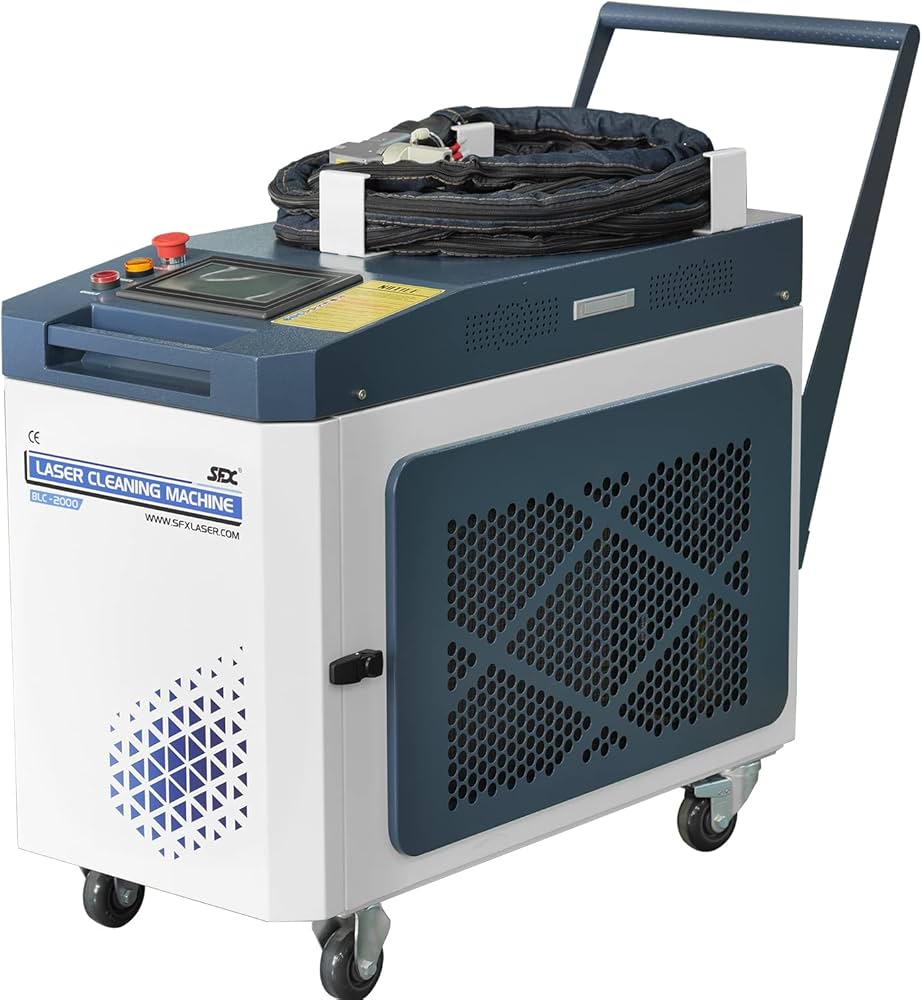
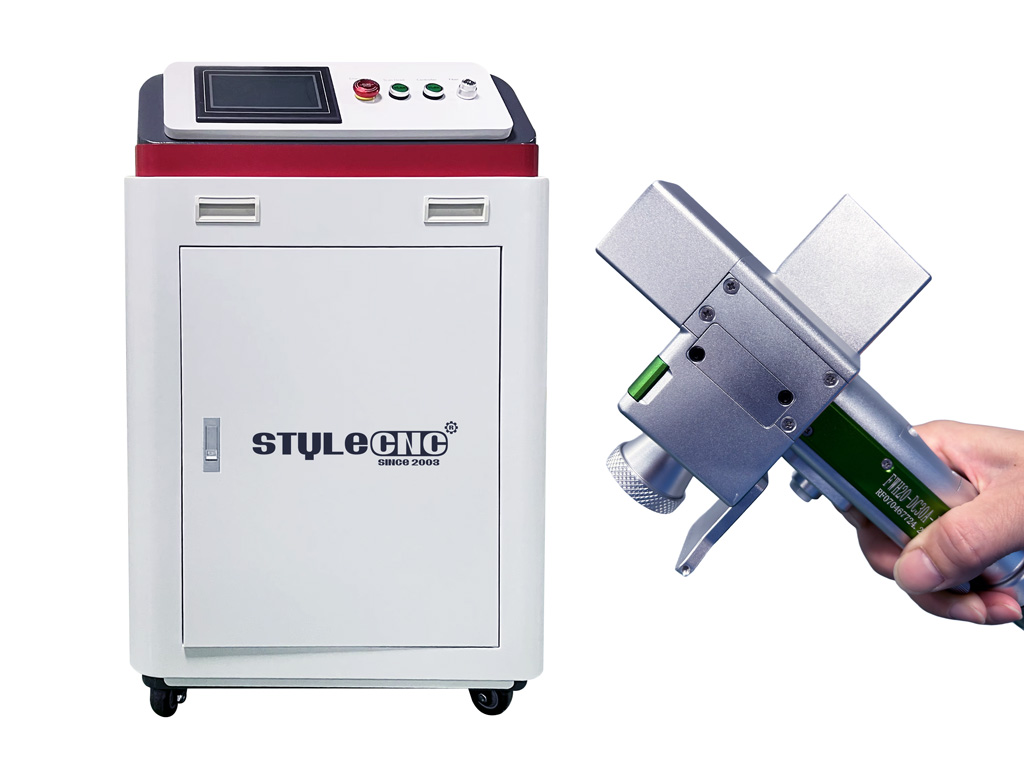
The global laser cleaning machine market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precise, and low-maintenance surface treatment solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 462.8 million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 1.15 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.3% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the shift away from traditional cleaning methods—such as sandblasting and chemical solvents—toward non-abrasive, automation-compatible alternatives that reduce waste and improve operational efficiency. Continuous wave (CW) laser cleaning machines, in particular, are gaining traction due to their ability to deliver stable, uninterrupted cleaning performance ideal for large-scale industrial applications. As adoption rises, a competitive landscape of manufacturers has emerged, with key players investing in R&D to enhance power output, portability, and integration with robotics. Here are the top 10 continuous laser cleaning machine manufacturers shaping the future of industrial surface preparation.
Top 10 Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Continuous Laser Cleaning Machines
Website: nuwavelaser.com
Key Highlights: Our Continuous Laser Cleaning Machines optimize your industrial cleaning with advanced technology for rust removal, steel stripping….
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Our laser cleaning machines are complete solutions with fume extraction, laser safety, performance optimization, and more. They are ready for robot lines, ……
#3 Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: Laser cleaning machines manufactured by PULSAR Laser are available in four dedicated product series: SHARK P CL – a universal professional laser cleaning ……
#4 SFX Laser
Website: sfxlaser.com
Key Highlights: SFX Laser is a 20+ years professional laser equipment manufacturer including laser cleaning machine, laser welding machine, fiber laser engraver, ……
#5 Industrial 1500W 2000W CW Laser Cleaning Machine Rusty Remove
Website: xinglaser.com
Key Highlights: XING Laser (6am Life LLC, DBA XING Laser) specializes in the development and manufacture of high-performance handheld laser cleaning and rust removal equipment….
#6 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser Photonics offers continuous wave (CW) laser systems for industrial cleaning applications. These units are designed for heavy duty, speedy surface ……
#7 Laser Cleaning Machine Manufacturers
Website: fortunelaser.com
Key Highlights: FL-C1000 Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine · Fortunelaser FL-C6000 6000W Continuous Wave Laser Cleaning Machine · Mopa 3-in-1 Backpack Pulse Laser Cleaner · FL-C300N ……
#8 Argento Lux
Website: argentolux.com
Key Highlights: Our company provides state-of-the-art Industrial Laser Equipment Sales and Mobile Laser Cleaning Services for a wide range of applications and industries….
#9 LC
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: This continuous laser equipment removes impurities with precision without damaging the material. It is ideal for sectors such as automotive, metallurgy, and ……
#10 Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine
Website: triumphlaser.com
Key Highlights: The pulse laser cleaning machine represents a cutting-edge solution designed for efficient and precise surface cleaning. Utilizing high-intensity, ultra-short ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Continuous Laser Cleaning Machines
The global market for continuous laser cleaning machines is poised for substantial transformation and expansion by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing environmental regulations, and rising demand across key industrial sectors. This analysis outlines the major trends expected to shape the continuous laser cleaning machine market in 2026.
-
Increased Industrial Automation and Integration
By 2026, continuous laser cleaning systems are expected to be more seamlessly integrated into automated production lines, particularly in the automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication industries. The push for Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing will drive demand for laser cleaning solutions that offer real-time monitoring, remote operation, and compatibility with robotic arms and IoT-enabled control systems. -
Expansion into New Application Segments
While traditionally used for rust, paint, and oxide removal, continuous laser cleaning machines are projected to expand into new applications by 2026, including nuclear decontamination, cultural heritage restoration, and semiconductor manufacturing. The non-abrasive, precision nature of laser cleaning makes it ideal for sensitive or high-value components, broadening its market reach. -
Growing Emphasis on Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Processes
Environmental regulations are tightening worldwide, with increasing restrictions on chemical cleaning methods and dry-ice blasting due to waste and emissions. Continuous laser cleaning, which produces no secondary waste and uses only light and minimal energy, aligns with green manufacturing goals. By 2026, regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability targets will accelerate adoption, especially in Europe and North America. -
Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency and Accessibility
Ongoing improvements in fiber laser technology—such as higher power outputs (up to 10 kW and beyond), improved beam quality, and enhanced cooling systems—are expected to make continuous laser cleaning faster, more reliable, and cost-effective. Additionally, modular and portable designs will increase accessibility for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), reducing the total cost of ownership. -
Regional Market Growth and Manufacturing Shifts
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will remain a high-growth region due to rapid industrialization and government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will lead in adopting high-end systems for precision applications. Localized production of laser components is also expected to reduce costs and supply chain dependencies by 2026. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market will likely see increased competition and consolidation, with major players acquiring niche innovators to expand their technological portfolios. Key vendors are expected to focus on R&D and strategic partnerships to differentiate their offerings through AI-driven process optimization, predictive maintenance, and cloud-based analytics. -
Cost Reduction and ROI Improvements
As production scales and component costs decline, the upfront investment for continuous laser cleaning machines is expected to decrease. Simultaneously, operational savings—such as reduced labor, consumables, and downtime—will improve return on investment (ROI), making laser cleaning a more attractive alternative to traditional methods.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the continuous laser cleaning machine market will be characterized by broader industrial adoption, enhanced technological capabilities, and strong alignment with environmental and automation trends. Companies that innovate in system integration, energy efficiency, and application-specific solutions will be best positioned to capture market share in this rapidly evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing a Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine (Quality and IP)
Sourcing a continuous laser cleaning machine involves significant investment and technical complexity. Overlooking critical aspects related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to performance issues, legal risks, and long-term operational setbacks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Underestimating Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many suppliers offer machines that appear cost-effective upfront but use substandard components. Poorly sourced laser sources, galvanometers, cooling systems, or mechanical frames can result in frequent breakdowns, inconsistent cleaning performance, and high maintenance costs. Always verify the origin and specifications of core components—especially the fiber laser module—and request reliability data or MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) metrics.
2. Inadequate Power and Duty Cycle Validation
Continuous laser cleaning demands stable, sustained output. Some machines may advertise high peak power but fail under continuous operation due to thermal throttling or inadequate cooling. Ensure the supplier provides tested performance data under continuous duty cycles relevant to your application. Request real-world test reports or on-site demonstrations using your actual workpieces.
3. Lack of Proper Safety and Compliance Certifications
Low-quality or non-compliant machines may lack essential safety features such as interlocks, emergency stops, laser shielding, or proper fume extraction integration. Verify that the machine meets international safety standards (e.g., IEC 60825 for laser safety, CE, FDA, or local regulations). Non-compliant systems pose safety hazards and may not be insurable or legally operable in your region.
4. Hidden IP Infringement Risks
Some suppliers, particularly in regions with lax IP enforcement, may use cloned or reverse-engineered laser control systems, scanning heads, or software algorithms. Purchasing such equipment exposes your company to legal liability, especially in export markets like the EU or U.S. where IP enforcement is strict. Always require documentation proving original design and ownership, including patents, software licenses, and component authenticity certificates.
5. Proprietary Software Lock-in and Limited Control
Many machines come with closed-source software that restricts customization, data access, or integration with existing production systems. This creates dependency on the supplier for updates, troubleshooting, or process optimization. Evaluate whether the machine supports open communication protocols (e.g., Modbus, Ethernet/IP) and inquire about SDK availability for in-house development.
6. Insufficient After-Sales Support and Technical Documentation
Poor-quality suppliers often lack comprehensive technical documentation, training programs, or accessible support channels. This becomes critical when troubleshooting or scaling operations. Confirm that manuals, maintenance guides, and firmware updates are provided in your language, and that the supplier offers responsive technical assistance—preferably with local service partners.
7. Overlooking IP in Customized Solutions
If you request machine modifications or process-specific configurations, ensure that any resulting IP developed during customization is clearly assigned. Ambiguity in contracts may result in the supplier claiming ownership of process innovations, limiting your competitive advantage. Use clear contractual terms to define IP ownership for custom developments.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, buyers can secure reliable, legally sound laser cleaning systems that support long-term operational success and innovation.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine
Introduction
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, import/export, handling, and operation of Continuous Laser Cleaning Machines. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe, legal, and efficient deployment across international and domestic markets.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine under the Harmonized System (HS) Code for customs purposes. Common classifications may fall under 8515 (Electro-thermic appliances) or 8479 (Machines having individual functions, not elsewhere specified). Confirm the correct code with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker. Required documentation includes:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Technical Specifications Sheet
– Laser Safety Certification (e.g., IEC 60825-1)
– Declaration of Conformity (CE, UKCA, or other regional marks as applicable)
Laser Safety Compliance
The machine must comply with international and regional laser safety standards:
– IEC 60825-1: Classification of laser products — Safety of laser products.
– FDA 21 CFR Part 1040.10 and 1040.11 (for U.S. market): Performance standards for laser products.
– EN 60825-1 (for EU market): European adaptation of IEC 60825-1.
Ensure the machine is properly labeled with laser class (typically Class 4), warning symbols, and safety instructions. Provide a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) manual and risk assessment documentation where required.
Transportation and Packaging
Due to the sensitive optical and electronic components, the machine must be:
– Packed in robust, shock-absorbent, and moisture-resistant packaging.
– Shipped on pallets with clear orientation and handling labels (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack”).
– Protected against vibration and extreme temperatures during transit.
For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if applicable (e.g., lithium batteries or high-power lasers). Most industrial laser systems are exempt if properly classified, but documentation must confirm non-hazardous status.
Import and Export Controls
Verify export control requirements based on the machine’s technical specifications:
– ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) under the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL) — typically 6A003.b.4 for high-power lasers used in industrial cleaning.
– Dual-Use Regulation (EU): Check if the machine falls under Annex I of Regulation (EU) 2021/821.
A license may be required for export to restricted countries or end-users. Conduct end-user screening and maintain records per EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or equivalent.
Electrical and EMC Compliance
Ensure compliance with regional electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and EMC Directive (2014/30/EU).
– UKCA Marking (UK): For post-Brexit UK market.
– UL/CSA (North America): Certification to UL 61010-1 or similar.
– PSE Mark (Japan): For the Japanese market.
Provide test reports from accredited laboratories where required.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Upon delivery:
– Verify site readiness (power supply, ventilation, workspace dimensions).
– Conduct a site safety audit to ensure compliance with local occupational health and safety regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK).
– Install appropriate safety barriers, interlocks, and emergency stops per ISO 13849-1 (Safety of machinery — Safety-related parts of control systems).
– Provide operator training on laser safety, maintenance, and emergency procedures.
– Maintain a log of all maintenance and safety checks.
Environmental and Waste Management
Dispose of packaging materials according to local environmental regulations. For end-of-life machines, follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive (EU) or equivalent for proper recycling of electronic and optical components. Do not incinerate laser optical parts.
After-Sales and Service Compliance
Ensure service technicians are certified and carry proper documentation when performing maintenance or repairs internationally. Spare parts must also comply with relevant safety and import standards. Maintain traceability of all components for compliance audits.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are critical to the successful deployment of Continuous Laser Cleaning Machines. Always consult with legal, customs, and safety experts in the target market to ensure full adherence to all applicable rules and standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Continuous Laser Cleaning Machine
After a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, performance requirements, supplier capabilities, and cost considerations, sourcing a continuous laser cleaning machine emerges as a strategic investment to enhance operational efficiency, improve cleaning quality, and support sustainable manufacturing practices. The selected machine offers consistent, non-abrasive, and environmentally friendly cleaning suitable for high-throughput applications across various materials, reducing downtime and eliminating the need for chemical solvents.
Key advantages include minimal maintenance, long-term cost savings, and compatibility with automated production lines. Based on supplier reliability, after-sales support, warranty terms, and successful pilot testing, the recommended supplier provides the optimal balance of performance, durability, and value.
In conclusion, procuring the specified continuous laser cleaning machine aligns with our goals of advancing technological capability, ensuring worker safety, and achieving long-term operational excellence. Implementation is advised with proper staff training and integration planning to maximize return on investment and realize full process benefits.