The global plumbing and piping components market has experienced steady expansion, driven by rising construction activities, infrastructure development, and growing demand for durable water distribution systems. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global copper pipe and tube market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by increased adoption in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Parallel growth is observed in the PVC piping sector, with Grand View Research valuing the global PVC pipe market at USD 69.5 billion in 2022 and projecting a CAGR of 5.8% through 2030. As systems increasingly integrate copper and PVC due to their respective advantages—thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance in copper, versus lightweight durability and chemical resistance in PVC—the demand for reliable transition solutions like copper-to-PVC couplings has surged. This convergence has elevated the importance of high-performance coupling manufacturers capable of ensuring leak-free, long-lasting connections across mixed-material installations. The following analysis highlights the top eight manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and market reach in copper-to-PVC coupling solutions.
Top 8 Copper To Pvc Coupling Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Fittings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nibco.com
Key Highlights: We offer metal and plastic fittings for industrial, commercial, mechanical, fire protection, and residential flow-control systems….
#2 Pipe couplings for industrial water supply
Domain Est. 1995
Website: romac.com
Key Highlights: Lightweight ductile iron coupling. Nominal Sizes 1/2 – 12 inches. Working Pressure Up to 200 psi. Pipe Compatibility Steel, copper and PVC pipe. FLANGED ……
#3 Copper
Domain Est. 1997
Website: magicplastics.com
Key Highlights: This is the ideal fitting for an easy and smooth transition from Copper to PVC pipe. Fittings are assembled with Buna-70 O-Rings that provide a positive water ……
#4 QuickFitting
Domain Est. 2006
Website: quickfitting.com
Key Highlights: Our quick connection technology provides a simpler, safer, and more cost-effective solution for connecting copper, PEX and CPVC piping in plumbing and heating ……
#5 Viega USA
Domain Est. 2002
Website: viega.us
Key Highlights: Providing secure pipe connections for 125 years. Viega piping systems deliver unparalleled quality and durability in plumbing projects across the nation and ……
#6 Push
Domain Est. 2003
Website: sharkbite.com
Key Highlights: PVC transition couplings allow plumbers to customize their fitting and connect PVC pipe with PEX, copper, CPVC, and HDPE pipe. Discover more….
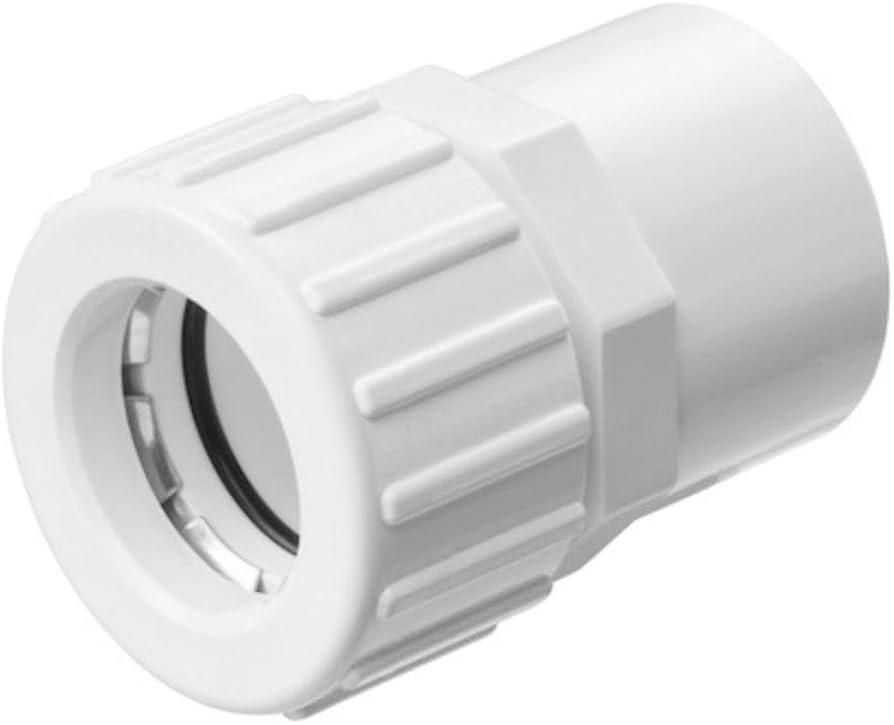
#7 Plumbing Fittings (Copper to PVC Adapter)
Domain Est. 2004
Website: c-m-p.com
Key Highlights: Copper to PVC Adapter. Get Details. Plumbing Fitting. Copper to PVC Adapter. CMP Part Number. Full Description. See More. Copper Adapter….
#8 Copper Thread Coupling
Domain Est. 2017
Website: erapipesale.com
Key Highlights: ERA High Quality PVC PN10 pressure pipe fitting female thread reducing coupling with DVGW Certificate PVC is the abbreviation of (Polyvinylchlorid)….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Copper To Pvc Coupling
2026 Market Trends for Copper to PVC Coupling
The market for copper to PVC couplings is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by construction dynamics, material advancements, regional development, and evolving regulatory landscapes. While facing competition from all-plastic and all-metal alternatives, copper to PVC couplings retain critical niche applications where their unique bridging capability is indispensable.
Resilient Demand in Repair and Retrofit Sectors
A primary driver sustaining the copper to PVC coupling market through 2026 will be the vast existing infrastructure requiring maintenance and upgrades. Millions of homes and commercial buildings worldwide have legacy copper plumbing systems. As these systems age, repairs often necessitate connecting new PVC or CPVC piping to existing copper lines. This creates consistent, recession-resistant demand for transition fittings like copper to PVC couplings, particularly in mature markets like North America and Western Europe. Plumbers and contractors will continue to rely on these couplings for cost-effective and code-compliant repairs, ensuring stable market volume.
Growth in Emerging Economies and Infrastructure Projects
Significant growth potential lies in developing regions such as Southeast Asia, Latin America, and parts of Africa. Rapid urbanization, expanding middle classes, and government investments in water and sanitation infrastructure are fueling new construction. In these projects, copper to PVC couplings offer a practical solution where initial budget constraints favor PVC for distribution lines, but copper is still preferred for specific fixtures or localized high-pressure zones. Large-scale infrastructure upgrades, including water treatment plants and district cooling systems, will also utilize these couplings at transition points, contributing to market expansion.
Innovation in Coupling Design and Materials
Technological advancements will shape the market by enhancing performance and ease of installation. Expect increased adoption of:
* Push-to-Connect and Press-Fit Couplings: These fittings, featuring pre-loaded seals and requiring no soldering or gluing, significantly reduce installation time and skill requirements, appealing to contractors facing labor shortages. Their reliability and leak resistance will drive market share gains.
* Improved Seal Technologies: Development of more durable, temperature-resistant, and chemically compatible elastomeric seals (e.g., EPDM, FKM) will improve long-term reliability and broaden the application scope, especially in hot water lines or aggressive chemical environments.
* Brass Alloys with Enhanced Properties: Wider use of lead-free brass (e.g., C84400, C87850) complying with stringent regulations (like NSF/ANSI 61-G) and potentially incorporating alloys with better corrosion resistance or machinability.
Regulatory Pressures and Material Competition
The market faces headwinds from two main sources:
* Stringent Water Quality Regulations: Increasing global focus on lead reduction and water safety (e.g., Lead and Copper Rule Revisions in the US, similar directives in EU/UK) mandates the use of certified lead-free materials. This pushes manufacturers towards compliant brass alloys and rigorous certification processes, potentially increasing costs but also solidifying trust in certified products. Non-compliant couplings will face market exclusion.
* Competition from Alternative Systems: The rise of all-PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) and all-CPVC systems, particularly in new residential construction, reduces the need for transition fittings. PEX’s flexibility, freeze resistance, and ease of installation make it highly competitive. However, copper to PVC couplings maintain an advantage in applications requiring the structural rigidity of copper (e.g., exposed risers, high-temperature zones) or where specific local codes still mandate copper for certain sections.
Supply Chain and Cost Volatility
The market will remain sensitive to fluctuations in the prices of base materials, particularly copper and brass. Geopolitical factors, mining output, and global demand for copper (driven significantly by electrification and renewables) can cause significant price swings, impacting coupling manufacturing costs and end-product pricing. Supply chain resilience, potentially enhanced by regional manufacturing or strategic sourcing, will be crucial for stability. PVC resin prices, influenced by oil and gas markets, will also play a role.
Sustainability and Recycling Focus
Environmental considerations will gain prominence. The recyclability of both copper and brass is a significant advantage, aligning with circular economy goals. Manufacturers may emphasize recyclability in marketing and explore ways to reduce the environmental footprint of production. While PVC recycling is more complex, the longevity of properly installed plumbing systems contributes to overall sustainability. Lifecycle assessments comparing different piping systems may influence specifiers.
Conclusion
By 2026, the copper to PVC coupling market will be characterized by steady, niche-driven demand rather than explosive growth. Its future hinges on its irreplaceable role in connecting disparate piping materials within repair/retrofit scenarios and specific new construction applications, particularly in emerging economies. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate with easier-to-install, highly reliable, and compliant fittings while navigating material cost volatility and competition from alternative piping systems. The demand for certified, lead-free, and high-performance couplings will define the competitive landscape.
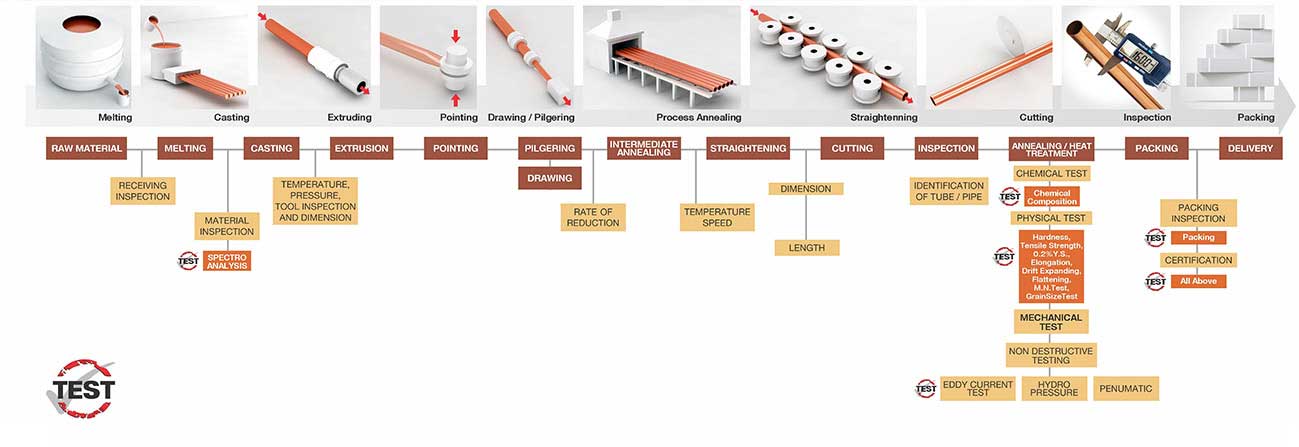
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Copper to PVC Couplings (Quality & IP)
Sourcing copper to PVC couplings may seem straightforward, but overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) factors can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and legal risks. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Non-Compliance
Using substandard materials is one of the most frequent and dangerous issues. Low-quality couplings may use impure copper alloys or inferior PVC, leading to premature corrosion, cracking, or joint failure under pressure or temperature fluctuations. Always verify compliance with recognized standards such as ASTM B68, ASTM D1785, or NSF/ANSI 61 for potable water applications. Couplings that lack proper certification may not withstand operational demands, risking leaks or contamination.
Inadequate Thread or Connection Integrity
A common quality flaw is poorly machined threads or inconsistent internal diameters. This can result in cross-threading, incomplete seals, or restricted flow. Couplings with weak or brittle solder joints (in solder-type fittings) are prone to cracking during installation or thermal cycling. Always inspect samples for smooth threading, uniform wall thickness, and precise tolerances before bulk ordering.
Misrepresentation of Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Some suppliers misstate the pressure (PSI) and temperature limits of couplings, especially those designed for transition between dissimilar materials. Copper to PVC couplings must accommodate differential expansion rates. Using a coupling beyond its rated capacity—particularly in hot water systems—can cause joint separation or burst failures. Always cross-check manufacturer specifications and ensure ratings match your application requirements.
Lack of Intellectual Property Due Diligence
Sourcing from unauthorized or counterfeit manufacturers can expose buyers to IP infringement risks. Reputable coupling designs, trademarks, and certifications are often protected. Purchasing counterfeit or cloned products not only violates IP laws but also compromises reliability and traceability. Always source from authorized distributors or manufacturers and request documentation proving authenticity and licensing.
Ignoring Regional Code and Certification Requirements
Building and plumbing codes vary by region (e.g., UPC in the U.S., WRAS in the UK). A coupling compliant in one jurisdiction may not meet another’s standards. Failure to verify local code acceptance can result in failed inspections or liability issues. Ensure products carry region-specific certifications (e.g., UPC, CSA, WRAS) relevant to your project location.
Inconsistent Quality Control from Overseas Suppliers
When sourcing internationally, inconsistent manufacturing practices can lead to batch-to-batch variability. Without third-party inspection or ISO certification (e.g., ISO 9001), there’s a higher risk of receiving non-conforming products. Implement supplier audits, request material test reports, and conduct incoming quality checks to mitigate this risk.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in vetting suppliers, verifying certifications, and prioritizing long-term performance over initial cost savings.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Copper to PVC Coupling
This guide provides essential information for the proper handling, transportation, and regulatory compliance when dealing with Copper to PVC Couplings in supply chain operations.
Product Overview
Copper to PVC couplings are plumbing fittings used to join copper and PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They typically consist of a copper side (for soldering or press connection) and a PVC side (for solvent welding). These fittings are commonly used in water supply, irrigation, and HVAC systems.
Packaging and Handling
- Packaging: Couplings are generally supplied in bulk packs, boxes, or shrink-wrapped bundles. Packaging must be moisture-resistant and durable to prevent damage during transit.
- Handling Precautions: Avoid dropping or crushing packages. Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent warping of PVC components and oxidation of copper.
- Labeling: Each package must include product specifications (size, type, material), manufacturer details, batch/lot number, and handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”).
Storage Requirements
- Environment: Store indoors away from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and humidity. UV exposure can degrade PVC over time.
- Shelving: Use dry, ventilated shelving. Avoid floor contact to prevent moisture absorption.
- Shelf Life: PVC components may degrade over extended periods; recommend rotation based on FIFO (First In, First Out) principles. Check manufacturer guidelines for specific shelf life.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, rail, sea, and air freight. Ensure containers are sealed and protected from weather.
- Stacking: Do not exceed recommended stack heights to prevent crushing lower layers.
- Temperature Control: Avoid prolonged exposure to temperatures above 60°C (140°F) or below freezing during transit, which may affect material integrity.
- Documentation: Include packing lists, commercial invoices, and safety data sheets (SDS) where required.
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards
- ASTM Standards: Comply with ASTM B88 (for copper tubes) and ASTM D1785 or ASTM D2846 (for PVC pipes and fittings).
- NSF/ANSI 61: Certifies product safety for drinking water applications. Required in the U.S. and many other markets.
- CSA B137.5: Canadian standard for plastic piping materials.
Regional Requirements
- United States: Must meet Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) or International Plumbing Code (IPC) standards. NSF certification is often mandatory.
- European Union: Subject to Construction Products Regulation (CPR) and may require CE marking. REACH and RoHS compliance for material safety.
- Australia/New Zealand: Comply with AS/NZS 2468 and AS/NZS 3500 plumbing codes.
Hazardous Materials Classification
- Copper to PVC couplings are generally non-hazardous for transport.
- PVC may release toxic fumes if burned, but intact fittings do not require hazardous labeling under IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations.
Customs and Import Documentation
- HS Code: Typically classified under 7412.10 (copper pipe fittings) or 3917.23 (PVC fittings), depending on dominant material. Confirm based on composition and country-specific tariff schedules.
- Required Documents:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Conformity (NSF, ASTM, etc.)
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
- Import Permits (if required by destination country)
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- Recyclability: Copper is highly recyclable; PVC can be recycled in designated facilities. Disassemble mixed-material fittings where possible.
- Waste Disposal: Follow local regulations for plastic and metal waste. Do not incinerate PVC due to dioxin emissions.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
- Batch Tracking: Maintain traceability through batch/lot numbers for recall readiness.
- Inspection: Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify dimensions, material quality, and compliance markings.
- Supplier Certification: Source from manufacturers with ISO 9001 and relevant product certifications.
Emergency Procedures
- Spill or Damage: In case of package damage, segregate affected units. No special spill response needed unless solvents or adhesives are involved.
- Fire Response: Use water spray to cool containers. Avoid breathing fumes from burning PVC.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for Copper to PVC couplings ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and customer safety. Emphasis should be placed on correct packaging, environmental controls, certification validation, and accurate documentation throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Copper to PVC Coupling:
Sourcing copper to PVC couplings requires careful consideration of material compatibility, application requirements, local plumbing codes, and environmental conditions. These fittings serve a critical function in transitioning between rigid copper piping and durable PVC systems, commonly used in plumbing, irrigation, and drainage applications. When selecting a supplier or product, it is essential to ensure compliance with industry standards such as ASTM or NSF, particularly for potable water systems.
Options such as brass or dielectric fittings with appropriate thread types (e.g., sweat x threaded or solvent weld x threaded) should be evaluated based on installation method and system pressure. Additionally, proper installation techniques—including the use of dielectric unions to prevent galvanic corrosion—are vital for long-term reliability.
After evaluating suppliers, cost, durability, and availability, it is recommended to source copper to PVC couplings from reputable manufacturers and certified distributors. This ensures product quality, adherence to safety standards, and performance consistency. Ultimately, a well-sourced coupling contributes to a leak-free, efficient, and code-compliant plumbing system.