The global cold rolled steel sheets market continues to expand, driven by rising demand from construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global cold rolled steel market was valued at approximately USD 194.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing infrastructure investments, stringent fuel efficiency standards in the automotive industry, and the preference for high-strength, dimensionally accurate steel products. In this evolving landscape, key manufacturers are focusing on production efficiency, product quality, and sustainability to maintain competitive advantage. Based on production capacity, product innovation, global reach, and market share, here are the top 9 cold rolled sheet manufacturers shaping the industry.
Top 9 Cold Rolled Sheets Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 JFE Steel Corporation
Website: jfe-steel.co.jp
Key Highlights: JFE produces high quality cold-rolled steel products using the latest equipment and technology, such as endless rolling, profile control, and Super -OLAC® H….
#2 SSAB high
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ssab.com
Key Highlights: SSAB is a Nordic and US-based steel company. SSAB offers value added … Hot rolled plate · Hot rolled sheet · Cold rolled sheet · SSAB Laser Plus · Customer ……
#3 Cold Rolled Sheets
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bobcometal.com
Key Highlights: $450 delivery 17-day returnsBobco Metals provides businesses and home users with quality cut to size cold rolled steel sheets supplies in Los Angeles….
#4 Customers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: US Steel provides world-class quality cold-rolled coil steel that’s designed for very specific applications, from electric motors and generators to high-end ……
#5 Cold Rolled Steel
Domain Est. 1998
Website: majesticsteel.com
Key Highlights: Cold rolled steel gains its strength from a cold rolling process in which the steel is formed into sheets at room temperature….
#6 Smooth and Versatile
Domain Est. 1999
Website: worthingtonsteel.com
Key Highlights: We make both cold rolled strip and cold rolled sheet to your specifications. Cold rolled steel is highly engineered steel made from hot rolled substrate….
#7 Cold rolled
Domain Est. 2006
Website: northamerica.arcelormittal.com
Key Highlights: Cold-rolled sheet steel is produced from hot-rolled sheet with additional processing steps such as pickling, cold reduction, annealing and temper rolling….
#8 BILSTEIN COLD ROLLED STEEL LP
Domain Est. 2014
Website: bilsteincrs.com
Key Highlights: BILSTEIN uses sophisticated manufacturing processes to produce high-performance cold-rolled steel strips with the greatest accuracy, leaving nothing to chance….
#9 Cold Rolled Steel Sheet Supplier
Domain Est. 2018
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cold Rolled Sheets
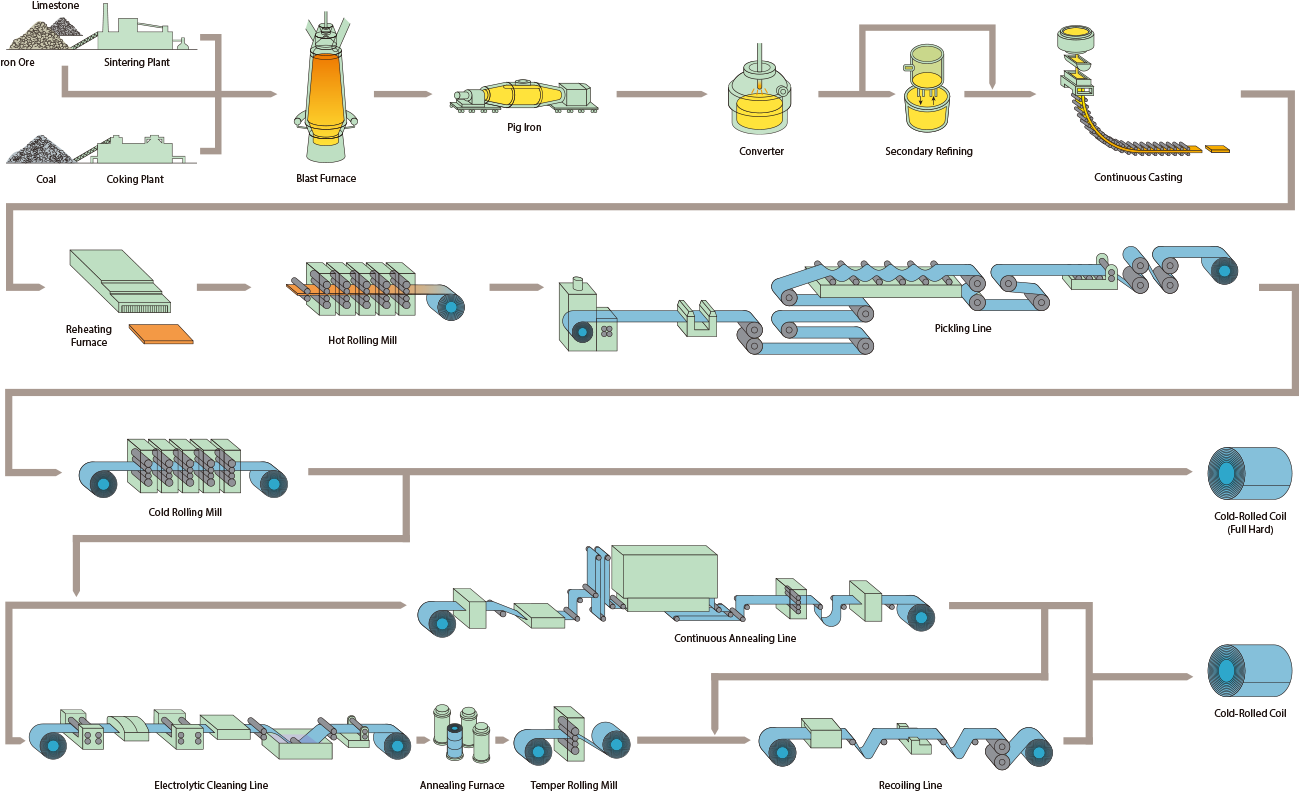
H2: Projected Market Trends for Cold Rolled Steel Sheets in 2026
The global cold rolled steel sheets (CRS) market is expected to experience moderate growth by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demand, technological advancements, and geopolitical shifts in raw material supply chains. Key trends shaping the 2026 landscape include increasing demand from the automotive and construction sectors, a rising focus on high-strength and lightweight materials, and the influence of sustainability mandates.
-
Automotive Industry Resurgence and Lightweighting
With the global push toward electric vehicles (EVs), automakers are prioritizing materials that reduce vehicle weight without compromising strength. Cold rolled sheets, particularly high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) variants, are seeing increased adoption due to their formability and strength-to-weight ratio. By 2026, the EV market expansion—especially in North America, Europe, and China—is projected to boost CRS demand for structural components, body panels, and battery enclosures. -
Construction and Infrastructure Development
Urbanization and government-led infrastructure programs in emerging economies (e.g., India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa) are expected to drive demand for cold rolled sheets in roofing, cladding, and prefabricated building systems. Energy-efficient building standards are also encouraging the use of coated and pre-painted cold rolled products, adding value and corrosion resistance. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Trade tensions and logistical disruptions have prompted steel producers to reevaluate supply chains. By 2026, a trend toward regional production hubs—such as in Eastern Europe, Southeast Asia, and Mexico—is likely to reduce dependency on traditional exporters like China. This shift may lead to more localized CRS manufacturing, improving delivery times and reducing tariffs. -
Sustainability and Decarbonization Efforts
Environmental regulations are pushing steelmakers to adopt greener production methods. The integration of electric arc furnaces (EAFs) using recycled scrap and investments in hydrogen-based steelmaking will influence CRS production. Buyers in the automotive and appliance sectors are increasingly demanding low-carbon certified steel, which could differentiate suppliers in the 2026 market. -
Price Volatility and Raw Material Costs
Fluctuations in iron ore, coking coal, and energy prices will continue to impact CRS pricing. Additionally, global scrap availability and carbon pricing mechanisms (e.g., EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) may increase production costs, potentially leading to price volatility in 2026. Producers investing in energy efficiency and alternative raw materials will have a competitive edge. -
Technological Innovations and Value-Added Products
There is growing demand for advanced cold rolled products, such as nano-coated sheets and tailor-welded blanks. These innovations enhance performance in harsh environments and reduce assembly costs. By 2026, manufacturers offering customized, high-precision CRS solutions are expected to capture premium market segments.
In summary, the 2026 cold rolled steel sheets market will be shaped by sector-specific demand, regional supply chain dynamics, and sustainability-driven innovation. Companies that adapt to these trends—through product diversification, decarbonization, and strategic localization—are likely to gain stronger market positioning.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Cold Rolled Sheets (Quality, IP)
Sourcing cold rolled steel sheets requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking key aspects can lead to production delays, product failures, or legal exposure. Below are critical pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Verification
Relying solely on supplier-provided certifications without independent verification can result in receiving substandard material. Common quality issues include inconsistent thickness tolerance, poor surface finish, inadequate flatness, and incorrect mechanical properties. Always require mill test certificates (MTCs) traceable to specific heat numbers and conduct third-party inspections or in-house testing when high precision or critical applications are involved.
Misunderstanding Grade Specifications
Confusing similar steel grades (e.g., SAE 1008 vs. SAE 1010) or failing to specify exact requirements (e.g., ASTM A1008 vs. EN 10130) can lead to performance issues. Ensure clear communication of required standards, chemical composition, yield strength, tensile strength, and intended application to avoid mismatched material properties.
Overlooking Surface Condition Requirements
Cold rolled sheets vary in surface finish (e.g., skin-passed, full-hard) and cleanliness. Failure to specify surface quality (e.g., freedom from scale, scratches, or oil residue) may result in defects during downstream processes like painting, coating, or forming. Define surface standards (e.g., ASTM A967 or internal benchmarks) to maintain consistency.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) in Tooling and Processes
When custom tooling or proprietary processing methods are used, suppliers may claim IP rights over designs or production techniques. Sourcing without clear contractual agreements can lead to ownership disputes or restricted reuse of tooling. Always formalize IP ownership, usage rights, and confidentiality in supplier contracts.
Assuming Global Standards Are Interchangeable
Using materials certified to one regional standard (e.g., JIS G 3141) in applications requiring another (e.g., ASTM or DIN) without proper equivalency assessment risks non-compliance. Validate cross-standard conformance through technical data reviews or testing to ensure compatibility.
Supply Chain Transparency Gaps
Lack of visibility into the origin of raw materials or production facilities can expose buyers to counterfeit materials or unethical sourcing practices. Require full supply chain disclosure and audit capabilities, especially when sourcing from regions with weak regulatory oversight.
Failure to Address Coating and Lubrication Needs
Cold rolled sheets often require specific lubricants or temporary protective coatings for forming or storage. Not specifying type and compatibility (e.g., drawing compounds, rust preventatives) can lead to processing issues or corrosion. Confirm lubrication requirements based on intended fabrication steps.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, buyers can ensure consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and protection of intellectual assets when sourcing cold rolled steel sheets.
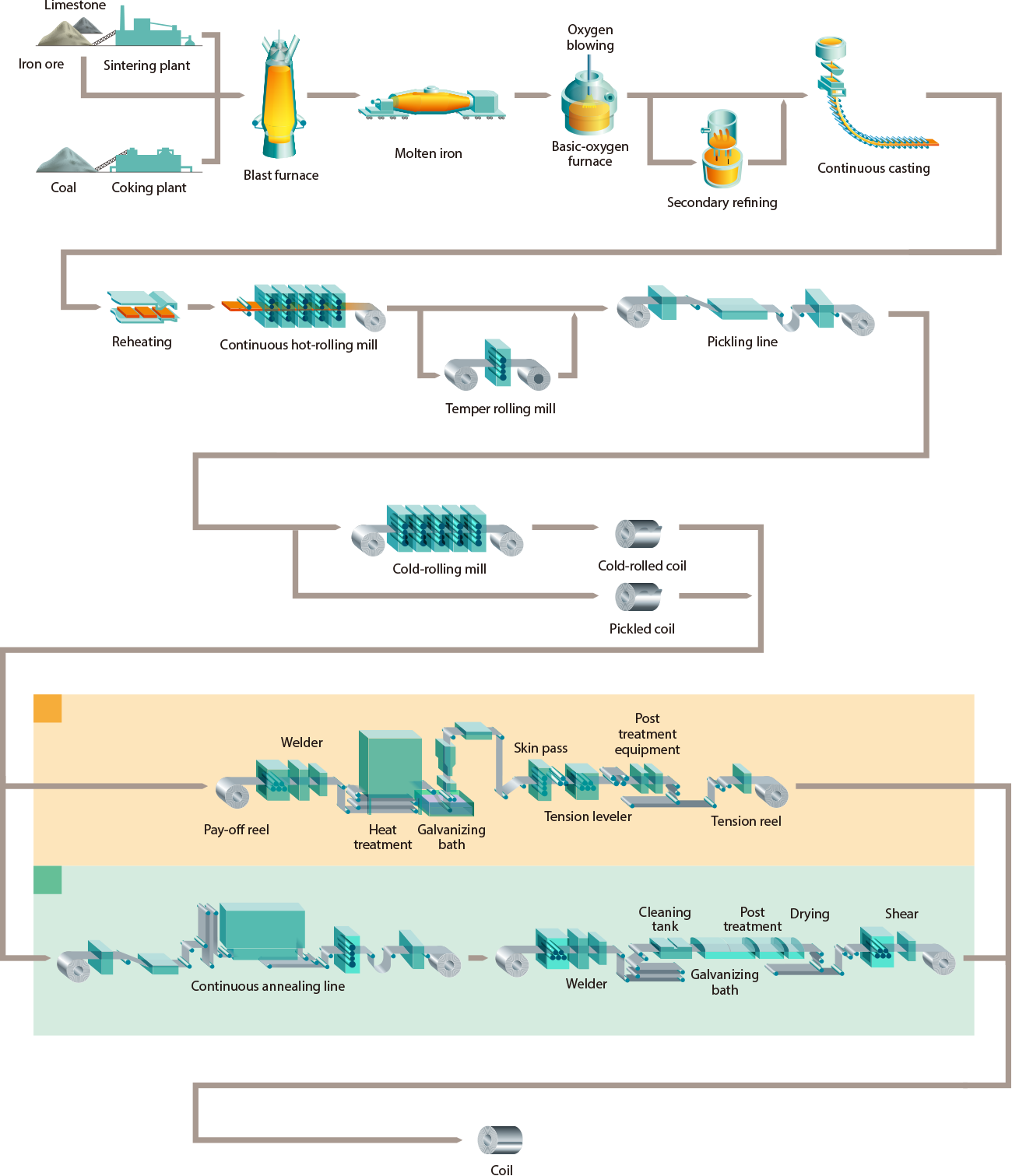
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cold Rolled Sheets
Overview of Cold Rolled Sheets
Cold Rolled Sheets (CRS) are steel sheets processed through cold reduction at room temperature after hot rolling. This process enhances strength, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy, making CRS ideal for automotive, appliance, construction, and manufacturing applications. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential due to their weight, susceptibility to damage, and regulatory requirements in international trade.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Cold Rolled Sheets must be protected from moisture, corrosion, and mechanical damage during transit. Standard packaging includes:
– Anti-corrosion coating: Oil or vapor corrosion inhibitors applied to sheet surfaces.
– Edge protectors: Applied to prevent chipping and edge damage.
– Strapping and bundling: Steel or composite straps to secure bundles; typical bundle weights range from 5 to 20 metric tons.
– Palletization or cradling: For containerized shipments, sheets are often placed on wooden pallets or in custom steel cradles.
– Wrapping: Plastic film or kraft paper with moisture barrier layers to prevent humidity exposure.
Transportation Modes and Considerations
Road Transport
- Use flatbed or lowboy trailers with adequate load securing (e.g., chains, straps).
- Ensure even weight distribution to prevent bending or deformation.
- Cover loads with tarpaulins to protect from rain and road debris.
Rail Transport
- Load sheets onto rail gondolas or flatcars; use dunnage to prevent direct metal-to-metal contact.
- Secure bundles to avoid shifting during transit, especially on curved tracks.
Sea Freight
- Containerized shipments: Use 20’ or 40’ dry containers; limit load weight per container based on sheet thickness and density.
- Breakbulk shipments: For oversized or heavy bundles, use open-top or flat-rack containers.
- Control humidity inside containers with desiccants to prevent condensation (cargo sweat).
- Follow IMSBC Code guidelines when applicable for bulk steel forms.
Storage Guidelines
- Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated warehouse to prevent rust.
- Elevate bundles off the floor using wooden dunnage to avoid ground moisture.
- Stack bundles no higher than manufacturer recommendations to prevent bottom-layer deformation.
- Separate different grades, thicknesses, and finishes to avoid mix-ups.
International Trade Compliance
Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice: Details product description, quantity, value, and Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF).
- Packing List: Specifies bundle count, weights, dimensions, and markings.
- Certificate of Origin: Required by customs in many countries; may be needed for tariff preferences.
- Mill Test Certificate (EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2): Confirms material meets specified chemical and mechanical properties.
Import Regulations
- Verify destination country’s steel import regulations, including anti-dumping or countervailing duties (e.g., U.S. Section 232, EU safeguard measures).
- Comply with local standards (e.g., ASTM, JIS, EN, GB) for material certification.
- Some countries require pre-shipment inspection (PSI) or SABER certification (e.g., Saudi Arabia).
Hazard and Safety Compliance
- Cold Rolled Sheets are not classified as hazardous goods under IMDG or ADR, but their weight and sharp edges pose handling risks.
- Follow OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent workplace safety standards:
- Use mechanical handling equipment (forklifts, cranes with steel clamps or vacuum lifters).
- Provide PPE (gloves, steel-toe boots, cut-resistant sleeves) for workers.
- Mark loads with center of gravity and weight labels.
Environmental and Sustainability Standards
- Adhere to REACH (EU) and RoHS regulations if sheets are used in electronics or consumer goods.
- Provide Environmental Product Declarations (EPD) upon request to support green building certifications (e.g., LEED).
- Recyclability: CRS is 100% recyclable; communicate end-of-life recovery options to customers.
Incoterms and Risk Management
- Clearly define responsibilities using internationally recognized Incoterms® 2020:
- EXW (Ex-Works): Buyer arranges pickup at seller’s facility.
- FOB (Free on Board): Seller delivers to port; risk transfers upon loading.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight): Seller covers cost, insurance, and freight to destination port.
- Insure shipments against damage, theft, and delay, especially for long-haul or maritime transport.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
- Implement traceability systems (e.g., heat number tracking) from mill to end customer.
- Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify dimensions, surface quality, and packaging.
- Maintain compliance with ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) if certified.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for Cold Rolled Sheets require careful coordination across packaging, transport, documentation, and regulatory adherence. Proactive risk management, adherence to international standards, and clear communication between suppliers, logistics providers, and customers ensure safe, timely, and compliant delivery of high-quality steel products.
Conclusion for Sourcing Cold Rolled Steel Sheets
In conclusion, sourcing cold rolled steel sheets requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, supplier reliability, and logistical efficiency. Cold rolled sheets offer superior surface finish, tighter tolerances, and enhanced mechanical properties compared to hot rolled alternatives, making them ideal for applications in automotive, construction, appliances, and precision manufacturing.
A successful sourcing strategy involves identifying certified suppliers with consistent quality standards, such as ISO or ASTM compliance, and evaluating factors like material specifications, production capacity, and delivery timelines. Global sourcing can provide cost advantages, but it must be weighed against lead times, import regulations, and supply chain risks. Establishing long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers, conducting regular quality audits, and leveraging volume purchasing can enhance cost-efficiency and supply continuity.
Ultimately, effective procurement of cold rolled steel sheets hinges on a thorough understanding of market dynamics, material requirements, and supplier capabilities. By adopting a proactive and informed sourcing approach, organizations can ensure the consistent supply of high-quality materials that meet both technical and economic objectives.