The global coolant for radiator market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising automotive production, increasing demand for high-performance engine cooling solutions, and stringent emission regulations. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global engine coolant market was valued at USD 10.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates the market will expand further due to growing industrialization and the proliferation of heavy-duty vehicles, with the Asia Pacific region leading in both consumption and production. As engine efficiency and longevity become critical performance indicators, manufacturers are investing heavily in advanced coolant formulations that offer superior thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and extended service life. Against this backdrop, nine leading coolant manufacturers have emerged as innovators, setting industry benchmarks in quality, performance, and technological advancement.
Top 9 Coolant For The Radiator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Coolants
Domain Est. 2005
Website: aisinaftermarket.com
Key Highlights: From the world’s number one maker of OE water pumps, AISIN Extended Life Coolant meets global OEM specifications and is suitable for all car makes and models….
#2 CSF Radiators
Domain Est. 2009
Website: csfradiators.com
Key Highlights: CSF manufactures high quality OEM replacement radiators, condensers, intercoolers, transmission oil coolers and more!…
#3 OEM
Domain Est. 2021
Website: oemeasymatch.com
Key Highlights: Specifically designed to match the needs of your car, OEM fluids keep your vehicle performing at its best. Drive with confidence. Drive with OEM. ANTIFREEZE/ ……
#4 PEAK® All Vehicles Antifreeze + Coolant
Domain Est. 1995
Website: owi.com
Key Highlights: PEAK® All Vehicles Antifreeze + Coolant is formulated to protect all cooling system metals, including aluminum. It immediately protects against damaging rust ……
#5 Prestone® Antifreeze+Coolant
Domain Est. 1996
Website: prestone.com
Key Highlights: Prestone® Antifreeze+Coolant prevents corrosion and keeps your radiator performing optimally. PROTECTED. 200,000 mi. Ordinary Coolant. BUILDUP & CLOGGING….
#6 VP Racing Coolants & Coolant Additives
Domain Est. 1998
#7 Engine Ice
Domain Est. 2000
Website: engineice.com
Key Highlights: Superior heat reduction for maximum performance. Engine Ice Hi-Performance Coolant provides superior heat transfer to maximize horsepower output in all ……
#8 Antifreeze & Coolants
Domain Est. 2014
Website: lubricants.totalenergies.com
Key Highlights: Discover our premium range of antifreeze and coolants to provide the most suitable protection for your engine and extend the life of your vehicle….
#9 Antifreeze & Coolant
Domain Est. 2022
Website: valvolineglobal.com
Key Highlights: Learn more about Valvoline’s #1 selling coolant and antifreeze. Whether you’re topping off your radiator or doing a complete system flush, you can trust Zerex….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Coolant For The Radiator
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Coolant for the Radiator
The global market for radiator coolant in 2026 is shaped by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory developments, and evolving consumer demands. As automotive industries transition toward electrification and sustainability, the role and composition of coolants are undergoing significant transformation. Below are the key trends expected to define the radiator coolant market in 2026:
1. Shift Toward Environmentally Friendly Formulations
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness are driving demand for eco-friendly coolant solutions. In 2026, there is a growing preference for biodegradable, low-toxicity coolants made from organic acid technology (OAT) and hybrid organic acid technology (HOAT). These formulations reduce environmental impact during production, use, and disposal. Governments in Europe and North America are enforcing stricter emissions and waste disposal standards, further accelerating the adoption of green coolants.
2. Increased Demand in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
While EVs do not use traditional engine radiators, they require advanced thermal management systems for batteries, power electronics, and motors. In 2026, radiator coolant manufacturers are expanding product lines to include dielectric coolants and specialized thermal fluids compatible with EV components. The surge in EV production globally is creating new revenue streams for coolant producers, with demand expected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% from 2021 to 2026.
3. Longer-Lasting and High-Performance Coolants
Extended-life coolants that offer protection for up to 150,000 miles or five years are becoming standard. Innovations in additive packages and inhibitor technologies enhance corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and compatibility with aluminum and copper components. Fleet operators and OEMs are prioritizing coolants that reduce maintenance frequency and downtime, especially in commercial and heavy-duty vehicles.
4. Regional Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia, is the fastest-growing market for radiator coolant in 2026. Rapid urbanization, rising vehicle ownership, and expanding manufacturing hubs are fueling demand. Local production of coolants is increasing to meet cost-efficiency goals, while multinational brands are forming joint ventures to penetrate emerging markets.
5. Integration of Smart Monitoring and Coolant Diagnostics
With the rise of connected vehicles and predictive maintenance, coolant systems are being integrated with sensors to monitor pH levels, concentration, and contamination in real-time. In 2026, smart coolant systems provide alerts for maintenance needs, improving engine longevity and performance. This trend is particularly prominent in premium and commercial vehicle segments.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Innovation
The coolant industry is adapting to supply chain challenges by diversifying sources of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. There is also increased R&D into bio-based glycols derived from renewable feedstocks, supporting sustainability goals and reducing dependence on petrochemicals.
7. OEM Partnerships and Custom Formulations
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are collaborating closely with coolant suppliers to develop proprietary formulations optimized for specific engine designs and operating conditions. These custom coolants improve efficiency and are often required to maintain warranty compliance, giving OEM-preferred brands a competitive advantage.
In summary, the 2026 radiator coolant market is characterized by innovation, sustainability, and adaptation to new propulsion technologies. While traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles still dominate coolant demand, the future lies in multifunctional, intelligent, and environmentally responsible thermal fluids that support both ICE and electric mobility ecosystems.
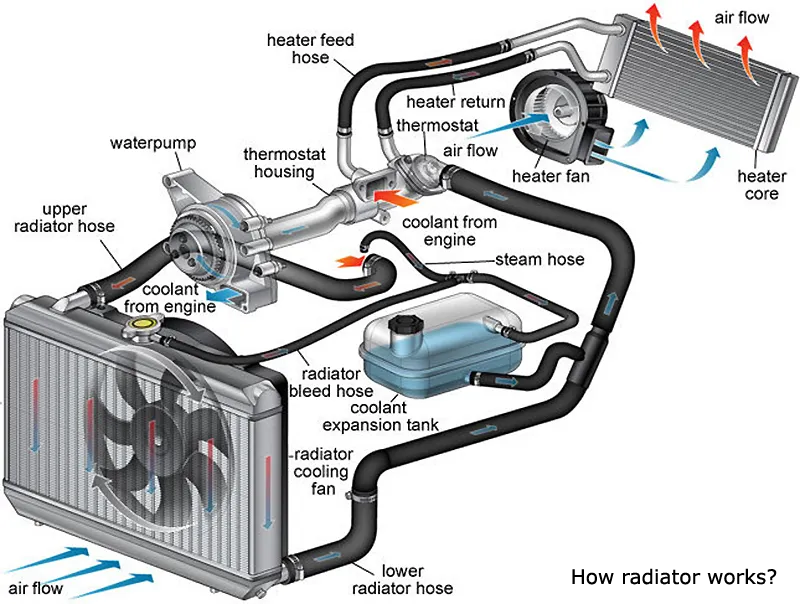
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Coolant for the Radiator (Quality, IP)
Sourcing the right coolant for radiator applications is critical for maintaining engine performance and longevity. However, several pitfalls can compromise quality and intellectual property (IP), leading to operational failures, safety risks, and legal issues. Below are the most common challenges:
Poor Quality Formulations
One of the most frequent issues is procuring coolant with substandard chemical composition. Low-quality coolants may lack adequate corrosion inhibitors, have incorrect glycol concentrations (ethylene or propylene), or use impure water sources. This can lead to internal corrosion, scale buildup, and reduced heat transfer efficiency, ultimately causing radiator and engine damage.
Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality
Suppliers—especially low-cost or unverified manufacturers—may not maintain consistent production standards. Variability in pH levels, inhibitor package concentration, or freeze/boil protection ranges between batches can result in unpredictable performance and premature system failure.
Misrepresentation of Specifications
Some suppliers falsely claim compliance with industry standards such as ASTM D3306, D4985, or OEM-specific requirements (e.g., G12, G48). This mislabeling can lead to incompatibility with engine materials, voiding warranties, and increased maintenance costs.
Counterfeit or Grey Market Products
The coolant market is vulnerable to counterfeit goods that mimic reputable brands. These products often lack proper formulation and testing. Purchasing through unauthorized distributors increases the risk of receiving fake or diluted coolants that do not meet required performance benchmarks.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
OEMs and specialty coolant formulators often hold patents or proprietary rights over unique additive packages and formulations. Sourcing coolant from third parties that reverse-engineer or illegally replicate these formulas poses significant IP risks. Using such products may expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated or commercial applications.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable coolants should come with certificates of analysis (CoA), safety data sheets (SDS), and batch traceability. Suppliers who cannot provide these documents may be cutting corners, making it difficult to verify quality or respond to failures during audits or investigations.
Inadequate Technical Support
Choosing a supplier without strong technical expertise can lead to incorrect product selection. Coolants vary based on climate, engine type, and materials used (e.g., aluminum vs. copper radiators). Without proper guidance, buyers may select incompatible coolants, risking system damage.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, always source coolant from reputable, certified suppliers with transparent quality control processes and respect for intellectual property. Verify certifications, demand full documentation, and ensure alignment with OEM or industry standards to protect both equipment performance and legal compliance.
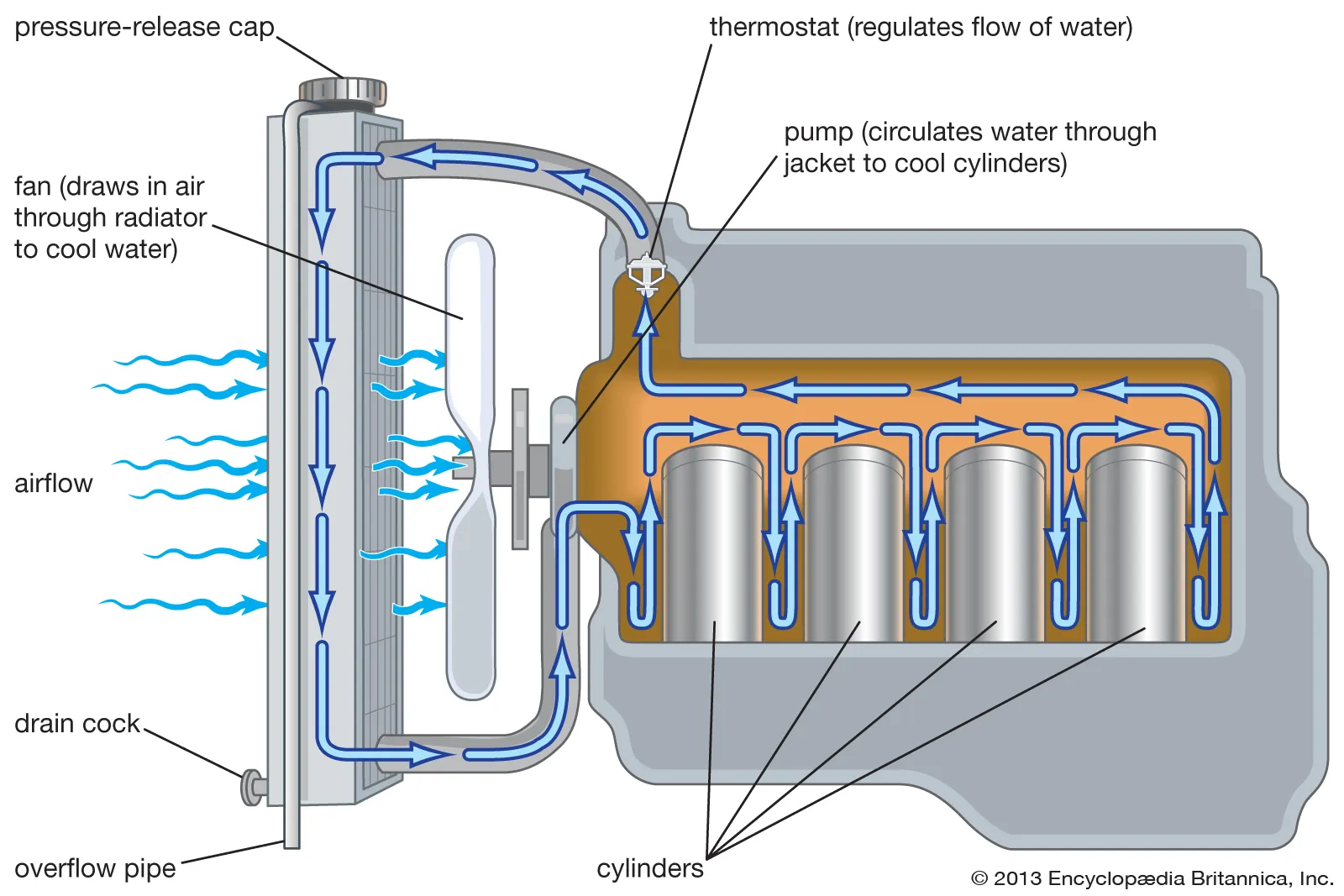
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Coolant for the Radiator
Handling, transporting, and storing coolant for radiators requires careful attention to logistics and regulatory compliance due to its chemical composition and potential environmental and health hazards. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant management of radiator coolant throughout the supply chain.
-
Classification & Hazard Identification
-
Chemical Composition: Most radiator coolants are based on ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, mixed with water and corrosion inhibitors.
- Hazard Classification (GHS):
- Flammable: Typically non-flammable, but may emit flammable vapors when heated.
- Acute Toxicity: Ethylene glycol is highly toxic if ingested.
- Environmental Hazard: Toxic to aquatic life; may cause long-term adverse effects.
-
Skin/Eye Irritation: May cause irritation upon prolonged contact.
-
Regulatory Compliance
-
UN Number: UN 1993 (Ethylene glycol solutions, flammable liquid, n.o.s.) or UN 3082 (Environmentally hazardous substance, liquid, n.o.s.), depending on formulation.
- Transport Regulations:
- Road (ADR): Class 3 (Flammable liquids) or Class 9 (Environmentally hazardous substances).
- Air (IATA): Compliance with IATA DGR, typically Class 9 or Class 3.
- Sea (IMDG): Class 9 (Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles).
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet): Must be available per GHS standards (16-section format) and provided to all handlers, transporters, and end-users.
- Country-Specific Regulations:
- U.S.: EPA, OSHA, and DOT regulations (49 CFR).
- EU: REACH, CLP, and ADR compliance.
-
Canada: WHMIS 2015 and TDG regulations.
-
Packaging & Labeling
-
Packaging: Use UN-certified containers resistant to corrosion (e.g., HDPE drums or IBCs).
- Labeling Requirements:
- GHS pictograms (toxicity, environmental hazard).
- Signal word: “Danger” or “Warning”.
- Hazard and precautionary statements.
- Proper shipping name and UN number.
-
Supplier identification.
-
Storage Guidelines
-
Environment: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Compatibility: Keep away from strong oxidizers, acids, and alkalis.
- Secondary Containment: Use spill pallets or bunded storage to prevent environmental contamination.
-
Fire Safety: No open flames; use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation if stored in large quantities.
-
Transportation Best Practices
-
Vehicle Requirements: Use vehicles equipped with spill containment and proper placarding.
- Segregation: Do not transport with foodstuffs, oxidizing agents, or incompatible chemicals.
- Documentation: Include transport documents, SDS, and emergency response information.
-
Driver Training: Ensure drivers are trained in hazardous materials handling (e.g., ADR certification).
-
Spill Response & Emergency Procedures
-
Spill Kit: Maintain spill kits with absorbents, neutralizers, and PPE nearby.
- Response Steps:
- Contain spill immediately using absorbent materials.
- Avoid entry into waterways or drains.
- Ventilate area and avoid inhalation.
- Report significant spills to local authorities as required.
-
PPE: Use gloves (nitrile), goggles, and protective clothing during handling.
-
Disposal & Waste Management
-
Do not dispose of coolant into sewers or the environment.
- Recycle where possible through approved reprocessing facilities.
-
If disposal is necessary, use licensed hazardous waste handlers compliant with local regulations (e.g., EPA, EEA).
-
Training & Documentation
-
Personnel Handling: Provide training on SDS, GHS, and emergency procedures.
-
Recordkeeping: Maintain logs of inventory, transport, spills, training, and disposal.
-
Sustainability & Environmental Responsibility
-
Promote use of biodegradable or propylene glycol-based coolants where feasible.
- Encourage closed-loop recycling programs to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management of radiator coolant helps prevent accidents, ensures regulatory adherence, and protects human health and the environment. Always consult local, national, and international regulations, and update procedures as formulations or laws evolve.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate coolant for a radiator is a critical step in maintaining the efficiency, longevity, and safe operation of any cooling system, whether in automotive, industrial, or HVAC applications. It is essential to select a coolant that is compatible with the radiator material and the system’s operating conditions, such as temperature range and pressure. Factors such as coolant type (ethylene glycol-based, propylene glycol-based, or organic acid technology), concentration, additives, and manufacturer specifications should be carefully considered. Additionally, sourcing coolant from reputable suppliers ensures quality, consistency, and adherence to industry standards. Regular maintenance and monitoring of coolant levels and condition further support optimal performance. By making informed decisions when sourcing coolant, users can prevent corrosion, overheating, and system failures, ultimately extending the lifespan of the radiator and improving overall system reliability.