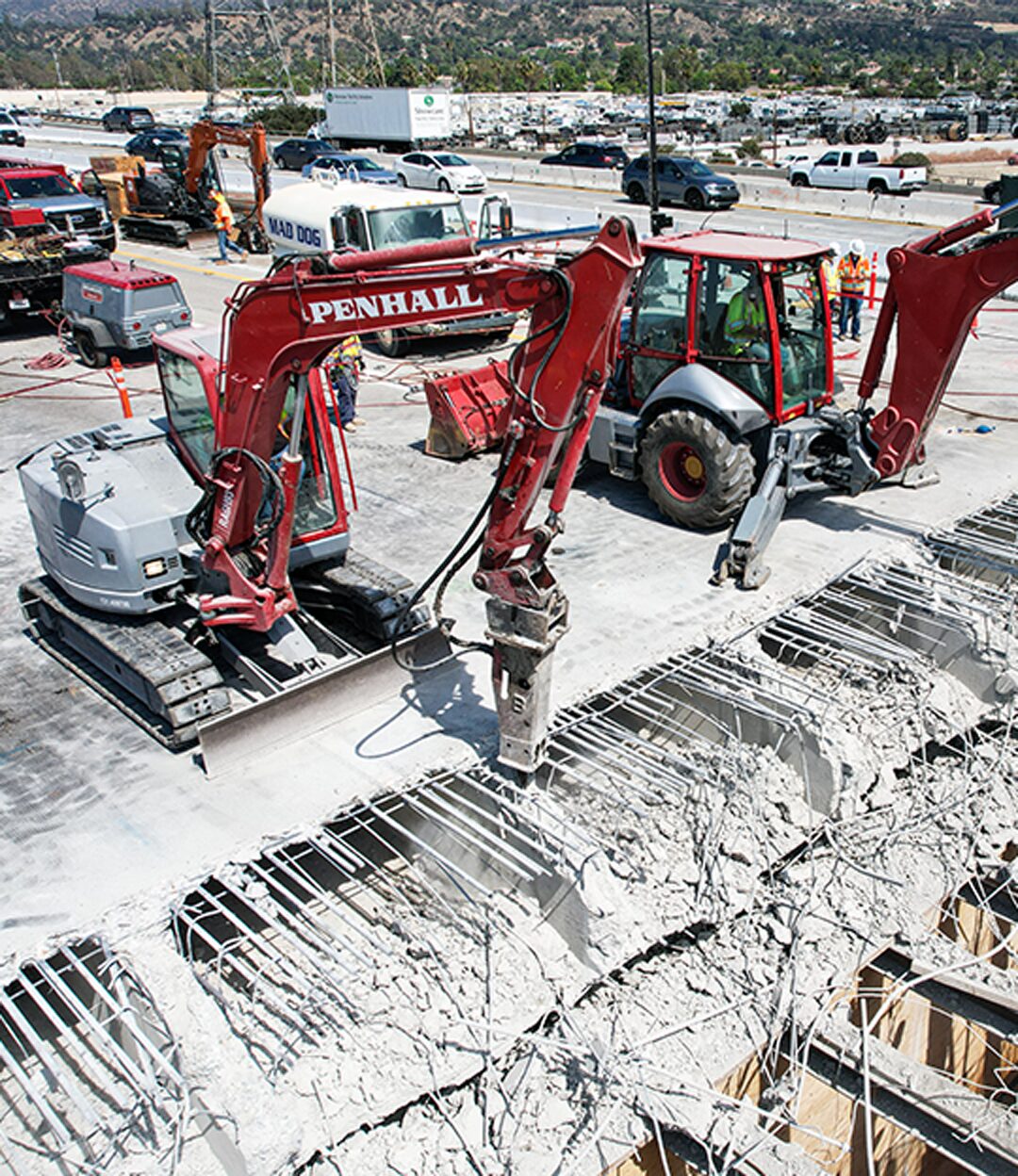
The global concrete breaking tools market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising infrastructure development, urbanization, and increased investments in construction and demolition activities. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global demolition equipment market—of which concrete breaking tools are a critical component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research valued the global power tools market at USD 48.4 billion in 2022 and forecasted a CAGR of 5.2% through 2030, with construction-grade tools like hydraulic breakers, demolition hammers, and rock splitters representing a significant share. With demand surging across residential, commercial, and civil engineering projects, manufacturers are innovating to deliver higher efficiency, reduced vibration, and improved operator safety. In this competitive landscape, a select group of global manufacturers have emerged as leaders, setting industry benchmarks in durability, performance, and technological integration.
Top 10 Concrete Breaking Tools Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Aggregates, Asphalt, Concrete & Road Equipment
Domain Est. 1998
Website: astecindustries.com
Key Highlights: Equipment and technology for aggregates processing, asphalt and concrete production, road construction, industrial heating and forestry applications, ……
#2 CORDED BREAKERS & DEMOLITION HAMMERS
Domain Est. 1995
Website: makitatools.com
Key Highlights: Makita USA: The Leader In Cordless with 18V LXT Lithium-Ion. The best in class for cordless power tool technology. A leader in power tool technology for the ……
#3 Homepage
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bontool.com
Key Highlights: Bon Tool Company is the preferred manufacturer and supplier of professional hand tools and equipment … Concrete Testing Tools · Drilling & Coring · Finishing ……
#4 Milwaukee® Tool
Domain Est. 2000
Website: milwaukeetool.com
Key Highlights: Milwaukee Tool is the most respected manufacturer of heavy-duty power tools, hand tools, instruments, and accessories….
#5 TE 1000
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hilti.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.8 326 Versatile TE-S breaker for demolishing concrete floors and occasional wall chiseling. Working direction: Floor, Wall; Tool chuck type: TE-S ……
#6 Concrete
Domain Est. 1996
Website: boschtools.com
Key Highlights: Bosch offers a wide range of expertly designed tools for the needs of the job, including demolition hammers, grinders, and dust collection systems….
#7 Concrete Demolition
Domain Est. 1997
Website: dewalt.com
Key Highlights: Take on trenching, slab removal, rebar inspection, wall breaching, and more with the right equipment for rigorous jobs. DEWALT delivers concrete crushing power….
#8 Penhall Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: penhall.com
Key Highlights: Penhall is the country’s largest provider of concrete cutting, scanning, and removal services, having served over 16000 clients across North America….
#9 Arrow Master
Domain Est. 1997
Website: arrowmaster.com
Key Highlights: Arrow Master delivers reliable, high-performance concrete-breaking equipment that ensures safety, speed, and cost-efficiency for your construction projects….
#10 Hydraulic Breakers for Excavators
Domain Est. 2017
Website: epiroc.com
Key Highlights: Our Heavy Breakers are highly adapted for primary blast-free rock excavation and secondary rock breaking on construction sites and in quarries, surface and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Concrete Breaking Tools
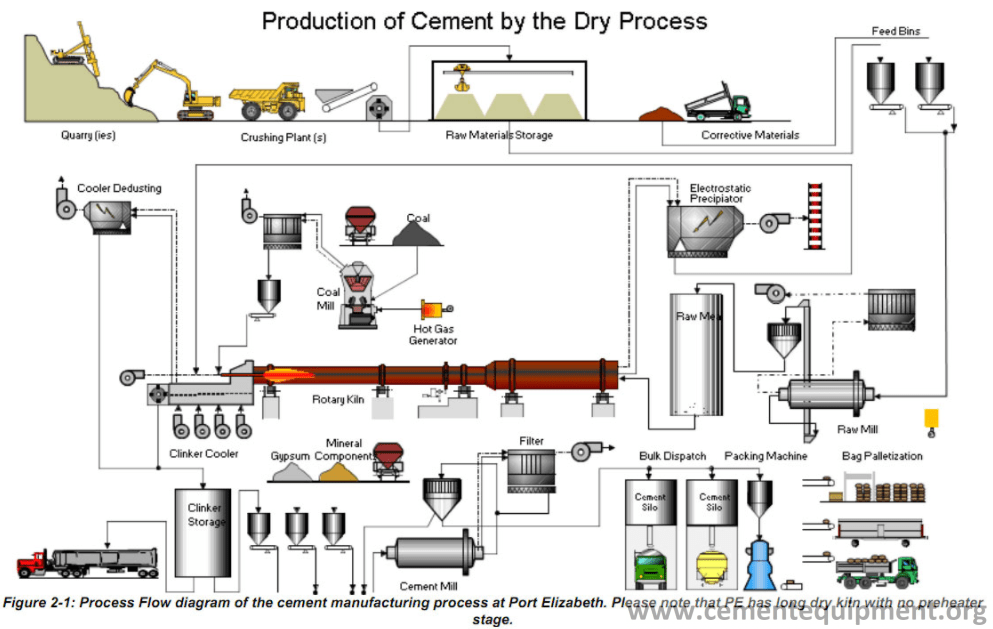
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Concrete Breaking Tools
The global market for concrete breaking tools is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in technology, growing infrastructure demands, and a shift toward sustainable construction practices. As urbanization accelerates and aging infrastructure requires renovation or demolition, the demand for efficient, durable, and innovative concrete breaking tools continues to rise. Below is an in-depth analysis of key market trends expected to shape the industry through 2026.
1. Rising Infrastructure Investment
Governments worldwide are increasing investments in infrastructure development—especially in emerging economies—to support economic growth and urban expansion. Projects such as road construction, subway systems, and building renovations are driving demand for high-performance concrete demolition tools. The U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, China’s Belt and Road Initiative, and similar programs across Southeast Asia and Africa are anticipated to boost procurement of hydraulic breakers, demolition hammers, and other concrete-breaking equipment.
2. Technological Advancements and Automation
By 2026, automation and smart technology integration will play a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and safety of concrete breaking tools. Major manufacturers are focusing on developing intelligent tools equipped with sensors, IoT connectivity, and real-time monitoring systems. These innovations allow operators to track tool performance, detect wear and tear, and optimize maintenance schedules—reducing downtime and increasing productivity on job sites.
3. Growth in Cordless and Electric-Powered Tools
Environmental regulations and the construction industry’s push toward sustainability are accelerating the adoption of electric and battery-powered concrete breakers. Cordless demolition hammers and electric breakers offer reduced emissions, lower noise levels, and improved portability—making them ideal for indoor and urban environments. Technological improvements in lithium-ion battery capacity are enabling longer run times and higher power outputs, narrowing the performance gap with traditional pneumatic and hydraulic tools.
4. Focus on Operator Safety and Ergonomics
With increasing awareness of occupational health and safety, manufacturers are redesigning concrete breaking tools to reduce vibration, noise, and operator fatigue. Anti-vibration systems, ergonomic handles, and lightweight composite materials are becoming standard features. Regulatory bodies such as OSHA and EU directives are enforcing stricter safety standards, further encouraging innovation in this area.
5. Expansion of Rental and Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS) Models
The construction sector is witnessing a shift from outright equipment ownership to rental and subscription-based models. Equipment rental companies are investing in modern concrete breaking tools to meet fluctuating project demands. By 2026, Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS) platforms are expected to gain traction, offering clients flexible access to high-end tools with maintenance and support included—lowering upfront costs and improving utilization rates.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the concrete breaking tools market by 2026, fueled by rapid urbanization in India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand due to infrastructure rehabilitation projects and stringent environmental regulations promoting cleaner tools. Meanwhile, the Middle East is emerging as a key market due to large-scale construction initiatives linked to economic diversification plans (e.g., Saudi Vision 2030).
7. Competitive Landscape and Strategic Collaborations
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with key players such as Stanley Black & Decker, Bosch, Hilti, Atlas Copco, and Furukawa Co. Ltd. investing in R&D and strategic partnerships. Mergers and acquisitions are expected to rise as companies aim to expand their product portfolios and geographic reach, particularly in developing markets.
Conclusion
By 2026, the concrete breaking tools market will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and digital transformation. The convergence of smart technology, electrification, and evolving construction needs will redefine industry standards. Stakeholders who adapt to these trends—through product innovation, service expansion, and sustainability initiatives—will be best positioned to capture growth opportunities in this dynamic market.
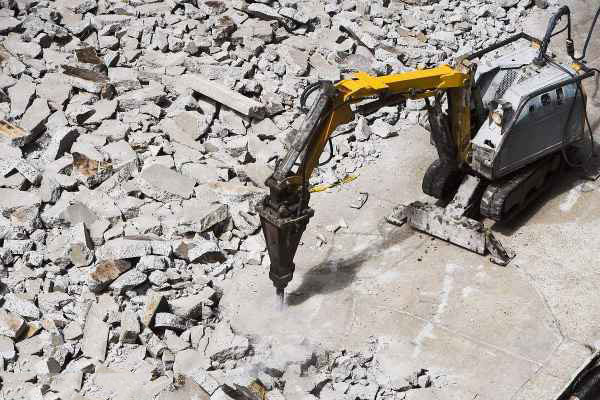

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Concrete Breaking Tools
Quality Inconsistencies
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing concrete breaking tools is inconsistent product quality. Many suppliers, especially from regions with less stringent manufacturing standards, may offer tools made from subpar materials or with poor heat treatment processes. This results in chisels and breaker bits that wear out quickly, deform under impact, or fracture during operation. Buyers often encounter discrepancies between sample quality and bulk shipments, leading to equipment downtime and increased replacement costs.
Lack of Standardization
Concrete breaking tools must conform to specific shank types (e.g., HEX, SDS-MAX, Toro) to be compatible with different breaker models. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers can result in tools that do not meet dimensional tolerances, leading to poor fit, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the breaker itself. Without adherence to international standards (such as ISO or DIN), performance and safety are compromised.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
A significant risk in sourcing concrete breaking tools—especially from low-cost manufacturing regions—is the potential for IP violations. Many suppliers produce counterfeit or “look-alike” versions of branded tools (e.g., copies of Furukawa, Montabert, or Atlas Copco designs), which mimic patented shank geometries or branding. While these may appear cost-effective, they can expose buyers to legal liability, customs seizures, and reputational damage. Additionally, these knock-offs often lack the engineering and metallurgical integrity of genuine products.
Inadequate Material Certification
Reputable concrete breaking tools are typically made from high-grade alloy steels with specific hardness and toughness characteristics. However, some suppliers fail to provide material test certificates (MTCs) or use misleading claims about steel composition. Without proper certification, there is no assurance that the tools can withstand repeated high-impact stress, increasing the risk of catastrophic failure.
Poor Quality Control and Testing
Many low-cost manufacturers lack robust quality control processes, such as impact testing, hardness verification, or batch traceability. Tools may not be individually tested for defects like internal cracks or improper heat treatment. As a result, end-users face unpredictable performance and shortened tool life, impacting productivity and safety on job sites.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Sourcing from distant or opaque supply chains makes it difficult to audit manufacturing practices, labor conditions, or environmental compliance. Without visibility into the production process, buyers risk supporting unethical practices or encountering sudden supply disruptions due to compliance issues or geopolitical factors.
Recommendations to Mitigate Risks
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Partner with reputable, certified suppliers who provide full material and quality documentation.
– Conduct on-site audits or third-party inspections.
– Verify IP compliance and avoid suppliers offering suspiciously low-priced branded equivalents.
– Specify compliance with recognized international standards in procurement contracts.
– Test sample batches under real-world conditions before scaling up orders.
Proactive due diligence significantly reduces the risks associated with quality and intellectual property when sourcing concrete breaking tools.
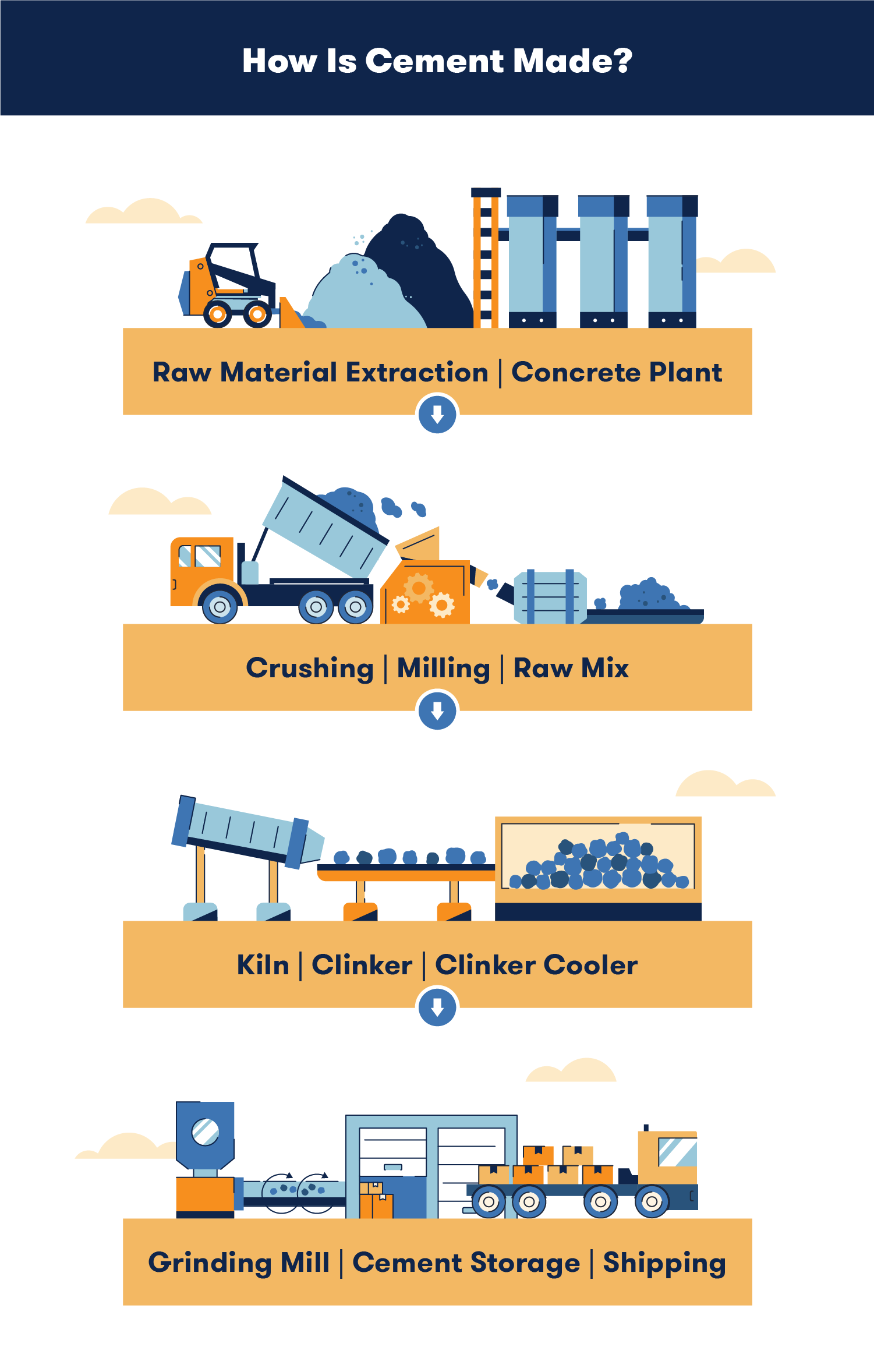
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Concrete Breaking Tools
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, storage, and use of concrete breaking tools—such as hydraulic breakers, pneumatic hammers, and demolition robots—to ensure operational efficiency, legal adherence, and workplace safety.
Regulatory Compliance
All concrete breaking tools must comply with relevant international, national, and regional regulations. Key compliance areas include:
Occupational Safety and Health Standards
Tools must meet OSHA (U.S.), HSE (UK), or equivalent national safety regulations. Operators must be trained in safe handling procedures, including proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as helmets, ear protection, safety goggles, gloves, and steel-toed boots.
Noise and Vibration Regulations
Concrete breakers generate high levels of noise and hand-arm vibration. Equipment must comply with EU Directive 2002/44/EC (vibration) and 2003/10/EC (noise), or local equivalents. Employers are required to monitor exposure levels and implement control measures such as job rotation and anti-vibration tools.
Equipment Certification and CE/UL Marking
Tools sold in the EU must carry the CE mark, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. In North America, tools may require UL or CSA certification. Documentation including Declaration of Conformity must be maintained.
Environmental Regulations
Use of hydraulic breakers may involve hydraulic fluid, which is subject to environmental regulations (e.g., EPA rules in the U.S.). Spill containment procedures and proper disposal of fluids are mandatory to prevent soil and water contamination.
Transportation and Logistics
Packaging and Handling
Concrete breaking tools must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use of wooden crates or heavy-duty pallets with corner protectors is recommended. Fragile components (e.g., chisels, seals, and hoses) should be individually wrapped and labeled.
Shipping Requirements
- Domestic Shipments: Comply with DOT (U.S.) or equivalent regulations for heavy machinery. Proper labeling, weight declarations, and secure load-securing are required.
- International Shipments: Adhere to IMDG Code (for sea freight), IATA (air), or ADR (road in Europe) as applicable. Export documentation, including commercial invoices and packing lists, must be accurate and complete.
Import/Export Compliance
Check for export controls (e.g., EAR in the U.S.) and import restrictions in destination countries. Tools with advanced electronics may require licenses. Ensure compliance with customs regulations and tariff classifications (HS Code: typically 8467.89 for powered hand tools).
Storage and Inventory Management
Store concrete breaking tools in a dry, secure, and temperature-controlled environment to prevent corrosion and damage. Keep tools off the floor on racks or pallets. Maintain an inventory log with serial numbers, maintenance dates, and calibration records.
Maintenance and Inspection
Implement a scheduled maintenance program in accordance with manufacturer guidelines. Inspect tools before and after each use for signs of wear, fluid leaks, or damage. Keep records of all inspections, repairs, and part replacements to support compliance audits.
Training and Documentation
Provide certified operator training, including equipment-specific instruction and emergency procedures. Maintain training records and ensure all documentation (manuals, safety data sheets, compliance certificates) is readily accessible.
Disposal and End-of-Life
Dispose of obsolete or damaged tools in accordance with local e-waste and hazardous material regulations. Recycle metal components and properly dispose of hydraulic oils and electronic parts through certified waste handlers.
In conclusion, sourcing concrete breaking tools requires a careful evaluation of several key factors including tool type (e.g., jackhammers, breaker hammers, hydraulic breakers), power source (electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic), durability, brand reputation, and compatibility with existing equipment. It is essential to consider the specific application needs, project scale, and safety requirements to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Additionally, evaluating supplier reliability, warranty options, maintenance support, and overall lifecycle costs will contribute to a more informed and cost-effective procurement decision. By balancing quality, performance, and long-term value, organizations can select the most suitable concrete breaking tools to enhance productivity and operational success on the job site.