The global cold rolled steel coil market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand from automotive, construction, and manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global cold rolled steel market was valued at USD 118.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.8% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies, and the automotive industry’s ongoing need for high-strength, precision-formed steel. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the growing adoption of cold rolled coils in appliance manufacturing due to their superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy, further strengthening market momentum. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in production capacity, technological innovation, and global reach. Based on market performance, output volume, and industry reputation, the following nine companies represent the top cold rolled steel coil manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 9 Cold Rolled Steel Coil Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Cold Rolled Steel Supplier
Domain Est. 1996
Website: millsteel.com
Key Highlights: Mill Steel is a leading cold rolled steel supplier offering high-quality, precision-processed coils for manufacturers and fabricators nationwide….
#2 Customers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: US Steel provides world-class quality cold-rolled coil steel that’s designed for very specific applications, from electric motors and generators to high-end ……
#3 Cold Rolled
Domain Est. 1997
Website: californiasteel.com
Key Highlights: As one of the largest suppliers of cold rolled products in the Western US market, CSI strives to produce cold rolled coil to meet the demands of our customers….
#4 Steel Coil Supplier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: steelwarehouse.com
Key Highlights: Steel Warehouse has a complete selection of customizable steel coil options available in a variety of sizes, grades, surface finishes, and forms….
#5 Cold Rolled Steel Coil Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chesterfieldsteel.com
Key Highlights: Chesterfield Steel specializes in Cold Rolled Steel Coils that are processed and packaged to your exact specifications. Request a quote today!…
#6 Cold Rolled Steel
Domain Est. 1998
Website: majesticsteel.com
Key Highlights: Cold rolled steel gains its strength from a cold rolling process in which the steel is formed into sheets at room temperature….
#7 Hascall Steel Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: hascallsteel.com
Key Highlights: Hascall is a one stop shop for automotive steel grades. We are the trusted choice for steel coils and sheets….
#8 Smooth and Versatile
Domain Est. 1999
Website: worthingtonsteel.com
Key Highlights: We make both cold rolled strip and cold rolled sheet to your specifications. Cold rolled steel is highly engineered steel made from hot rolled substrate….
#9 Siegal Steel Company: Steel Coil Supplier & Processor
Domain Est. 1999
Website: siegalsteel.com
Key Highlights: As a steel coil supplier & processor, we are experts in oscillate & traverse winding of Cold Rolled, High Carbon, HSLA, Low Carbon, and Stainless Steels….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cold Rolled Steel Coil
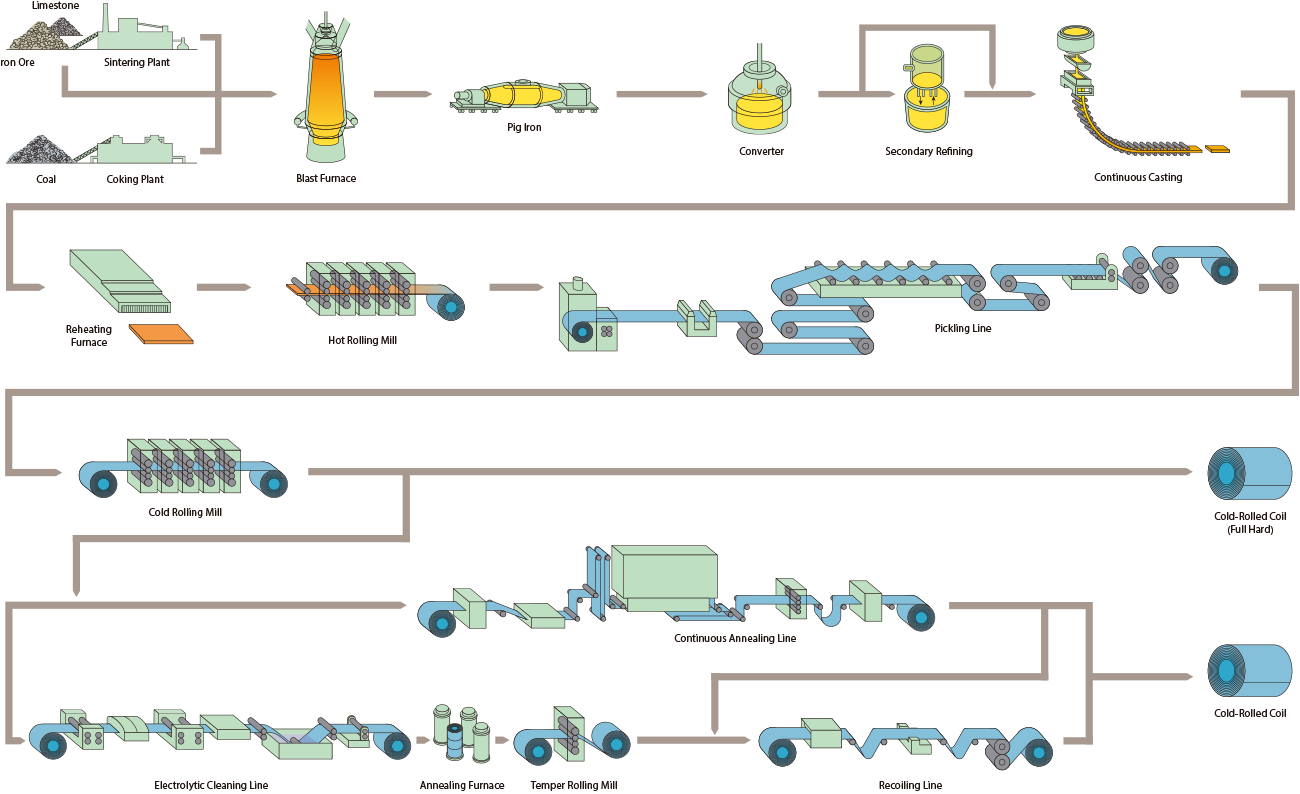
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cold Rolled Steel Coil
The global Cold Rolled Steel Coil (CRS) market in 2026 is expected to navigate a complex landscape shaped by evolving demand dynamics, supply chain recalibrations, technological advancements, and heightened environmental pressures. While growth is anticipated, it will be characterized by regional disparities and structural shifts within key end-use industries.
1. Demand Drivers and Sectoral Shifts:
* Automotive Resilience & Transformation: The automotive sector, a primary consumer of CRS, will remain a cornerstone of demand. However, the nature of demand will shift significantly. Growth in electric vehicles (EVs) will drive demand for specialized high-strength, lightweight steels, including advanced high-strength steel (AHSS) grades produced from CR coils. While overall auto production growth might moderate compared to post-pandemic rebounds, the content per vehicle for these advanced CR grades is increasing. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle demand may plateau or decline in mature markets, partially offsetting EV gains.
* Construction & Infrastructure Modulation: Demand from construction and appliances will be regionally diverse. Government infrastructure spending (e.g., in the US, India, parts of Southeast Asia) will support demand, particularly for structural applications using coated CR products. However, high interest rates could dampen residential construction in some regions (e.g., North America, Europe), impacting appliance demand. Energy efficiency regulations will continue to favor CR in efficient appliances.
* Industrial Machinery & Diversification: Demand from industrial equipment and machinery is expected to grow steadily, supported by global manufacturing activity and industrial automation trends, providing a stable base for CRS consumption.
2. Supply Chain & Geopolitical Influences:
* Regionalization & Trade Flows: Ongoing efforts to diversify supply chains and reduce reliance on single sources (particularly China) will continue. This may lead to increased regional production capacity, especially in Southeast Asia, India, and potentially the Americas. Trade policies, potential new tariffs (e.g., under CBAM implications), and geopolitical tensions (e.g., Ukraine conflict, US-China relations) will remain critical factors influencing global trade flows and pricing.
* Raw Material Volatility: Prices for key inputs like hot-rolled coil (HRC – the feedstock for CR), iron ore, and coking coal will remain susceptible to supply disruptions, energy costs, and inventory cycles. Steelmakers’ ability to pass on cost increases to consumers will be tested, impacting margins.
3. Technological Advancements & Product Evolution:
* Focus on Value-Added Grades: Competition will intensify beyond commodity grades. Producers will increasingly focus on R&D and production of higher-margin, value-added products: ultra-high-strength steels (UHSS), improved surface finishes, specialized coatings (e.g., for corrosion resistance in harsh environments), and steels optimized for specific manufacturing processes (like laser welding).
* Digitalization & Efficiency: Wider adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies (AI, IoT, predictive maintenance) in CR production lines will enhance yield, consistency, quality control, and energy efficiency, crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
4. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Imperatives:
* Decarbonization Pressure: This is the most significant structural trend. Regulatory pressures (carbon taxes, emissions trading schemes like EU ETS/ CBAM), investor demands, and customer (especially automotive OEMs) sustainability targets are forcing steelmakers to decarbonize. This involves:
* Electrification: Increased use of Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) using scrap, reducing reliance on blast furnaces (BF-BOF route).
* Hydrogen-Based Reduction: Pilots and early commercialization of hydrogen direct reduced iron (H2-DRI) feeding EAFs will gain traction, though widespread impact by 2026 may be limited but strategically crucial.
* Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS): Implementation at BF-BOF sites will be explored, though costs and scalability remain challenges.
* Recycling Focus: The circular economy will gain prominence. CRS’s inherent recyclability is a strength, but demand for low-carbon “green steel” (produced with minimal emissions) will surge, potentially creating a price premium for certified low-CO2 CRS.
5. Price & Margin Outlook:
* Prices in 2026 are expected to be more stable than the extreme volatility seen in 2021-2022 but will remain sensitive to input costs, energy prices, and regional supply-demand balances.
* Margins for producers will be under pressure from rising energy and compliance (carbon) costs. Profitability will increasingly depend on operational efficiency, product mix (shift to high-value grades), and success in securing long-term contracts with customers committed to low-carbon steel.
Conclusion for 2026:
The Cold Rolled Steel Coil market in 2026 will be defined by transformation. While underlying demand from key sectors like automotive (especially EVs) and infrastructure provides a foundation, the market will be reshaped by the imperative of decarbonization and the shift towards value-added, specialized products. Success will belong to producers who can navigate geopolitical complexities, invest in low-carbon technologies (EAF, H2-DRI), leverage digitalization for efficiency, and meet the stringent sustainability requirements of their customers, particularly in the automotive sector. The era of commoditized CRS is fading, giving way to a market increasingly segmented by quality, specialty, and carbon footprint.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Cold Rolled Steel Coil (Quality, IP)
Sourcing cold rolled steel coil involves several risks, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Buyers, especially those procuring from international suppliers, must be vigilant to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to production delays, financial losses, or legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Mechanical Properties
Cold rolled steel coils must meet specific mechanical standards (e.g., tensile strength, yield strength, elongation). A common issue is inconsistent batch-to-batch performance due to variations in raw materials or rolling processes. Suppliers may provide test reports that do not reflect actual coil properties, leading to material failure during fabrication.
Surface Defects and Imperfections
Defects such as scratches, roll marks, rust, oil residue, or edge cracks are frequent quality concerns. These imperfections can compromise downstream processes like painting, coating, or stamping. Inadequate surface inspection at the supplier level often allows defective coils to pass undetected until final use.
Non-Compliance with International Standards
Some suppliers claim compliance with ASTM, JIS, or EN standards but fail to adhere strictly to specifications. Mislabeling grades (e.g., selling SPCC as SPCEN) or providing falsified mill test certificates is a significant risk, especially when sourcing from regions with weak regulatory oversight.
Improper Packaging and Handling
Poor packaging can result in coil deformation, corrosion, or edge damage during transit. Exposure to moisture due to inadequate wrapping or storage leads to rust, affecting the usability of the material upon delivery.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Steel Grades
Some suppliers may illegally produce or market steel grades protected by IP rights, such as high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) or advanced high-strength steels (AHSS). Using such materials can expose buyers to legal liability, especially in regulated industries like automotive or aerospace.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Absence of proper mill certifications or heat traceability makes it difficult to verify the origin and authenticity of the steel. This opacity increases the risk of inadvertently sourcing counterfeit or cloned materials that infringe on patented manufacturing processes or chemical compositions.
Reverse Engineering and Technology Leakage
When working closely with suppliers—especially in custom alloy development—there is a risk of IP leakage. Suppliers may reverse-engineer proprietary specifications or share technical data with third parties, undermining competitive advantage.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough supplier audits, require independent third-party inspections, and insist on full documentation (including mill test reports and IP compliance statements). Establishing clear contractual terms around quality specifications and IP rights is essential for protecting both product integrity and legal standing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cold Rolled Steel Coil
Overview of Cold Rolled Steel Coil
Cold Rolled Steel Coil (CRS Coil) is a high-precision steel product manufactured through cold reduction of hot rolled steel, resulting in tighter dimensional tolerances, improved surface finish, and enhanced mechanical properties. It is widely used in automotive, appliance, construction, and machinery manufacturing. Due to its weight, susceptibility to corrosion, and handling requirements, specialized logistics and strict compliance protocols are essential for safe and efficient transportation and trade.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging and handling are critical to prevent physical damage and corrosion during transit.
– Standard Packaging: Coils are typically wrapped in inner plastic film to prevent moisture ingress, followed by outer steel or waterproof paper wrapping. Edge protectors and center plugs are used to protect coil ends.
– Palletization: Coils are placed on sturdy wooden or steel pallets with secure strapping to prevent shifting.
– Lifting Procedures: Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., C-hooks, coil cradles) to avoid deformation. Never use slings that could damage edges.
– Storage Conditions: Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area on level surfaces. Keep coils off the ground using skids to prevent moisture absorption.
Transportation Modes and Considerations
Selecting the right transportation method depends on distance, cost, and delivery timelines.
– Maritime Shipping: Most common for international trade. Coils are shipped in containers (20′ or 40′) or as break-bulk cargo on flat racks. Containerized shipping offers better protection against weather and theft.
– Rail Transport: Suitable for long-distance domestic shipments; requires specialized coil cars or flatbeds with secure lashing.
– Road Transport: Ideal for regional distribution. Use low-bed trailers with proper load securing (straps, chains, dunnage) to prevent rolling or shifting.
– Weight and Dimensions: Typical coil weights range from 5 to 25 metric tons. Ensure transport vehicles and infrastructure (bridges, roads) can handle the load.
Regulatory and Trade Compliance
Compliance with international and local regulations ensures smooth customs clearance and legal shipment.
– HS Code Classification: The Harmonized System (HS) code for cold rolled steel coil is typically 7209.17 or 7209.18, depending on alloy content, width, and thickness. Accurate classification is crucial for tariffs and import duties.
– Import/Export Documentation: Required documents include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and material test report (MTR).
– Anti-Dumping and Countervailing Duties: Be aware of trade remedies applied by importing countries (e.g., the U.S., EU, India) on steel imports from certain regions. Verify current duty rates and country-specific regulations.
– REACH, RoHS, and Other Standards: Comply with environmental and safety regulations, particularly in the EU. Ensure coatings (if any) meet substance restrictions.
Quality and Certification Standards
Buyers and regulators often require proof of material quality and origin.
– Common Standards: ASTM A1008/A1008M (U.S.), EN 10131 (Europe), JIS G 3141 (Japan).
– Material Test Reports (MTR): Must include chemical composition, mechanical properties (tensile strength, yield strength, elongation), and inspection results.
– Third-Party Inspection: Independent inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) may be required for large contracts to verify weight, dimensions, and surface quality.
Risk Management and Insurance
Mitigate risks associated with damage, delay, and non-compliance.
– Cargo Insurance: Obtain all-risk marine insurance covering physical loss or damage during transit. Specify coverage for rust, denting, and water exposure.
– Force Majeure and Incoterms: Use clear Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DAP) to define responsibilities. Common choice: FOB (Free On Board) for exporter control up to port of shipment.
– Contingency Planning: Have plans for port delays, weather disruptions, and customs holds. Maintain communication with freight forwarders and customs brokers.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Growing emphasis on green logistics and supply chain transparency.
– Carbon Footprint: Optimize routing and consolidate loads to reduce emissions. Consider rail over road where feasible.
– Recyclability: Cold rolled steel is 100% recyclable; document recycling rates and sustainable sourcing practices for ESG reporting.
– Eco-Packaging: Use recyclable or reusable packaging materials where possible.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for Cold Rolled Steel Coil require attention to packaging, transportation safety, regulatory adherence, and quality assurance. By following industry best practices and staying updated on international trade policies, shippers can ensure timely delivery, minimize risks, and maintain customer satisfaction. Partnering with experienced freight forwarders and compliance experts is highly recommended.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cold Rolled Steel Coil
Sourcing cold rolled steel coil requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and supply chain efficiency. After evaluating key factors such as material specifications, supplier credibility, pricing trends, and logistical considerations, it becomes evident that establishing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers is essential for consistent product quality and timely delivery.
The demand for high-strength, precision-finished steel in industries like automotive, construction, and appliance manufacturing underscores the importance of adhering to international standards (e.g., ASTM, JIS, or EN). Moreover, monitoring global market dynamics—including raw material costs, trade regulations, and freight conditions—enables better forecasting and risk mitigation.
In conclusion, an effective sourcing strategy for cold rolled steel coil should emphasize supplier vetting, quality assurance, cost optimization, and supply chain resilience. By doing so, businesses can ensure a reliable supply of high-performance material that meets technical requirements and supports operational excellence.











