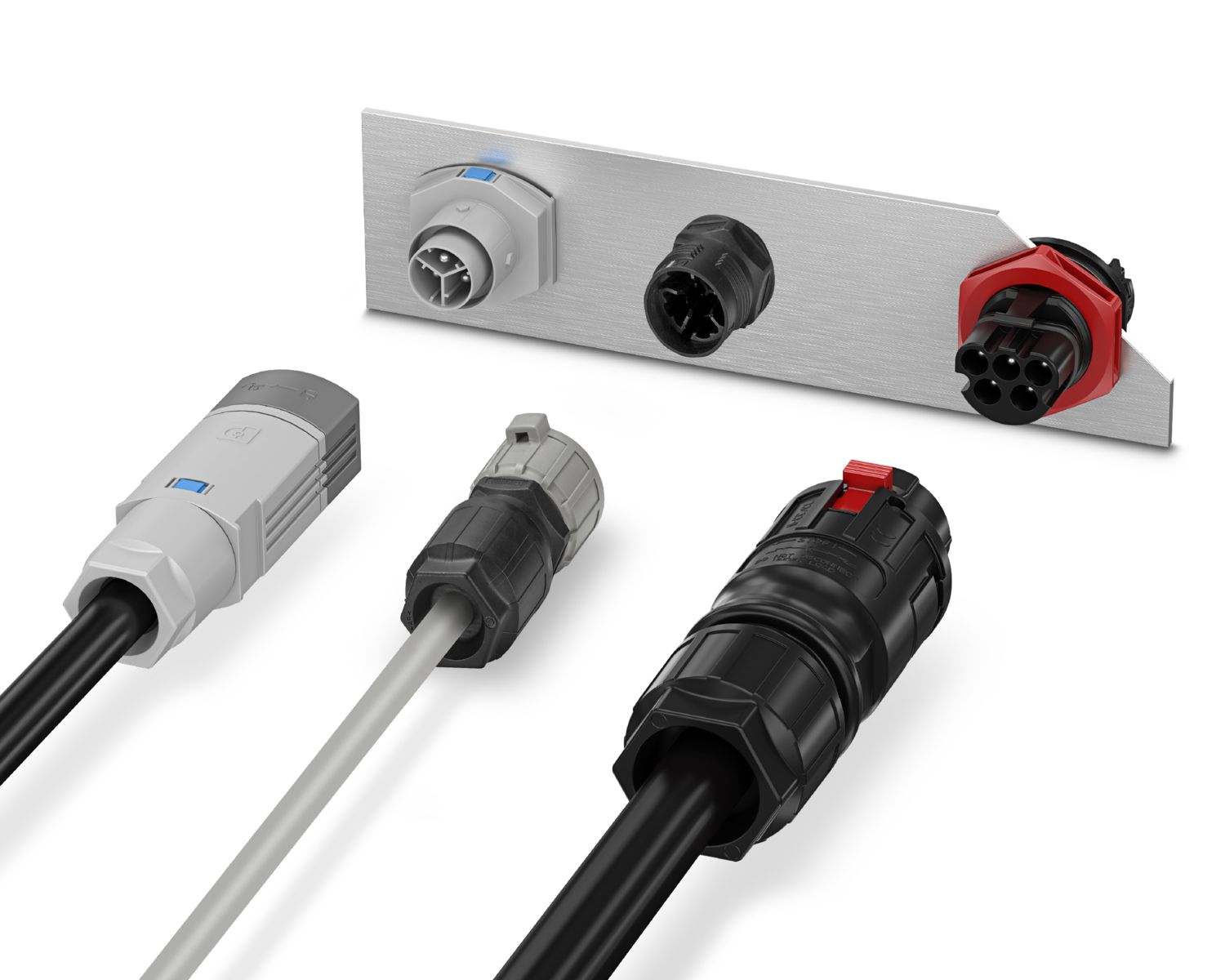
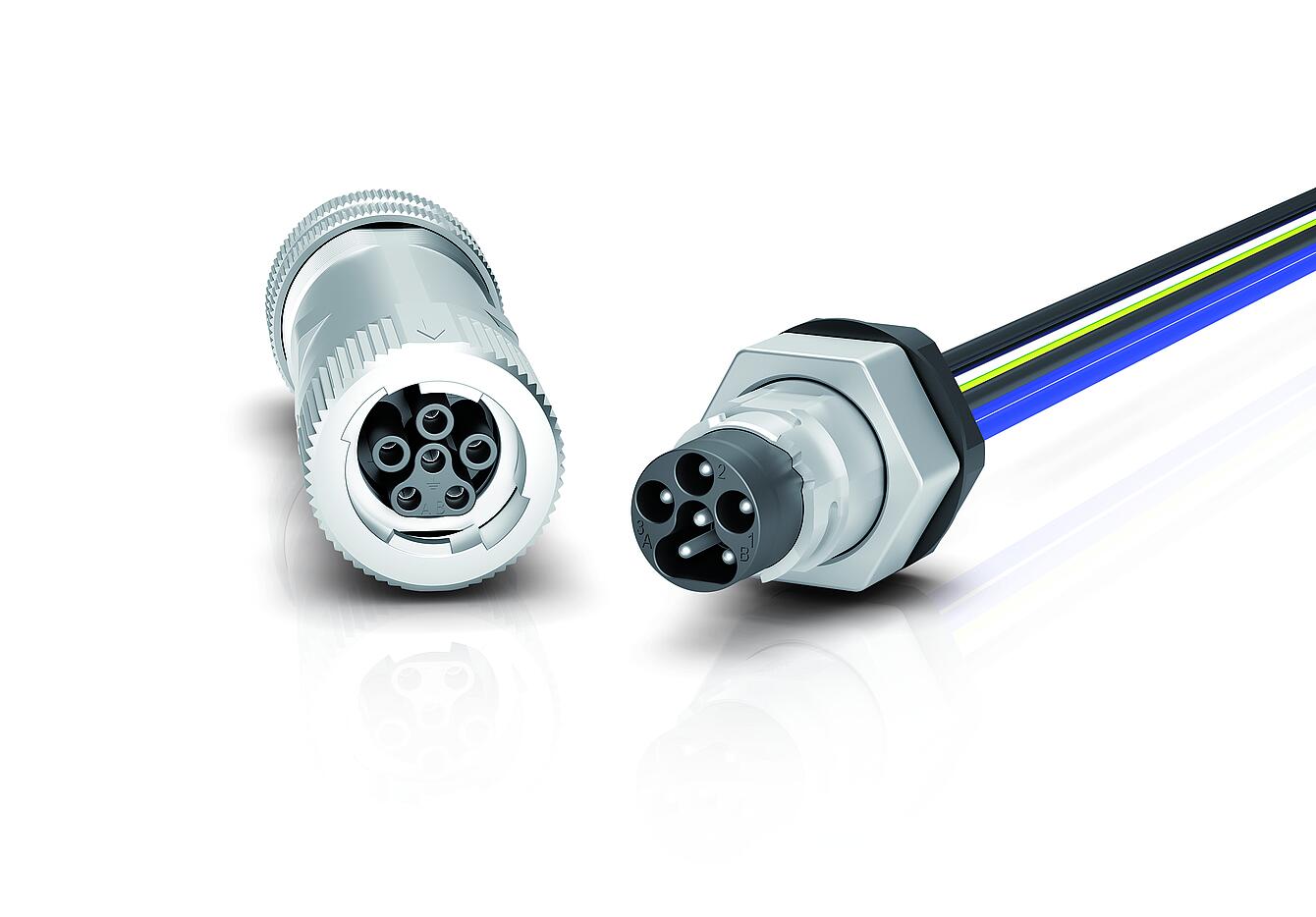
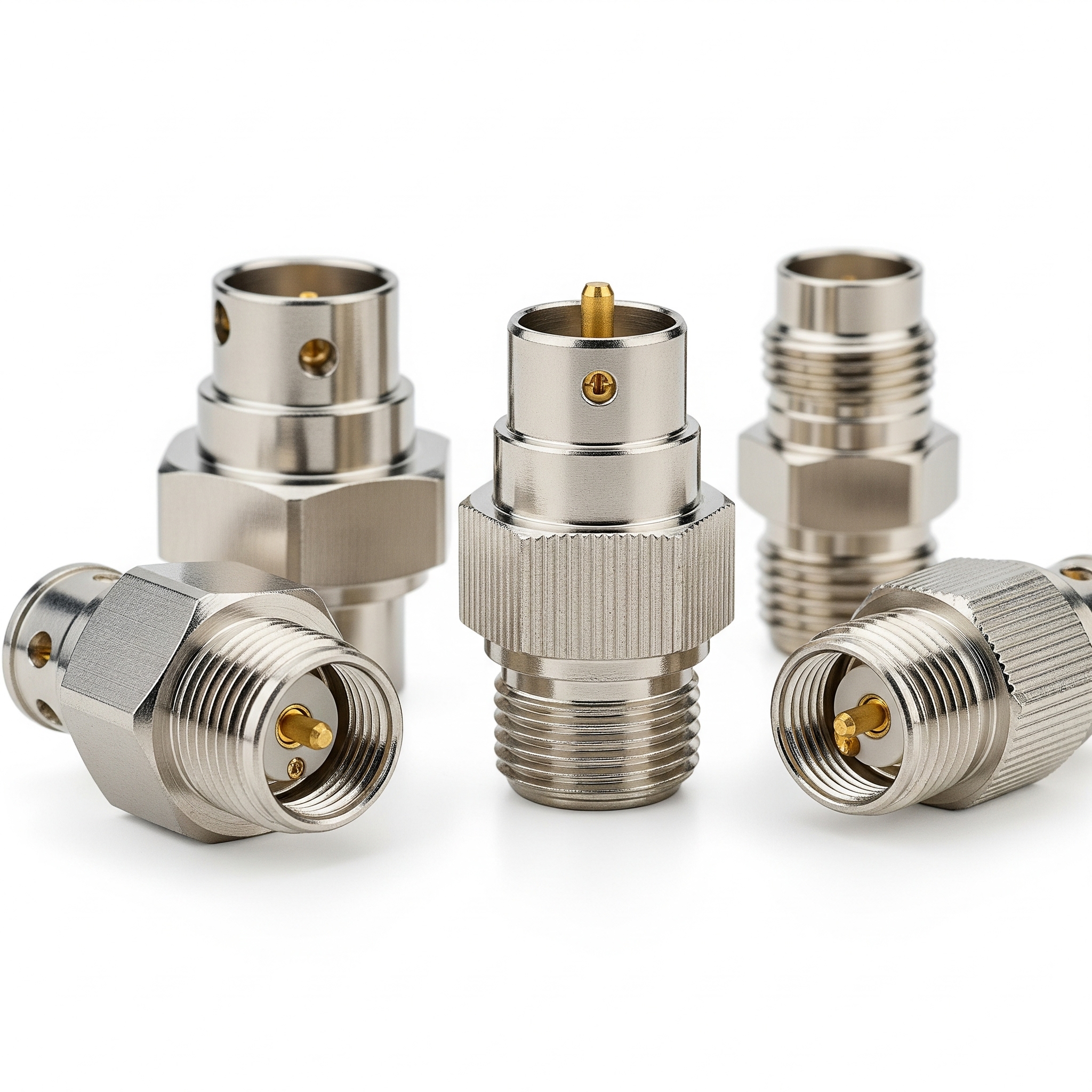
The global electrical connectors market is undergoing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across automotive, industrial machinery, telecommunications, and consumer electronics sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 79.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 109.4 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% during the forecast period. This growth is further fueled by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, the proliferation of IoT devices, and advancements in 5G infrastructure—all of which require reliable, high-performance electrical connections. As innovation accelerates and industries prioritize miniaturization, durability, and signal integrity, the role of leading connector manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. The following list highlights the top 10 electrical connector manufacturers shaping the industry through technological leadership, global reach, and consistent R&D investment.
Top 10 Connectors Electrical Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
#2 Connectors, Cables, Optics, RF, Silicon to Silicon Solutions
Domain Est. 1995
Website: samtec.com
Key Highlights: Samtec is the service leader in the electronic interconnect industry and a global manufacturer of Connectors, Cables, Optics and RF Systems, ……
#3 Types of Electrical Connectors and Wire Connectors
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: From USB connectors and RJ45 connectors to TE’s DEUTSCH connectors and AMP connectors, we design and manufacture the electrical connectors and wire connectors ……
#4 Connectors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: molex.com
Key Highlights: Molex offers a wide variety of Board-to-Board Connectors for microminiature, high-speed, high-density, and high-power applications….
#5 Glenair
Domain Est. 1995
Website: glenair.com
Key Highlights: Glenair, Inc: Glenair manufactures high-reliability connectors and cables for mission-critical land, sea, air, and space applications….
#6 Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: amphenol.com
Key Highlights: Our wide array of electrical and electronic connectors come in multiple form factors and are designed to meet the latest market needs….
#7 Electrical and Electronic Connectors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hirose.com
Key Highlights: Connector Selector Categories, Applications, Customer Support, Partners, Locations, Contact Us, Privacy Policy | Terms of Use | Membership Agreement…
#8 Omnetics Connector Corp.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: omnetics.com
Key Highlights: Omnetics is a world-class miniature connector design and manufacturing company with over 30 years of experience, focused on Micro-miniature and Nano-miniature ……
#9 Terminal Supply Company
Domain Est. 2000
Website: terminalsupplyco.com
Key Highlights: We carry a wide inventory of Cole Hersee switches and solenoids. 3M electrical tape and Hellerman Tyton cable ties also complement our electrical product line….
#10 Winchester Interconnect
Domain Est. 2016
Website: winconn.com
Key Highlights: Winchester Interconnect is a global leader in connectors, RF & microwave, hermetic, fiber optic & cable assemblies. Trusted interconnect solutions for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Connectors Electrical

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electrical Connectors
The global electrical connectors market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, rising demand across key industries, and an intensified focus on sustainability and performance. Several macroeconomic and sector-specific trends are shaping the trajectory of this market, positioning it for robust growth and strategic evolution.
1. Expansion in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Automotive Electrification
The automotive sector remains the largest end-user of electrical connectors, and the shift toward electric vehicles is a primary growth catalyst. By 2026, rising EV production—fueled by government emissions regulations and consumer demand for sustainable transport—will significantly increase the need for high-voltage, high-reliability connectors. These connectors must support fast charging, battery management systems, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), driving innovation in designs that offer enhanced thermal management, miniaturization, and resistance to vibration and moisture.
2. Growth in Industrial Automation and Industry 4.0
The proliferation of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies is accelerating demand for rugged, high-performance connectors in factories and industrial systems. By 2026, increased deployment of robotics, IoT-enabled sensors, and real-time data analytics will require connectors capable of reliable signal transmission in harsh environments. Modular and scalable connector solutions are expected to gain traction to support flexible production lines and predictive maintenance systems.
3. Advancements in Consumer Electronics and 5G Connectivity
The consumer electronics market continues to demand smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient connectors. With the global rollout of 5G infrastructure and the emergence of next-generation devices such as AR/VR headsets, foldable smartphones, and wearable tech, there is a growing need for high-speed data transmission connectors. By 2026, high-density interconnects (HDI) and board-to-board connectors with low latency and high bandwidth will be critical, especially in compact device architectures.
4. Rising Adoption in Renewable Energy and Power Infrastructure
The global push toward clean energy is boosting demand for electrical connectors in solar, wind, and energy storage systems. As renewable installations expand, particularly in emerging markets, connectors that offer durability, corrosion resistance, and efficient power handling will be essential. By 2026, standardized and plug-and-play connector solutions are expected to improve installation speed and reduce maintenance costs in distributed energy systems.
5. Emphasis on Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly materials and recyclable designs. By 2026, increased use of bio-based plastics, lead-free soldering, and modular connectors that support repairability and upgrades will become industry norms. This trend is also reducing e-waste and aligning with circular economy principles.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical tensions and past disruptions (e.g., pandemic-related shortages) are prompting companies to reevaluate supply chain strategies. By 2026, there will be a greater emphasis on regional manufacturing, nearshoring, and dual-sourcing of critical components. This shift is likely to benefit local connector producers in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia, reducing dependency on single-source suppliers.
7. Technological Convergence and Smart Connectors
Emerging trends include the integration of intelligence into connectors—such as embedded sensors for monitoring temperature, current, and connection status. These “smart connectors” will play a vital role in predictive maintenance and system reliability across aerospace, medical devices, and data centers. By 2026, such innovations will begin transitioning from niche applications to broader commercial adoption.
In summary, the electrical connectors market in 2026 will be defined by rapid technological advancement, sector diversification, and a strong emphasis on performance and sustainability. Companies that innovate in miniaturization, high-speed data transfer, and environmentally responsible design will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving opportunities.
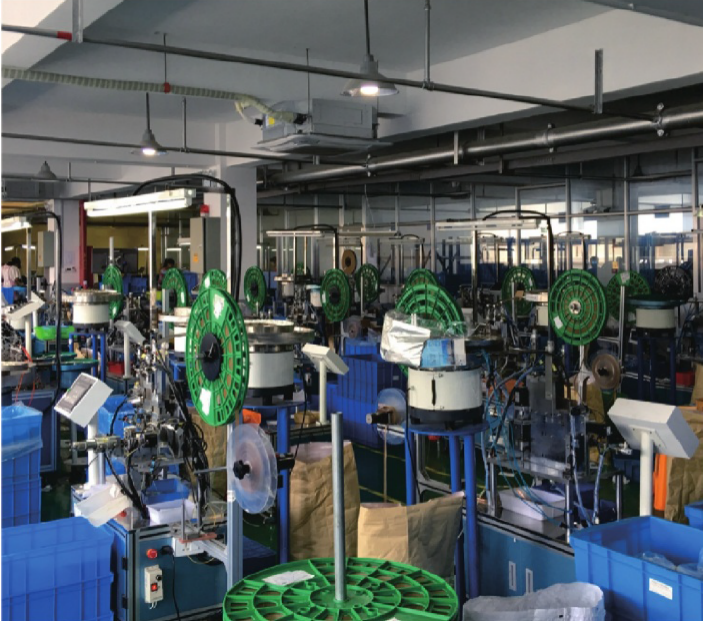

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Electrical Connectors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing electrical connectors involves more than selecting the right pin count and shape. Overlooking critical quality and ingress protection (IP) factors can lead to field failures, safety hazards, and increased costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate IP Rating Verification
Assuming a connector is suitable for harsh environments without verifying its actual IP (Ingress Protection) rating is a frequent mistake. Suppliers may claim “water-resistant” without formal IP certification. Always request test reports or certification documents confirming the connector meets the required IP standard (e.g., IP67, IP68). Using a connector with an insufficient IP rating in outdoor or industrial settings can result in moisture ingress, corrosion, and electrical failure.
Overlooking Material Quality and Durability
Low-cost connectors may use inferior plastics or plating materials that degrade over time, especially under thermal cycling or UV exposure. Poor contact materials (e.g., inadequate gold or tin plating) increase contact resistance, leading to overheating and failure. Always verify material specifications and insist on connectors made from UL or RoHS-compliant materials suitable for the application environment.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Quality
Sourcing from suppliers without robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of inconsistent tolerances, poor crimping, or defective molding. Batch-to-batch variations can compromise reliability. Conduct supplier audits and request samples for independent testing to ensure consistent quality before full-scale procurement.
Misalignment Between IP Rating and Real-World Conditions
Even with a correct IP rating, improper installation (e.g., incomplete sealing, damaged O-rings, or incorrect torque on locking mechanisms) can nullify protection. Ensure connectors are installed per manufacturer guidelines and consider environmental factors like vibration, pressure differentials, or chemical exposure that may affect sealing integrity.
Lack of Long-Term Supply and Obsolescence Planning
Electrical connectors, especially custom or high-spec variants, may be discontinued without notice. Relying on single-source suppliers without lifecycle management strategies can lead to costly redesigns. Choose connectors with long-term availability commitments and consider standard, widely available models when possible.
Insufficient Testing and Qualification
Skipping real-world environmental testing (e.g., thermal cycling, humidity, salt spray, mating cycles) exposes systems to unforeseen failure modes. Always perform qualification testing—especially for mission-critical or safety-related applications—to validate connector performance under expected operating conditions.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier selection, rigorous specification review, and proactive risk management throughout the sourcing process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Connectors Electrical
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations essential for the safe, efficient, and lawful distribution and handling of electrical connectors. Adherence to these standards ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and customer safety.
1. Regulatory Compliance
Electrical connectors must comply with national and international standards to ensure safety and performance. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): Standards such as IEC 60512 (connector testing methods) and IEC 60320 (appliance couplers) are widely adopted globally.
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories): UL 498 and UL 1977 are critical for connectors used in North America, ensuring fire and electrical safety.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Compliance is mandatory in the EU and increasingly required worldwide. Prohibits the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials in electrical equipment.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Applies to chemical substances in connectors, requiring disclosure and safe handling of SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern).
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- UKCA Marking: Required for goods placed on the market in Great Britain (England, Wales, Scotland) post-Brexit.
Ensure all connectors are certified by accredited bodies and documentation (test reports, certificates of conformity) is maintained for audit purposes.
2. Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling are vital for protection during transit and regulatory compliance.
- Packaging: Use anti-static, moisture-resistant, and shock-absorbent materials to protect sensitive electrical components. Individual connectors or reels should be sealed in ESD-safe bags.
- Labeling:
- Include part number, manufacturer name, date of manufacture, and lot/batch number.
- Clearly display compliance marks (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS).
- Include handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Way Up,” “ESD Sensitive”).
- For hazardous materials (if applicable), comply with GHS labeling under REACH.
3. Storage Conditions
Maintain optimal storage conditions to preserve connector integrity:
- Temperature: Store between 15°C and 30°C (59°F–86°F).
- Humidity: Keep relative humidity below 65% to prevent corrosion and insulation degradation.
- ESD Protection: Use grounded storage racks and ESD-safe containers in designated electrostatic-protected areas (EPAs).
- Shelf Life: Monitor expiration dates for connectors with time-sensitive materials (e.g., certain polymers or contact platings). Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices.
4. Transportation & Shipping
Transportation must safeguard product quality and meet international shipping regulations.
- Mode of Transport: Choose carriers experienced in handling electronic components. Use air freight for urgent shipments and sea freight for bulk orders.
- Climate Control: For long-distance or extreme climate shipments, use temperature-controlled containers.
- Documentation: Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of compliance. Include HS codes (e.g., 8536.69 for electrical connectors) for customs clearance.
- Hazardous Materials: While most connectors are non-hazardous, confirm classification under IATA/IMDG/ADR if plating materials (e.g., cadmium) are present.
5. Import/Export Compliance
Cross-border shipments require adherence to trade regulations:
- Export Controls: Verify if connectors fall under dual-use regulations (e.g., ECCN in the U.S. Commerce Control List). High-performance or military-grade connectors may require export licenses.
- Customs Declarations: Accurately declare value, origin, and technical specifications. Use Incoterms (e.g., EXW, FCA, DDP) to define responsibilities.
- Duty & Tariff Optimization: Leverage Free Trade Agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-South Korea) where applicable to reduce tariffs.
6. Quality Assurance & Traceability
Maintain robust quality systems aligned with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 (for automotive connectors).
- Incoming Inspection: Verify connector specifications, certifications, and packaging upon receipt.
- Traceability: Implement batch/lot tracking from supplier to end customer using barcodes or RFID.
- Non-Conformance Handling: Establish procedures for quarantining, reporting, and correcting defective shipments.
7. Environmental & Sustainability Practices
Support corporate sustainability goals through responsible logistics:
- Recyclable Packaging: Use minimal, recyclable packaging materials.
- Waste Management: Partner with certified e-waste recyclers for defective or obsolete connectors.
- Carbon Footprint: Optimize routing and consolidate shipments to reduce emissions.
8. Training & Documentation
Ensure personnel are trained in:
- ESD handling procedures
- Regulatory compliance requirements
- Hazardous material awareness (if applicable)
- Customs documentation processes
Maintain up-to-date records of training, compliance certificates, audit reports, and shipping logs.
By following this guide, Connectors Electrical can ensure reliable supply chain operations while meeting global compliance standards and delivering high-quality products to customers.
Conclusion for Sourcing Electrical Connectors
Sourcing electrical connectors is a critical aspect of ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of electrical and electronic systems. A strategic approach to procurement must balance technical specifications, quality standards, cost-efficiency, and supply chain resilience. Key considerations include compatibility with application requirements (such as current rating, environmental resistance, and mating cycles), adherence to industry certifications (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS), and the reputation of manufacturers and suppliers.
Leveraging trusted suppliers, conducting thorough due diligence, and maintaining strong supplier relationships help mitigate risks related to counterfeit components, delivery delays, and performance failures. Additionally, staying informed about technological advancements and market trends enables procurement teams to make forward-looking decisions.
Ultimately, effective sourcing of electrical connectors supports product durability and system integrity, contributing to the overall success of engineering and manufacturing projects. A well-executed sourcing strategy not only reduces total cost of ownership but also enhances operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.