The global contact lens market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising prevalence of vision disorders, increased aesthetic demand for cosmetic lenses, and technological advancements in lens materials. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 11.62 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the market size reached USD 12.1 billion in 2022 and anticipates a CAGR of 5.1% over the same period, citing growing myopia rates and the popularity of daily disposable lenses as key drivers. Amid this upward trajectory, a select group of manufacturers lead innovation, production scale, and market penetration. Here are the top 10 contact lens manufacturers shaping the future of vision correction worldwide.
Top 10 Contact Lens Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Contact Us
Domain Est. 1996
Website: coopervision.com
Key Highlights: Contact CooperVision customer support or professional services. Includes CooperVision email, address and phone for the contact lens manufacturer….
#2 Manufacturers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: contactsdirect.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryThe MANUFACTURERS page includes all the contact lenses from several brands: Acuvue, Dailies, Biofinity, Air Optix, Bausch and Lomb, Proclear, Clariti and Fresh ……
#3 Art Optical Contact Lens, Inc.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: artoptical.com
Key Highlights: Intended for: · Myopia management · Up to -5.00D myopia correction · 1.50D astigmatism correction · Approved for overnight orthokeratology by the US FDA….
#4 ABB Contact Lens
Domain Est. 1998
Website: abboptical.com
Key Highlights: Abby makes it simple for patients and doctors to order contact lenses from every major manufacturer — and offers direct to patient shipping ……
#5 Contact Lens Manufacturers Association
Domain Est. 1999
Website: clma.net
Key Highlights: The Contact Lens Manufacturers Association (CLMA), organized in 1961, is made up of contact lens laboratories and material, solution and equipment manufacturers ……
#6 SynergEyes
Domain Est. 2003
Website: synergeyes.com
Key Highlights: SynergEyes is the provider of High Performance, Advanced Technology Specialty and Hybrid Contact Lenses For Astigmatism, Presbyopia and Keratoconus….
#7 Specialty and Gas Permeable Contact Lenses
Domain Est. 1995
Website: bausch.com
Key Highlights: A family of custom soft contact lenses that combine innovative lens features and technologies to address patients with vision needs beyond standard parameters….
#8 CooperVision
Domain Est. 1996
Website: coopercos.com
Key Highlights: CooperVision is a global leader in the contact lens industry, dedicated to helping improve the way people see each day….
#9 Alcon
Domain Est. 1998
Website: alcon.com
Key Highlights: Our mission is to provide innovative vision products that enhance quality of life by helping people see better. From vision research to eye health, ……
#10 Johnson & Johnson Vision for Eye Care Professionals
Domain Est. 2017
Website: jnjvisionpro.com
Key Highlights: J&J Vision Pro, your go-to resource for eye care professionals. Access cutting-edge products, educational materials, and expert support in one platform….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Contact Lens

H2 2026 Market Trends for the Contact Lens Industry
As we approach the second half of 2026, the global contact lens market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological innovation, shifting consumer preferences, demographic changes, and evolving retail landscapes. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Daily Disposables & Silicone Hydrogel Dominance:
* Hygiene & Convenience: Daily disposable lenses continue to dominate new user acquisition and existing user conversion. Concerns about hygiene, ease of use (no cleaning required), and reduced risk of complications solidify their position as the preferred modality, particularly among younger demographics (Gen Z, Millennials).
* Material Innovation: Silicone hydrogel remains the gold standard material, offering superior oxygen permeability. Innovations focus on improving surface wettability, deposit resistance, and mechanical strength within daily disposable formats, enhancing comfort and wear time.
2. Smart Contact Lenses: From Hype to Niche Reality:
* Medical Applications Lead: While consumer-focused AR/VR smart lenses remain distant, H2 2026 sees tangible progress in medically-oriented smart lenses. Products focused on glaucoma monitoring (measuring intraocular pressure continuously) and diabetic management (non-invasive glucose sensing via tears) are moving through late-stage clinical trials or entering limited commercialization in specific regulated markets.
* Data Integration: Early adopters are beginning to see integration of smart lens data (e.g., IOP trends) with electronic health records and patient apps, enabling proactive management. Regulatory hurdles (FDA, EMA) remain significant, limiting widespread availability, but the proof-of-concept phase is maturing.
3. Personalization and Customization Gaining Traction:
* Beyond Standard Parameters: Demand is growing for lenses tailored to specific needs: enhanced optics for presbyopia (using advanced multifocal or extended depth of focus designs), optimized lenses for astigmatism (toric), and lenses designed for specific ocular surface conditions (dry eye, irregular corneas).
* Digital Eye Strain Solutions: Lenses incorporating features specifically aimed at mitigating digital eye strain – such as optimized blue light filtering (with proven efficacy), enhanced contrast, or designs reducing accommodative demand during near work – are becoming more prominent, driven by increased screen time.
4. Sustainability Becomes a Competitive Imperative:
* Packaging Focus: Major manufacturers are actively reducing plastic in blister packs and secondary packaging, switching to recyclable materials (e.g., paperboard, mono-materials) and minimizing overall packaging volume. Clear communication of sustainability efforts is becoming crucial for brand image.
* Recycling Programs Expand: Take-back and recycling programs (e.g., Bausch + Lomb’s ONE by ONE, CooperVision’s Recycle Your Contacts) are becoming more established and geographically widespread, addressing consumer and regulatory pressure regarding plastic waste.
* Material R&D: Long-term R&D is exploring more biodegradable lens materials, though significant commercial availability is still likely years away.
5. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) & Omnichannel Evolution:
* DTC Maturation: Pure DTC players continue to grow, leveraging digital marketing and subscription models. However, they face increasing competition from traditional players and heightened regulatory scrutiny regarding eye health and prescription compliance.
* Omnichannel Dominance: The most successful players offer seamless experiences: online ordering with home delivery, easy prescription renewals via telehealth partnerships, and integration with brick-and-mortar optometry practices (e.g., “buy online, pick up in store,” practice dispensing online). The ECP (Eye Care Professional) remains central to the patient journey for exams, fittings, and trust.
6. Growth in Emerging Markets & Addressing Unmet Needs:
* Asia-Pacific Focus: Rapid urbanization, rising disposable incomes, increasing myopia prevalence (especially in youth), and growing access to eye care are driving significant market expansion in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asia. Localized marketing and pricing strategies are key.
* Myopia Management: While primarily driven by ortho-k and specialty spectacles, contact lenses (especially soft multifocal designs and novel daily disposables) are a growing segment within the broader myopia management market, particularly for older children and teens.
7. Integration of AI and Data Analytics:
* Fitting & Design: AI is increasingly used in lens design optimization and predictive modeling for fitting success, especially for complex prescriptions (high astigmatism, presbyopia).
* Supply Chain & Retail: Enhanced demand forecasting, personalized marketing, and inventory optimization using AI are improving efficiency for manufacturers and retailers.
* Patient Engagement: Apps leveraging data from wear patterns (where available) and user feedback to provide personalized wear tips and reminders are becoming more sophisticated.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The contact lens market in the second half of 2026 is characterized by consolidation around daily disposables, enhanced comfort, and convenience, while significant innovation pushes forward in smart medical lenses and personalized solutions. Sustainability is no longer optional but a core brand differentiator. Success requires a sophisticated omnichannel strategy that respects the vital role of the ECP while meeting digital-native consumers’ expectations. The market is poised for steady growth, fueled by technological advancements, expanding access in emerging economies, and the ongoing need for vision correction and eye health solutions.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Contact Lenses: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing contact lenses, whether for retail, private labeling, or distribution, involves navigating complex regulatory and legal landscapes. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to significant risks, including product recalls, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Regulatory Compliance
Contact lenses are classified as medical devices in most jurisdictions (e.g., Class II devices in the U.S. under FDA regulation and Class IIa/IIb in the EU under MDR). A major sourcing pitfall is partnering with manufacturers that lack proper certifications such as FDA 510(k) clearance, CE marking, or ISO 13485 certification. Sourcing non-compliant lenses can result in shipment seizures, import bans, or legal liability.
Poor Manufacturing Standards
Even if a supplier claims compliance, inconsistent quality control processes can lead to defective lenses—such as incorrect prescriptions, surface imperfections, or material inconsistencies. These defects pose health risks like corneal abrasions or infections. Always conduct on-site audits or third-party inspections to verify Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) adherence.
Substandard Materials and Design
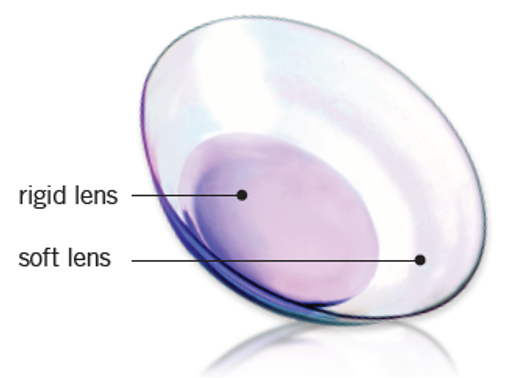
Some low-cost suppliers may use inferior hydrogel or silicone hydrogel materials that reduce oxygen permeability, increasing the risk of hypoxia and eye discomfort. Additionally, sourcing lenses with unproven or poorly designed geometries (e.g., edge design, curvature) can compromise fit and safety. Ensure materials and designs are clinically validated and meet international standards.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reliable suppliers must provide full documentation, including batch numbers, sterilization records, and shelf-life data. Poor traceability increases the risk during recalls and hampers compliance with post-market surveillance requirements.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Technologies
Many contact lens innovations—such as proprietary lens materials (e.g., silicone hydrogels), surface treatments (e.g., plasma coating for wettability), or manufacturing processes—are protected by patents. Sourcing lenses that replicate these technologies without licensing can expose your business to infringement lawsuits, especially in markets like the U.S. and EU.
Counterfeit or Grey Market Products
Beware of suppliers offering well-known brands at unusually low prices. These may be counterfeit, expired, or diverted “grey market” goods. Distributing such products violates trademark laws and can damage your brand’s credibility and customer trust.
Private Labeling Without IP Clearance
When developing a private-label contact lens, ensure your design does not infringe on existing patents or trademarks. Conduct a freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis before finalizing product specifications. Additionally, verify that your supplier respects your brand’s trademark rights and does not re-sell identical products under another label.
Weak Contractual IP Protections
Supplier agreements must clearly define IP ownership, especially for custom designs or formulations. Ambiguous contracts may result in disputes over who owns tooling, molds, or product specifications—potentially allowing competitors to access your innovations.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Verify certifications (FDA, CE, ISO) and conduct due diligence on suppliers.
- Perform independent product testing for optical accuracy, material quality, and biocompatibility.
- Consult legal experts to conduct IP risk assessments and draft robust supply agreements.
- Maintain thorough documentation throughout the sourcing and distribution chain.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, businesses can ensure safe, compliant, and legally secure contact lens sourcing.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Contact Lenses
Regulatory Classification and Approvals
Contact lenses are classified as medical devices in most jurisdictions, typically falling under Class II (moderate risk) in the United States (regulated by the FDA) and Class IIa or IIb in the European Union (regulated under the EU MDR). Manufacturers and distributors must ensure that all contact lenses are approved or cleared by the relevant regulatory authority before sale. In the U.S., this involves obtaining 510(k) clearance or PMA approval. In the EU, CE marking under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745 is required. Each product must have a unique device identifier (UDI) for traceability.
Import and Export Documentation
International shipping of contact lenses requires comprehensive documentation to ensure compliance. Essential documents include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and regulatory permits (e.g., FDA Import Notification for the U.S., CE Certificate for the EU). For controlled goods, an export license may be required depending on the destination country. Always verify import regulations in the destination market, as some countries require local representation or pre-market authorization.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Packaging must comply with local and international regulations. Labels should include the product name, power (diopter), base curve, diameter, material composition, expiration date, UDI, and manufacturer details. In the U.S., labels must adhere to FDA 21 CFR Part 801, including adequate directions for use and cautionary statements. Multilingual labeling is required in regions like the EU and Canada. Tamper-evident, sterile packaging is mandatory to maintain product integrity.
Storage and Transportation Conditions
Contact lenses must be stored and transported under controlled conditions to preserve sterility and efficacy. Most lenses require storage at room temperature (typically 15–25°C or 59–77°F), away from direct sunlight and moisture. Transport containers must be sealed and designed to prevent physical damage. Temperature monitoring devices should be used during transit, especially in extreme climates. Cold chain logistics are not typically required unless specified by the manufacturer.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Contact lenses may be subject to customs duties, import taxes, and excise fees depending on the destination country. Accurate HS (Harmonized System) code classification is essential—common codes include 9001.30 (optical instruments and lenses) or 9021.31 (optical contact lenses). Work with customs brokers to ensure proper valuation and compliance with trade agreements. Be prepared for inspections, particularly for medical devices, which may involve additional documentation or sampling.
Distribution and Fulfillment Compliance
Distributors must be licensed if required by local law (e.g., wholesale distributor license in certain U.S. states). Online sales must comply with e-commerce regulations, including age verification and prescription validation where applicable. Direct-to-consumer fulfillment should include secure packaging, discreet shipping, and compliance with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) when handling patient information. Returns must follow strict hygiene and safety protocols; opened or used lenses generally cannot be resold.
Recordkeeping and Traceability
Maintain detailed records for at least 5–10 years (depending on jurisdiction), including batch numbers, expiration dates, distribution logs, and adverse event reports. Implement a robust UDI system to enable rapid traceability in the event of a recall. All parties in the supply chain—from manufacturer to distributor—must be able to track and trace products through each transaction.
Adverse Event Reporting and Recalls
Establish procedures for monitoring and reporting adverse events to regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EUDAMED in the EU). In the event of a product defect or safety issue, initiate a recall in accordance with local requirements. Recall plans must include communication strategies for distributors, retailers, and end users, as well as coordination with regulatory authorities.
Training and Staff Compliance
Ensure all personnel involved in logistics, handling, and distribution are trained in medical device regulations, GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) standards, and company-specific SOPs. Regular audits and compliance checks help maintain adherence to regulatory requirements and minimize risk.
Sustainability and Disposal
Develop environmentally responsible practices for packaging (e.g., recyclable materials) and collaborate with manufacturers on take-back or recycling programs for lens cases and solution bottles. Proper disposal of expired or damaged lenses in accordance with medical waste regulations is essential to prevent environmental contamination.
Conclusion: Sourcing Contact Lens Manufacturer
After thorough evaluation of potential contact lens manufacturers, it is evident that selecting the right partner requires careful consideration of regulatory compliance, manufacturing capabilities, product quality, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Manufacturers based in regions with strong regulatory frameworks—such as the United States, European Union, and certified facilities in countries like China and South Korea—offer reliable options, provided they adhere to ISO standards, FDA or CE regulations, and maintain rigorous quality control protocols.
Partnering with a manufacturer that has experience in producing the specific type of contact lenses (e.g., daily disposables, toric, or colored lenses) ensures technical expertise and reduces time-to-market. Additionally, transparency in sourcing materials, robust R&D support, and the ability to customize products are key advantages that enhance long-term competitiveness.
Ultimately, the ideal manufacturer balances quality, compliance, and cost while demonstrating reliability and scalability. Conducting on-site audits, reviewing certifications, and initiating small trial productions are recommended final steps before finalizing the partnership. With the right manufacturer, the foundation is set for delivering safe, high-quality contact lenses that meet market demands and regulatory expectations.