The global CO₂ enrichment market for controlled environment agriculture is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for higher crop yields and advancements in indoor farming technologies. According to Mordor Intelligence, the carbon dioxide enrichment market was valued at USD 262.8 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 368.4 million by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 7.0% during the forecast period. This expansion is further supported by rising adoption of hydroponics, vertical farming, and greenhouse cultivation, where precise CO₂ dosing significantly enhances photosynthetic efficiency and plant growth. As commercial growers seek reliable and scalable solutions, the demand for high-performance CO₂ generators has surged, prompting innovation among manufacturers. In this competitive landscape, nine key manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining technological precision, energy efficiency, and scalability to meet the evolving needs of modern horticulture.
Top 9 Co2 Generator For Plants Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CO2 generator
Domain Est. 2016
Website: agriexpo.online
Key Highlights: CO2 is scientifically proven to improve the performance of plants! The Ares® Series CO2 generators provide a clean & efficient way to enrich your grow….
#2 Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Power Systems
Domain Est. 1995
Website: swri.org
Key Highlights: SwRI is collaborating with a team to design, build, and operate a 10-MWe (megawatt electric) pilot plant for demonstrating supercritical carbon dioxide ……
#3 CO2 and Dry Ice Solutions
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ascoco2.com
Key Highlights: As a supplier of complete CO 2 solutions we have dry ice production machines for every need. We are also your competent partner for setting up your in-house ……
#4 CO2 Generators, Burners
Domain Est. 2011
#5 TNB Naturals
Domain Est. 2012
Website: tnbnaturals.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $149 30-day returnsBoost plant growth with TNB Naturals—CO2 Enhancer, Refill, Enricher, Kelptastic, pH Up & Down. Shipping in Canada & USA. Trusted by growers wo…
#6 Mother Nature CO2 Generator 10 Liter Kit with Single Outlet Air Pump
Domain Est. 2012
#7 Johnson CO2 Generator
Domain Est. 2018
Website: johnsonco2.com
Key Highlights: A Johnson CO2 Generator automatically provides ideal carbon dioxide level when plants need it most, year round to maximize plant growth-efficiently & ……
#8 CO2GRO
Domain Est. 2018
Website: thehydrobros.com
Key Highlights: In stock $80 deliveryThis CO2 generator works using mixing two materials (Material A + Material B sold separately) which once charged will generate high-purity CO2!…
#9 BluePrint CO2 Generator NG 10
Domain Est. 2022
Expert Sourcing Insights for Co2 Generator For Plants

H2: 2026 Market Trends for CO2 Generators for Plants
The global market for CO2 generators for plants is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by rising demand for sustainable agriculture, advancements in controlled environment farming, and increasing adoption of vertical and indoor farming technologies. The following analysis outlines key trends shaping the CO2 generator market for plant cultivation in 2026.
-
Surge in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
By 2026, Controlled Environment Agriculture—including greenhouses, vertical farms, and indoor grow facilities—is expected to dominate the demand for CO2 enrichment systems. As urbanization limits arable land and climate change disrupts traditional farming, CEA offers a resilient alternative. CO2 generators are critical in these systems, enhancing photosynthesis and boosting crop yields by up to 30–40%. This trend is particularly strong in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, where food security and sustainable production are policy priorities. -
Technological Advancements and Smart Integration
CO2 generators in 2026 are increasingly integrated with smart farming technologies. IoT-enabled sensors, AI-driven climate control systems, and automated CO2 dosing mechanisms allow precise regulation of CO2 levels based on real-time plant needs. These intelligent systems reduce waste, improve efficiency, and ensure optimal growth conditions. Leading manufacturers are offering modular, scalable CO2 solutions compatible with existing CEA infrastructure, driving broader adoption. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Models
Environmental concerns are pushing manufacturers to develop eco-friendly CO2 generators. By 2026, there is growing preference for electric CO2 generators and systems that utilize renewable energy sources or recycle CO2 from on-site processes (e.g., combined heat and power units). Additionally, innovations in catalytic combustion and low-emission burners are minimizing harmful byproducts, aligning with stricter environmental regulations. -
Expansion of Urban and Vertical Farming
Urban agriculture is gaining momentum, with vertical farms multiplying in cities worldwide. These high-density growing environments rely heavily on CO2 enrichment to maximize productivity in limited spaces. The compact design and scalability of modern CO2 generators make them ideal for vertical farming applications. By 2026, partnerships between CO2 technology providers and vertical farm operators are expected to increase, fostering co-developed solutions tailored to specific crops and environments. -
Regulatory Support and Incentives
Governments and agricultural agencies in several countries are introducing incentives for sustainable farming technologies. In 2026, subsidies and tax breaks for energy-efficient CO2 systems are accelerating adoption, especially among small-to-medium greenhouse operators. Regulatory frameworks promoting carbon utilization and circular economy practices are also encouraging farms to adopt CO2 generators that capture and reuse carbon emissions. -
Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe remain the largest markets due to advanced agricultural infrastructure and strong investment in agri-tech. However, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and South Korea—is emerging as a high-growth region, driven by food demand and government initiatives to modernize agriculture. Latin America and the Middle East are also showing increased interest, especially in greenhouse expansion projects in arid regions where CO2 enrichment improves crop resilience. -
Rising Demand for High-Value Crops
The economic incentive to grow high-value crops such as leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, and medicinal plants is pushing growers to optimize yields using CO2 generators. In 2026, the cannabis industry—legal in more jurisdictions—continues to be a major driver, as precise CO2 control is essential for maximizing cannabinoid production and flowering cycles.
Conclusion
By 2026, the CO2 generator market for plants will be shaped by technological innovation, sustainability imperatives, and the global shift toward efficient, high-yield farming. As food production systems evolve to meet environmental and demographic challenges, CO2 generators will play an increasingly strategic role in enhancing agricultural productivity and resilience. Companies that invest in smart, scalable, and eco-conscious solutions are well-positioned to lead this expanding market.
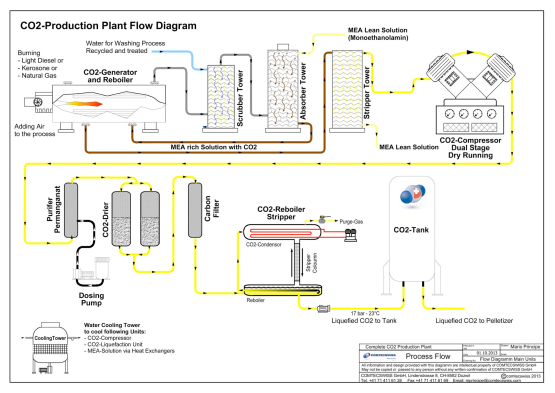
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing CO2 Generators for Plants (Quality & IP)
Sourcing CO2 generators for plant cultivation—whether for greenhouses, indoor farms, or research—requires careful evaluation to avoid costly mistakes. Two critical areas where buyers often stumble are product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these can lead to poor performance, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial loss.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Inadequate CO2 Output and Precision
- Pitfall: Many low-cost generators fail to deliver consistent or sufficient CO2 levels required for optimal plant growth. Units may have inaccurate flow controls or sensors, leading to under- or over-enrichment.
- Impact: Inconsistent CO2 levels stress plants, reduce yields, and waste energy. Poor calibration can also create unsafe environments.
-
Solution: Verify specifications with third-party test reports. Look for units with calibrated sensors, digital controllers, and adjustable output tailored to your grow space size.
-
Use of Low-Grade Materials and Components
- Pitfall: Some manufacturers use substandard materials (e.g., non-corrosion-resistant metals, cheap plastics) that degrade quickly when exposed to heat, moisture, or CO2 byproducts.
- Impact: Shortened lifespan, frequent breakdowns, and potential contamination of the growing environment.
-
Solution: Prioritize suppliers who use industrial-grade materials (e.g., stainless steel burners, high-temp ceramics) and request material certifications.
-
Poor Safety Features
- Pitfall: Lack of essential safety mechanisms such as flame failure detection, overheat protection, automatic shutoff, or oxygen depletion sensors.
- Impact: Risk of fire, carbon monoxide (CO) buildup, or asphyxiation in enclosed spaces.
-
Solution: Ensure compliance with safety standards (e.g., UL, CE, CSA). Require documentation of safety testing and certifications.
-
Inefficient Combustion and Byproduct Emissions
- Pitfall: Incomplete combustion in propane or natural gas burners can produce harmful byproducts like ethylene, carbon monoxide, and excess moisture.
- Impact: Plant damage, health risks, and increased humidity leading to mold.
-
Solution: Choose generators with catalytic or high-efficiency burners and demand emission test data. Consider pure liquid CO2 systems for sensitive environments.
-
Lack of After-Sales Support and Warranty
- Pitfall: Vendors, especially offshore suppliers, may offer little to no technical support, repair services, or warranty coverage.
- Impact: Downtime during critical growth phases and high maintenance costs.
- Solution: Partner with suppliers offering comprehensive warranties, accessible customer service, and spare parts availability.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
- Sourcing Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Products
- Pitfall: Some suppliers clone patented CO2 generator designs, control systems, or sensor technologies without authorization.
- Impact: Purchasing infringing products can expose your business to legal liability, especially in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement (e.g., EU, USA). Seizures, fines, or injunctions may follow.
-
Solution: Work only with reputable suppliers. Request proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements. Avoid deals that seem too good to be true.
-
Lack of Transparency in Technology Origin
- Pitfall: Suppliers may obscure the origin of critical components (e.g., using patented algorithms in controllers or proprietary burner designs).
- Impact: Risk of unintentional IP infringement and dependency on unstable supply chains.
-
Solution: Conduct due diligence—ask for technical documentation, bill of materials (BOM), and design schematics. Use legal agreements to require IP indemnification.
-
Custom or OEM Designs Without IP Assignment
- Pitfall: When commissioning a custom CO2 generator, the supplier may retain ownership of design improvements or embedded software.
- Impact: Loss of control over your investment; inability to reproduce or modify the design without permission.
-
Solution: Clearly define IP ownership in contracts. Ensure all custom developments are assigned to your organization via written agreement.
-
Use of Open-Source or Unlicensed Software
- Pitfall: Some generators use open-source firmware or software without complying with licensing terms (e.g., GPL).
- Impact: Legal exposure if the software is used commercially without compliance (e.g., releasing source code).
- Solution: Ask for software compliance statements and audit trails, especially for IoT-enabled or smart CO2 systems.
Conclusion
To avoid pitfalls in sourcing CO2 generators, prioritize verified quality through certifications, material standards, and safety features. Simultaneously, mitigate IP risks by vetting suppliers, securing proper legal agreements, and ensuring transparency in design and software use. Due diligence upfront protects your operation, ensures regulatory compliance, and supports long-term success in controlled environment agriculture.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for CO₂ Generators for Plants
H2: Overview of CO₂ Generators for Plants
CO₂ generators for plants are devices designed to increase the concentration of carbon dioxide in indoor growing environments (e.g., greenhouses, grow rooms) to enhance plant growth and yield. These generators typically operate by burning natural gas or propane to produce CO₂ as a byproduct. Due to the nature of their operation—using flammable fuels and generating gases—logistics and compliance considerations are critical for safe and legal deployment.
H2: Key Logistics Considerations
1. Storage and Handling of Fuel Sources
- Propane/Natural Gas Cylinders:
- Store in well-ventilated, dry, and secure outdoor areas away from ignition sources.
- Keep cylinders upright and secured to prevent tipping.
- Follow local fire codes for maximum allowed storage quantities.
- Fuel Delivery:
- Coordinate regular propane delivery with licensed suppliers.
- Ensure delivery vehicles have proper access and comply with site safety protocols.
2. Transportation Regulations
- Domestic (e.g., U.S. DOT Regulations):
- Propane tanks are classified as hazardous materials (Hazard Class 2, UN1978).
- Transport must comply with 49 CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) for labeling, packaging, and documentation.
- Drivers must have appropriate training and, if required, a Hazardous Materials Endorsement (HME) on their CDL.
- International (e.g., IMDG, IATA):
- Air and sea shipments require adherence to IMDG (sea) or IATA (air) regulations.
- Use UN-certified cylinders and proper hazard labeling (Class 2.1 Flammable Gas).
3. Installation and Placement
- Install CO₂ generators:
- At least 3 feet away from combustible materials.
- Near the ceiling (CO₂ is slightly heavier than air but disperses quickly).
- With adequate clearance for maintenance and ventilation.
- Use only in well-ventilated areas or with CO₂ monitoring systems to prevent dangerous buildup.
4. Supply Chain Management
- Source CO₂ generators from certified manufacturers.
- Maintain inventory logs for fuel and equipment.
- Establish preventive maintenance schedules to avoid operational disruptions.
H2: Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
1. Safety Standards
- NFPA 58 (Liquefied Petroleum Gas Code):
- Governs the safe storage and use of propane in the U.S.
- Applies to tank size, location, ventilation, and fire protection.
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.106:
- Covers flammable liquid and gas handling.
- Requires proper labeling, ventilation, and employee training.
- ANSI Z83.20 / CSA 2.17:
- Safety standards for gas-fired greenhouse heaters and CO₂ generators.
2. Environmental and Air Quality Regulations
- EPA and Local Air Quality Boards:
- Combustion byproducts (CO, NOx) must be within permissible limits.
- In some jurisdictions, permits may be required for emissions from combustion devices.
- Indoor CO₂ levels should not exceed 5,000 ppm (OSHA PEL) for occupational safety.
3. Building and Fire Codes
- International Fire Code (IFC) and International Building Code (IBC):
- Regulate fuel storage, ventilation, and fire suppression systems.
- May require CO detectors, flame failure devices, and automatic shutoff valves.
- Local Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) may impose additional rules.
4. Electrical Compliance
- Ensure power connections comply with:
- NEC (National Electrical Code) Article 501 for hazardous locations if applicable.
- Proper grounding and use of explosion-proof components in high-risk areas.
H2: Monitoring and Documentation
1. Gas Monitoring
- Install CO₂ sensors with alarms to alert when levels exceed safe thresholds (typically >1,500–2,000 ppm for prolonged exposure).
- Use carbon monoxide (CO) detectors—critical due to incomplete combustion risks.
2. Recordkeeping
- Maintain logs of:
- Fuel deliveries and consumption.
- Equipment inspections and maintenance.
- Safety training for staff.
- Regulatory permit documentation.
3. Training and Compliance Audits
- Train personnel on:
- Safe operation of CO₂ generators.
- Emergency shutdown procedures.
- Response to gas leaks or fire.
- Conduct regular safety audits and compliance reviews.
H2: International Considerations
- CE Marking (Europe):
- Required for CO₂ generators sold in the EU.
- Must comply with Gas Appliances Regulation (GAR) and Low Voltage Directive.
- UKCA Marking (UK):
- Post-Brexit equivalent to CE for the UK market.
- Transportation Abroad:
- ADR regulations for road transport in Europe.
- Ensure bilingual labeling and documentation where required.
H2: Best Practices Summary
| Area | Best Practice |
|——|—————|
| Storage | Store fuel in approved, ventilated outdoor areas. |
| Installation | Follow manufacturer guidelines and local codes. |
| Ventilation | Ensure adequate airflow and use exhaust fans if needed. |
| Monitoring | Use CO₂ and CO detectors with alarms. |
| Compliance | Obtain permits, maintain records, and train staff. |
| Maintenance | Schedule regular servicing and inspections. |
By adhering to proper logistics protocols and regulatory standards, operators can safely and effectively use CO₂ generators to optimize plant growth while minimizing risks to people, property, and the environment. Always consult with local authorities and certified professionals before installation and operation.
Conclusion: Sourcing a CO2 Generator for Plants
Sourcing a CO2 generator for plant cultivation is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance plant growth, yield, and overall crop quality—especially in enclosed environments such as greenhouses and indoor grow rooms. After evaluating various options, including propane or natural gas burners, DIY fermentation systems, and commercial CO2 tanks with regulators, it is clear that the most suitable choice depends on the scale of operation, budget, safety considerations, and desired level of control.
Commercial CO2 generators powered by propane or natural gas offer reliable, consistent CO2 output and are ideal for medium to large-scale operations where automation and efficiency are critical. Although they require proper ventilation and safety installations, their long-term benefits in boosting photosynthesis and shortening growth cycles make them a worthwhile investment.
For smaller setups or budget-conscious growers, alternative methods such as CO2 bags (using mycelium) or fermentation systems may provide a simpler, low-tech solution—albeit with less precision and output.
Ultimately, when sourcing a CO2 generator, it is essential to prioritize safety, compatibility with existing systems, ease of maintenance, and environmental controls. Monitoring equipment such as CO2 sensors should be used in conjunction with the generator to maintain optimal levels (typically 800–1200 ppm) without risking plant or human safety.
In summary, integrating a properly sourced CO2 generator into your cultivation system can lead to substantial productivity gains. By selecting the right system for your needs and ensuring proper installation and monitoring, you can create an optimized growing environment that maximizes plant health and yield.