The global compressing machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, chemicals, and ceramics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by increasing automation, stricter regulatory standards requiring consistent compression quality, and advancements in machine efficiency and precision. As manufacturers seek higher throughput, reduced downtime, and improved energy efficiency, the competition among compressing machine suppliers intensifies. In this evolving landscape, identifying leading manufacturers with proven innovation, global reach, and strong performance metrics becomes critical for businesses aiming to optimize their production lines. Based on market presence, technological capability, and customer reviews, the following list highlights the top 10 compressing machine manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Compressing Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
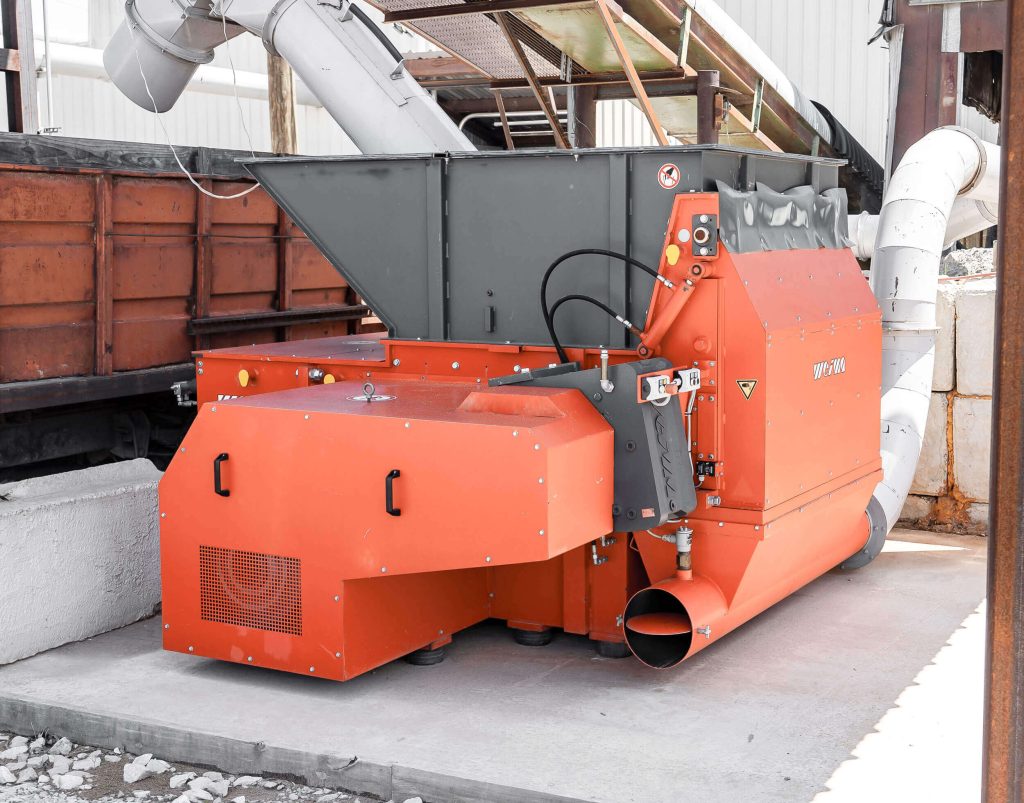
#1 Industrial shredders & compressing technology by WEIMA
Domain Est. 1997
Website: weima.com
Key Highlights: WEIMA is a leading manufacturer of machines for shredding, briquetting and dewatering of waste and residual materials from plastics, wood, paper, metal, biomass ……
#2 Chicago Pneumatic Homepage
Domain Est. 1994
Website: cp.com
Key Highlights: We are a global manufacturer of high-performance power tools, air compressors, generators, light towers, and hydraulic equipment for professional and industrial ……
#3 FS
Domain Est. 2003
Website: fs-elliott.com
Key Highlights: FS-Elliott is an air compressor manufacturer specializing in oil-free, centrifugal technology. Learn more about our compressed air solutions for ……
#4 Bauer Compressors: High
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bauercomp.com
Key Highlights: Bauer Compressors manufactures a broad range of compressor systems for various breathing-air and industrial applications….
#5 Ingersoll Rand Air Compressors, Power Tools, Lifting and Fluid …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ingersollrand.com
Key Highlights: Ingersoll Rand is a worldwide manufacturer and distributor of unrivalled compressed air solutions, parts and accessories and services for a wide range of ……
#6 Kaishan USA
Domain Est. 2018
Website: kaishanusa.com
Key Highlights: Kaishan USA offers a variety of air compressors for industrial and commercial use. Contact our team for expert customer service and support….
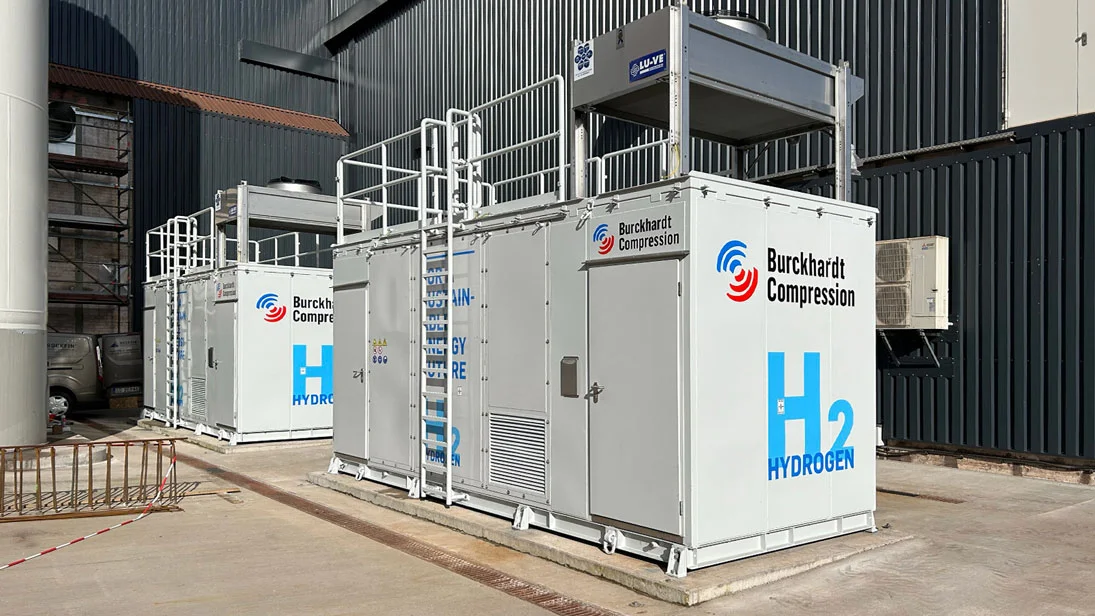
#7 Burckhardt Compression
Domain Est. 2000
Website: burckhardtcompression.com
Key Highlights: We – Burckhardt Compression – are a leading provider of reciprocating compressor systems and services. Discover our innovative solutions for various ……
#8 Natural Gas Compression Services & Equipment
Domain Est. 2000
Website: archrock.com
Key Highlights: Archrock (AROC) is the premier provider of natural gas compression services and equipment to customers in the oil and natural gas industry throughout the ……
#9 Blowers, Compressors & Turbos – Made by AERZEN
Domain Est. 2001
Website: aerzen.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to AERZEN. Since 1864 we design High-Performance Machines for the Industry. Profitability starts when compressor systems are tailored to the process….
#10
Domain Est. 2021
Website: kobelco-compressors.com
Key Highlights: KOBELCO COMPRESSORS is a global compressed air solution provider from Japan, having over 100 years history. Introducing corporate philosophy, history, locations ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Compressing Machine

H2: Projected Market Trends for Compressing Machines in 2026
The global compressing machine market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. H2, a clean energy vector gaining momentum, is emerging as a critical catalyst influencing the design, application, and demand for compressing machines across multiple sectors.
-
Increased Demand in Hydrogen Infrastructure
With global investments accelerating in hydrogen economy initiatives, compressing machines capable of handling high-pressure H2 are expected to see robust demand. By 2026, the expansion of hydrogen refueling stations for fuel cell vehicles—especially in regions like Europe, North America, and East Asia—will drive the need for specialized hydrogen compressors. These machines must meet stringent safety, efficiency, and purity standards, spurring innovation in diaphragm, ion-liquid, and reciprocating compressor technologies. -
Advancements in Hydrogen-Ready Compression Technologies
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing compressors specifically engineered for H2 service. Challenges such as hydrogen embrittlement, leakage prevention, and material compatibility are driving R&D in advanced alloys and sealing mechanisms. By 2026, smart compressors integrated with IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of H2 purity, pressure, and equipment health are expected to become standard, enhancing reliability and reducing downtime. -
Growth in Industrial and Energy Storage Applications
Beyond transportation, H2 compressing machines are set to play a pivotal role in industrial decarbonization and renewable energy storage. Sectors such as steel, chemicals, and power generation are adopting green hydrogen as a feedstock or energy carrier. This shift will require large-scale compression systems for H2 storage in underground caverns or high-pressure tanks, creating opportunities for high-capacity, energy-efficient compressing solutions. -
Regulatory and Safety Standards Harmonization
As H2 usage expands, regulatory bodies worldwide are expected to standardize safety protocols for H2 compression equipment by 2026. Compliance with ISO 19880 (gaseous hydrogen fueling) and ASME BPVC Section VIII will become mandatory, influencing design certifications and market access. This regulatory clarity will boost investor confidence and accelerate deployment of H2-compatible compressing infrastructure. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, is projected to lead in H2 compressor adoption due to aggressive national hydrogen strategies. Europe’s Green Deal and North America’s Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) incentives are also expected to stimulate demand. Meanwhile, emerging markets may witness slower uptake due to infrastructure and cost barriers, though pilot projects could pave the way for future growth. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Energy efficiency will be a key differentiator in the compressing machine market. By 2026, manufacturers will emphasize low-leakage designs, waste heat recovery, and integration with renewable-powered compression systems to minimize the carbon footprint of H2 compression processes.
In conclusion, the 2026 compressing machine market will be profoundly shaped by the rise of H2 as a clean energy carrier. Companies that innovate in H2-specific compression technologies, comply with evolving standards, and align with decarbonization goals will be best positioned to capitalize on this transformative trend.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Compressing Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing compressing machines—especially from international or low-cost suppliers—can present significant challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing compressing machines is inconsistent quality. Suppliers, particularly in regions with less stringent regulatory oversight, may cut corners on materials, assembly, or testing procedures. This can result in machines that fail prematurely, consume more energy, or pose safety risks. Buyers often discover discrepancies only after deployment, leading to costly downtime and replacement.
To mitigate this:
– Require third-party quality inspections before shipment.
– Verify compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, CE, ASME).
– Request performance testing data and conduct pilot runs.
Lack of Transparency in Component Sourcing
Many suppliers outsource critical components (e.g., motors, valves, control systems) without disclosing their origins. Low-quality or counterfeit parts can compromise machine reliability and longevity. Hidden supply chains also make it difficult to trace defects or ensure compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
Best practices include:
– Demanding a bill of materials (BOM) with component specifications.
– Auditing sub-suppliers where feasible.
– Requiring warranties on key components.
Inadequate or Missing Intellectual Property Protections
When developing or customizing compressing machines, IP risks become critical. Suppliers may copy design specifications, replicate proprietary technology, or sell similar machines to competitors. In jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement, legal recourse can be limited or ineffective.
To safeguard IP:
– Execute strong non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) before sharing technical details.
– Apply for patents or design rights in target markets.
– Include IP ownership clauses in supply contracts specifying that custom designs remain the buyer’s property.
Reverse Engineering and Design Theft
Some manufacturers, especially in regions known for industrial mimicry, may reverse engineer machines provided as samples or references. This can lead to unauthorized production and distribution of knock-offs, eroding competitive advantage.
Preventive measures:
– Limit the exposure of sensitive design features during site visits.
– Use modular designs where core IP is isolated and protected.
– Monitor global markets for potential infringement.
Misrepresentation of Certifications and Compliance
Suppliers may falsely claim certifications (e.g., CE, UL, ATEX) to appear more credible. These fake certifications can expose buyers to regulatory penalties, especially in safety-sensitive industries like oil & gas or pharmaceuticals.
Ensure authenticity by:
– Verifying certification numbers directly with issuing bodies.
– Requiring test reports from accredited laboratories.
– Conducting unannounced factory audits.
Failure to Secure Ongoing Support and Spare Parts
Even if initial quality is acceptable, many buyers face challenges with after-sales service. Suppliers may disappear, lack technical expertise, or charge exorbitant fees for spare parts—especially if they hold IP over critical components.
Protect your investment by:
– Negotiating long-term service agreements.
– Securing rights to source spare parts independently.
– Obtaining full technical documentation and software access.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable performance, reduce risk, and maintain a competitive edge when sourcing compressing machines.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Compressing Machine
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for transporting and operating a compressing machine, such as a baler, compactor, or industrial compressor. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe handling, legal compliance, and smooth operations.
Classification & Regulatory Requirements
Identify the type of compressing machine (e.g., hydraulic baler, waste compactor, air compressor) to determine applicable regulations. Machines may be subject to:
– International standards (e.g., ISO, CE marking in the EU)
– Occupational safety and health regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S.)
– Electrical safety standards (e.g., IEC, UL)
– Pressure equipment directives (if applicable, such as PED in Europe for pressurized systems)
Ensure all machines are certified and accompanied by technical documentation, including Declaration of Conformity, user manuals, and safety data sheets where applicable.
Packaging & Handling for Transport
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit:
– Secure moving parts with bracing or transit locks.
– Protect hydraulic lines, electrical connections, and control panels with protective covers.
– Use wooden crates or robust skids for heavy machinery.
– Clearly label packages with orientation arrows, fragile indicators, and handling instructions.
For oversized or heavy compressing machines, coordinate with freight specialists for appropriate rigging and lifting equipment.
International Shipping & Customs Compliance
When shipping across borders:
– Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
– Classify the machine using the correct Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 8474.80 for sorting, grinding, or compacting machines).
– Comply with import/export regulations, including potential permits for dual-use or heavy machinery.
– Ensure compliance with regional environmental and energy efficiency standards (e.g., CE, UKCA, Energy Star).
Verify any restrictions or duties based on destination country regulations.
Installation & Site Compliance
Upon delivery:
– Confirm site readiness, including floor load capacity, ventilation (for air compressors), and access to power supply.
– Follow manufacturer’s installation guidelines, including anchoring requirements and utility connections.
– Conduct initial safety checks and commissioning by qualified personnel.
– Verify compliance with local building, fire, and electrical codes.
Document all installation steps and retain records for audits or insurance purposes.
Operational Safety & Maintenance
Maintain ongoing compliance through:
– Regular preventive maintenance as per manufacturer schedule.
– Employee training on safe operation, lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, and emergency shutdown.
– Use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
– Keeping service logs and inspection records.
Report and address any malfunctions or safety incidents promptly.
End-of-Life & Environmental Compliance
At decommissioning:
– Follow environmental regulations for disposal of hydraulic fluids, oils, and electrical components.
– Recycle or dispose of machine parts in accordance with local waste management laws (e.g., WEEE in the EU).
– Use authorized waste handlers for hazardous materials.
Ensure compliance with extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes where applicable.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide minimizes risks, supports regulatory audits, and promotes safe, efficient operation of compressing machinery throughout its lifecycle.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Compressing Machine
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, production capacity, cost considerations, and supplier capabilities, sourcing a compressing machine is a critical step toward enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring product quality. The selected machine should align with current production needs while offering scalability for future growth. Key factors such as energy efficiency, durability, maintenance support, and compliance with safety and environmental standards must be prioritized during vendor selection.
Engaging with reputable suppliers offering strong after-sales service, warranty coverage, and technical support will minimize downtime and optimize long-term performance. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—rather than initial purchase price alone—ensures a cost-effective and sustainable investment.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing decision, backed by comprehensive market research and clear specifications, will lead to the acquisition of a reliable, high-performance compressing machine that supports business objectives and contributes to overall manufacturing excellence.