The global conveyor belt market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing automation in retail and grocery distribution. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global conveyor system market was valued at USD 7.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2029, fueled by demand for efficient material handling solutions in supermarkets and distribution centers. As grocery retailers prioritize speed, accuracy, and operational efficiency, conveyor belt systems have become integral to checkout automation, backroom logistics, and order fulfillment in both brick-and-mortar and e-grocery models. This rising adoption has spurred innovation among manufacturers specializing in food-safe, durable, and energy-efficient conveyor solutions. Based on industry performance, technological capability, and market reach, the following eight manufacturers have emerged as leaders in supplying conveyor belt systems tailored specifically for grocery retail environments.
Top 8 Conveyor Belt Grocery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Supermarket Conveyor Belt
Domain Est. 2007
Website: hongsbelt.com
Key Highlights: We’ve got more than 10 years experience of production and export business. We always develop and design kinds of novel items to meet the market demand and help ……
#2 Industrial Conveyor Belting
Domain Est. 1998
Website: beltpower.com
Key Highlights: We supply industrial conveyor belting that keeps the manufacturing and distribution sectors moving forward, conveying everything INCLUDING the kitchen sink….
#3 Conveyor belts for the food industry
Domain Est. 1996
Website: forbo.com
Key Highlights: Our high-quality, conveyor belts are the result of in-depth process expertise. Custom-developed for the food industry, they will help you produce food safely ……
#4 Esbelt Conveyor Belts for Food Applications
Domain Est. 1996
Website: esbelt.com
Key Highlights: Esbelt offers a wide range of food conveyor belts that suit the specific needs of the diverse production processes that exist in the food industry….
#5 Conveyor Handling Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: conveyorhandling.com
Key Highlights: CHC is a full line material handling systems integrator, providing custom designed solutions for those material handling challenges….
#6 Grocery Store Conveyor Belts & Casters
Domain Est. 2003
Website: miprcorp.com
Key Highlights: Conveyor belts and casters are essential to keeping today’s supermarkets and grocery store chains running smoothly. Contact us to learn more….
#7 Food Grade Conveyor Belts for Food Handling and Processing
Domain Est. 2007
Website: dornerconveyors.com
Key Highlights: Food conveyors for bakery, confectionery, RTE, meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy. Provides custom engineered solutions designed for specific applications….
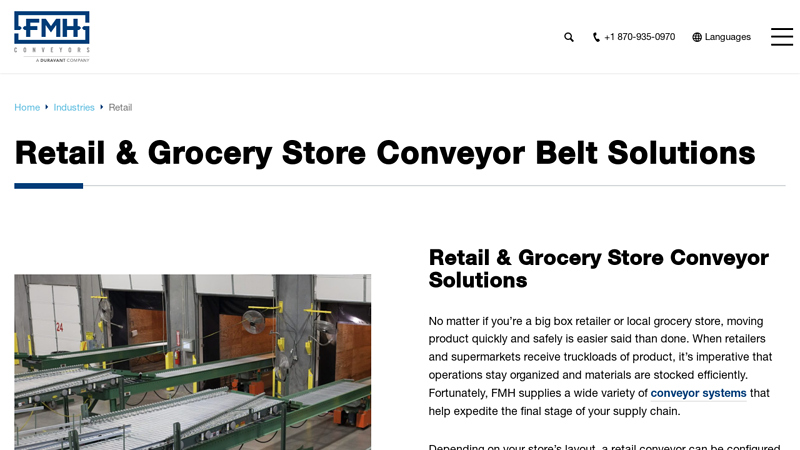
#8 Retail & Grocery Store Conveyor Belt Solutions
Domain Est. 2014
Website: fmhconveyors.com
Key Highlights: FMH Conveyors provides grocery store and retail conveyor belt systems that streamline restocking, reduce labor, and improve efficiency….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Conveyor Belt Grocery

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Conveyor Belt Grocery
By 2026, the conveyor belt grocery market (often referred to as conveyor belt supermarkets or automated retail formats) is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer behaviors, and intensified competition. While still a niche compared to traditional grocery retail, key trends will shape its trajectory:
-
Accelerated Integration of AI and Computer Vision:
- Trend: AI-powered checkout systems will become the de facto standard, moving beyond simple barcode scanning to sophisticated item recognition using computer vision and deep learning.
- Impact: This will drastically reduce friction, enabling true “just walk out” experiences where customers grab items and leave without any manual scanning or payment interaction. Expect fewer errors in identifying produce, bulk items, or similar-looking packaged goods, improving accuracy and consumer trust. AI will also optimize inventory management by predicting demand patterns for individual items on the belt.
-
Expansion of Product Assortment & Premiumization:
- Trend: Moving beyond basic snacks and beverages, conveyor belt stores will expand into higher-margin, fresher, and more diverse categories.
- Impact: Expect greater availability of fresh produce, prepared meals, chilled items (using integrated cooling on belts or adjacent stations), artisanal goods, health-focused snacks, and even limited household essentials. This caters to evolving consumer demands for convenience and quality, blurring the lines between convenience stores and mini-markets.
-
Focus on Sustainability and Waste Reduction:
- Trend: Sustainability will be a major competitive differentiator. This includes reducing food waste inherent in the conveyor model and minimizing packaging.
- Impact: Advanced inventory algorithms will dynamically adjust rotation speeds based on real-time sales data to minimize spoilage. Partnerships with food rescue organizations for unsold items will become standard. Expect a noticeable shift towards reusable containers for prepared foods and bulk items, potentially integrated with deposit schemes. Stores may highlight their “low-waste” credentials as a key marketing message.
-
Strategic Location Diversification and Niche Targeting:
- Trend: Expansion beyond high-traffic transit hubs (airports, train stations) into diverse urban and suburban locations.
- Impact: Growth in office complexes, university campuses, residential buildings (as a building amenity), hotels, and mixed-use developments. Operators will increasingly target specific demographics (e.g., tech campuses for younger professionals, retirement communities for seniors valuing convenience) and tailor assortments accordingly.
-
Enhanced Personalization and Loyalty Integration:
- Trend: Leveraging customer data (opt-in) to move from anonymous transactions to personalized experiences.
- Impact: Mobile apps will offer personalized recommendations based on past purchases displayed on the app or suggested via in-store screens. Dynamic pricing or instant discounts for preferred items could be pushed to app users. Seamless integration with broader retail loyalty programs will be crucial for customer retention.
-
Increased Competition and Consolidation:
- Trend: The market will see more entrants (tech startups, traditional retailers experimenting) alongside existing players like Zippin, Trigo, and Standard Cognition.
- Impact: Intensified competition will drive innovation but may also lead to consolidation as smaller players struggle with high technology and operational costs. Partnerships between technology providers and established grocery chains (like Amazon Go influencing others) will become more common, accelerating adoption but potentially diluting the pure “conveyor belt” model.
-
Hybrid Models and Omnichannel Integration:
- Trend: Pure conveyor belt stores may evolve into hybrid formats or become integrated components within larger stores.
- Impact: We may see conveyor belts used for high-turnover items in traditional supermarkets, or conveyor belt stores incorporating pickup points for online grocery orders. The technology (AI checkout) might be more widely adopted than the literal conveyor belt, becoming a feature within various store formats.
Conclusion for 2026:
By 2026, conveyor belt grocery will be less about the novelty of the moving belt and more about the seamless, automated, and increasingly personalized shopping experience it enables. Success will hinge on mastering AI accuracy, expanding into fresher and more desirable product categories, demonstrating tangible sustainability benefits, and achieving critical scale through strategic partnerships or consolidation. While unlikely to displace traditional grocery, it will establish a significant foothold in the convenience and urban quick-commerce segments, redefining expectations for speed, ease, and technology integration in everyday shopping.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Conveyor Belt Grocery Systems (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing conveyor belt systems for grocery applications involves complex considerations, particularly regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Companies often encounter challenges that can compromise performance, safety, and legal compliance if not addressed proactively. Below are key pitfalls to avoid in both quality and IP aspects.
1. Overlooking Material Quality and Food-Grade Compliance
One of the most frequent quality pitfalls is selecting conveyor belts made from non-food-grade materials. In grocery environments—especially those handling produce, meat, or packaged goods—belts must comply with FDA, USDA, or EU food safety standards. Using non-compliant materials can lead to contamination, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
2. Inadequate Belt Durability for Operational Demands
Grocery conveyors often run for extended hours and transport varied load types. Sourcing belts without assessing abrasion resistance, load capacity, or temperature tolerance can lead to premature wear, increased downtime, and higher maintenance costs.
3. Poor Supplier Verification and Lack of Certifications
Failing to verify supplier credentials—such as ISO certifications, third-party testing reports, or compliance documentation—can expose businesses to substandard products. Unverified suppliers may offer lower prices but deliver inconsistent quality or counterfeit components.
4. Ignoring Hygiene and Cleanability Features
In grocery settings, hygiene is critical. Belts with hard-to-clean surfaces, crevices, or porous materials can harbor bacteria and biofilms. Selecting belts without considering clean-in-place (CIP) compatibility or antimicrobial properties is a major oversight.
5. Underestimating Environmental and Operational Conditions
Operating environment factors—such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to cleaning chemicals—are often underestimated. Belts not rated for specific conditions may degrade quickly, leading to safety hazards and frequent replacements.
6. Infringing on Patented Conveyor Technologies
Many advanced conveyor systems incorporate patented designs, such as specific belt tracking mechanisms, modular configurations, or sanitation features. Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate these designs without licensing can result in IP infringement lawsuits, product seizures, or forced redesigns.
7. Using Generic Components That Mimic Branded Systems
Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “equivalent” conveyor parts that closely resemble proprietary systems (e.g., from major brands like Intralox or Habasit). While seemingly cost-effective, these may violate design patents or trademarks, exposing the buyer to legal risk even if the supplier is overseas.
8. Lack of Documentation and Traceability
Proper IP and quality assurance require clear documentation, including material traceability, manufacturing origin, and patent disclaimers. Sourcing without these records makes it difficult to verify authenticity or defend against IP claims.
9. Choosing Solely on Price Without Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Low upfront cost often masks long-term expenses related to maintenance, replacement, and downtime. Additionally, cheaply sourced belts may incorporate infringing technology, leading to unforeseen legal costs.
10. Failure to Conduct IP Due Diligence
Before finalizing a supplier, businesses should perform IP audits—reviewing patents, trademarks, and design rights related to the conveyor system. Skipping this step increases the risk of inadvertently sourcing counterfeit or infringing products.
Conclusion
To avoid quality failures and IP exposure when sourcing grocery conveyor belt systems, businesses must conduct thorough supplier evaluations, prioritize food-grade and durable materials, and verify both compliance and intellectual property rights. A proactive approach ensures long-term reliability, regulatory adherence, and legal safety.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Conveyor Belt Grocery
Overview
Conveyor Belt Grocery systems streamline the movement of goods from storage to point-of-sale or packaging by utilizing automated conveyor belts. Efficient logistics and strict regulatory compliance are critical to ensure food safety, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction. This guide outlines best practices for managing logistics and maintaining compliance in such environments.
Equipment & Infrastructure Requirements
Ensure all conveyor systems are constructed from food-grade, non-porous, and corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or FDA-approved polymers. Regular maintenance schedules must be established to inspect belts, motors, and support structures for wear and contamination risks. Conveyor systems should include clean-in-place (CIP) capabilities or be easily disassembled for cleaning.
Food Safety & Hygiene Standards
Adhere to FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) guidelines and local health department regulations. Conveyor belts must be cleaned and sanitized between product runs, especially when handling allergens or raw vs. ready-to-eat items. Implement a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan specific to conveyor operations, identifying contamination risks and mitigation protocols.
Temperature Control & Cold Chain Management
For perishable goods, maintain proper temperature zones along the conveyor path. Use insulated enclosures and refrigerated conveyor sections where necessary. Install temperature monitoring devices at key points and integrate data logging systems to ensure compliance with cold chain requirements (e.g., 0–4°C for refrigerated items, ≤-18°C for frozen).
Product Segregation & Allergen Control
Designate separate conveyor lines or implement rigorous cleaning procedures when switching between allergen-containing and allergen-free products. Clearly label conveyor zones and use color-coded belts or signage to prevent cross-contact. Train staff on allergen handling protocols and emergency shutdown procedures.
Packaging & Labeling Compliance
Ensure all products moved via conveyor belts have accurate, legible labeling meeting FDA and USDA standards. Labels must include product name, ingredients, allergen statements, net weight, and expiration dates. Implement automated label verification systems at discharge points to catch errors before distribution.
Staff Training & Operational Procedures
Train all personnel on conveyor safety, hygiene practices, and emergency stop protocols. Provide ongoing education on food safety regulations and equipment handling. Document all training and maintain records for audit purposes.
Recordkeeping & Audit Readiness
Maintain detailed logs of equipment maintenance, cleaning schedules, temperature monitoring, staff training, and incident reports. Ensure records are securely stored and readily accessible for internal or regulatory audits. Implement a digital tracking system for traceability from source to sale.
Regulatory Compliance Checklist
- [ ] FDA FSMA preventive controls implemented
- [ ] HACCP plan in place and updated annually
- [ ] Compliance with 21 CFR Part 117 (Current Good Manufacturing Practice)
- [ ] OSHA-compliant safety guards and emergency stops installed
- [ ] USDA or local health department inspections passed
- [ ] Allergen control and sanitation logs up to date
Continuous Improvement & Technology Integration
Leverage IoT sensors and warehouse management systems (WMS) to monitor conveyor performance, detect bottlenecks, and predict maintenance needs. Use data analytics to optimize throughput and reduce waste. Regularly review compliance protocols and update them in response to regulatory changes or operational feedback.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance in Conveyor Belt Grocery operations require a proactive approach to equipment maintenance, food safety, staff training, and regulatory adherence. By following this guide, grocery operations can ensure safe, efficient, and compliant product handling from warehouse to customer.
Conclusion:
Sourcing a conveyor belt system for a grocery operation is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance efficiency, improve customer experience, and streamline in-store logistics. By carefully evaluating suppliers, considering factors such as durability, customization, ease of maintenance, and cost-effectiveness, retailers can select a solution that aligns with their operational needs and long-term goals. Automation through conveyor systems not only reduces labor strain at checkout points but also supports faster service, minimizes errors, and contributes to a more organized shopping environment. Ultimately, the right conveyor belt system, when properly integrated, serves as a valuable asset in optimizing grocery store performance and maintaining a competitive edge in the evolving retail landscape.