h from $194.00 $1,752.00….
#6 Genuine OE Injectors
Domain Est. 2004
Website: boschautoparts.com
Key Highlights: Bosch is the leading OE supplier of diesel fuel systems for diesel passenger cars, SUVs, van and pickup trucks. End of line testing using the exact OE test ……
#7 Injector Dynamics
Domain Est. 2007
Website: injectordynamics.com
Key Highlights: As a results based engineering company, we have a strict no BS policy. Our product information is backed by data, and sound engineering principles….
#8 Automotive products: Fuel Injectors (FIJ)
Domain Est. 2014
Website: aftermarket.astemo.com
Key Highlights: Astemo fuel injectors deliver rapid, precise fuel spray that will prevent vehicle hesitation and ensure it operates at maximum performance and efficiency….
#9 Atomizer fuel injectors
Domain Est. 2019
Website: atomizerfuelcomponents.com
Key Highlights: 6-day deliveryAtomizer is the only fully rebuildable, high-performance, purpose-built fuel injector on the market, setting the standard for racers who demand the best….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cost Fuel Injectors
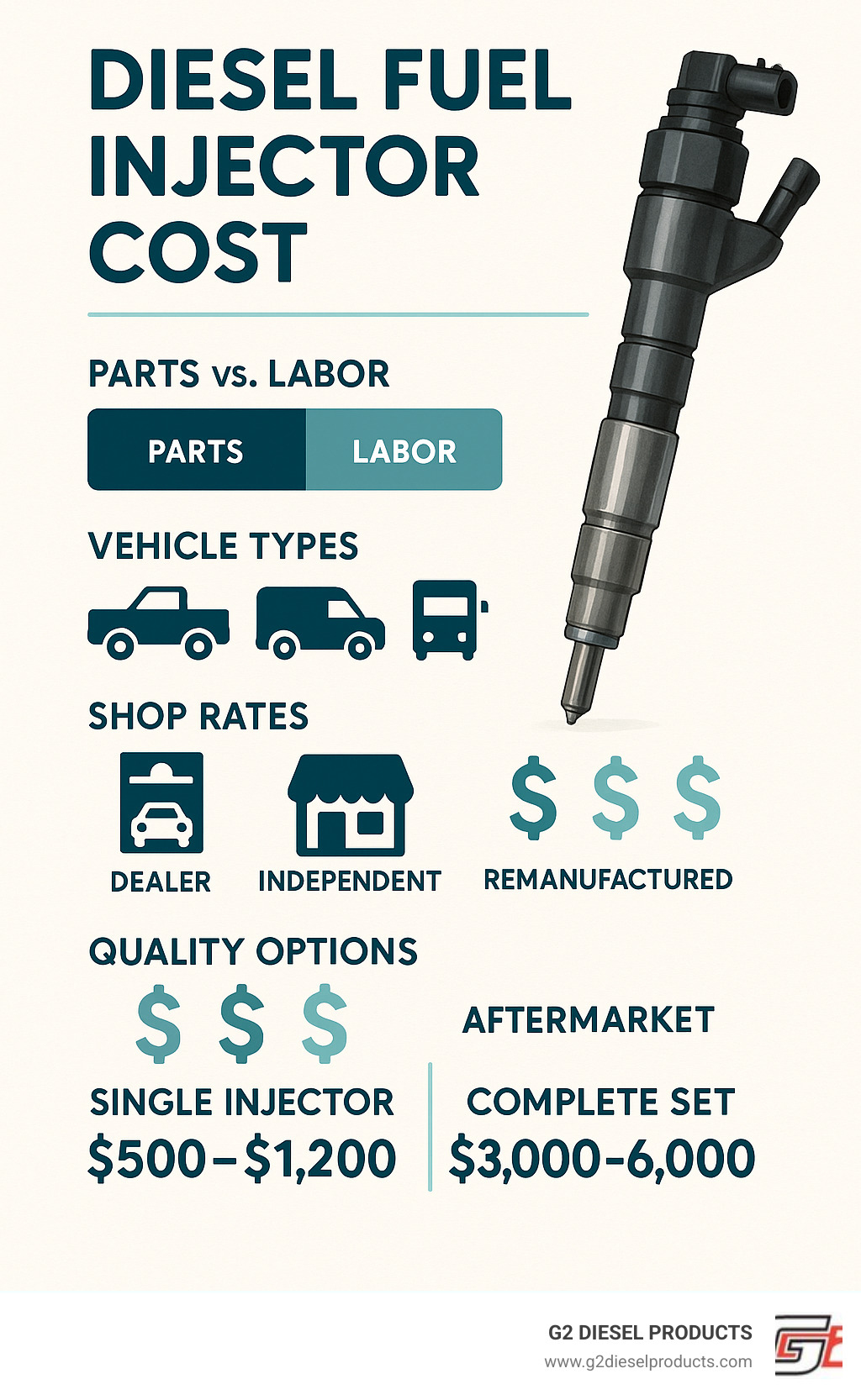
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cost of Fuel Injectors
The global market for fuel injectors is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, regulatory pressures, and shifts in vehicle propulsion systems. These dynamics are directly influencing the cost structure of fuel injectors across various engine types and regions.
-
Downward Pressure on Costs Due to Mass Production and Automation
By 2026, continued investments in automation and high-volume manufacturing processes—especially in emerging markets such as India, China, and Southeast Asia—are expected to reduce the unit cost of fuel injectors. Economies of scale, particularly in the production of gasoline direct injection (GDI) systems, will contribute to lower prices for OEMs and aftermarket suppliers. Increased competition among Tier-1 suppliers like Bosch, Denso, and Delphi is also driving price optimization. -
Rising Material and Compliance Costs
Despite manufacturing efficiencies, raw material volatility—especially for high-grade alloys, precision nozzles, and electronic components—could exert upward pressure on injector costs. Additionally, increasingly stringent emissions regulations (e.g., Euro 7, China 6b, and U.S. Tier 4 standards) require advanced injector designs capable of ultra-precise fuel delivery and reduced particulate emissions. These compliance-related engineering enhancements may offset cost reductions, particularly for high-performance diesel and GDI injectors. -
Shift Toward Electrification Impacting Demand
The accelerated adoption of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) means that internal combustion engines (ICEs) will remain in use but in more optimized, smaller-displacement configurations. This trend favors advanced, cost-effective fuel injectors designed for improved efficiency. However, as full battery electric vehicles (BEVs) gain market share—projected to exceed 30% of global light-duty sales by 2026—overall demand for traditional fuel injectors may decline, leading to consolidation in the supplier base and potential cost rationalization. -
Growth in Aftermarket and Remanufactured Injectors
With vehicle lifespans extending and maintenance costs under scrutiny, the aftermarket for fuel injectors is expected to grow. By 2026, remanufactured and recycled injectors are likely to capture a larger share of the market, particularly in developing economies. This trend will place downward pressure on average selling prices and offer cost-saving alternatives without compromising performance. -
Regional Cost Variations
Regional disparities in production costs, labor, and regulatory environments will persist. Asian manufacturers are expected to maintain a cost advantage, exporting lower-priced injectors globally. In contrast, injectors produced in North America and Europe may carry a premium due to higher compliance and labor standards, though localized production near OEM hubs could mitigate logistics costs.
In summary, the cost of fuel injectors in 2026 will reflect a balance between technological sophistication and cost efficiency. While innovation and regulation may increase per-unit complexity and cost, economies of scale, automation, and market shifts will help contain or even reduce average prices—particularly in the aftermarket and emerging markets.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cost Fuel Injectors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing low-cost fuel injectors presents significant risks, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) rights. While the initial price may be attractive, hidden pitfalls can lead to long-term costs, legal exposure, and reputational damage. Understanding these risks is crucial for informed procurement decisions.
Quality Compromises in Low-Cost Injectors
Fuel injectors are precision-engineered components critical to engine performance, emissions control, and fuel efficiency. Sacrificing on cost often leads to unacceptable quality trade-offs:
- Inferior Materials & Manufacturing: Cheap injectors frequently use substandard metals, seals, and solenoids. This results in premature wear, internal leakage (dribbling), clogging, and failure under high pressure and temperature cycles.
- Inconsistent Performance & Calibration: Low-cost manufacturers often lack the sophisticated calibration equipment and processes of OEMs. This leads to significant flow rate variations between injectors in the same set, causing engine misfires, rough idling, reduced power, and increased emissions.
- Poor Sealing & Reliability: Inadequate machining tolerances and lower-quality seals increase the risk of fuel leaks (external or internal) and contamination ingress, drastically shortening injector lifespan.
- Lack of Rigorous Testing: Reputable manufacturers subject injectors to extensive durability, surge, and environmental testing. Budget alternatives often skip or minimize these tests, meaning failures manifest only after installation, leading to costly comebacks and warranty claims.
- Incompatibility with Modern Systems: Modern engines rely on precise injector response times and spray patterns. Cheap injectors may not meet these exacting specifications, potentially causing engine control unit (ECU) errors, poor drivability, and failure to meet emissions standards.
Intellectual Property (IP) Violations and Legal Risks
Sourcing extremely low-cost injectors, especially from certain regions, carries a high risk of encountering counterfeit or IP-infringing products:
- Counterfeiting & Cloning: Many budget injectors are direct, unauthorized copies of OEM designs (e.g., Bosch, Denso, Delphi). These are produced without licenses, infringing on patents, trademarks, and design rights.
- Patent Infringement: Key technologies in fuel injectors (e.g., solenoid design, nozzle tip geometry, internal flow paths) are protected by patents. Sourcing non-licensed copies exposes the buyer and end-user to potential patent infringement lawsuits.
- Trademark Infringement: Counterfeit injectors often bear fake logos or branding identical to OEMs, constituting trademark violation.
- Legal Liability & Recalls: If a vehicle or equipment manufacturer uses infringing parts, they can face legal action from the IP holder, costly product recalls, and significant damage to their brand reputation.
- Voided Warranties & Lack of Support: Using non-OEM or counterfeit parts typically voids OEM warranties. Furthermore, there is no technical support or liability coverage from the original patent holder if failures occur.
- Supply Chain Reputational Risk: Associating with suppliers involved in IP theft damages a company’s reputation for ethical sourcing and can lead to loss of business partnerships.
Conclusion: Prioritizing the lowest initial cost when sourcing fuel injectors is a false economy. The risks of poor quality (leading to reliability issues, safety hazards, and high total cost of ownership) and potential IP infringement (resulting in legal liability, recalls, and brand damage) far outweigh the upfront savings. A strategic approach focusing on reputable suppliers, rigorous quality validation, and respect for intellectual property is essential for sustainable and responsible procurement.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cost Fuel Injectors
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the import, export, distribution, and handling of cost-effective (budget or replacement) fuel injectors. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, minimizes supply chain risks, and supports efficient operations.
Regulatory Classification & Documentation
Accurately classifying fuel injectors under international trade systems is critical for compliance. These components typically fall under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 8409.91 (Parts suitable for use solely or principally with internal combustion engines). Confirm the specific code with your local customs authority, as sub-classifications may vary by country. Required documentation includes commercial invoices with detailed product descriptions, packing lists, bills of lading or air waybills, and, where applicable, certificates of origin to claim preferential tariffs under trade agreements. For imports into regions like the EU or US, ensure all documentation is prepared in the required language and format.
International Shipping & Transportation
Fuel injectors are generally non-hazardous and can be shipped via standard air, ocean, or ground freight. However, proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit—use anti-static materials and secure cushioning to protect sensitive components. Coordinate with freight forwarders experienced in automotive parts logistics to optimize routing and transit times. For air shipments, comply with IATA regulations; for sea freight, adhere to IMO standards. Implement tracking systems to monitor shipment status and ensure timely delivery. Consider incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) carefully to define responsibility for shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer.
Import/Export Controls & Restrictions
While fuel injectors are not typically subject to strict export controls like dual-use or military items, verify compliance with national regulations in both origin and destination countries. Some countries may impose restrictions on automotive parts to protect domestic industries or ensure emissions compliance. Check for any import licensing requirements, especially in emerging markets. Ensure that the injectors meet local emissions standards (e.g., EPA in the US, Euro norms in the EU), as non-compliant parts may be denied entry or subject to penalties.
Product Compliance & Certification
Cost fuel injectors must meet technical and safety standards applicable in target markets. In the United States, compliance with EPA emission regulations is mandatory; in the European Union, CE marking and adherence to the e-mark (ECE R100 or similar) may be required depending on vehicle application. Conduct third-party testing where necessary to validate performance and durability. Maintain records of conformity assessments and keep technical documentation available for inspection by regulatory bodies.
Environmental & Waste Management Compliance
Fuel injectors may contain small amounts of residual fuel or oils. Handle and dispose of returned or defective units in accordance with local environmental regulations (e.g., RCRA in the US, WEEE or ELV directives in the EU). Partner with certified waste management providers for recycling or proper disposal. Avoid landfill disposal whenever possible. Ensure packaging materials are recyclable and comply with packaging waste directives such as the EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive.
Recordkeeping & Audit Preparedness
Maintain comprehensive records for a minimum of five to seven years, including transaction documents, compliance certifications, test reports, and correspondence with regulatory agencies. These records support customs audits, duty recovery claims, and investigations. Implement a digital document management system to ensure easy retrieval and data integrity.
Risk Mitigation & Supply Chain Security
Assess suppliers for quality control and regulatory compliance to avoid counterfeiting or substandard products. Conduct regular audits and require ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certification where possible. Enroll in trusted trader programs (e.g., C-TPAT in the US, AEO in the EU) to expedite customs clearance and enhance supply chain security. Monitor geopolitical and regulatory changes that could impact trade flows.
By following this guide, businesses can efficiently manage the logistics of cost fuel injectors while ensuring full compliance with international and local regulations. Regular review and adaptation to evolving standards are recommended to maintain seamless operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cost of Fuel Injectors:
After a comprehensive evaluation of the sourcing costs associated with fuel injectors, it is evident that a strategic approach is essential to balance cost-efficiency, quality, and reliability. Key factors influencing sourcing costs include supplier location, production volume, material specifications, technological complexity, and supply chain logistics. Sourcing from global suppliers, particularly in regions with lower manufacturing costs, can yield significant savings; however, these benefits must be weighed against potential risks such as longer lead times, import tariffs, and quality control challenges.
Alternative sourcing strategies—such as dual sourcing, supplier partnerships, and bulk purchasing—can enhance cost savings while mitigating supply chain vulnerabilities. Additionally, investing in high-quality, durable fuel injectors may reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses, contributing to total cost of ownership savings.
In conclusion, optimizing the sourcing cost of fuel injectors requires a holistic view that goes beyond initial purchase price. Organizations should prioritize supplier reliability, product consistency, and lifecycle costs to ensure performance and cost-effectiveness. A well-structured procurement strategy, supported by market analysis and supplier evaluation, will enable businesses to achieve sustainable cost advantages without compromising on quality or operational efficiency.