The global cosmetics market continues to experience robust expansion, driven by rising consumer demand for skincare, makeup, and personal care products across both established and emerging economies. According to Grand View Research, the global cosmetics market size was valued at USD 380.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 5% through 2028, fueled by increasing disposable incomes, growing e-commerce penetration, and a surge in demand for clean, sustainable, and premium beauty products. As competition intensifies and innovation accelerates, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as industry leaders—combining advanced R&D, regulatory compliance, and scalable production capabilities. These top nine cosmetic manufacturers are shaping the future of beauty by serving global brands and private labels with high-quality, compliant, and trend-responsive formulations.
Top 9 Cosmetic Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Global Cosmetics
Domain Est. 2012
Website: global-cosmetics.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture trend-setting beauty products. From lipsticks to perfumes, we provide expert OEM and ODM manufacturing for beauty products….
#2 Columbia Cosmetics
Domain Est. 1998
Website: columbiacosmetics.com
Key Highlights: Explore top makeup & skin care manufacturers offering white label cosmetics & private label solutions. Discover beauty products & cosmetics development….
#3 Intercos Group
Domain Est. 1999
Website: intercos.com
Key Highlights: Intercos Group is a leading cosmetic contract manufacturer specialized in Development, Production and Packaging for major beauty labels….
#4 Beauty Manufacturing Solutions Corp
Domain Est. 2006
Website: beautymanufacture.com
Key Highlights: BMSC is a leading US manufacturer of innovative cosmetic, beauty, and personal care products and a top competitor in the industry. We have set ourselves apart ……
#5 Cosmetic Group USA
Domain Est. 2013
Website: cosmeticgroupusa.com
Key Highlights: Cosmetic Group USA, Inc. is a premiere, innovation-driven cosmetics and personal care development and manufacturing facility….
#6 Tokiwa Cosmetics
Domain Est. 2014
Website: tokiwacosmetics.com
Key Highlights: TOKIWA has been a world-renowned creator, manufacturer, and supplier of cosmetics, formulations, and componentry for over 7 decades….
#7 Applechem
Domain Est. 2013
Website: applechem.com
Key Highlights: Applechem is a functional cosmetic ingredient supplier with a diverse range of products for cosmetics, personal care, suncare, hair care and homecare ……
#8 PinkPro Beauty Supply
Domain Est. 2016
Website: pinkprobeauty.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $89 30-day returns…
#9 SBLC Cosmetics
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sblcomp.com
Key Highlights: We are your one-stop-shop for bringing cosmetic products to market. From private label and formulation development to custom packaging, brand development, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cosmetic
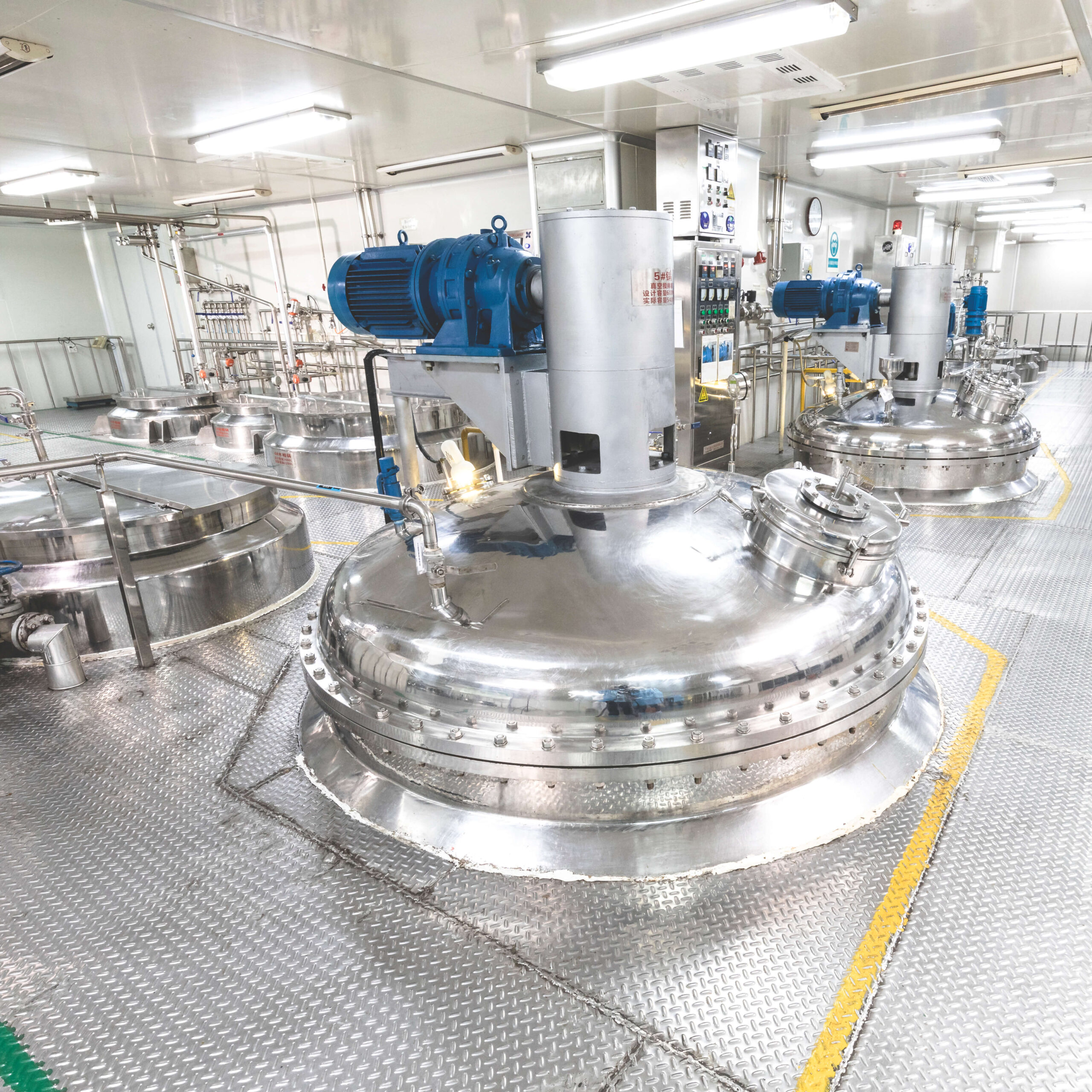

H2 2026 Market Trends in the Cosmetic Industry
As we approach the second half of 2026, the global cosmetic market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by evolving consumer values, technological innovation, and heightened regulatory scrutiny. Key trends shaping the industry landscape include:
1. Radical Transparency & Clean Beauty 3.0:
Consumer demand for ingredient transparency has evolved beyond simple “free-from” claims. In H2 2026, brands are adopting blockchain traceability for raw materials, providing real-time supply chain data via QR codes. “Clean Beauty 3.0” emphasizes not just safety but bioavailability and proven efficacy of natural actives, supported by clinical data. Regulators in the EU and US are enforcing stricter definitions of “natural” and “organic,” forcing reformulations and clearer labeling.
2. AI-Driven Personalization at Scale:
Artificial intelligence has moved from hype to mainstream implementation. By H2 2026, major brands and DTC players leverage AI for hyper-personalization:
Smart Diagnostics: At-home devices and smartphone apps using AI-powered skin analysis (beyond basic imaging to assess microbiome signals and environmental stress) generate personalized product recommendations.
Custom Formulations: On-demand manufacturing kiosks in retail stores and home delivery of truly customized serums and foundations based on real-time skin data are becoming commercially viable.
Predictive Skincare:* AI models predict skin aging trajectories and recommend preventative regimens, shifting focus from correction to prevention.
3. Sustainability as Non-Negotiable:
Environmental concerns are paramount. H2 2026 sees accelerated adoption of:
Refillable & Reusable Systems: Premium brands are standardizing modular packaging (e.g., magnetic compacts, glass bottles with durable sleeves) with widespread refill networks.
Waterless & Concentrated Formulas: To reduce weight, shipping emissions, and plastic, waterless products (solid serums, concentrates requiring user-added water) dominate new launches.
Biodegradable & Compostable Materials:* Innovation in marine-safe, home-compostable films and molded fiber packaging is overcoming previous durability issues. Carbon footprint labeling is becoming common.
4. Inclusivity Beyond Shade Matching:
Inclusivity has deepened. Brands now address diverse needs like:
Hair Diversity: Expanding beyond texture to specific scalp conditions (e.g., seborrheic dermatitis, folliculitis) across all ethnicities.
Skin Conditions: Developing effective, aesthetically pleasing products for sensitive skin, rosacea, and post-procedure care, marketed without stigma.
Gender Fluidity:* Continued blurring of gender lines, with unisex product lines and marketing focusing on skin/hair needs rather than identity.
5. The Rise of “Cosmeceutical” Regulation & Efficacy:
The line between cosmetics and drugs is under intense regulatory pressure. H2 2026 witnesses:
Stricter global regulations (especially in EU, US, and China) limiting claims for ingredients like retinoids, peptides, and certain antioxidants without robust clinical proof.
Increased investment by brands in clinical trials to substantiate anti-aging, brightening, and barrier-repair claims, leading to a tiered market: mass-market “wellness” cosmetics vs. premium “clinical” skincare with proven bioactivity.
6. Phygital (Physical + Digital) Retail Integration:
The retail experience is seamlessly blending online and offline:
AR/VR Try-On Maturity: Advanced augmented reality allows realistic simulation of makeup and skincare results under various lighting and skin conditions, integrated into e-commerce and in-store mirrors.
Social Commerce Dominance: TikTok Shop and Instagram Shopping are primary discovery and purchase channels, with real-time influencer demos driving impulse buys.
Experiential Flagships:* Physical stores focus on sensory experiences, professional consultations, and community events, acting as brand hubs rather than just points of sale.
Conclusion:
H2 2026 marks a pivotal point where cosmetic brands must demonstrate authenticity, scientific rigor, and environmental responsibility to succeed. Success hinges on leveraging technology for genuine personalization, achieving radical supply chain transparency, and meeting the sophisticated, values-driven demands of a globally connected consumer. The market favors agile innovators who prioritize long-term sustainability and measurable efficacy over fleeting trends.
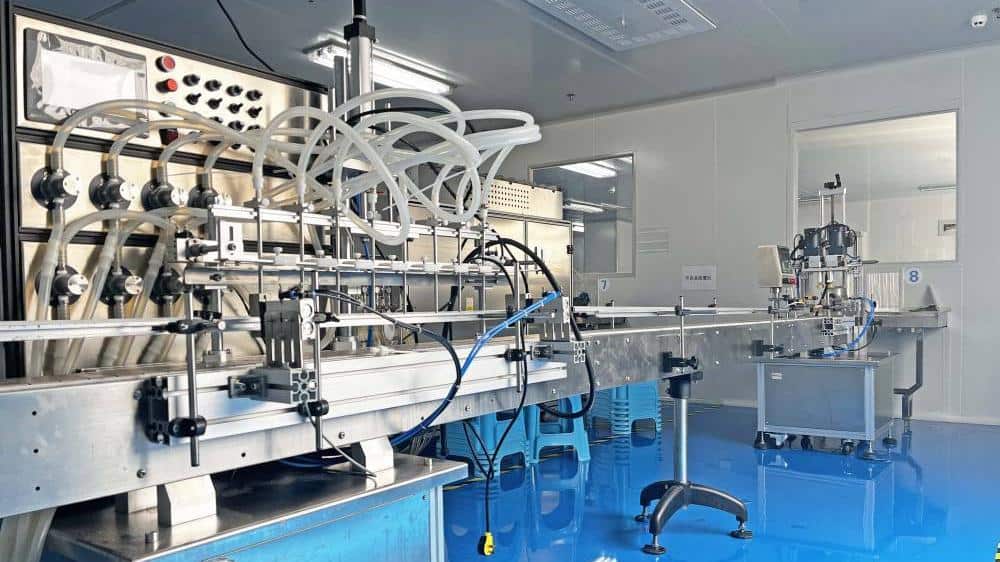

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Cosmetics: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing cosmetic products, especially from international or third-party manufacturers, presents several potential challenges. Two of the most critical areas where businesses commonly encounter issues are product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to regulatory non-compliance, reputational damage, legal disputes, and financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Product Formulation and Performance
A major risk when sourcing cosmetics is receiving products that vary in composition, texture, scent, or efficacy between batches. This inconsistency often stems from suppliers using alternative ingredients without notification, poor quality control processes, or lack of standardized manufacturing procedures. Such variations can alienate customers and result in negative reviews or returns.
2. Use of Substandard or Non-Compliant Ingredients
Suppliers may cut costs by using low-grade, expired, or banned ingredients that do not meet regional regulatory standards (e.g., EU’s Annex restrictions, FDA guidelines). This can lead to product recalls, legal penalties, and health risks for consumers.
3. Inadequate Testing and Safety Validation
Some manufacturers skip essential safety and stability testing, such as challenge testing, preservative efficacy testing, or dermatological assessments. Without proper validation, products may spoil prematurely or cause skin irritation, increasing liability exposure.
4. Poor Packaging and Shelf-Life Management
Cosmetic products are sensitive to light, air, and temperature. Inadequate packaging materials or improper storage during transit can degrade product quality. Additionally, inaccurate or missing expiration dates mislead consumers and compromise safety.
5. Lack of Transparency in Manufacturing Processes
Suppliers may not provide full disclosure about their production facilities, sourcing practices, or certifications (e.g., GMP—Good Manufacturing Practice). This lack of transparency makes it difficult to verify quality claims or ensure ethical production standards.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Unprotected Formulations and Brand Elements
Many cosmetic brands fail to secure trademarks for their brand names, logos, or distinctive packaging designs. Similarly, proprietary formulations may not be protected through trade secrets or patents, making them vulnerable to reverse engineering and copying by suppliers or competitors.
2. Supplier Ownership of Developed IP
Contracts with manufacturers sometimes include clauses that assign ownership of newly developed formulations, designs, or processes to the supplier. Without careful negotiation, brands may lose control over their innovations and face restrictions on future production or modifications.
3. Risk of IP Theft and Counterfeiting
When working with overseas manufacturers, especially in regions with weaker IP enforcement, there is a heightened risk that your product designs or formulas will be copied and sold without authorization. Some suppliers may even produce “knock-off” versions for other clients or sell them under different brands.
4. Inadequate Legal Agreements
Failure to establish clear contractual terms regarding confidentiality, IP ownership, and non-compete clauses leaves brands exposed. Verbal agreements or vague contracts are insufficient to protect against IP misuse or disputes.
5. Shared Tooling and Equipment Risks
If molds, packaging tools, or production equipment are not exclusively owned or controlled by the brand, suppliers may reuse them to produce similar products for competitors, diluting market uniqueness and brand identity.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, businesses should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including audits and sample testing.
– Require compliance with international quality standards (e.g., ISO 22716 for GMP).
– Secure all IP through trademarks, trade secrets, and well-drafted contracts.
– Include explicit IP ownership and confidentiality clauses in supplier agreements.
– Regularly monitor and test incoming shipments for quality consistency.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns during the sourcing process, cosmetic brands can protect their reputation, ensure regulatory compliance, and safeguard their competitive advantage.
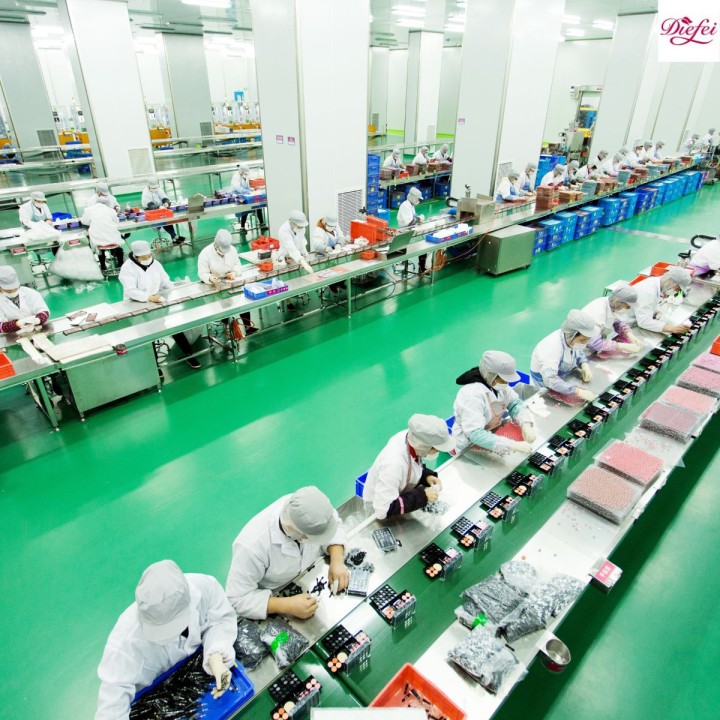

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cosmetics
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Understanding and adhering to the regulatory requirements in your target markets is essential for the legal distribution of cosmetic products. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees cosmetics under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act). Key compliance elements include:
- Product Labeling: Labels must include the product identity, net quantity, ingredient list (using INCI names), name and place of business of the manufacturer, and any required warnings.
- Registration: While pre-market approval is not required, manufacturers and distributors must register their facilities and list their products with the FDA via the Voluntary Cosmetic Registration Program (VCRP) or the new Cosmetics Direct program.
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Follow internationally recognized GMP standards (such as ISO 22716) to ensure product safety, quality, and consistency.
- Prohibited & Restricted Ingredients: Avoid using ingredients banned or limited by regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, EU Commission). The EU maintains a comprehensive list of prohibited and restricted substances in Annexes II and III of the EU Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009.
In the European Union, the EU Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 mandates additional requirements such as:
- Responsible Person (RP): A designated entity within the EU must ensure compliance, maintain the Product Information File (PIF), and report serious adverse effects.
- Product Information File (PIF): A comprehensive dossier including safety assessment, formulation, manufacturing method, and labeling.
- CPNP Notification: All cosmetic products placed on the EU market must be notified in the Cosmetic Products Notification Portal (CPNP) before launch.
Product Safety and Testing
Cosmetic products must be safe for consumer use under labeled or customary conditions. Key actions include:
- Safety Assessment: A qualified safety assessor must conduct a Cosmetic Product Safety Report (CPSR), especially required in the EU.
- Microbiological Testing: Ensure products are free from harmful microorganisms and include preservation efficacy testing (challenge testing).
- Stability Testing: Perform shelf-life testing under various conditions (e.g., temperature, light exposure) to validate expiration dates.
- Patch Testing: Conduct human repeat insult patch testing (HRIPT) as needed to evaluate potential skin sensitization.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Manufacturing facilities must follow strict quality assurance protocols:
- GMP Compliance: Implement documented procedures for raw material sourcing, contamination control, equipment sanitation, and batch record keeping.
- Batch Traceability: Maintain records for raw materials and finished products to ensure full traceability in case of recalls.
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): Require CoAs from suppliers to verify the identity, purity, and quality of raw materials.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling are critical for compliance and consumer safety:
- Primary & Secondary Packaging: Ensure materials are inert, safe, and compatible with the formulation.
- Label Content: Include all mandatory information (e.g., ingredient list in descending order, expiration date or Period After Opening (PAO) symbol, usage instructions).
- Language Requirements: Labels must be in the official language(s) of the target market (e.g., French in France, bilingual labels in Canada).
- Eco-Labeling & Claims: Avoid misleading claims (e.g., “dermatologically tested,” “hypoallergenic”) unless substantiated; comply with environmental claims regulations (e.g., EU Green Claims Directive).
Import and Export Logistics
When shipping cosmetics internationally, consider the following:
- Customs Documentation: Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of free sale or manufacture. Some countries require product-specific certifications.
- HS Code Classification: Use the correct Harmonized System (HS) code (typically 3304 for beauty/makeup products) for customs clearance.
- Restricted Components: Be aware of import restrictions on ingredients (e.g., animal-derived components in certain countries, alcohol content limits).
- Cold Chain & Storage: For temperature-sensitive formulations, ensure controlled transport conditions and validate storage environments (e.g., 15–25°C).
Regulatory Monitoring and Updates
Cosmetic regulations are dynamic. Stay compliant by:
- Monitoring Regulatory Changes: Subscribe to updates from the FDA, EU Commission, Health Canada, and other relevant authorities.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Implement systems to collect and report adverse events.
- Recall Preparedness: Develop a product recall plan that includes communication protocols, batch tracing, and coordination with regulatory bodies.
Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
Increasingly important for brand reputation and compliance:
- Packaging Regulations: Comply with Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes (e.g., France’s Triman logo, UK Packaging Waste Regulations).
- Ingredient Sourcing: Avoid substances of very high concern (SVHCs) under REACH; prioritize biodegradable and sustainably sourced ingredients.
- Animal Testing: Adhere to bans on animal testing (e.g., EU-wide ban, UK, India, and others); use alternative testing methods (e.g., in vitro).
By integrating these logistics and compliance practices, cosmetic businesses can ensure legal market access, consumer safety, and sustainable operations across global markets.
Conclusion on Sourcing Cosmetic Suppliers
Sourcing the right cosmetic suppliers is a critical factor in building a successful beauty brand. It requires a strategic approach that balances quality, compliance, ethics, cost, and supply chain reliability. After evaluating various suppliers, it is clear that prioritizing transparency, regulatory adherence—such as compliance with FDA, EU Cosmetics Regulation, or ISO certifications—and sustainable practices leads to long-term brand credibility and customer trust.
Partnering with suppliers who offer innovation, scalability, and responsive communication ensures agility in a fast-evolving market. Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence, including sample testing, facility audits, and reference checks, minimizes risks associated with product safety and consistency.
Ultimately, the ideal cosmetic supplier is not just a vendor, but a collaborative partner aligned with your brand’s values, vision, and standards. By establishing strong, ethical, and reliable supplier relationships, brands can deliver high-quality products, foster consumer loyalty, and maintain a competitive edge in the global cosmetics industry.