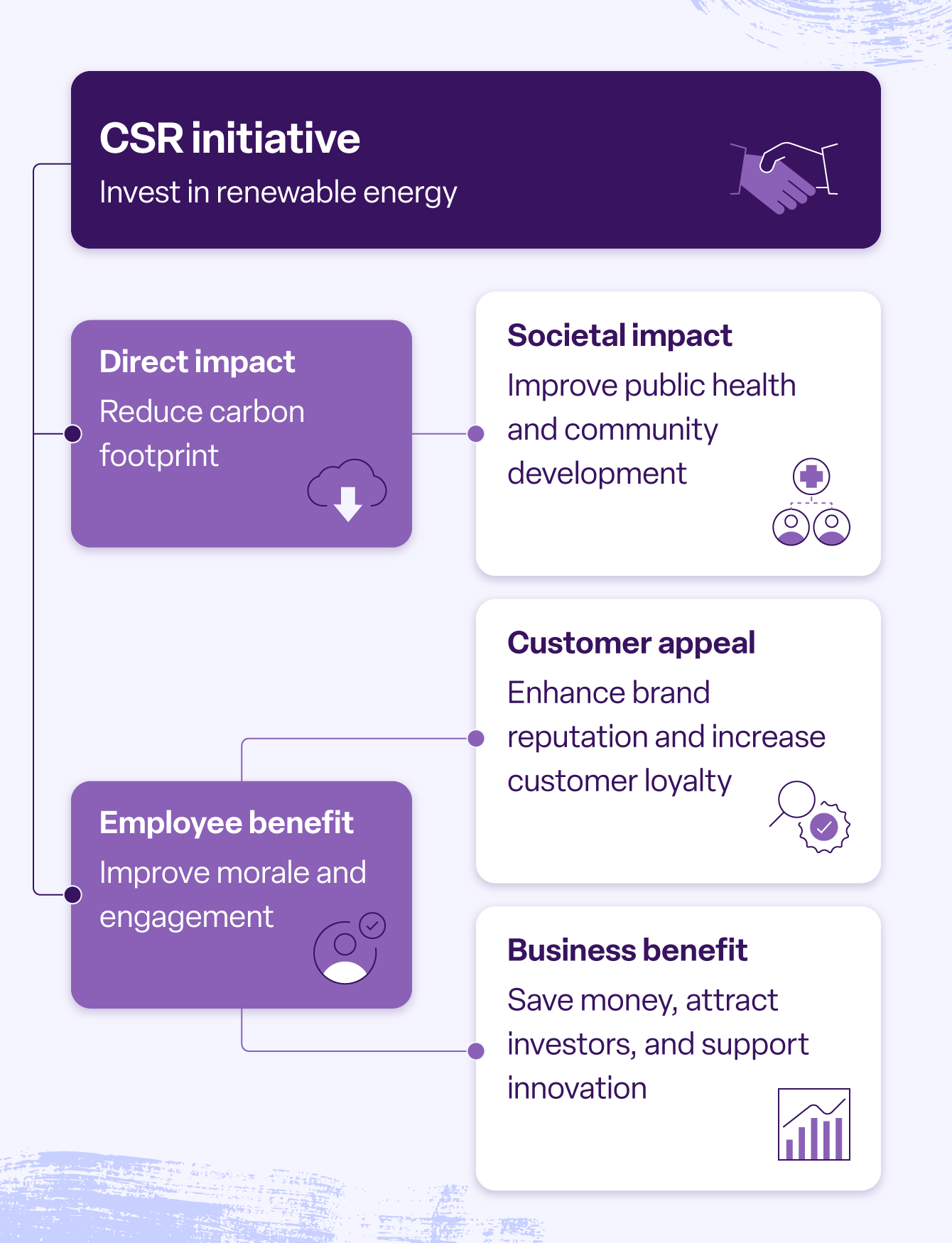
The global corporate social responsibility (CSR) market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing consumer demand for ethical business practices and sustainable supply chains. According to Grand View Research, the global CSR market size was valued at USD 22.86 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2024 to 2030. This growth reflects a heightened emphasis on environmental stewardship, labor practices, and community engagement across industries. As sustainability becomes a competitive differentiator, a growing number of manufacturers are embedding CSR into their core operations. In response, leading companies are setting new benchmarks by integrating ethical sourcing, carbon reduction initiatives, and circular economy principles into their manufacturing processes. The following list highlights eight industry leaders that exemplify corporate social responsibility in manufacturing, combining data-driven performance with transparent, impactful practices.
Top 8 Companies With Corporate Social Responsibility Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 12 Brands Doing Corporate Social Responsibility Successfully (DMI)
Domain Est. 2003
Website: tko-communications.com
Key Highlights: In fact, 90 percent of companies on the S&P 500 index published CSR reports in 2019—up from 86 percent in 2018, 75 percent in 2014, and only 20 ……
#2 11 Socially Responsible Companies to Applaud
Domain Est. 2010
Website: pro.gofundme.com
Key Highlights: Developers plan to rely completely on rooftop solar panels and a nearby solar farm to generate all power throughout the facility. Additionally, ……
#3 16 Brands Doing Corporate Social Responsibility Successfully
Domain Est. 2011
Website: digitalmarketinginstitute.com
Key Highlights: As a brand, Coca-Cola is putting a huge focus on sustainability. The key areas are climate, packaging and agriculture along with water …Missing: “-ebay” “-pinterest”…
#4 12 Corporate Social Responsibility Examples by Top Brands
Domain Est. 2011
Website: goodera.com
Key Highlights: Their focus on nutrition and safe access to food accounts for Food Safety, Sustainable Chemistry and Animal Welfare practices. Amazon. CSR Goals ……
#5 19 socially responsible companies to inspire your CSR efforts
Domain Est. 2022
Website: bonterratech.com
Key Highlights: For 2025, the company is focused on sourcing local produce, understanding employee sentiment, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Examples of …Missing: “-ebay” “-pinterest”…
#6 Best CSR Companies
Domain Est. 2011
Website: doublethedonation.com
Key Highlights: Read on to explore our selection of standout CSR initiatives and see which elements you can adopt in your efforts. Chipotle is one of the best ……
#7 14 Best Socially Responsible Companies Making an Impact
Domain Est. 2013
Website: donorbox.org
Key Highlights: Rating 4.8 (234) · $0.00 to $475.00In this blog, we discuss the concept of CSR, provide examples of socially responsible companies, and offer tips on how to make the most of CS…
#8 Top 10 Socially Responsible Companies
Domain Est. 2023
Website: theconnectaverse.com
Key Highlights: Discover the top 10 socially responsible companies making a positive impact. Learn how their CSR initiatives drive change and inspire ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Companies With Corporate Social Responsibility
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Companies With Corporate Social Responsibility
As we approach 2026, corporate social responsibility (CSR) is evolving from a peripheral corporate initiative into a core strategic driver shaping market competitiveness, consumer behavior, and investment decisions. Companies embedding CSR deeply into their operations are not only enhancing their reputations but also gaining measurable financial and operational advantages. Below are key market trends expected to define the CSR landscape in 2026:
1. Regulatory Pressure and Standardized Reporting
Governments and international bodies are advancing mandatory ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) disclosures. The European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and similar frameworks in the U.S. and Asia are pushing companies toward transparent, auditable CSR reporting. By 2026, firms without robust, standardized sustainability reporting risk regulatory penalties and diminished investor confidence.
2. Consumer-Driven CSR Accountability
Consumers, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, increasingly favor brands that demonstrate authentic social and environmental commitments. By 2026, purchasing decisions will be more influenced by a company’s demonstrable impact—such as carbon neutrality, ethical sourcing, and diversity—than by price or convenience alone. Brands perceived as “greenwashing” will face swift public backlash and reputational damage.
3. Integration of CSR into Core Business Strategy
Leading companies are moving beyond philanthropy to integrate CSR into product development, supply chain management, and innovation. In 2026, successful firms will treat sustainability as a driver of efficiency and innovation—for example, reducing waste to cut costs or launching circular economy models to attract eco-conscious customers.
4. ESG Investing Reaches Mainstream Dominance
By 2026, ESG-focused funds are projected to control over 50% of global managed assets. Institutional investors are using advanced analytics to assess long-term CSR performance, linking financing terms to sustainability KPIs. Companies with strong CSR track records will enjoy lower capital costs and expanded access to green bonds and sustainability-linked loans.
5. Technology-Enabled CSR Transparency
Blockchain, AI, and IoT are enabling real-time tracking of supply chains and carbon footprints. By 2026, consumers and regulators will demand verifiable data on a company’s environmental and social impact. Firms leveraging technology for transparency—such as blockchain-tracked sourcing or AI-driven emissions modeling—will gain trust and market share.
6. Focus on Social Equity and Inclusion
CSR is expanding beyond environmental concerns to include DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion), fair wages, and community investment. By 2026, companies will be evaluated not just on carbon metrics but on their contributions to social justice. Workforce diversity, living wage policies, and inclusive hiring practices will become key differentiators.
7. Rise of B Corps and Purpose-Driven Business Models
The number of certified B Corporations and benefit corporations is growing rapidly. In 2026, these purpose-driven entities will influence broader market norms, pressuring traditional firms to adopt stakeholder capitalism over shareholder primacy. Investors and talent will increasingly favor companies with legal commitments to social and environmental performance.
Conclusion
By 2026, corporate social responsibility will no longer be a “nice-to-have” but a fundamental determinant of market success. Companies that proactively embed CSR into strategy, operations, and culture will lead in innovation, talent attraction, customer loyalty, and financial performance. Those lagging will face increasing regulatory, financial, and reputational risks in an accountability-driven global economy.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Companies With Corporate Social Responsibility (Quality, IP)
When sourcing companies that claim strong Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) practices—particularly related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection—organizations often encounter several recurring challenges. Being aware of these pitfalls can help mitigate risks and ensure ethical, reliable partnerships.
1. Overreliance on Marketing Claims Without Verification
Many suppliers promote CSR initiatives as part of their branding, but these claims are not always backed by verifiable data. Relying solely on brochures, websites, or certifications without independent audits can lead to misinformation. Conduct third-party assessments or on-site evaluations to confirm CSR compliance.
2. Inadequate Due Diligence on IP Protection Practices
Even companies with strong CSR reputations may lack robust IP safeguards. Suppliers in certain regions may have weak enforcement of IP laws or informal practices that increase the risk of design theft, reverse engineering, or unauthorized production. Ensure contractual protections and verify past IP incidents during the vetting process.
3. Misalignment Between Local Practices and Global CSR Standards
A company may meet local regulatory requirements but fall short of international CSR benchmarks. For example, labor conditions or environmental policies may be legally compliant locally but considered unethical by global standards. Use globally recognized frameworks (e.g., UN Guiding Principles, ISO 26000) to evaluate alignment.
4. Supply Chain Opacity and Subcontracting Risks
A responsible primary supplier might subcontract work to unvetted third parties, undermining quality and ethical standards. This lack of visibility increases exposure to poor labor practices, counterfeit materials, or IP breaches. Demand full supply chain transparency and include subcontracting clauses in contracts.
5. Inconsistent Quality Standards Despite CSR Claims
CSR initiatives often focus on labor and environmental issues, but may not correlate with consistent product quality. A supplier might treat workers fairly but lack quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), leading to defects or non-compliance. Evaluate both ethical practices and operational excellence.
6. Certification Fraud or “CSR Washing”
Some suppliers obtain certifications through questionable means or exaggerate their CSR achievements—a practice akin to “greenwashing” or “ethics washing.” Verify certifications through issuing bodies and seek evidence of continuous improvement, not one-time compliance.
7. Lack of Ongoing Monitoring and Accountability
Initial assessments are not enough. Without regular audits, performance reviews, and corrective action plans, CSR standards can deteriorate over time. Establish long-term monitoring mechanisms and key performance indicators (KPIs) tied to both quality and ethical performance.
8. Cultural and Communication Barriers
Differences in language, business practices, or cultural norms can lead to misunderstandings about CSR expectations, especially regarding IP rights or quality protocols. Invest in clear communication, training, and local representation to bridge gaps.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, organizations can build resilient, ethical sourcing strategies that uphold both quality standards and intellectual property integrity.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Companies With Corporate Social Responsibility
Implementing Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in logistics operations is not only an ethical imperative but also a strategic advantage. This guide outlines key considerations and best practices to ensure your logistics and supply chain activities align with CSR goals while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Establish Ethical Sourcing and Supplier Standards
Develop and enforce a supplier code of conduct that emphasizes labor rights, environmental stewardship, and ethical business practices. Conduct regular audits and assessments of suppliers, prioritizing partnerships with vendors who share your CSR values. Require transparency in sourcing practices, including traceability of raw materials to prevent exploitation and environmental degradation.
Optimize for Environmental Sustainability
Reduce the environmental footprint of your logistics operations through sustainable transportation, packaging, and warehousing. Transition to low-emission or electric vehicles, optimize delivery routes using data analytics, and consolidate shipments to minimize fuel consumption. Use recyclable or biodegradable packaging materials and implement energy-efficient technologies in distribution centers.
Ensure Labor Rights and Fair Working Conditions
Guarantee fair wages, safe working environments, and respect for human rights across your logistics network, including third-party contractors. Provide training on labor laws and anti-discrimination policies. Monitor working hours and prevent forced or child labor through due diligence and third-party certifications such as Fair Trade or SA8000.
Comply with International and Local Regulations
Stay current with global and regional compliance requirements, including customs regulations, import/export controls, environmental laws (e.g., EU Green Deal, EPA standards), and transportation safety rules (e.g., FMCSA, IATA). Implement compliance management systems to track regulatory changes and ensure documentation accuracy across borders.
Enhance Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Leverage technology such as blockchain, IoT, and cloud-based platforms to increase visibility across the supply chain. Provide stakeholders with accessible data on product origins, transportation methods, and environmental impact. Transparency builds trust and supports accountability in CSR reporting.
Promote Community Engagement and Responsible Practices
Support local communities near logistics hubs through job creation, infrastructure development, and environmental initiatives. Minimize disruptions caused by transportation (e.g., noise, congestion) and partner with local organizations for social impact projects. Communicate CSR efforts clearly to customers and investors.
Monitor, Report, and Continuously Improve
Set measurable CSR goals for logistics performance (e.g., carbon emissions reduction, waste diversion rates). Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and conduct regular internal reviews. Publish annual sustainability reports aligned with frameworks such as GRI, SASB, or UN SDGs to demonstrate commitment and drive continuous improvement.
By integrating CSR into logistics and compliance strategies, companies can build resilient, responsible supply chains that deliver long-term value for business, society, and the planet.
In conclusion, sourcing from companies that prioritize corporate social responsibility (CSR) offers significant long-term benefits for businesses, society, and the environment. By partnering with socially responsible suppliers, organizations enhance their brand reputation, build consumer trust, and reduce risks related to labor practices, environmental damage, and ethical violations. CSR-aligned sourcing also promotes sustainable supply chains, drives innovation, and supports long-term profitability. As stakeholders increasingly demand transparency and ethical accountability, integrating CSR into sourcing strategies is no longer optional but a strategic imperative. Ultimately, responsible sourcing fosters a more equitable and sustainable global economy while positioning companies as leaders in ethical business practices.