The global commercial kitchen equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand from restaurants, hotels, and foodservice providers seeking efficient, scalable, and energy-saving solutions. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 63.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, the proliferation of quick-service restaurants, and a growing emphasis on kitchen automation and sustainability. As operators prioritize turnkey kitchen installations that integrate functionality with compliance and energy efficiency, manufacturers are stepping up with innovative, modular, and smart-enabled systems. In this evolving landscape, a select group of industry leaders has emerged, combining engineering excellence, global reach, and data-informed design to dominate the commercial kitchen installation space. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and customer adoption metrics, the following are the top 10 commercial kitchen installation manufacturers shaping the future of foodservice operations worldwide.
Top 10 Commercial Kitchen Installation Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Middleby
Domain Est. 1995
Website: middleby.com
Key Highlights: Middleby is a world leader in manufacturing innovative cooking equipment for the commercial, residential, and industrial foodservice markets….
#2 Winston Foodservice
Domain Est. 1996
Website: foodservice.winstonind.com
Key Highlights: Get to know Winston Foodservice! Foodservice equipment manufacturers specializing in cook and hold ovens, holding cabinets and pressure ……
#3 Commercial Kitchen Installations
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hobartcorp.com
Key Highlights: We’re the only nationwide installer who’s dedicated to commercial food equipment. You’ve invested significantly in your new equipment….
#4 Southbend Restaurant Equipment
Domain Est. 1998
Website: southbendnc.com
Key Highlights: Southbend offers 100+ years of innovation in commercial kitchen equipment. Find top-quality restaurant equipment backed by our commitment to excellence….
#5 EMRCO
Domain Est. 1998
Website: emrco.com
Key Highlights: Our business is caring about your business. COMMERCIAL KITCHENS Parts, service and installation for commercial kitchen equipment of any size….
#6 Singer Equipment Co.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: singerequipment.com
Key Highlights: We offer a full suite of services to support the construction of commercial kitchens, from design through installation. Singer Equipment Company will bring ……
#7 Sam Tell
Domain Est. 2000
Website: samtell.com
Key Highlights: Sam Tell provides unparalleled design, build and supply services for commercial kitchen operations….
#8 Kitchen Brains
Domain Est. 2010
Website: kitchenbrains.com
Key Highlights: Digital tools are available to streamline every process in the commercial kitchen, yielding data for the manager to boost top-line revenue….
#9 Moffat
Domain Est. 2012
Website: moffatusa.com
Key Highlights: Moffat specializes in the design, manufacture, distribution and after-sales support of commercial convection ovens, proofers and holding cabinets….
#10 Capabilities
Domain Est. 2017
Website: vollrathfoodservice.com
Key Highlights: Our robust team can assist with: design, stainless steel fabrication, millwork, fiber laser cutting, electrical, refrigeration, commercial kitchen installation, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Commercial Kitchen Installation
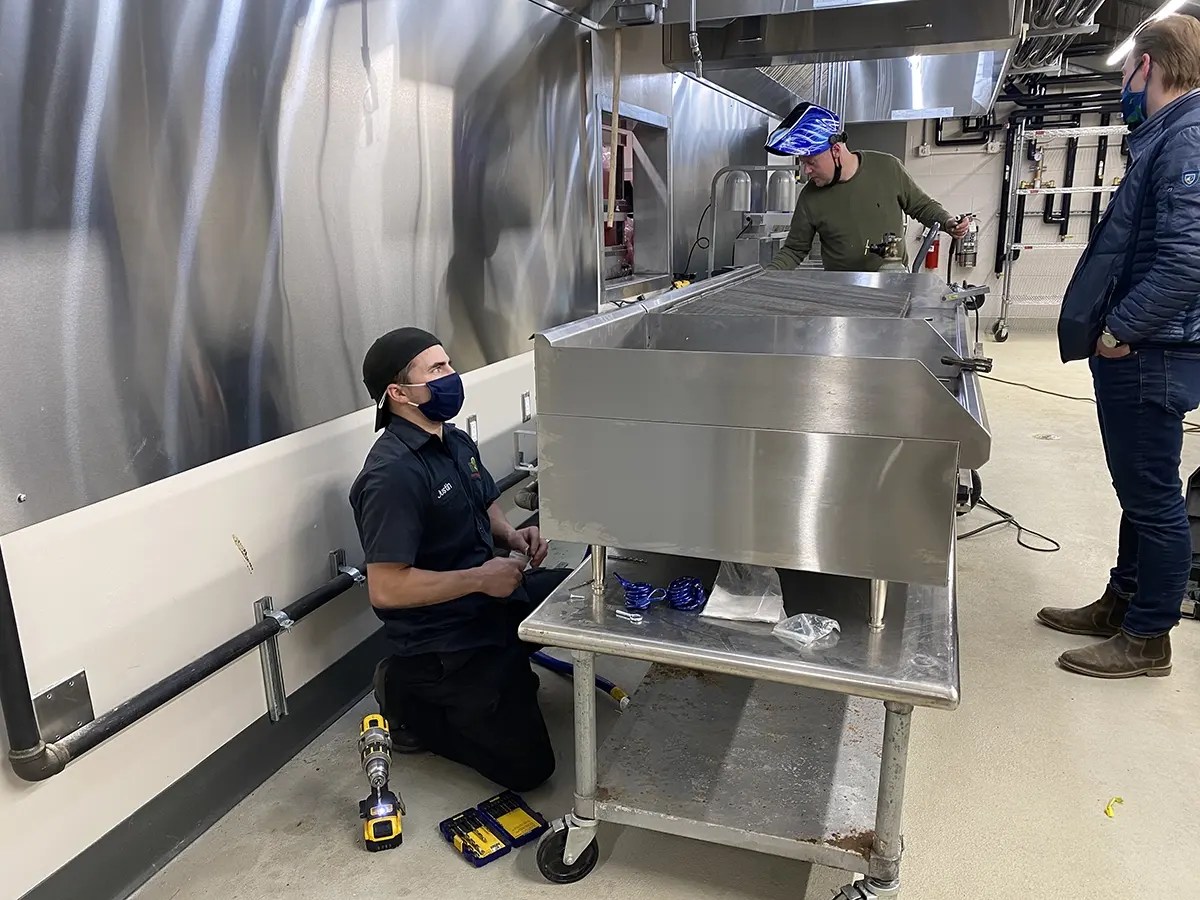

2026 Market Trends for Commercial Kitchen Installation
The commercial kitchen installation industry is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, sustainability mandates, evolving consumer preferences, and post-pandemic shifts in food service operations. This analysis explores the key market trends expected to shape the sector in the coming years.
1. Increased Demand for Modular and Prefabricated Kitchen Solutions
Modular kitchen installations are gaining momentum due to their speed of deployment, cost efficiency, and scalability. By 2026, more foodservice operators—especially in fast-casual chains, pop-up concepts, and delivery-only kitchens—will adopt prefabricated kitchen modules. These off-site manufactured units reduce on-site construction time by up to 50%, minimize disruption, and offer greater design consistency across multiple locations.
2. Integration of Smart Technology and IoT
Smart kitchens equipped with Internet of Things (IoT) devices will become standard in new installations. Operators will rely on connected appliances for real-time monitoring of energy usage, predictive maintenance, inventory tracking, and food safety compliance. By 2026, commercial kitchen installations will increasingly include integrated control systems that optimize workflow, reduce labor costs, and improve operational efficiency.
3. Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals will drive demand for energy-efficient appliances, water-saving fixtures, and sustainable materials in kitchen builds. By 2026, installations will routinely feature ENERGY STAR-rated equipment, induction cooking, heat recovery systems, and low-carbon construction materials. Green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM will influence design and equipment selection.
4. Growth of Ghost Kitchens and Delivery-Focused Concepts
The rise of food delivery platforms continues to fuel demand for delivery-only (ghost) kitchens. These facilities require optimized layouts for throughput, minimal front-of-house space, and specialized ventilation and utility setups. By 2026, commercial kitchen installers will need to master compact, high-efficiency designs tailored to digital-first food brands and multi-brand kitchen hubs.
5. Labor Shortages Driving Automation and Ergonomic Design
With ongoing labor challenges in the hospitality sector, kitchens will be designed to maximize productivity with fewer staff. This includes automated cooking systems, robotic prep stations, and ergonomic layouts that reduce fatigue and improve workflow. Installations will prioritize intuitive equipment placement and ease of cleaning to reduce training time and maintenance costs.
6. Health, Safety, and Hygiene-Centric Installations
Post-pandemic hygiene standards have become permanent expectations. By 2026, commercial kitchen installations will emphasize touchless fixtures, antimicrobial surfaces, advanced ventilation with air filtration (including UV-C), and layouts that support strict sanitation protocols. Compliance with updated health codes and third-party safety certifications will be a key selling point.
7. Regionalization and Customization
As consumer tastes diversify, commercial kitchens will be increasingly tailored to regional cuisines and local supply chains. Installers will need to accommodate specialized equipment—such as tandoor ovens, wok stations, or charcuterie rooms—requiring greater flexibility in design and utility planning. Customization will extend to branding integration and experiential elements in open kitchens.
8. Supply Chain Resilience and Local Sourcing
Disruptions in global supply chains have prompted operators to favor locally sourced materials and domestic equipment manufacturers. By 2026, commercial kitchen projects will prioritize vendors with shorter lead times, transparent sourcing, and modular compatibility. Installers who offer end-to-end project management with supply chain oversight will gain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
By 2026, the commercial kitchen installation market will be defined by speed, intelligence, sustainability, and adaptability. Companies that embrace modular design, smart technology, and eco-conscious practices will lead the industry. As foodservice evolves, the role of the kitchen installer will expand from contractor to strategic partner, ensuring kitchens are not just functional, but future-ready.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Commercial Kitchen Installation (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing commercial kitchen installation services involves more than just comparing quotes—it requires careful attention to quality standards and the protection of intellectual property (IP), especially in custom kitchen designs. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and compromised brand integrity.
Poor Workmanship and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent pitfalls is engaging contractors who cut corners by using inferior materials or employing unqualified labor. This can result in equipment malfunction, code violations, and recurring maintenance issues. For example, improper ventilation installation due to poor ductwork can compromise air quality and fire safety, leading to health code failures.
Inadequate Compliance with Health and Safety Codes
Commercial kitchens must adhere to strict local, national, and industry-specific regulations (e.g., NFPA 96, HACCP, ADA). Sourcing providers without proven experience in compliant installations risks project delays, costly retrofits, or operational shutdowns. A lack of understanding of fire suppression requirements or grease management systems can lead to dangerous situations and regulatory fines.
Misalignment with Operational Workflow Design
A kitchen may be built to specification, but if the layout doesn’t support efficient workflow (e.g., improper spacing between prep stations and cooking lines), productivity suffers. Poor sourcing decisions often stem from selecting vendors who prioritize cost over functionality, failing to involve end-users or culinary experts in the design phase.
Lack of Documentation and As-Built Drawings
Many installers fail to provide comprehensive as-built documentation, including plumbing, electrical, and ventilation schematics. This omission creates long-term maintenance challenges and can become a liability during equipment servicing, renovations, or insurance claims.
Intellectual Property Infringement in Custom Designs
When sourcing installation for proprietary kitchen layouts—especially in branded restaurant chains or high-end hospitality—there’s a risk of IP theft. Contractors or third-party designers may reuse custom floor plans, equipment configurations, or workflow systems for competing clients without permission. Without clear contractual IP clauses, businesses may lose control over their unique designs.
Absence of IP Ownership Clauses in Contracts
A critical legal oversight is failing to specify who owns the design and engineering work post-installation. If contracts do not explicitly assign IP rights to the client, the installer or design firm may retain ownership, limiting the client’s ability to replicate, modify, or license the kitchen design elsewhere.
Use of Counterfeit or Non-Certified Equipment
Some installers source equipment from unauthorized suppliers to reduce costs, introducing counterfeit or non-certified appliances that don’t meet safety or energy standards. These units may lack proper warranties, fail inspections, or void insurance policies, posing both financial and safety risks.
Inadequate Post-Installation Support and Warranties
Sourcing based solely on upfront cost often means sacrificing after-sales service. Poorly defined maintenance agreements or ambiguous warranty terms leave operators vulnerable when issues arise post-installation. This is especially critical for integrated systems like combi ovens or automated refrigeration units.
Failure to Protect Digital Design Files
With the rise of CAD and BIM modeling, digital kitchen plans are valuable IP assets. If installers host or retain copies of design files without restrictions, there’s a risk of unauthorized distribution or replication. Clients must ensure digital assets are secured and access is contractually limited.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, businesses should:
– Vet installers for certifications, past projects, and compliance history.
– Require detailed contracts with explicit IP ownership and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs).
– Insist on material specifications, compliance documentation, and as-built drawings.
– Engage independent third-party inspections during and after installation.
– Use escrow or controlled access for digital design files until final payment and IP transfer.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns during sourcing, organizations can ensure a safe, efficient, and legally protected commercial kitchen installation.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Commercial Kitchen Installation
Installing a commercial kitchen requires careful planning, coordination, and adherence to numerous regulations to ensure safety, efficiency, and legal operation. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations to help streamline the process.
Project Planning & Site Assessment
Begin with a comprehensive site evaluation to determine space limitations, utility access (water, gas, electricity, ventilation), structural capacity, and existing building systems. Confirm zoning permits allow for commercial food service operations. Develop a detailed kitchen layout that complies with workflow standards (e.g., flow from storage to prep to cooking to cleaning) and allows sufficient clearance for equipment, staff movement, and emergency access.
Equipment Procurement & Delivery Logistics
Create a procurement schedule aligned with the project timeline. Order equipment well in advance, considering lead times for manufacturing and shipping. Coordinate with suppliers to ensure delivery windows match site readiness—delivered equipment should not arrive before utilities are available or floor protection is in place. Verify access routes (door sizes, elevators, hallways) can accommodate large appliances and arrange for rigging if necessary.
Utility Requirements & Infrastructure
Ensure all utility services meet equipment specifications:
– Electrical: Verify voltage, phase, amperage, and dedicated circuits for large appliances (ovens, fryers, refrigeration).
– Gas: Confirm gas line size, pressure, and proper shutoff valves if gas appliances are used.
– Plumbing: Provide adequate hot and cold water supply lines, drainage, grease interceptors (as required), and floor drains.
– Ventilation: Install a commercial hood system with proper makeup air, ductwork, and exhaust fans compliant with local and national codes (e.g., International Mechanical Code, NFPA 96).
Regulatory Compliance & Permits
Obtain all required permits before installation begins. Common permits include:
– Building and construction permits
– Mechanical (HVAC/hood system) permits
– Plumbing and gas permits
– Electrical permits
– Health department approvals
– Fire suppression system permits (e.g., Ansul system)
All installations must comply with local building codes, the International Building Code (IBC), National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards, and Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements where applicable.
Health & Safety Standards
Design the kitchen to meet health code requirements:
– Use NSF-certified equipment.
– Install proper handwashing sinks with hot water and soap dispensers.
– Provide adequate refrigeration with temperature monitoring.
– Include a commercial-grade grease trap or interceptor sized to handle expected waste.
– Ensure surfaces are non-porous, easily cleanable, and resistant to moisture and heat.
Fire Suppression & Emergency Systems
Commercial kitchens must have an automatic fire suppression system (typically integrated with the hood and ductwork) installed by a certified technician. This system must be UL-listed and connected to all cooking equipment. Regular inspection and maintenance records are required by fire departments and insurance providers.
Installation by Licensed Professionals
All mechanical, electrical, and plumbing work must be performed by licensed and insured contractors. Refrigeration, gas lines, electrical connections, and hood systems require specialized knowledge and certification. Never attempt DIY installation of critical systems.
Final Inspections & Certifications
Schedule final inspections with local authorities having jurisdiction (AHJ), including:
– Building department
– Fire marshal
– Health department
– Gas and electric utility providers
Obtain certificates of occupancy and operational permits before opening. Maintain records of all inspections, equipment manuals, and compliance documentation for audits and insurance purposes.
Post-Installation Considerations
Develop a maintenance schedule for all equipment and systems, including hood cleaning, grease trap pumping, and filter replacements. Train staff on safety procedures, equipment use, and sanitation practices. Keep updated copies of all compliance documents on-site for regulatory inspections.
Conclusion for Sourcing Commercial Kitchen Installation
Sourcing a commercial kitchen installation is a critical investment that directly impacts the efficiency, safety, and long-term success of any foodservice operation. A well-planned and professionally executed installation ensures compliance with health and safety regulations, optimizes workflow, and enhances operational productivity. By carefully selecting experienced contractors, prioritizing high-quality equipment, and adhering to design standards, businesses can create a functional and durable kitchen environment tailored to their specific needs.
Emphasizing energy efficiency, future scalability, and proper maintenance during the sourcing process further contributes to cost savings and sustainability. Ultimately, investing time and resources in a strategic kitchen installation lays a solid foundation for consistent food quality, staff satisfaction, and uninterrupted service—key drivers of success in the competitive hospitality and foodservice industry.