The global copper PVC (polyvinyl chloride) composite market has experienced steady growth, driven by rising demand in electrical wiring, plumbing, and HVAC systems across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global copper market size was valued at USD 146.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by increasing urbanization and infrastructure development. Simultaneously, the global PVC market, as reported by Mordor Intelligence, was valued at over USD 55 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% through 2028, supported by its cost-effectiveness and durability in construction and electrical applications. As demand for reliable, corrosion-resistant, and electrically efficient materials rises, copper-PVC hybrid solutions—especially in cables and piping—have emerged as critical components across industries. This confluence of market forces has positioned key manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and production scalability. Below are the top 10 copper PVC manufacturers shaping the industry through technological advancement, strategic market presence, and commitment to quality.
Top 10 Copper Pvc Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Mueller Industries
Domain Est. 1996
Website: muellerindustries.com
Key Highlights: Mueller Industries, Inc. is an industrial manufacturer that specializes in copper and copper alloy manufacturing while also producing goods made from aluminum, ……
#2 Sioux Chief: Rough Plumbing Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: siouxchief.com
Key Highlights: SiouxChief.com. American made rough plumbing products that save time and money on the job….
#3 JM Eagle™
Domain Est. 2007
Website: jmeagle.com
Key Highlights: JM Eagle · Delivering life’s essentials through the most eco-friendly plastic pipe products on the market. · Express Service Trucks (ESTs) Deliver within 24 hours ……
#4 PVC Coated Copper Pipe Manufacturer, Dealer, Exporter in the USA
Domain Est. 2017
Website: kanchansales.com
Key Highlights: Kanchan Copper Industries is one of the prominent PVC Coated Copper Pipe Manufacturers, Dealers, and Exporters operating in the USA….
#5 Westlake Pipe
Domain Est. 2021
Website: westlakepipe.com
Key Highlights: From PVC pipe to fittings, Westlake Pipe is pioneering the piping industry, developing innovations that propel your business forward faster and more ……
#6 PVC Pipe Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: unitedpipe.com
Key Highlights: With our wide range of inventory, you can break bundles to meet weight minimums and match your PVC pipe products with copper or steel for delivery to your store ……
#7 Spears Manufacturing, PVC & CPVC Plastic Pipe Fittings & Valves
Domain Est. 1996
Website: spearsmfg.com
Key Highlights: ISO9001 Certified – PVC & CPVC Sch 40 and 80 fittings molded from 1/8 – 14 inch….
#8 PVC & Copper Pipe
Domain Est. 1997
Website: herculesindustries.com
Key Highlights: PVC & Copper Pipe … A hose is a flexible hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes where the word ……
#9 Copper
Domain Est. 2002
Website: adani.com
Key Highlights: Explore Adani’s high-quality copper offerings, supporting industries with essential materials for electrical, construction, and manufacturing sectors….
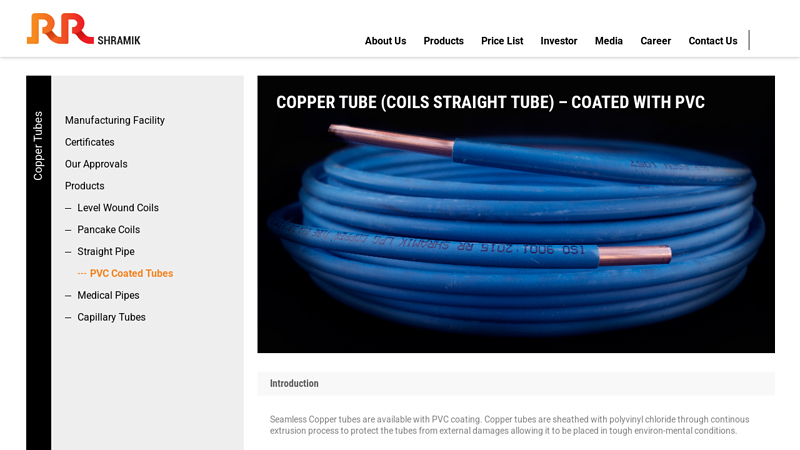
#10 PVC Coated Tubes
Domain Est. 2009
Website: rrshramik.com
Key Highlights: Seamless Copper tubes are available with PVC coating. Copper tubes are sheathed with polyvinyl chloride through continous extrusion process to protect the tubes ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Copper Pvc

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Copper and PVC
As the global economy continues to evolve through technological advancement, infrastructure development, and sustainability initiatives, the demand for key industrial materials such as copper and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is expected to undergo significant shifts by 2026. Both materials remain integral to construction, electrical systems, and emerging green technologies, but their market dynamics are being shaped by distinct supply-demand fundamentals, regulatory environments, and macroeconomic trends.
Copper Market Trends (2026 Outlook):
-
Rising Demand from Electrification and Renewable Energy:
Copper is a cornerstone of the global energy transition. By 2026, demand is projected to grow robustly, driven by electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy installations (solar and wind), and grid modernization. EVs use up to four times more copper than internal combustion engine vehicles, and expanding charging infrastructure will further amplify demand. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), copper demand from clean energy technologies alone could double by 2030, placing 2026 as a pivotal year for supply chain readiness. -
Supply Constraints and Geopolitical Risks:
Despite rising demand, copper supply faces challenges. Major mining regions—including Chile and Peru—are experiencing operational disruptions, water scarcity, and increasing regulatory scrutiny. New mine development is capital-intensive and time-consuming, often taking 10–15 years from discovery to production. By 2026, supply deficits may emerge unless investment in exploration and mining accelerates. Recycling will play a growing role, but secondary supply alone cannot close the gap. -
Price Volatility and Investment Interest:
Copper prices are expected to remain volatile through 2026, influenced by macroeconomic factors, the strength of the U.S. dollar, and speculative trading. However, long-term fundamentals remain bullish. Institutional investors and sovereign funds are increasingly allocating capital to copper as a strategic asset, anticipating supply shortfalls. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and physical holdings may rise. -
Technological and Substitution Pressures:
While aluminum and fiber optics serve as partial substitutes in certain applications, copper’s superior conductivity and durability limit substitution in high-performance uses. Innovations in copper recycling and efficiency improvements in manufacturing may help alleviate pressure, but are unlikely to significantly reduce net demand.
PVC Market Trends (2026 Outlook):
-
Steady Growth in Construction Sector:
PVC remains one of the most widely used plastics globally, primarily in construction for piping, window profiles, flooring, and insulation. Urbanization in Asia, Africa, and Latin America will continue to drive demand. In developed markets, aging infrastructure and renovation activities will support PVC consumption. By 2026, the global PVC market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4–5%, with rigid PVC (used in construction) dominating. -
Environmental and Regulatory Challenges:
The environmental footprint of PVC—particularly concerns around chlorine use, dioxin emissions during production, and end-of-life disposal—is under increased scrutiny. Regulations such as the EU’s Green Deal and REACH are pushing for safer additives and circular economy practices. By 2026, demand may shift toward bio-based or recyclable PVC alternatives, and manufacturers will need to adopt more sustainable practices to remain competitive. -
Feedstock Cost Volatility:
PVC is derived from chlorine and ethylene (from oil or natural gas), making it sensitive to energy prices. With the global push toward decarbonization, natural gas markets—especially in North America and Europe—could see volatility that impacts PVC production costs. However, cheaper shale gas in the U.S. continues to provide a competitive advantage for North American PVC producers. -
Recycling and Circular Economy Initiatives:
Recycling rates for PVC are improving, especially in Europe through programs like VinylPlus. By 2026, closed-loop recycling systems are expected to expand, reducing reliance on virgin material and meeting corporate sustainability targets. Innovations in chemical recycling may further enhance PVC’s lifecycle sustainability.
Conclusion:
By 2026, both copper and PVC markets will be shaped by the dual forces of infrastructure growth and environmental responsibility. Copper is poised for structural demand growth due to electrification, despite supply-side risks. PVC will maintain steady demand in construction, but must navigate tightening environmental regulations and the need for sustainable innovation. Companies investing in responsible sourcing, recycling, and energy-efficient production will be best positioned to thrive in the evolving 2026 landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Copper PVC (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Copper PVC (typically referring to copper conductors with Polyvinyl Chloride insulation, often in cables or wiring) requires careful attention to both material quality and Intellectual Property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, legal risks, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Substandard Copper Conductors
Using impure or undersized copper reduces conductivity, increases resistance, and leads to overheating. Suppliers may substitute with lower-grade copper (e.g., oxygen-free copper vs. recycled copper) or misrepresent cross-sectional area, compromising electrical efficiency and safety compliance.
2. Inferior PVC Insulation
Low-quality PVC may lack proper flame retardancy, UV resistance, or flexibility. It can degrade prematurely under heat or environmental stress, leading to insulation failure, short circuits, or fire hazards. Ensure PVC meets standards like UL, IEC, or BS for dielectric strength and thermal rating.
3. Inadequate Testing and Certification
Procuring cables without verified third-party testing (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS) risks non-compliance with safety and environmental regulations. Some suppliers provide fake or outdated certifications, exposing buyers to liability.
4. Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Variability in extrusion, stranding, or jacketing processes affects product reliability. Poor workmanship increases the likelihood of defects such as air gaps, inconsistent thickness, or mechanical weakness.
5. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Without proper batch tracking and material test reports (MTRs), it becomes difficult to verify origin, perform root cause analysis during failures, or comply with industry audits.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Patented Designs or Technologies
Some cable designs, shielding methods, or manufacturing processes may be protected by patents. Sourcing from suppliers using such IP without licensing exposes the buyer to infringement claims, especially in regulated markets.
2. Counterfeit or Knockoff Products
Suppliers may replicate branded cables (e.g., mimicking well-known trademarks or performance specs) without authorization. These counterfeit products often fail to meet stated performance claims and can lead to legal action if distributed under false pretenses.
3. Misrepresentation of Compliance Marks
Using counterfeit or unlicensed certification marks (e.g., fake UL labels) constitutes IP violation and misleads end-users about safety and compliance. This poses legal and safety risks.
4. Breach of Confidentiality and Design Theft
When providing custom specifications or proprietary designs to suppliers, inadequate contractual protections can lead to IP theft, reverse engineering, or unauthorized reproduction by the supplier or third parties.
5. Inadequate Supplier IP Due Diligence
Failing to audit suppliers for IP compliance—such as verifying patent licenses, trademark rights, or freedom to operate—can result in downstream liability, product recalls, or import bans.
Mitigation Strategies
- Require detailed material specifications and test reports from suppliers.
- Conduct independent lab testing on sample batches.
- Audit suppliers’ manufacturing facilities and certification status.
- Include IP warranties and indemnification clauses in contracts.
- Work with reputable, certified suppliers and avoid unusually low bids.
- Consult legal experts to assess IP risks, especially for custom or high-volume procurement.
By addressing both quality and IP pitfalls proactively, organizations can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and legal protection in their Copper PVC sourcing.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Copper PVC
H2: Overview
Copper PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) typically refers to cables or conduits that incorporate copper conductors encased in a PVC insulation jacket. These products are widely used in electrical and construction industries due to their conductivity, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Proper logistics and compliance management is essential to ensure safe handling, regulatory adherence, and timely delivery.
H2: Transportation & Handling
– Packaging: Copper PVC cables must be packaged on wooden or plastic reels, secured with protective end caps, and wrapped to prevent moisture ingress and mechanical damage.
– Storage Conditions: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (ideally 5°C to 35°C). Avoid direct sunlight and extreme humidity to prevent PVC degradation.
– Handling: Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts with reel clamps) to avoid deformation. Do not drop or drag reels.
– Transportation Modes: Suitable for road, rail, sea, and air freight. Reels must be secured to prevent rolling or shifting during transit.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensure PVC insulation is free from restricted substances such as lead, cadmium, and phthalates (where applicable).
– REACH (EU Regulation): Confirm that all chemical components in PVC comply with REACH regulations, including registration and safe use of SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern).
– IEC Standards: Copper PVC cables must meet international standards such as IEC 60227 (for PVC-insulated cables) and IEC 60245 (for rubber-insulated, but often referenced).
– National Electrical Codes: Comply with local regulations (e.g., NEC in the U.S., BS 7671 in the UK) for insulation thickness, conductor size, and fire resistance.
H2: Import/Export Documentation
– Commercial Invoice: Must include product description, HS code (e.g., 8544.49 for insulated copper wire), value, and origin.
– Packing List: Detail reel sizes, weights, lengths, and packaging type.
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC): Required in many countries to prove compliance with safety and technical standards.
– Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Essential for shipment tracking and customs clearance.
– Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS): Required if PVC contains any regulated chemicals.
H2: Environmental & Safety Considerations
– Fire Safety: PVC emits toxic fumes (e.g., hydrogen chloride) when burned. Ensure proper labeling and handling instructions for fire risk.
– Recycling & Disposal: Copper is recyclable; PVC requires specialized processing. Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in the EU and local e-waste regulations.
– Worker Safety: Provide PPE during handling to protect against sharp edges and PVC dust (if cutting).
H2: Labeling & Traceability
– Clearly label reels with:
– Manufacturer name and batch number
– Conductor size (e.g., 2.5 mm²)
– Voltage rating (e.g., 300/500V)
– Standards met (e.g., IEC 60227)
– “RoHS Compliant” or equivalent
– Maintain batch traceability for quality control and recall readiness.
H2: Audit & Certification
– Regular third-party audits to verify compliance with ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management).
– Obtain product certifications such as CE (Europe), UL (USA), or CCC (China) as required by the target market.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance guide, businesses can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient distribution of Copper PVC products across global markets.
In conclusion, sourcing copper PVC (typically referring to PVC-insulated copper wire or cable) requires a careful evaluation of material quality, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. Copper remains the preferred conductor due to its excellent electrical conductivity, durability, and thermal performance, while PVC insulation offers cost-effective, flexible, and flame-retardant properties suitable for a wide range of electrical applications.
To ensure a successful procurement process, buyers should prioritize certified suppliers who adhere to international standards such as IEC, ASTM, or BS. Conducting thorough due diligence—assessing product specifications, price competitiveness, lead times, and sustainability practices—helps mitigate risks related to counterfeit materials or substandard products. Additionally, building long-term relationships with trusted manufacturers can lead to better pricing, consistent quality, and improved supply chain resilience.
Ultimately, strategic sourcing of copper PVC cables not only supports reliable electrical system performance but also contributes to project efficiency, safety, and long-term cost savings.