The global commercial kitchen equipment market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand from the foodservice industry for efficient, high-capacity cooking solutions. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global commercial foodservice equipment market was valued at USD 69.8 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023 to 2028. A key driver within this segment is the increasing popularity of smoked cuisine in restaurants, fueled by consumer preference for bold flavors and artisanal cooking methods. This trend has led to a surge in demand for reliable, high-performance commercial smokers. As operators seek durable and scalable equipment, manufacturers are responding with innovations in temperature control, fuel efficiency, and smart monitoring systems. Against this backdrop, we examine the top 10 commercial smoker manufacturers equipping restaurants with the tools to meet evolving culinary demands.
Top 10 Commercial Smokers For Restaurants Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Cookshack Smokers, Grills & Pizza Ovens; Commercial …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cookshack.com
Key Highlights: Premium cooking equipment, accessories, sauces & cookbooks straight from Cookshack, Inc.—engineered for residential and commercial BBQ excellence….
#2 Bradley Smoker: Food Smokers
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bradleysmoker.com
Key Highlights: 4-day delivery 30-day returnsBradley electric smokers use Pure Smoke technology to give you the purest smoke possible. Our uniquely designed wood bisquettes are burned for a precis…
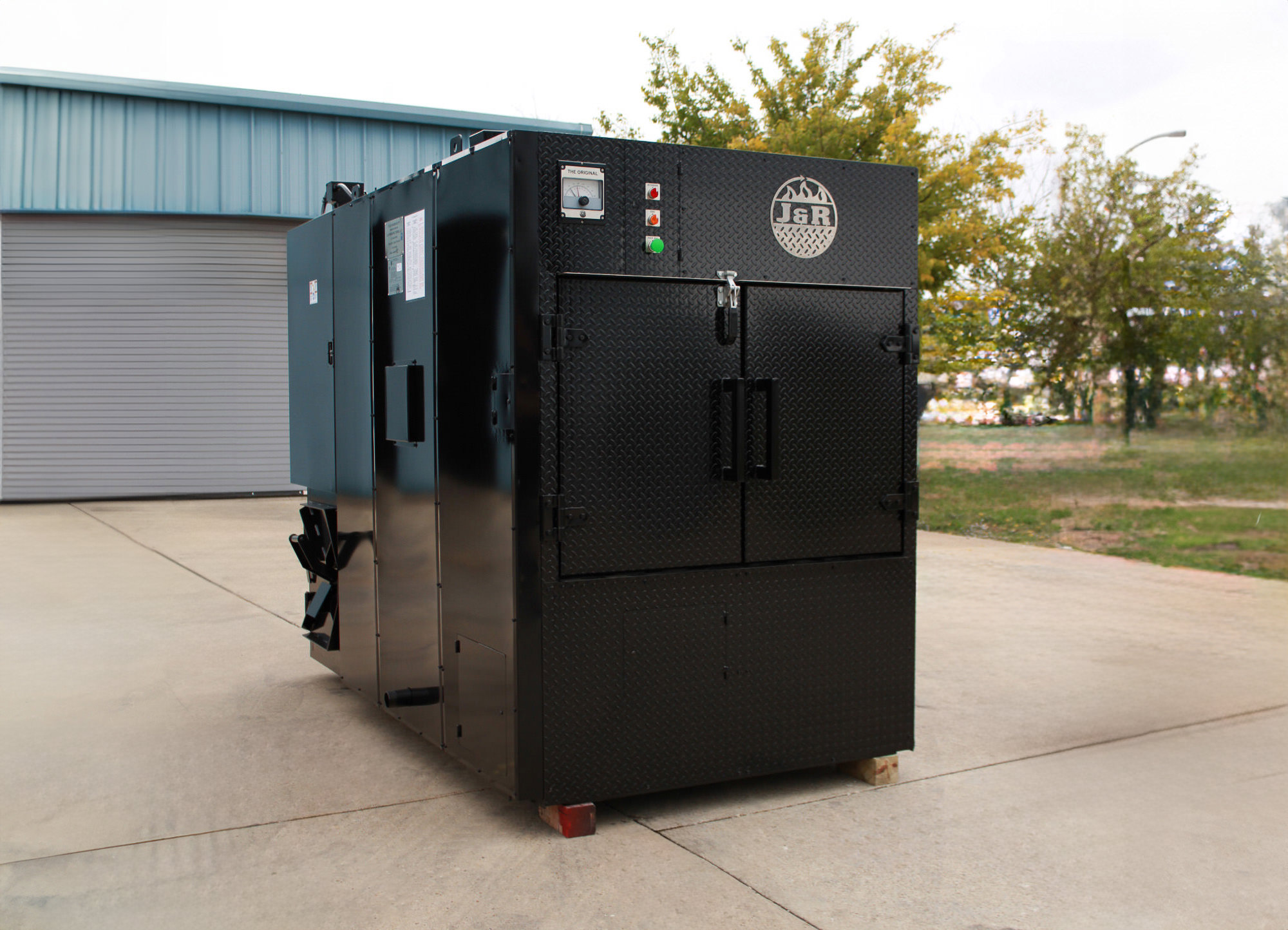
#3 J&R Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jrmanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: J&R takes pride in crafting top-quality commercial smokers in the USA, including commercial rotisserie smoker models designed and built in TEXAS….
#4 Restaurant & Commercial Kitchen Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: alto-shaam.com
Key Highlights: Alto-Shaam guarantees unmatched performance, precision and quality. Explore our full line of commercial kitchen & restaurant ovens & supplies today!…
#5 Meadow Creek BBQ Smokers, Pig Roasters, and Grills
Domain Est. 2002
Website: meadowcreekbbq.com
Key Highlights: Pro pitmasters worldwide choose Meadow Creek BBQ smokers and grills to cook the finest barbecue under the most demanding conditions….
#6 Smokers for Restaurants
Domain Est. 2006
Website: americanbarbecuesystems.com
Key Highlights: American Barbecue Systems offers customizable smokers designed with restaurateurs in mind. ABS smokers are proudly made in Kansas City of American made steel….
#7 Commercial Smokers
Domain Est. 2007
Website: pro-smoker.com
Key Highlights: Pro Smokers® Commercial Smokehouses offer unparalleled durability and design. All our commercial smokers are made in the USA and are custom built to meet ……
#8 Commercial
Domain Est. 2012
#9 Rotisserie Grills for Sale Online
Domain Est. 2020
Website: semosmokers.com
Key Highlights: We have a wide array of insulated rotisserie smokers & cookers for sale. You will love our commercial & residential smokers….
#10 Hakka Digital Electric Smoker Grill 8 Racks Outdoor BBQ …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: hakkabros.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (9) Enhance your BBQ experience with this 9-layer stainless steel electric smoker. Featuring a digital temperature control (86-248°F), 12-hour timer, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Commercial Smokers For Restaurants
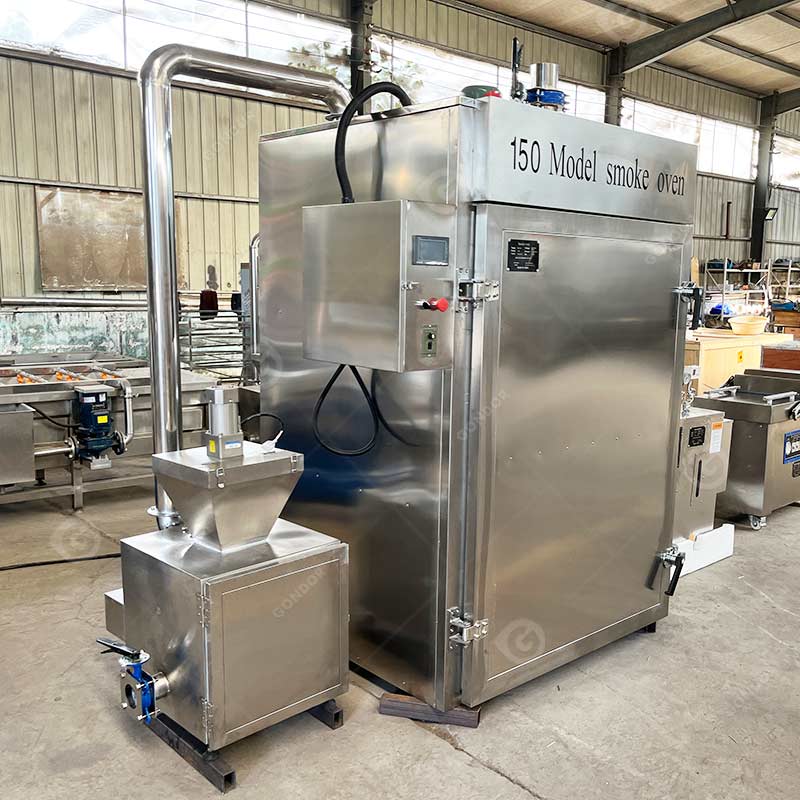

2026 Market Trends for Commercial Smokers in Restaurants
As the restaurant industry evolves with shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability demands, commercial smokers are undergoing significant transformation. The 2026 outlook for commercial smokers in the restaurant sector reflects a convergence of culinary innovation, automation, and eco-conscious practices. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the adoption and development of commercial smokers for restaurants in 2026.
Rising Demand for Authentic and Smoked Specialty Cuisine
Consumer interest in bold, authentic flavors—particularly barbecue, smoked meats, and globally inspired smoked dishes—is driving restaurants to invest in high-performance commercial smokers. In 2026, establishments are increasingly offering smoked plant-based proteins, seafood, cheeses, and vegetables to meet diverse dietary preferences. This trend is expanding the role of smokers beyond traditional barbecue joints into upscale steakhouses, gastropubs, and fusion restaurants.
Integration of Smart Technology and IoT
By 2026, commercial smokers are becoming smarter and more connected. Leading manufacturers are incorporating Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities, allowing chefs to monitor and control smoking processes remotely via mobile apps. Features such as real-time temperature tracking, automated smoke level adjustments, and predictive maintenance alerts are enhancing operational efficiency, consistency, and food safety. These smart systems also enable data collection for recipe optimization and energy use tracking.
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Environmental regulations and rising energy costs are pushing restaurants to adopt energy-efficient equipment. In 2026, commercial smokers are designed with improved insulation, hybrid fuel options (e.g., electric and wood pellet combos), and lower emissions profiles. Manufacturers are increasingly using recyclable materials and offering carbon footprint labeling. Additionally, wood pellet smokers utilizing sustainably sourced biomass are gaining favor over traditional charcoal or gas models.
Modular and Space-Optimized Designs
With urban restaurants facing space constraints, compact and modular smokers are in high demand. In 2026, manufacturers are introducing stackable units, under-counter models, and multi-functional smoker-ovens that maximize utility in limited kitchen footprints. These designs cater to fast-casual concepts and pop-up eateries seeking to offer smoked items without a dedicated smoking area.
Emphasis on Food Safety and Compliance
Regulatory scrutiny around food safety and airborne emissions continues to intensify. Commercial smokers in 2026 are engineered to meet stricter health codes, including advanced filtration systems to reduce smoke and grease discharge. Built-in HACCP-compliant logging and automated sanitation cycles are becoming standard features, helping restaurants maintain compliance and reduce labor burdens.
Growth of Cloud Kitchens and Virtual Brands
The rise of delivery-only cloud kitchens and virtual brands focused on smoked specialties (e.g., smoked wings, smoked tacos) is fueling demand for compact, high-throughput smokers. These operations prioritize fast turnaround and flavor consistency, favoring automated smokers that support batch processing and seamless integration with digital kitchen management systems.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for commercial smokers in restaurants is characterized by innovation, efficiency, and adaptability. As culinary trends favor smoked and artisanal flavors, and operational demands emphasize sustainability and automation, commercial smokers are evolving into intelligent, eco-friendly, and versatile kitchen assets. Restaurants that leverage these advancements will be well-positioned to meet consumer expectations, reduce costs, and stand out in a competitive foodservice landscape.
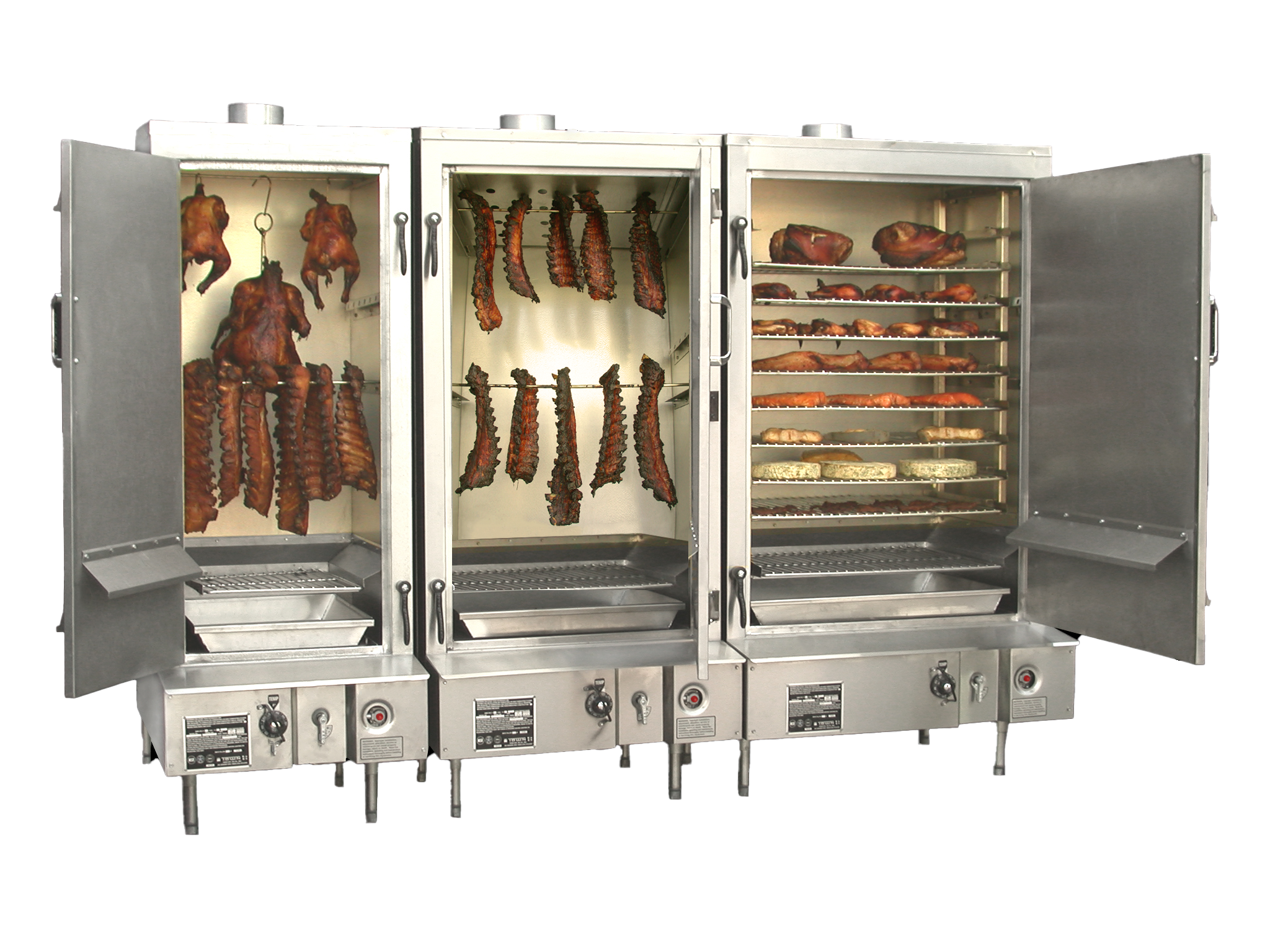

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Commercial Smokers for Restaurants (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing commercial smokers for restaurant use involves more than just selecting a model that fits the kitchen space. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety risks, legal exposure, and damage to brand reputation. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Overlooking Build Quality and Material Standards
One of the most frequent mistakes is prioritizing upfront cost over long-term durability. Low-cost smokers may use thin-gauge steel, inferior insulation, or substandard welding, leading to warping, heat loss, and shortened equipment lifespan. Restaurants should verify that units are constructed from food-grade stainless steel (typically 304 or 430 grade), have proper insulation for consistent temperature control, and meet NSF/ANSI certification standards for commercial foodservice equipment.
Ignoring Temperature Control and Consistency
Inconsistent smoking results can compromise menu quality and customer satisfaction. Some budget smokers lack precise thermostatic controls, adequate airflow management, or proper heat distribution. This leads to uneven cooking, extended cook times, and potential food safety hazards. Ensure the smoker offers digital controls, reliable calibration, and the ability to maintain stable temperatures within ±5°F, especially during prolonged use.
Failing to Verify Safety and Compliance Certifications
Using uncertified equipment poses serious health, safety, and legal risks. Always confirm that the smoker carries certifications from recognized bodies such as NSF International, UL (Underwriters Laboratories), or ETL. These verify compliance with electrical, fire, and sanitation codes. Operating non-certified equipment may void insurance policies and result in failed health inspections.
Neglecting Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Custom or Branded Designs
Restaurants seeking custom smoker designs—especially those replicating patented features from established brands (e.g., specific smoke stack configurations, proprietary heat circulation systems)—risk infringing on intellectual property rights. Using knock-off equipment that mimics patented technology can expose the operator to legal action, even if the restaurant did not manufacture the unit. Always source from reputable manufacturers who can provide documentation confirming their designs do not infringe on existing patents or trademarks.
Assuming All “Commercial Grade” Equipment Is Equal
The term “commercial grade” is not regulated and can be misleading. Some suppliers rebrand residential units or import uncertified foreign models as commercial equipment. Due diligence is essential: review product specifications, warranty terms, and service support. Request third-party test reports or references from other restaurant operators using the same model.
Overlooking After-Sales Support and Service Availability
Even high-quality smokers require maintenance and occasional repairs. Sourcing from manufacturers or distributors without reliable technical support, spare parts availability, or service networks can lead to extended downtime. Confirm service coverage in your region and evaluate warranty terms—especially labor coverage and response time—before purchase.
Disregarding Ventilation and Installation Requirements
Many commercial smokers, especially wood-fired or pellet models, require specific ventilation systems, clearance distances, and gas or electrical provisions. Installing a smoker without verifying compatibility with existing infrastructure can lead to safety code violations, poor performance, or costly retrofits. Consult with a qualified technician during the sourcing phase to ensure seamless integration.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—focusing on verified quality, compliance, and IP integrity—restaurants can invest in commercial smokers that deliver consistent performance, ensure food safety, and avoid legal and operational complications.
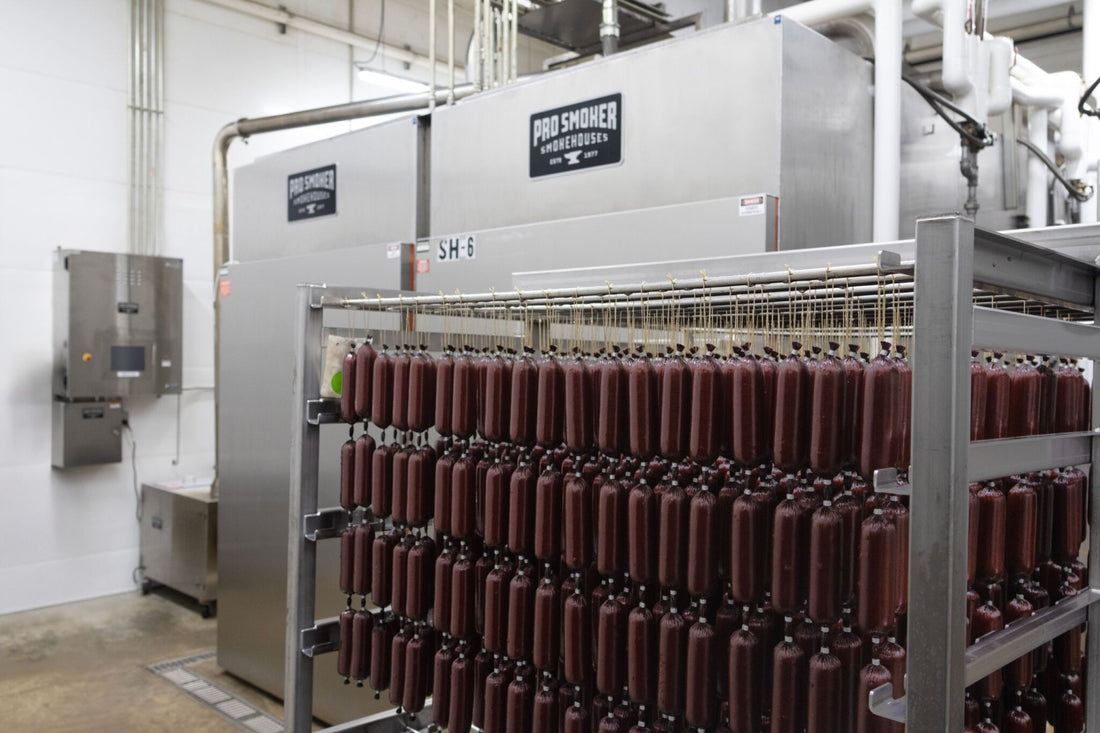

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Commercial Smokers in Restaurants
Understanding Equipment Requirements and Sourcing
When integrating a commercial smoker into a restaurant kitchen, selecting the right equipment is critical. Commercial smokers must meet stringent health, safety, and performance standards. Choose models certified by recognized agencies such as NSF International, which ensures food safety and sanitation compliance. Consider fuel type—electric, gas, charcoal, or wood—as each has different ventilation, installation, and operational requirements. Ensure the smoker is appropriately sized for your menu volume and kitchen layout, allowing for proper clearance and workflow integration.
Ventilation and Exhaust System Compliance
Commercial smokers produce significant smoke, grease, and particulate matter, making proper ventilation essential. Install a UL 710–certified exhaust hood designed specifically for high-heat and smoke-producing appliances. This hood must be connected to a Type I grease duct system and a properly rated exhaust fan that meets local fire and building codes. Regular cleaning and maintenance of filters, ducts, and fans are required to prevent fire hazards and maintain compliance with health department regulations.
Installation and Gas/Electrical Specifications
Engage licensed professionals for the installation of gas or electric smokers. Gas units require proper gas line sizing, shutoff valves, and leak testing per local utility and plumbing codes. Electrical models need dedicated circuits with correct voltage (e.g., 208V or 240V) to prevent overloads. All installations must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local jurisdiction requirements. Submit plans to the authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) for approval before operation begins.
Food Safety and HACCP Plan Integration
Smoking food introduces specific food safety risks, particularly related to time and temperature control. Develop a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan tailored to your smoking processes. Key control points include proper brining, maintaining smoking temperatures within safe zones (typically 165°F–225°F depending on the method), and ensuring final internal temperatures meet FDA Food Code standards (e.g., 145°F for fish, 165°F for poultry). Document all temperature logs and sanitation procedures.
Permits and Health Department Regulations
Before using a commercial smoker, obtain necessary permits from your local health department and fire marshal. These may include a food service establishment permit, a special ventilation permit, or approvals for open-flame cooking. Schedule pre-operational inspections to verify compliance with local health codes, fire safety regulations, and building ordinances. Keep all permits visible and up to date.
Smoke Management and Environmental Regulations
In urban or densely populated areas, smoke emissions may be subject to environmental or nuisance regulations. Check with local air quality management districts (e.g., AQMD in California) for restrictions on outdoor smoke discharge. Some jurisdictions require filtration systems like electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) or catalytic converters to reduce visible emissions and odor. Non-compliance can result in fines or operational shutdowns.
Staff Training and Operational Procedures
Train kitchen staff thoroughly on smoker operation, safety protocols, and emergency procedures. Training should cover fire suppression system activation (e.g., Ansul system), safe fuel handling, and proper use of thermometers and timers. Maintain written Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for cleaning, maintenance, and daily startup/shutdown routines. Document all training sessions for compliance audits.
Maintenance and Equipment Servicing
Implement a preventive maintenance schedule for the smoker, exhaust system, and fire suppression equipment. Clean smoker racks, trays, and interior components regularly to prevent grease buildup. Schedule professional inspections of the exhaust hood and ductwork at least every three months (or per NFPA 96 standards). Service the fire suppression system annually by a certified technician.
Waste Disposal and Grease Management
Used wood chips, charcoal, and grease byproducts must be disposed of properly. Store ash and spent fuel in non-combustible, covered containers away from heat sources. Recycle or dispose of grease through licensed rendering services—never pour it down drains. Maintain a grease log if required by your municipality and ensure grease traps are cleaned regularly.
Recordkeeping and Audit Preparedness
Maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance during health inspections or insurance audits. Essential documents include temperature logs, maintenance records, employee training logs, HACCP plans, permit renewals, and inspection reports. Store these records securely and make them readily accessible to management and regulators.
Final Compliance Checklist Before Launch
Before operating your commercial smoker, verify the following:
– Equipment is NSF-certified and properly installed
– Ventilation system meets UL 710 and NFPA 96 standards
– All required permits are obtained and displayed
– HACCP and SOPs are documented and staff trained
– Fire suppression system is installed and inspected
– Emergency shutoffs and fire extinguishers are accessible
– Waste and grease disposal procedures are in place
Adhering to these logistics and compliance guidelines ensures safe, legal, and efficient use of commercial smokers, protecting both your customers and your business.
Conclusion: Sourcing Commercial Smokers for Restaurants
Sourcing the right commercial smoker is a critical decision for restaurants aiming to deliver high-quality, flavorful smoked dishes consistently and efficiently. When selecting a smoker, operators must consider factors such as capacity, fuel type (electric, gas, wood, or pellet), ease of use, maintenance requirements, available kitchen space, and compliance with local health and safety regulations. Additionally, reliability and durability are essential to withstand the demands of a high-volume commercial environment.
Investing in a reputable brand with solid customer support and service ensures long-term performance and minimizes operational downtime. While cost is an important factor, prioritizing quality and functionality over initial price will yield better returns through improved food quality, energy efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Conducting thorough research, reading industry reviews, and consulting with culinary experts or equipment suppliers can help make an informed decision.
Ultimately, the right commercial smoker not only enhances menu offerings but also supports operational efficiency and brand reputation. By aligning equipment choices with the restaurant’s concept, volume demands, and long-term goals, owners can ensure a successful and sustainable smoking program that delights customers and sets their establishment apart in a competitive market.