The global coal mining equipment market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising energy demand, ongoing modernization of mining operations, and increased investments in automation and efficiency-enhancing machinery. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 85 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by the continued reliance on coal in key markets such as China, India, and Indonesia, where thermal coal remains integral to power generation despite broader shifts toward renewable energy. Additionally, aging equipment fleets and the need for improved safety and productivity are accelerating demand for advanced mining technologies. In this competitive landscape, leading manufacturers are focusing on innovation, fuel efficiency, and smart machine integration to capture market share. Based on market presence, technological capabilities, and global reach, the following ten companies represent the forefront of coal mining machine manufacturing worldwide.
Top 10 Coal Mining Machines Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MacLean Engineering
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1973
Website: macleanengineering.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1973 in Ontario, Canada, MacLean Engineering is the world’s largest Canadian-based manufacturer of underground mining equipment….
#2
Domain Est. 2015
Website: hitachicm.com
Key Highlights: We are now a leading global manufacturer of mining machinery. We will continuously work on resolving issues which our customers face in the mining sites….
#3 Mining
Domain Est. 1993
Website: cat.com
Key Highlights: Our surface mining product line is unmatched, with equipment for drilling, digging and cutting; loading and hauling material; and maintaining efficient mine ……
#4
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1937
Website: jhfletcher.com
Key Highlights: J.H Fletcher & Co. has custom engineered and manufactured underground mining equipment since 1937. Offerings include established product lines and the ability ……
#5 Mining Equipment
Domain Est. 2005
Website: miningequipmentltd.com
Key Highlights: Mining Equipment specializes in rail mounted equipment. We have a very large inventory of diesel, battery and trolley locomotives in stock….
#6 Mining
Domain Est. 2015
Website: home.sandvik
Key Highlights: We offer a complete range of equipment and tools, services and technical solutions for the mining and infrastructure industries….
#7 Mining Machinery and Processing Equipment
Domain Est. 2016
Website: global.weir
Key Highlights: We offer a diverse portfolio of mining processing equipment that covers the entire flowsheet, from extraction to mineral processing and beneficiation….
#8 Epiroc USA – Mining Equipment
Domain Est. 2017
Website: epiroc.com
Key Highlights: We provide innovative mining equipment, consumables and services for drilling and rock excavation. Whether the application is surface and underground mining ……
#9 Mining machines & Machinery
Domain Est. 2021
Website: gainwellengineering.com
Key Highlights: We engineer, manufacture, service, repair, rebuild underground mining equipment for the global market. · exp. 80+. years of engineering expertise · emp. 150+….
#10 Mining Equipment, Parts & Services
Website: mining.sandvik
Key Highlights: Our range of rock tools, ground support products and parts and components ensure your equipment operates at peak performance whilst maximising project safety ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Coal Mining Machines
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Coal Mining Machines
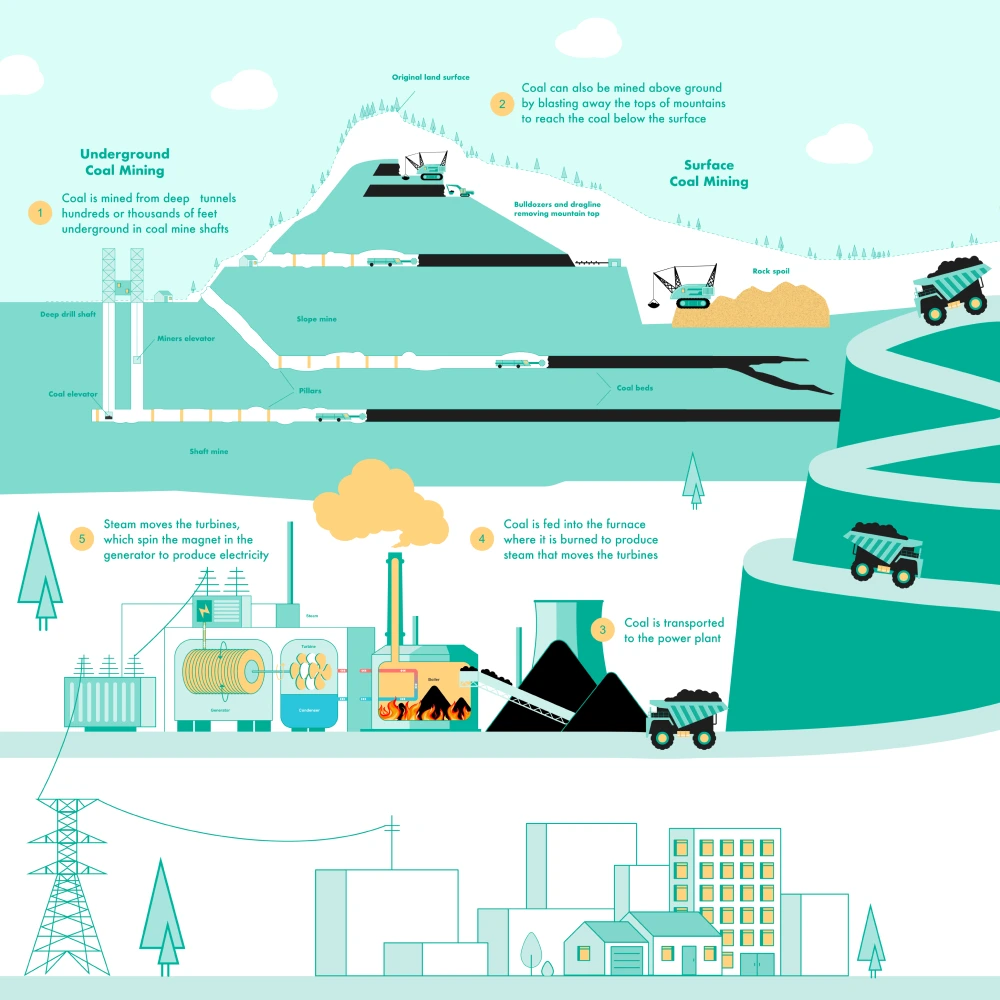
The global market for coal mining machines is expected to experience a complex and regionally divergent trajectory by 2026, shaped by evolving energy policies, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and shifting demand dynamics. While the long-term decline of coal as an energy source continues in many developed economies, emerging markets and industrializing nations are sustaining demand for coal, thereby influencing investments in mining equipment.
-
Regional Demand Disparities
By 2026, coal mining machine demand will remain strong in Asia-Pacific, particularly in India, Indonesia, and Mongolia, where coal continues to play a critical role in power generation and steel production. China, despite its push toward carbon neutrality, will maintain a significant domestic coal mining sector, driving demand for modern, efficient machinery to replace aging fleets. In contrast, North America and Western Europe are expected to see stagnation or decline in coal mining machine purchases due to accelerated transitions toward renewable energy and stricter emissions regulations. -
Technological Advancements and Automation
Automation and digitalization will be key drivers in the coal mining machinery sector by 2026. Leading manufacturers are increasingly integrating IoT-enabled sensors, remote monitoring systems, and AI-driven analytics into equipment such as continuous miners, longwall shearers, and roof bolters. These technologies enhance operational efficiency, improve safety, and reduce downtime—critical factors for operators under pressure to cut costs and comply with safety standards. Autonomous haulage systems and semi-automated drilling rigs are expected to gain traction, particularly in large-scale surface and underground mines. -
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Emissions Reduction
As environmental scrutiny intensifies, machinery manufacturers are responding with more energy-efficient and low-emission equipment. Electric-powered mining machines, such as battery-electric load-haul-dump (LHD) vehicles and electric longwall systems, are gaining interest. These technologies reduce underground ventilation requirements and lower carbon footprints, aligning with sustainability goals even in coal-dependent regions. -
Supply Chain and Raw Material Constraints
The production of advanced mining machinery relies on critical minerals such as rare earth elements, copper, and lithium. By 2026, supply chain volatility and geopolitical tensions may impact the availability and cost of these materials, potentially increasing machine prices and delivery lead times. Manufacturers are expected to diversify sourcing and invest in recycling technologies to mitigate these risks. -
Aftermarket Services and Digital Integration
The aftermarket segment—including maintenance, spare parts, and equipment upgrades—is projected to grow faster than the primary equipment market by 2026. Mining companies are increasingly adopting predictive maintenance platforms and remote diagnostics, creating new revenue streams for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). This shift supports machine longevity and operational continuity, particularly in cost-sensitive markets. -
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Stricter environmental regulations and global climate commitments (e.g., Paris Agreement) will continue to influence investment in coal mining infrastructure. While this may dampen overall market growth, it also incentivizes the adoption of cleaner, more efficient machinery to extend the operational life of existing mines under compliance frameworks.
Conclusion
By 2026, the coal mining machines market will reflect a dichotomy: technological innovation and modernization in regions where coal remains essential, contrasted with market contraction in areas phasing out coal. Success for equipment manufacturers will depend on adaptability—offering smarter, cleaner, and more efficient solutions tailored to regional energy strategies and regulatory landscapes.
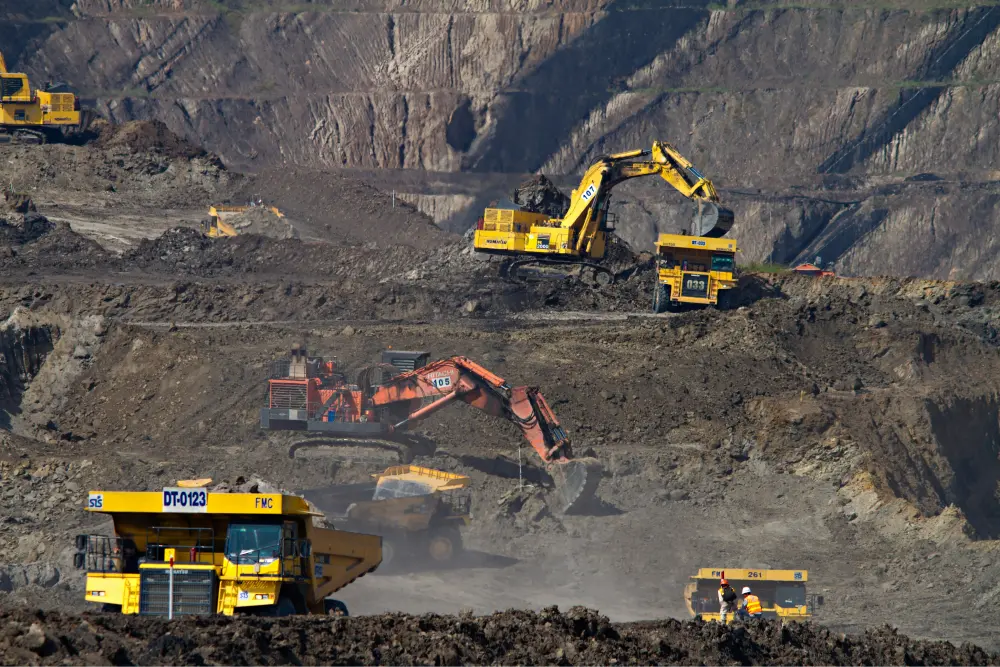

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Coal Mining Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing coal mining machinery, especially from emerging markets or unfamiliar suppliers, involves significant risks beyond simple procurement. Two critical areas prone to pitfalls are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these can lead to costly downtime, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Substandard Materials and Manufacturing Processes
A major risk is receiving equipment built with inferior materials or poor workmanship. Suppliers may cut corners by using low-grade steel, subpar electrical components, or inadequate welds to reduce costs. This compromises machine durability, safety, and performance—especially in the harsh conditions of underground or surface mining. Without rigorous third-party inspections and material certifications, buyers may only discover these issues after deployment, resulting in frequent breakdowns and unsafe operations.
2. Lack of Compliance with Safety and Industry Standards
Coal mining machines must meet strict safety regulations (e.g., MSHA in the U.S., ATEX in Europe, or national standards like GB in China). Some suppliers may falsely claim compliance or provide counterfeit certifications. Non-compliant equipment can lead to regulatory fines, operational shutdowns, and increased risk of accidents. Buyers must independently verify documentation and conduct audits to ensure adherence to required standards.
3. Inadequate Testing and Validation
Reputable manufacturers conduct extensive factory acceptance tests (FAT) and site commissioning. However, some suppliers skip or falsify these procedures, delivering untested or poorly calibrated machinery. Without witnessing FATs or requiring performance guarantees, buyers risk receiving equipment that fails under real mining conditions, leading to project delays and increased operational costs.
4. Poor After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if the initial machine is of good quality, sourcing from unreliable suppliers often results in poor technical support, delayed spare parts delivery, and lack of trained service personnel. This undermines equipment uptime and lifecycle value. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s service infrastructure and demand clear SLAs (Service Level Agreements) before purchase.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Counterfeit or Clone Machinery
A pervasive issue in mining equipment sourcing is the sale of counterfeit or reverse-engineered machines that copy patented designs from established OEMs (e.g., Caterpillar, Komatsu, Eickhoff). These clones may resemble genuine equipment but lack performance, reliability, and safety features. Purchasing such machines exposes buyers to IP infringement claims and voids warranties, potentially implicating the buyer in legal action if the original IP holder pursues enforcement.
2. Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Technology
Some suppliers integrate patented technologies—such as cutting heads, conveyor systems, or automation controls—without licensing. Buyers may unknowingly acquire machinery that infringes on third-party IP. If discovered, this can lead to legal challenges, forced equipment removal, or costly redesigns, disrupting mining operations.
3. Weak or Ambiguous Contractual IP Clauses
Procurement contracts often lack clear terms defining IP ownership, especially for custom-designed or modified equipment. Without explicit clauses, buyers may not secure rights to technical drawings, software, or modifications—limiting their ability to maintain, repair, or upgrade machinery independently. This dependence on the supplier can lead to inflated future costs and operational vulnerability.
4. Risk of Technology Leakage
When engaging suppliers for custom solutions, especially in joint development scenarios, there’s a risk that sensitive operational data or proprietary design information could be misused or shared with competitors. Inadequate confidentiality agreements or poor data security practices by the supplier increase exposure to industrial espionage or loss of competitive advantage.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site audits and reference checks.
– Require third-party quality inspections and certification documentation.
– Engage independent legal counsel to review contracts for IP clauses and compliance.
– Specify clear warranty, testing, and after-sales support terms.
– Avoid unusually low bids that may indicate compromised quality or IP issues.
Proactive risk management in both quality and IP domains is essential to ensure reliable, compliant, and legally secure coal mining operations.
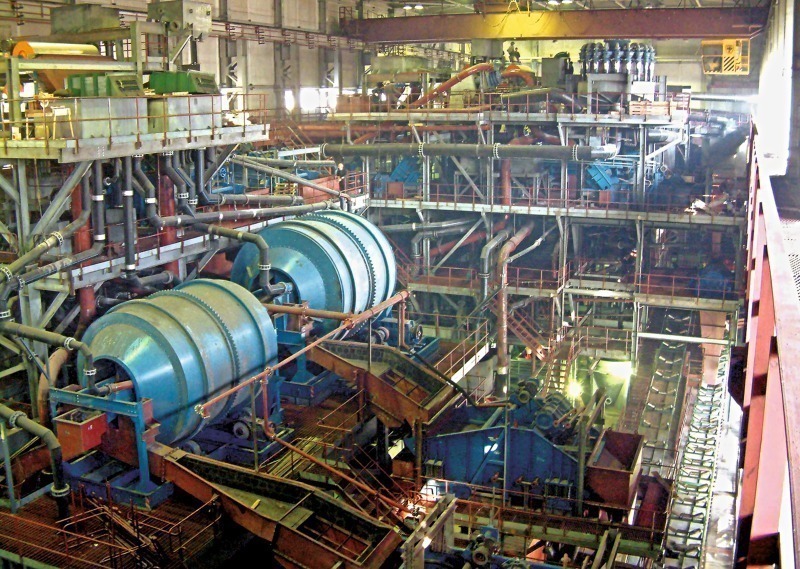

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Coal Mining Machines
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for transporting and operating coal mining machines. These heavy, high-value assets require specialized handling, documentation, and adherence to international and local regulations to ensure safe, efficient, and legal deployment.
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards and Certifications
Coal mining machines must meet international safety and environmental standards such as ISO, IECEx (for explosive atmospheres), and ATEX (in the EU). Exporters and importers must ensure machines are certified for use in the destination country, including conformity with local electrical, mechanical, and emissions standards.
Environmental and Emissions Regulations
Machines must comply with environmental regulations related to noise, dust, and exhaust emissions. In many jurisdictions, diesel-powered mining equipment must meet Tier 3 or Tier 4 Final emissions standards (e.g., U.S. EPA or EU Stage V). Environmental impact assessments may be required during transport and installation.
Safety and Operational Compliance
All equipment must adhere to mine safety regulations such as MSHA (U.S. Mine Safety and Health Administration) or equivalent standards in other countries. This includes mandatory safety features like emergency stop systems, fire suppression, and gas detection systems. Documentation such as risk assessments, operation manuals, and maintenance logs must be maintained.
Transportation Logistics
Pre-Shipment Planning
Plan transport routes considering machine dimensions, weight, and infrastructure limitations (e.g., bridge weight limits, road width). Obtain necessary permits for oversized or overweight loads, especially for cross-border shipments. Coordinate with local authorities for road closures or escort requirements if necessary.
Packaging and Protection
Use weather-resistant, secure packaging for components and control systems. Sensitive electronics should be packed in anti-static, moisture-proof materials. Machines should be coated with anti-corrosive agents and stored in dry, ventilated containers during transit.
Modes of Transport
- Road: Suitable for regional movement; requires low-bed trailers and route surveys.
- Rail: Cost-effective for long distances; requires compatible loading gauges and cranes.
- Sea: Used for international shipments; machines are typically containerized or shipped as breakbulk cargo. Ensure compliance with IMDG Code for hazardous components (e.g., batteries, fuels).
- Air: Rarely used due to size and cost, but may be considered for urgent spare parts.
Customs and Documentation
Prepare a complete documentation package including:
– Commercial invoice
– Packing list
– Bill of lading or air waybill
– Certificate of origin
– Export/import licenses
– Equipment conformity certificates (e.g., CE, MSHA)
– Risk assessment and safety data sheets (SDS) for any hazardous materials
Ensure Harmonized System (HS) codes are correctly classified to avoid delays or penalties.
On-Site Handling and Installation
Site Preparation
Ensure the mine site has adequate infrastructure—reinforced ground, power supply, and crane access—for receiving and assembling large machines like continuous miners, longwall shearers, or draglines.
Unloading and Assembly
Use certified lifting equipment and trained personnel for unloading. Follow manufacturer’s assembly instructions and conduct pre-operational safety checks. Perform alignment, lubrication, and system integration with existing mine controls.
Commissioning and Testing
Conduct functional and safety tests before full operation. Verify all safety interlocks, monitoring systems, and emergency functions. Document test results and obtain sign-off from compliance officers.
Maintenance and Ongoing Compliance
Scheduled Maintenance
Adhere to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules to ensure operational safety and regulatory compliance. Maintain detailed logs of inspections, repairs, and component replacements.
Regulatory Audits and Reporting
Prepare for periodic audits by regulatory bodies. Keep records of machine certifications, operator training, incident reports, and environmental monitoring data. Report any equipment failures or safety incidents as required by law.
Decommissioning and Disposal
At end-of-life, follow environmental regulations for dismantling and disposal. Recycle metals and hazardous components (e.g., oils, batteries) through authorized facilities. Document disposal procedures to meet sustainability and compliance requirements.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and strict adherence to compliance standards are essential for the safe and legal operation of coal mining machines. Proactive coordination among manufacturers, logistics providers, mine operators, and regulators ensures smooth deployment, reduces downtime, and mitigates legal and environmental risks.
In conclusion, sourcing coal mining machines is a critical process that directly impacts the efficiency, safety, and profitability of mining operations. It requires a comprehensive evaluation of machinery specifications, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, after-sales support, and compliance with industry and environmental standards. With technological advancements, modern coal mining equipment offers improved automation, durability, and energy efficiency, contributing to higher productivity and safer working conditions.
A strategic sourcing approach—considering both short-term needs and long-term operational goals—ensures the selection of appropriate machinery tailored to specific mining conditions. Additionally, engaging with reputable manufacturers, conducting thorough market research, and leveraging expert consultations can substantially reduce procurement risks.
Ultimately, investing in high-quality, well-maintained coal mining machines not only enhances operational performance but also supports sustainable and responsible mining practices. Proper sourcing lays the foundation for a resilient and competitive mining operation in an evolving global energy landscape.