The global Conditional Access System (CAS) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for secure digital content delivery across broadcast, OTT, and IPTV platforms. According to Grand View Research, the global CAS market size was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing instances of content piracy, the proliferation of high-definition and 4K streaming services, and the ongoing transition from traditional broadcast to internet-based media platforms. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence forecasts steady market expansion, citing heightened investments in secure pay-TV infrastructure and the growing adoption of hybrid CAS solutions that support multi-device access. As content providers prioritize user authentication and subscription management, competition among key manufacturers has intensified. Here are the top 8 conditional access system manufacturers leading innovation and market share in this evolving landscape.
Top 8 Conditional Access System Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
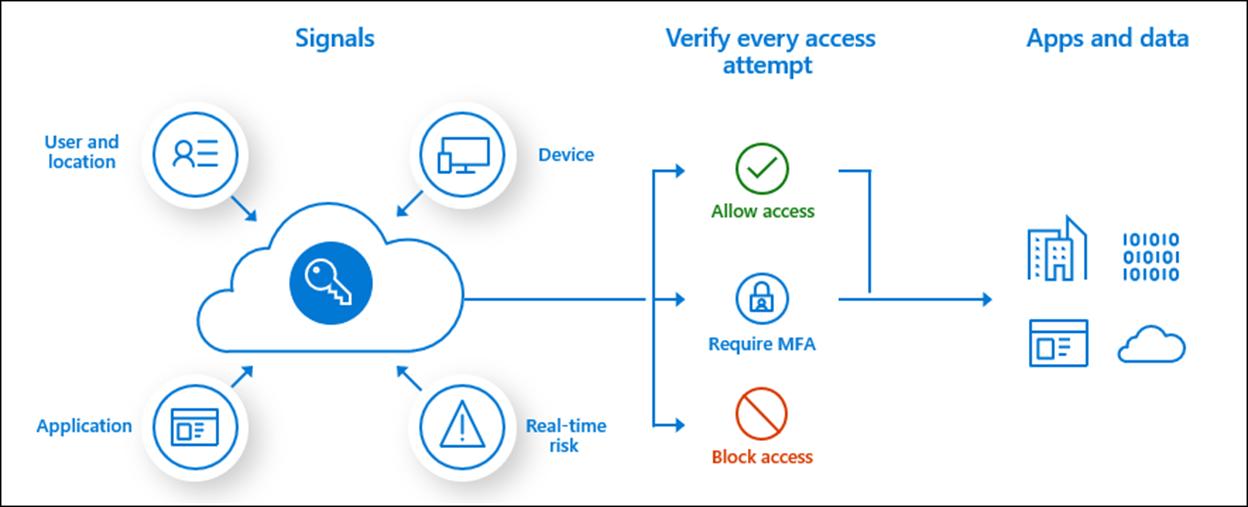
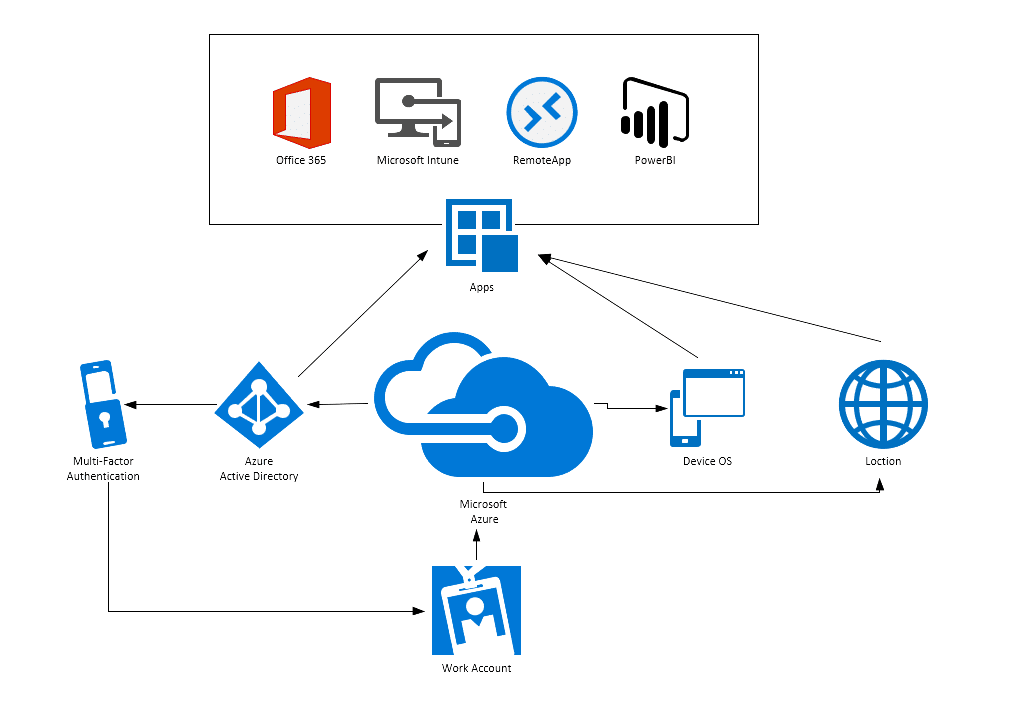
#1 Microsoft Entra Conditional Access
Domain Est. 1991
Website: learn.microsoft.com
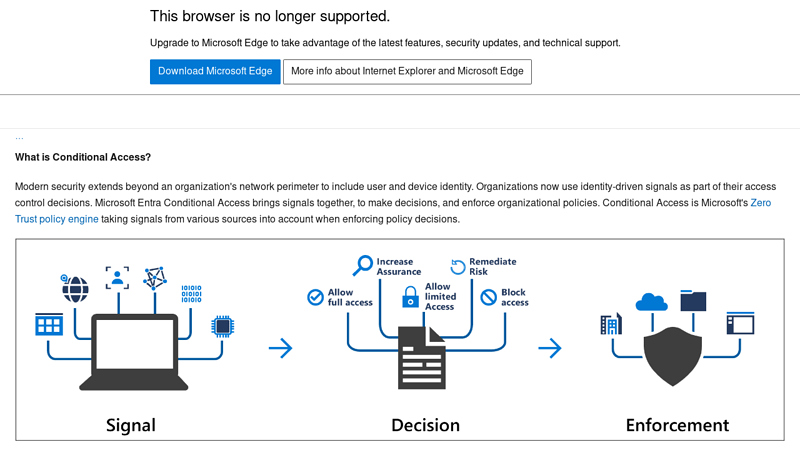
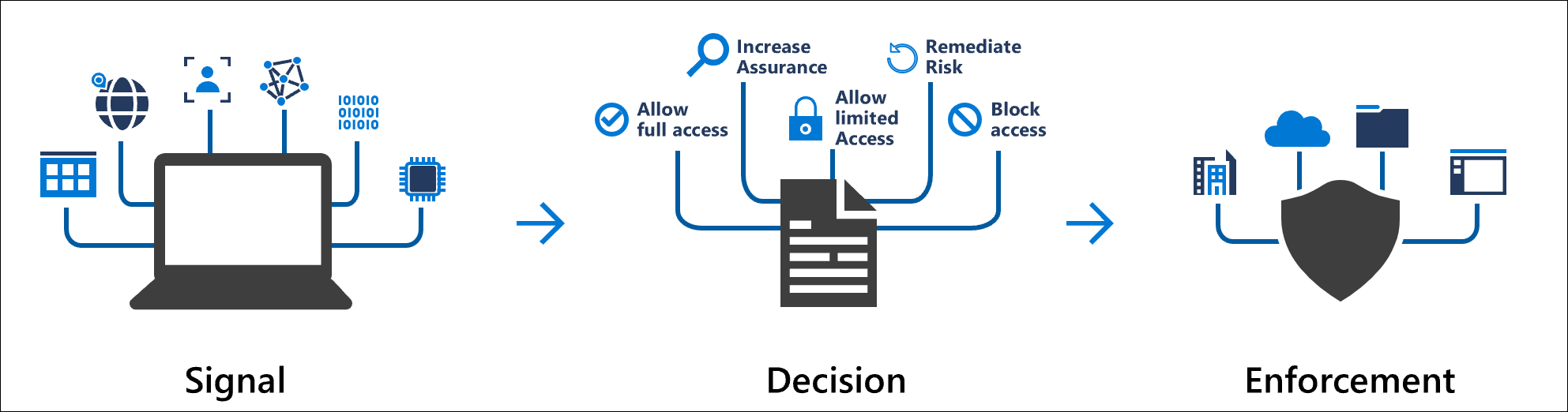
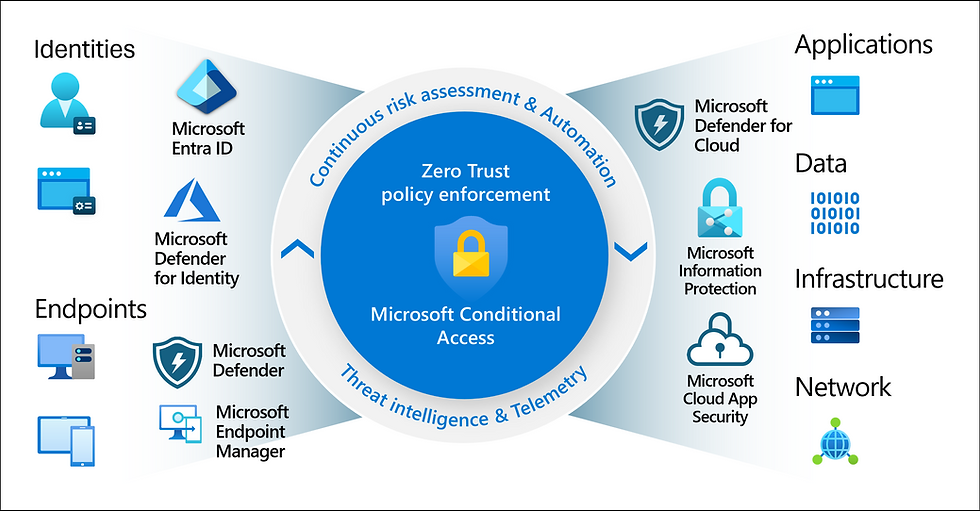
Key Highlights: Explore Microsoft Entra Conditional Access, the Zero Trust policy engine that integrates signals to secure access to resources….
#2 Conditional Access Systems
Domain Est. 1994
Website: commscope.com
Key Highlights: CommScope’s conditional access systems (CAS) protect content critical to studios, service providers and consumers—ensuring quality and protecting rights….
#3 Conditional Access System Hospitality
Domain Est. 1996
Website: axing.com
Key Highlights: Conditional Access System Hospitality. AXING CAS – Hospitality Solution enables you to offer value-added TV services for your hospitality at low cost….
#4 What is Conditional Access System (CAS)?
Domain Est. 2000
Website: verimatrix.com
Key Highlights: Learn about Conditional Access System (CAS) – a system that manages conditional access to digital content, often for video and streaming services….
#5 DVB Conditional Access System
Domain Est. 2003
Website: cryptoguard.com
Key Highlights: Conditional Access System (CAS) including Subscriber Management System (SMS). Affordable Video Content Protection for DVB-S/S2, C, T/T2 & IPTV….
#6 Conditional Access for Applications
Domain Est. 2005
Website: portnox.com
Key Highlights: Portnox’s conditional access for applications extends access, risk, and remediation capabilities to SaaS and on-premises applications….
#7 Conditional Access System
Domain Est. 2012
Website: viaccess-orca.com
Key Highlights: With VO’s dual-mode Conditional Access System, there is no need to choose: Gain maximum flexibility and security for both card and cardless devices. Learn More….
#8 Hexnode Conditional Access
Domain Est. 2014
Website: hexnode.com
Key Highlights: Conditional access is a set of policies and configurations that dictates which devices and users can access specific data and services….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Conditional Access System

2026 Market Trends for Conditional Access Systems
The Conditional Access System (CAS) market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer behaviors, technological advancements, and shifting content delivery models. As traditional pay-TV operators adapt to increasing competition from streaming platforms, CAS solutions are evolving beyond basic encryption to become integral components of comprehensive content protection and user experience strategies.
Rise of Hybrid and IP-Based Delivery Models
By 2026, the CAS market will increasingly support hybrid broadcast-broadband and fully IP-based delivery systems. As more operators transition from legacy set-top boxes to app-based and OTT (over-the-top) platforms, CAS solutions will need to integrate seamlessly with digital rights management (DRM) systems like Widevine, PlayReady, and FairPlay. This convergence will lead to unified content protection frameworks, where traditional CAS and modern DRMs coexist or merge, enabling secure access across multiple devices and networks.
Growth in Multi-DRM and CAS Integration
A key trend will be the adoption of multi-DRM solutions that coexist with or extend traditional CAS. Operators will leverage integrated CAS-DRM platforms to secure content delivered via satellite, cable, IPTV, and internet streaming. This hybrid approach allows service providers to maintain control over premium content while offering flexibility in device compatibility, a necessity in a market where consumers expect content access on smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs.
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity and Anti-Piracy Measures
With the rise in digital piracy and cyberattacks targeting content distribution, CAS providers will prioritize advanced security features by 2026. Expect wider adoption of hardware-based security (e.g., secure elements, Trusted Execution Environments), forensic watermarking, and AI-driven anomaly detection to identify and block unauthorized access. Regulatory pressures and high-profile breaches will push operators to invest in next-generation CAS with real-time threat monitoring and adaptive encryption.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
While mature markets focus on modernization, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will see growing CAS deployment as pay-TV penetration increases. Governments and operators in these regions are launching digital migration initiatives, creating demand for cost-effective, scalable CAS solutions. Localized content bundling and affordable subscription models will drive CAS adoption, particularly in satellite and terrestrial broadcasting.
AI and Personalization Integration
CAS platforms will increasingly incorporate AI to enhance user experience and operational efficiency. By 2026, intelligent CAS systems will leverage viewing data to enable personalized content recommendations, dynamic ad insertion, and tiered access control. These capabilities not only improve user engagement but also support targeted monetization strategies, making CAS a strategic tool beyond security.
Consolidation and Ecosystem Partnerships
The market will likely see consolidation among CAS vendors as competition intensifies and integration with broader content management ecosystems becomes essential. Strategic partnerships between CAS providers, cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure), and content delivery networks (CDNs) will become common, enabling end-to-end secure delivery solutions. This trend will favor vendors offering modular, cloud-native CAS architectures that support scalability and rapid deployment.
In conclusion, by 2026, the Conditional Access System market will shift from a siloed security solution to a dynamic, integrated component of the digital content ecosystem. Success will depend on adaptability, interoperability with DRM, and the ability to support secure, personalized, and multi-platform content delivery in an increasingly connected world.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Conditional Access System (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing a Conditional Access System (CAS) is a critical decision for pay-TV operators, broadcasters, and content distributors. Poor choices can lead to service disruptions, revenue loss, and legal complications. Two of the most significant areas of risk involve quality and intellectual property (IP). Below are the key pitfalls to avoid.
Inadequate Quality Assurance and Testing
One of the most frequent pitfalls is selecting a CAS provider that lacks rigorous quality assurance processes. A CAS is mission-critical—any failure can result in widespread service outages or unauthorized access to premium content.
-
Insufficient Integration Testing: Many vendors deliver a CAS that works in isolation but fails when integrated with set-top boxes, headends, or middleware. Without end-to-end testing across real-world environments, performance issues may only surface post-deployment.
-
Poor Firmware and Software Updates: CAS components require regular updates to address security flaws and add features. Providers with slow, unreliable, or poorly documented update cycles can leave systems vulnerable and increase operational overhead.
-
Lack of Scalability and Performance Under Load: Some systems perform well in lab conditions but falter under peak user loads. Operators must verify that the CAS can handle high channel counts, frequent entitlement updates, and large subscriber bases without latency or downtime.
Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Ownership and Licensing
Intellectual property rights are often underestimated during CAS procurement, leading to long-term legal and operational constraints.
-
Unclear IP Ownership: Some vendors retain full ownership of the CAS software, firmware, or encryption algorithms. This can limit customization, increase dependency, and expose operators to vendor lock-in or unexpected licensing fees.
-
Use of Third-Party Patented Technologies: Many CAS solutions rely on patented encryption or key management technologies. If the vendor hasn’t secured proper licenses, the operator could face infringement claims from third parties—even if unintentional.
-
Open-Source License Compliance Risks: Some CAS providers incorporate open-source components without proper compliance (e.g., GPL, LGPL). This can lead to unintended obligations to disclose proprietary code or face legal action.
-
Limited Rights to Modify or Audit: Operators may require the ability to audit code for security or adapt the system to local regulations. Vendors that restrict access to source code or charge exorbitant fees for audits can hinder compliance and innovation.
Choosing Vendors Without Proven Security Track Records
Security is central to any CAS, but not all vendors demonstrate consistent track records.
-
History of Compromises or Reverse Engineering: Some CAS platforms have been widely compromised in the past. Sourcing from a vendor whose technology has a history of breaches increases the risk of piracy and revenue leakage.
-
Proprietary vs. Standardized Cryptography: Vendors using obscure or proprietary encryption (rather than industry-standard, peer-reviewed algorithms) may create a false sense of security. These systems are often more vulnerable due to lack of public scrutiny.
Neglecting Long-Term Support and Roadmap Alignment
A CAS must evolve with changing threats and technologies.
-
Short Product Lifespan or Discontinued Support: Operators risk investing in systems that are soon abandoned. Always verify the vendor’s commitment to long-term maintenance, security patches, and compatibility with future platforms (e.g., OTT, hybrid set-top boxes).
-
Misalignment with Industry Standards: Choosing a CAS that doesn’t support emerging standards (like DVB-CI Plus, SIM-based CAS, or cloud-based entitlements) can hinder interoperability and future-proofing.
Conclusion
Sourcing a Conditional Access System demands careful due diligence, especially regarding quality and intellectual property. Operators must assess not only the technical capabilities but also the legal and operational implications of vendor agreements. Prioritizing vendors with transparent IP policies, proven security practices, and robust QA processes can prevent costly failures and protect content and revenue in the long term.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Conditional Access System (CAS)
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance requirements for the deployment, operation, and maintenance of a Conditional Access System (CAS), commonly used in pay-TV, broadcasting, and content distribution networks to control access to digital content.
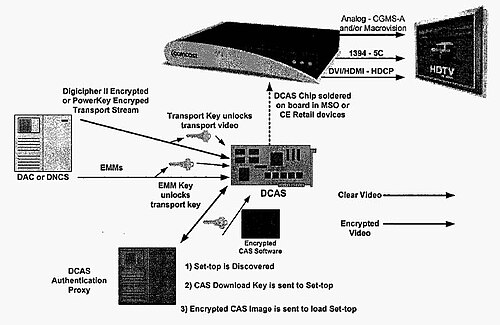
System Architecture and Component Logistics
Ensure proper planning and coordination for the physical and digital components of the CAS. This includes secure delivery and installation of:
- Smart Cards and Secure Elements: Track issuance, distribution, and lifecycle management of smart cards or embedded secure elements used for subscriber authentication.
- Set-Top Boxes (STBs) and Client Devices: Coordinate logistics for CAS-enabled devices, ensuring firmware compatibility and secure provisioning.
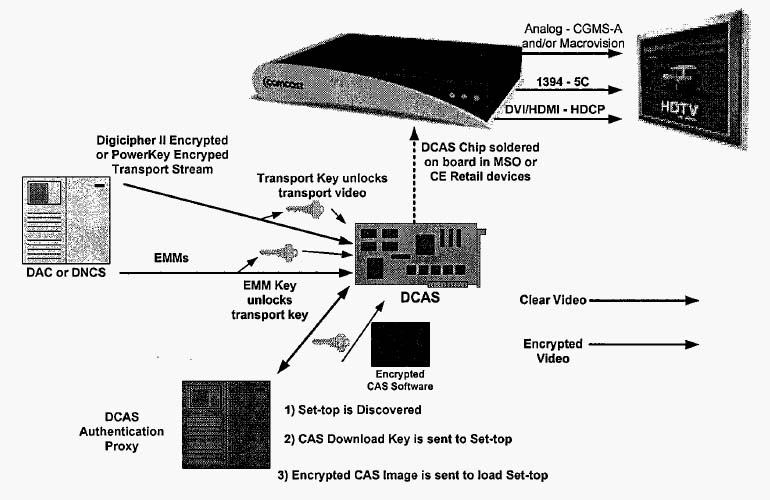
- Headend Equipment: Deploy and maintain CAS servers, entitlement management systems (EMS), and entitlement control message (ECM) generators at broadcast centers.
- Key Management Infrastructure: Safeguard hardware security modules (HSMs) and key vaults used for encryption key generation and storage.
All components must be sourced from vetted suppliers and stored securely to prevent tampering or unauthorized access.
Regulatory and Industry Compliance
Adhere to regional and international standards governing content protection and data privacy:
- Content Protection Standards: Comply with DRM and CAS standards such as DVB Simulcrypt, CableCARD, or proprietary systems (e.g., Verimatrix, Nagravision).
- Data Privacy Regulations: Follow GDPR, CCPA, or equivalent laws when handling subscriber data, including personal identifiers and viewing habits.
- Export Control Laws: Abide by regulations like the Wassenaar Arrangement when transferring encryption technologies across borders.
- Broadcast Licensing Requirements: Meet conditions set by national telecommunications or broadcasting authorities regarding access control and encryption strength.
Regular audits and documentation are required to demonstrate compliance.
Access Control and Authentication Protocols
Implement robust mechanisms to authorize and authenticate users:
- Subscriber Authentication: Use secure two-way authentication between the CAS and client devices using encrypted challenge-response protocols.
- Entitlement Management: Ensure the EMS accurately reflects active subscriptions, promotions, and service tiers.
- Renewal and Deactivation Processes: Establish automated workflows for subscription renewals, suspensions, and terminations to prevent unauthorized access.
All authentication logs must be retained for audit and forensic purposes.
Security and Anti-Piracy Measures
Protect the CAS against compromise and content redistribution:
- Firmware and Software Integrity: Digitally sign all CAS-related software and verify integrity before deployment.
- Tamper Resistance: Design client devices and smart cards with anti-tamper features to deter reverse engineering.
- Monitoring and Detection: Deploy systems to detect anomalies such as cloned cards, unauthorized decoders, or unusual decryption patterns.
- Revocation Mechanisms: Enable rapid revocation of compromised devices or credentials via over-the-air (OTA) updates.
Maintain a response plan for security incidents, including forensic investigation and regulatory reporting.
Operational Maintenance and Updates
Ensure continuous reliability and security of the CAS:
- Patch Management: Apply security updates and system patches promptly across all CAS components.
- Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: Maintain failover systems for critical CAS infrastructure to ensure service continuity.
- Version Control: Track software and configuration versions across the network to support troubleshooting and compliance audits.
- Change Management: Follow formal procedures for any modification to the CAS, including testing in isolated environments prior to deployment.
Documentation and Audit Readiness
Maintain comprehensive records to support compliance and operational transparency:
- System Architecture Diagrams: Keep up-to-date documentation of CAS components and data flows.
- Access Logs and Audit Trails: Retain logs of authentication attempts, entitlement changes, and administrative actions.
- Compliance Certificates: Store valid certifications from third-party auditors or standards bodies.
- Incident Reports: Document and analyze any security breaches or system failures.
Regular internal audits and third-party assessments are recommended to verify adherence to this guide.
By following this logistics and compliance framework, organizations can ensure the secure, lawful, and efficient operation of their Conditional Access System.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Conditional Access System (CAS):
In conclusion, sourcing a Conditional Access System (CAS) is a critical decision that directly impacts the security, scalability, and operational efficiency of a content delivery platform. A well-chosen CAS ensures robust protection against unauthorized access, supports a seamless subscriber experience, and enables flexible business models such as pay-per-view, subscription tiers, and content rental.
Key factors to consider when sourcing a CAS include system interoperability with existing infrastructure (such as headends and set-top boxes), compliance with industry standards (e.g., DVB-CA, DCAS), scalability to accommodate future growth, resistance to piracy through advanced encryption and secure key management, and vendor reliability with a proven track record in support and updates.
Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—encompassing licensing fees, integration complexity, maintenance, and upgrade paths—is essential to ensure long-term viability. As the media landscape evolves with the rise of OTT and hybrid delivery models, selecting a CAS that supports both traditional broadcast and IP-based services will be instrumental in remaining competitive.
Ultimately, a strategic, future-ready approach to sourcing a Conditional Access System safeguards content investments, enhances user satisfaction, and supports sustainable business growth in a dynamic digital environment.