The global coal torch market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand in industrial heating, metalworking, and blacksmithing applications. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial torch market—encompassing fuel-specific tools like coal torches—was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising metal fabrication activities, infrastructure development, and renewed interest in traditional forging techniques within artisan and niche manufacturing sectors. As demand for durable, high-temperature torches persists, particularly those optimized for coal and solid fuel use, manufacturers are innovating to improve efficiency, safety, and user control. In this evolving landscape, a select group of companies have emerged as leaders in coal torch production, combining engineering excellence with practical design to meet diverse industrial and craft-based needs.
Top 10 Coal Torch Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Zibo Torch Energy Co., Ltd._Lead
Domain Est. 1998
Website: en.torchbat.com.cn
Key Highlights: Zibo Torch Energy Co., Ltd. (formerly Zibo Storage Battery Factory), founded in January 1944, is one of the earliest manufacturers developing and producing lead ……
#2 Wall Lenk Corporation
Domain Est. 2001
Website: wlenk.com
Key Highlights: Wall Lenk Corporation has been proudly manufacturing quality heated tools in the USA since 1864. Explore the extensive range of soldering irons, ……
#3 Tiger Torch
Domain Est. 2017
Website: tigertorch.ca
Key Highlights: Welcome to the “real” Tiger Torch website. Tiger Torch Ltd. is the manufacturer and seller of the original Tiger Torch® model propane and natural gas torches ……
#4 Tiger Torch
Domain Est. 2017
Website: tigertorchltd.com
Key Highlights: Tiger Torch is the manufacturer and seller of Tiger Torch propane and natural gas torches, located in Southern Alberta. Our torches are renowned for their ……
#5 Torch Lighter
Domain Est. 2024
Website: honestlighters.com
Key Highlights: HONEST Blow Torch Sleek Adjustable Butane Torch Cooking Torch Lighter Camping Home Use Welding Culinary Chef Coal Cocktail etc. 2 reviews….
#6 Royal Oak Charcoal
Domain Est. 1996
Website: royaloak.com
Key Highlights: Royal Oak 100% Natural Hardwood Lump Charcoal lights easily, burns hotter, longer and cleaner for the best smoking and grilling experience….
#7 CAMPINGMOON Camping Grill Torch Dual Fuel Head Flame …
Domain Est. 2012
Website: grijana.com
Key Highlights: 47,000 BTU output power. Ideal for charcoal/wood start for camping, BBQ etc.. (Gas Fuel Not Included). Gas fuel type : isobutane gas or 1lb ……
#8 RocketFire™ Torch for Grills, Campfires & Pits
Domain Est. 2019
Website: rocketfiretorch.com
Key Highlights: Discover the quickest way to light your fire without matches or chemicals. Perfect for BBQs, camping, and outdoor fun. Simple, safe, and ready when you are….
#9 Torch charcoal 30 pieces
Domain Est. 2024
Website: centerco.co
Key Highlights: Home Torch charcoal 30 pieces. فحم الشعلة 30حبة. Sold outPre order. Click to enlarge. Torch charcoal 30 pieces. 6.00. Tax included….
#10 Gas Torch
Website: kovea.com
Key Highlights: The Master is an ergonomic multiplayer torch designed for the user. It can be used for various purposes such as charcoal burning, copper pipe welding and PVC ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Coal Torch

H2: Market Trends for Coal Torch in 2026
As the global energy landscape continues its transition toward cleaner and more sustainable sources, the coal industry faces persistent challenges. However, niche applications such as coal torch technology—used primarily in industrial heating, metallurgy, and specialized combustion processes—may experience unique dynamics in 2026. Below is an analysis of key market trends influencing the Coal Torch sector in the second half (H2) of 2026.
1. Regional Demand Divergence
- Asia-Pacific (China, India, Southeast Asia): These regions remain the primary markets for coal-based technologies due to ongoing industrialization and reliance on coal in steel and cement production. In H2 2026, increased infrastructure development in India and continued use of coal in Chinese heavy industries are expected to sustain demand for coal torches, particularly in applications where high-intensity, localized heat is required.
- Europe & North America: Stringent environmental regulations and aggressive decarbonization policies are likely to suppress coal torch adoption. However, limited use in legacy industrial facilities and niche research applications may persist, especially in foundries or refractory maintenance.
2. Technological Advancements and Efficiency Improvements
- By H2 2026, coal torch systems are expected to integrate improved combustion efficiency and emission control technologies. Innovations such as oxygen-enriched coal torches and hybrid systems (coal-gas co-firing) may extend the operational lifespan of coal-based tools in emission-sensitive environments.
- Automation and digital monitoring—such as IoT-enabled flame control and predictive maintenance—are becoming more prevalent, enhancing safety and reducing downtime in industrial operations using coal torches.
3. Environmental and Regulatory Pressures
- Global momentum toward net-zero emissions will continue to impact the coal torch market. In H2 2026, carbon pricing mechanisms and stricter air quality standards in key markets may drive operators to retrofit or replace coal torches with cleaner alternatives like plasma or electric arc systems.
- Nevertheless, in emerging economies with less stringent enforcement, coal torches may still be favored due to lower capital costs and existing coal infrastructure.
4. Competition from Alternative Technologies
- The rise of hydrogen-fueled torches, electric plasma systems, and advanced oxy-fuel combustion technologies is displacing coal torches in many applications. These alternatives offer lower emissions and better controllability.
- However, in regions with abundant coal and limited access to alternative fuels or grid reliability, coal torches maintain a cost advantage, especially in small-scale or remote industrial operations.
5. Supply Chain and Coal Quality Factors
- Volatility in global coal supply due to geopolitical tensions, mine closures, and transportation constraints may affect coal torch operations. In H2 2026, operators are likely to prioritize consistent supply of high-calorific coal to maintain torch efficiency.
- Increased use of coal beneficiation techniques (e.g., coal washing) may improve combustion performance and reduce slag formation in torch applications.
6. Niche Industrial Applications and Retrofitting
- Coal torches are expected to retain relevance in specific applications such as boiler decoking, furnace relining, and metallurgical tapping. In H2 2026, retrofitting older industrial plants with modernized coal torch systems may represent a growth segment, particularly in countries phasing out coal power but still dependent on coal for industrial processes.
7. Market Outlook and Forecast
- The global coal torch market is projected to experience modest decline or stagnation in H2 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) near -1.5% to 0% through 2026. However, regional pockets of growth—especially in South Asia and parts of Africa—may offset declines in more regulated markets.
- Market consolidation among manufacturers and a shift toward service-based models (e.g., torch operation as a service) are emerging trends aimed at extending product lifecycles and reducing customer operational burdens.
Conclusion:
While the broader energy shift away from coal continues to challenge the coal torch market, H2 2026 will likely see sustained, albeit limited, demand in industrial sectors of developing economies. Technological adaptation, regional disparities in energy policy, and cost considerations will define the market’s trajectory. Long-term viability will depend on innovation, emission mitigation, and strategic positioning within niche industrial applications.
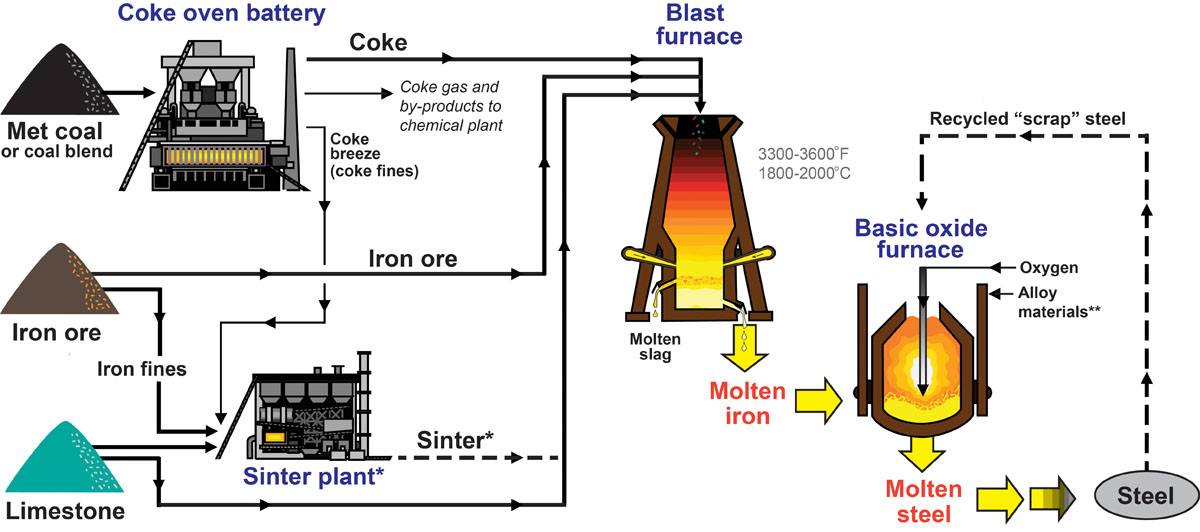
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Coal Torches: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing coal torches—whether for industrial use, historical reenactment, or decorative purposes—can present several challenges, particularly regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable supply, legal compliance, and brand protection.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Combustion Performance
One of the most frequent quality issues with coal torches is inconsistent burn time and flame stability. Low-grade coal or poor manufacturing can result in torches that sputter, extinguish prematurely, or emit excessive smoke. Buyers must verify specifications such as coal composition, moisture content, and ignition temperature to ensure reliable performance.
Poor Construction and Safety Hazards
Substandard torches may use weak or flammable handles, inadequate binding materials, or improper sealing of the coal chamber. This increases the risk of breakage, accidental burns, or fire hazards. Always inspect for durable materials (e.g., metal housings, heat-resistant bindings) and compliance with safety standards.
Inadequate Weather Resistance
For outdoor or maritime use, coal torches must withstand wind, rain, and humidity. Poorly sealed units may fail in wet conditions. Sourcing from suppliers who test for environmental resilience is crucial for mission-critical applications.
Lack of Standardization and Testing Documentation
Many manufacturers, especially smaller or overseas producers, fail to provide batch testing results or quality certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Without verifiable data, assessing consistency across orders becomes difficult. Demand documentation such as material test reports and burn performance logs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Replication of Patented Designs
Some coal torch models—particularly those with innovative ignition systems, fuel containment, or ergonomic features—may be protected by patents. Sourcing from third parties that replicate these designs without licensing exposes buyers to infringement claims, shipment seizures, or legal liability.
Trademark Infringement
Using branding, logos, or product names that resemble those of established manufacturers can lead to trademark violations. Even if the torch design is generic, packaging or marketing that mimics a known brand can trigger legal action.
Counterfeit or Grey Market Goods
Dealers may offer “branded” coal torches at suspiciously low prices, but these are often counterfeit or diverted from authorized distribution channels. These products lack quality control and may infringe IP rights, putting the buyer at legal and reputational risk.
Failure to Secure IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When commissioning custom coal torches, failure to sign agreements that assign IP rights (e.g., design patents, trade dress) to the buyer can result in losing control over the product. Suppliers may later sell the same design to competitors or claim ownership.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Assess manufacturing processes, material sourcing, and quality control measures.
- Require Certifications: Insist on compliance with relevant safety and performance standards.
- Perform IP Due Diligence: Search patent databases and consult legal counsel before sourcing new designs.
- Use Clear Contracts: Include warranties, IP assignment clauses, and audit rights in procurement agreements.
- Source from Reputable Suppliers: Prefer vendors with verifiable track records and transparent supply chains.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures that coal torch sourcing supports both operational reliability and legal compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Coal Torch
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, storage, and regulatory adherence associated with Coal Torch—a specialized product involving coal-based materials. Ensuring safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations is essential for minimizing risk, avoiding penalties, and maintaining operational continuity.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with national and international regulations is mandatory. Key regulatory frameworks include:
– Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Standards – Adhere to air quality, emissions, and waste management regulations, particularly concerning particulate matter and sulfur dioxide.
– Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) – Follow workplace safety standards for handling coal products, including dust control, respiratory protection, and hazard communication.
– Department of Transportation (DOT) – Comply with hazardous material transportation rules if applicable; classify and label shipments correctly.
– International Maritime Organization (IMO) – For overseas shipments, observe MARPOL Annex III for prevention of pollution by harmful substances in packaged form.
– Local Permits and Zoning Laws – Secure required permits for storage, handling, and emissions at all operational sites.
Transportation Logistics
Efficient and safe transportation is critical:
– Modal Selection: Choose appropriate transport modes (rail, truck, or barge) based on volume, destination, and infrastructure availability. Rail is typically preferred for bulk coal movements.
– Packaging & Containment: Use sealed, weather-resistant containers or covered hopper cars to prevent spillage and dust emission.
– Load Securing: Ensure loads are properly secured to prevent shifting during transit.
– Route Planning: Optimize routes to minimize transit time, fuel use, and environmental impact; avoid restricted or environmentally sensitive zones.
– Tracking & Documentation: Implement real-time GPS tracking and maintain digital logs for shipment visibility and audit readiness.
Storage & Handling
Proper storage and handling practices reduce risks:
– Storage Facilities: Store Coal Torch in designated, well-ventilated, and fire-resistant areas. Use covered stockpiles or silos to control dust and moisture.
– Fire Prevention: Implement fire detection systems, maintain safe distances from ignition sources, and have fire suppression equipment on-site.
– Dust Suppression: Use water sprays, chemical binders, or enclosures to minimize airborne particulates.
– Material Handling Equipment: Employ appropriate machinery (e.g., conveyor belts, loaders) with routine maintenance to ensure operational safety.
Environmental & Sustainability Considerations
- Emissions Monitoring: Regularly monitor and report emissions in accordance with local and federal requirements.
- Spill Response Plan: Maintain a spill containment and response protocol, including absorbent materials and trained personnel.
- Waste Management: Recycle or dispose of byproducts and packaging in compliance with environmental regulations.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Explore efficiency improvements and alternative energy sources to reduce environmental impact.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Accurate records are vital for compliance audits:
– Maintain shipping manifests, safety data sheets (SDS), inspection reports, and training logs.
– Keep records of emissions testing, incident reports, and regulatory filings for a minimum of five years.
– Utilize a digital compliance management system for easy access and reporting.
Training & Personnel
- Conduct regular training on hazardous material handling, emergency response, and regulatory updates.
- Certify personnel involved in transportation and storage operations as required by DOT, OSHA, or other relevant bodies.
Emergency Preparedness
- Develop and communicate an emergency response plan covering fire, spills, and exposure incidents.
- Conduct periodic drills and ensure communication channels with local emergency services are established.
Conclusion
Adhering to this Logistics & Compliance Guide ensures safe, legal, and sustainable operations for Coal Torch. Regular audits, continuous improvement, and proactive engagement with regulatory agencies are essential to maintaining compliance and operational excellence.
Conclusion for Sourcing Coal Torches
In conclusion, sourcing coal torches—whether for historical reenactment, decorative purposes, or traditional mining simulations—requires careful consideration of authenticity, safety, availability, and environmental impact. While true coal-burning torches are largely obsolete due to modern safety standards and fire regulations, alternatives such as replica designs, LED-lit versions, or controlled demonstration pieces offer practical and safe solutions. Reliable sourcing can be achieved through specialty suppliers, historical reenactment vendors, or custom artisans who prioritize material quality and safety compliance. It is essential to verify local regulations regarding open flames and combustion, especially when used in public or indoor settings. Ultimately, responsible sourcing ensures both the aesthetic and functional goals are met while maintaining safety and sustainability.