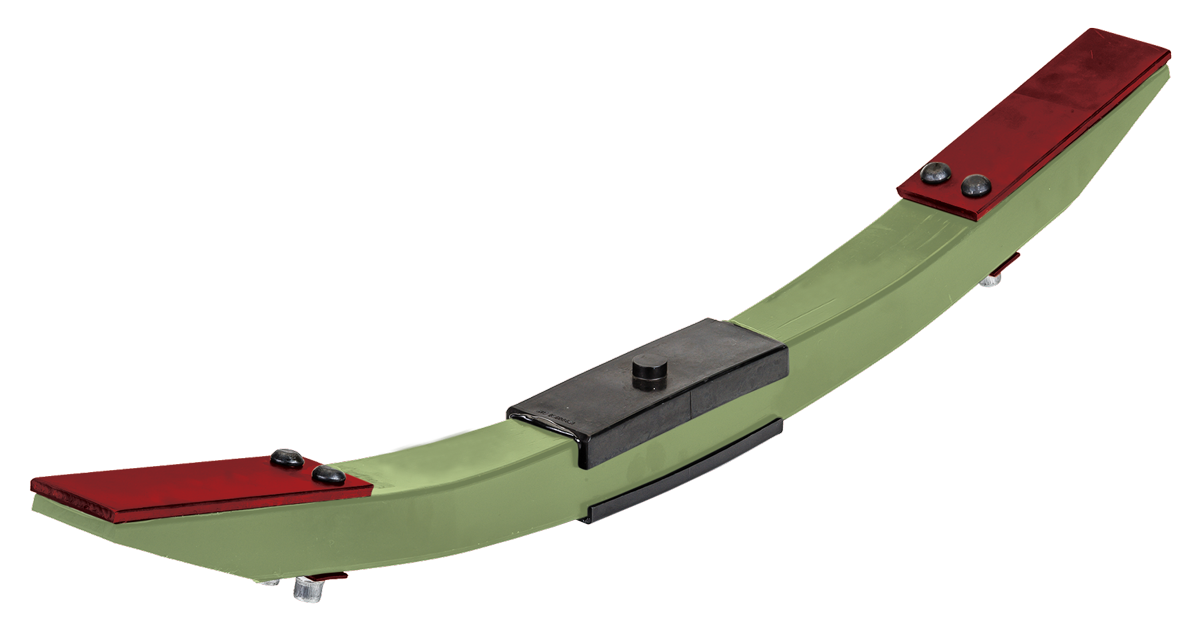
The global composite leaf spring market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the automotive industry’s increasing focus on vehicle lightweighting to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global automotive composites market, which includes composite leaf springs, was valued at USD 10.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.4% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, projecting the composite leaf spring market to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, fueled by rising demand in commercial vehicles and electric vehicles (EVs) where weight reduction directly enhances battery range. As automakers intensify efforts to meet stringent regulatory standards and improve performance, composite leaf springs—offering up to 70% weight savings compared to traditional steel springs—are emerging as a critical component in next-generation suspension systems. This performance advantage, combined with advancements in material technology and manufacturing scalability, has positioned a select group of manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and market share. Below, we profile the top 10 composite leaf spring manufacturers leading this transformation through technical excellence, strategic partnerships, and global supply chain integration.
Top 10 Composite Leaf Spring Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Composite Leaf Spring Factory and Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2023
Website: chleafspring.com
Key Highlights: Find a reliable composite leaf spring manufacturer, supplier, and factory in China. High-quality products and competitive prices available….
#2 Composite Leaf Springs
Domain Est. 1999
Website: heathcotes.com
Key Highlights: World leaders in the manufacture and supply of composite leaf springs for vibratory conveyors and feeders, offering unparalleled levels of service and support….
#3 Composite leaf spring Manufacturer & Supplier in China
Domain Est. 2014
Website: schybh.com
Key Highlights: Company Profile · Products · Parabolic Leaf Spring · Trailing arms spring · Multi leaf spring … Composite leaf spring leaf springs, and traditional leaf springs ……
#4 Composite Leaf Springs – Leaf Spring Suspension Parts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hypercoils.com
Key Highlights: Composite leaf springs are a lightweight, high-performance alternative to traditional coil suspension springs. Shop front & rear leaf spring suspension….
#5 Composite Components
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mubea.com
Key Highlights: Our transverse leaf spring designs offer a wide range of benefits: Vertical spring action and roll stabilization; Vertical spring action and wheel guidance ……
#6 Hendrickson Lightweight Composite Springs
Domain Est. 1997
Website: micro.hendrickson-intl.com
Key Highlights: Hendrickson composite springs offer many unique benefits over steel suspension systems. Among them is weight reduction for improved range, improved ride and ……
#7 Chassis Components
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sglcarbon.com
Key Highlights: SGL Carbon supplies high-quality leaf springs made from glass fiber-reinforced plastic for the automotive industry….
#8 Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mbha.com
Key Highlights: Composite Leaf Springs Our lightweight structural products are designed for both light and heavy duty vehicles and are developed entirely by our company Ziur ……
#9 Advanced Composite Springs
Domain Est. 2003
Website: avient.com
Key Highlights: Avient Advanced Composites are engineered with proprietary vinyl ester or epoxy resins and unidirectional glass or carbon fiber reinforcement technologies….
#10 Composite Leaf Spring
Domain Est. 2019
Website: huntsman-transportation.com
Key Highlights: We offer a range of resin systems for the production of composite leaf springs, that can be up to five times more durable than steel springs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Composite Leaf Spring

H2: Projected Market Trends for Composite Leaf Springs in 2026
By 2026, the global composite leaf spring market is poised for significant transformation, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, stringent regulatory pressures, and shifting industry demands. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Adoption in Commercial and Passenger Vehicles:
Driven by the imperative to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, automakers are increasingly integrating composite leaf springs into mainstream commercial fleets (trucks, buses) and higher-end passenger vehicles. By 2026, widespread adoption beyond niche applications is expected, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) where weight reduction directly extends battery range. Leading OEMs are anticipated to offer composite springs as standard or optional equipment across multiple models.
2. Dominance of Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Integration:
The rapid growth of the EV market is a primary catalyst. Composite leaf springs—being 40–70% lighter than traditional steel counterparts—play a crucial role in offsetting the weight of heavy battery packs. Automakers will increasingly specify composites to maximize energy efficiency and driving range, making them a strategic component in EV platform design by 2026.
3. Technological Advancements in Materials and Manufacturing:
Innovation in resin systems (e.g., thermoplastic vs. thermoset composites), fiber reinforcement (including hybrid glass/carbon fiber), and automated production techniques (such as pultrusion and compression molding) will enhance performance, durability, and cost-efficiency. These improvements will reduce production costs and scale up output, enabling broader market penetration and improving return on investment for manufacturers.
4. Intensifying Focus on Sustainability and Lifecycle Management:
Environmental regulations and consumer demand will push the industry toward greener solutions. By 2026, recyclability and end-of-life management of composite materials will become critical differentiators. Manufacturers investing in bio-based resins, recyclable thermoplastics, and closed-loop production systems will gain competitive advantage and meet tightening sustainability standards.
5. Regional Market Expansion and Supply Chain Localization:
While North America and Europe lead in composite spring adoption due to stringent CAFE and Euro 7 standards, Asia-Pacific (especially China and India) will see accelerated growth by 2026. Localized production hubs are expected to emerge to meet regional demand, reduce logistics costs, and comply with local content requirements, particularly in countries promoting EV manufacturing.
6. Strategic Partnerships and Vertical Integration:
Automakers and Tier-1 suppliers will deepen collaborations with composite material specialists and technology providers to co-develop optimized spring systems. Vertical integration—where suppliers control both material sourcing and component manufacturing—will increase to ensure quality, reduce lead times, and protect intellectual property in high-performance applications.
In summary, by 2026, the composite leaf spring market will transition from a high-performance alternative to a mainstream automotive solution, underpinned by electrification, lightweighting mandates, and continuous innovation. Companies that align with these trends will be best positioned to capture growing market share.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Composite Leaf Springs: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing composite leaf springs presents unique challenges compared to traditional steel springs, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, and legal exposure.
Quality Consistency and Performance Reliability
Composite materials are highly sensitive to manufacturing processes, making consistent quality a major challenge. Variations in fiber alignment, resin content, curing cycles, or layup techniques can significantly affect mechanical properties such as fatigue life, stiffness, and load capacity. Suppliers without rigorous process controls may deliver springs that fail prematurely under real-world conditions. Additionally, environmental factors like temperature and UV exposure can degrade composite performance if materials are not properly engineered and tested, leading to long-term reliability issues.
Hidden Defects and Inspection Limitations
Unlike metal springs, composite leaf springs can harbor internal defects—such as delamination, voids, or dry fibers—that are not visible during standard visual inspections. Without access to advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing or X-ray CT scanning, buyers may accept substandard components. Many suppliers, especially lower-tier or unfamiliar vendors, may lack comprehensive quality assurance systems, increasing the risk of undetected flaws compromising vehicle safety and durability.
Intellectual Property Exposure and Reverse Engineering Risks
Composite spring designs often incorporate proprietary resin formulations, fiber architectures, and manufacturing know-how protected as trade secrets or patents. When sourcing from third parties—especially in regions with weaker IP enforcement—there is a heightened risk of design replication or unauthorized technology transfer. Sharing detailed specifications or CAD models without proper legal safeguards (e.g., NDAs, licensing agreements) can expose core innovations. Furthermore, suppliers may use similar-looking designs that infringe on existing patents, potentially implicating the buyer in IP disputes.
Supply Chain Transparency and Material Traceability
The performance of composite springs depends heavily on the quality and origin of raw materials (e.g., carbon fiber, epoxy resins). Lack of transparency in the supply chain can result in the use of subpar or counterfeit materials, impacting both product quality and compliance with industry standards. Without strict traceability protocols, it becomes difficult to verify material certifications or respond effectively to field failures, increasing liability risks.
Overlooking Long-Term Support and Scalability
Many composite spring suppliers are niche players or startups with limited production capacity and unclear long-term viability. Relying on such suppliers without assessing their scalability, financial stability, and ability to support future volume demands can jeopardize production continuity. Additionally, lack of documented processes and engineering support may hinder troubleshooting, design iterations, or technology transfer if a supplier relationship ends.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Composite Leaf Spring
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe, efficient, and legal handling, transportation, and use of Composite Leaf Springs. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational safety throughout the supply chain.
Handling and Storage
- Packaging: Composite Leaf Springs must be transported in protective packaging (e.g., corrugated cardboard with corner boards or custom crates) to prevent surface damage, edge chipping, or deformation. Avoid direct exposure to moisture or contaminants.
- Lifting and Moving: Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., vacuum lifters or padded forklifts) to avoid point loading or impact on the spring surface. Never drag or drop components.
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, climate-controlled environment (ideally 15–25°C and 30–60% relative humidity). Keep away from direct sunlight, UV exposure, and sources of heat or chemicals (e.g., solvents, oils).
- Positioning: Store flat on pallets or in designated racks to prevent bending or warping. Avoid stacking unless designed for it; if stacking is required, use separators and limit height.
Transportation Requirements
- Mode of Transport: Composite Leaf Springs can be shipped via road, rail, sea, or air. Select transport modes that minimize vibration, shock, and temperature extremes. Use climate-controlled containers when necessary.
- Securing Loads: Ensure springs are securely fastened within containers or vehicles using straps, braces, or dunnage to prevent movement during transit.
- Labeling: Packages must be clearly labeled with:
- “Fragile – Handle with Care”
- “This Side Up” (if orientation-sensitive)
- Part number, quantity, and destination
- Hazard symbols (if applicable, based on resin system or additives)
- Documentation: Include packing list, bill of lading, and any required export documentation (e.g., Commercial Invoice, Certificate of Origin).
Regulatory Compliance
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS): Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheets for the composite materials used (e.g., carbon fiber, epoxy resin). These must be accessible to handlers and emergency responders.
- Transport Regulations:
- IATA/ICAO (air): Comply with dangerous goods regulations if resin components are classified as hazardous.
- IMDG Code (sea): Follow guidelines for packaging and labeling if shipping internationally by vessel.
- ADR/RID (road/rail in Europe): Adhere to hazardous materials transport rules if applicable.
- Environmental Compliance:
- Follow local and international regulations (e.g., REACH, RoHS) regarding restricted substances in materials.
- Ensure proper disposal/recycling procedures for damaged or end-of-life springs in compliance with waste management laws.
Import/Export Considerations
- Customs Classification: Use correct HS (Harmonized System) code for composite automotive components (typically under 8708.29 or material-specific codes). Confirm with local customs authorities.
- Export Controls: Verify if carbon fiber components are subject to export restrictions (e.g., ITAR, EAR in the U.S.). Obtain necessary licenses if required.
- Duty and Tariff: Be aware of import duties, taxes, and trade agreements affecting shipment costs.
Quality and Traceability
- Batch Traceability: Maintain lot numbers and manufacturing dates for full traceability from production to delivery.
- Inspection Upon Receipt: Recipients should inspect shipments for damage and verify contents against packing lists before acceptance.
- Non-Conformance Reporting: Establish a process to report and handle damaged or non-compliant shipments promptly.
End-User Compliance and Installation
- Installation Guidelines: Provide clear instructions for proper installation, torque specifications, and alignment to prevent premature failure.
- Compliance Certification: Supply relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or customer-specific approvals) upon request.
- Warranty and Liability: Define warranty terms and ensure compliance with automotive safety standards (e.g., FMVSS, ECE Regulations) where applicable.
Adhering to this guide ensures the safe and compliant movement of Composite Leaf Springs from manufacturing to end-use, minimizing risk and supporting sustainable, efficient logistics operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Composite Leaf Spring:
Sourcing composite leaf springs presents a strategic opportunity to enhance vehicle performance, reduce weight, and improve fuel efficiency or electric vehicle range. Compared to traditional steel leaf springs, composite variants—typically made from materials like glass or carbon fiber-reinforced polymers—offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and fatigue life, contributing to longer service life and lower lifecycle costs.
Successful sourcing requires careful evaluation of suppliers based on technical expertise, production capabilities, quality certifications, and proven track record in automotive applications. It is essential to ensure material consistency, compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO/TS 16949), and support for design integration and testing. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—not just initial price—helps justify the investment through gains in efficiency, durability, and sustainability.
In conclusion, sourcing composite leaf springs aligns with goals of lightweighting and innovation in modern automotive and commercial vehicle designs. With the right supplier partnership and due diligence, composite leaf springs can deliver significant performance advantages and support long-term competitiveness in an evolving transportation market.