The global CNC turning center market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the CNC machine tool market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in automation, Industry 4.0 integration, and rising adoption of smart manufacturing practices. Grand View Research further supports this trajectory, estimating the global CNC machine market to exceed USD 140 billion by 2030, with CNC turning centers representing a significant segment due to their critical role in high-precision, high-efficiency production environments. As manufacturers worldwide prioritize productivity and consistency, the demand for advanced CNC turning solutions continues to rise, positioning leading suppliers at the forefront of industrial innovation. The following list highlights the top 10 CNC turning center manufacturers shaping the future of modern manufacturing.
Top 10 Cnc Turning Center Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kitamura Machinery
Domain Est. 2000
Website: kitamura-machinery.com
Key Highlights: Uniquely intuitive, user-focused CNC technology for easier part programming, part set-up and operation. Software upgrades available for the life of the control….
#2 YEONG CHIN MACHINERY INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 1954
Website: ycmcnc.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1954, YCM is a world-class manufacturer, providing a wide range of 5-axis, CNC, lathes and total solutions for Industry 4.0 … CNC Turning Center; 5 ……
#3 Makino
Domain Est. 1996
Website: makino.com
Key Highlights: Achieve superior results with Makino’s CNC machining. Makino machines and engineering services provide precision and reliability across applications….
#4 Haas Automation Inc.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: haascnc.com
Key Highlights: Haas Automation is the largest machine tool builder in the western world, manufacturing a complete line of CNC vertical machining centers, ……
#5 Ellison Technologies: Advanced CNC Machining Solutions
Domain Est. 2005
Website: ellisontechnologies.com
Key Highlights: We’ve got just what your application needs with our full product offering in the latest CNC machine tool technology: horizontal turning centers, 3 – 5-axis ……
#6 STYLE CNC Machines
Domain Est. 2012
Website: stylecncmachines.com
Key Highlights: STYLE: manufacturer of CNC turning and milling machines, CNC slantbed bed and machining centers, from development to end product with STYLE control….
#7 Okuma America
Domain Est. 1996
Website: okuma.com
Key Highlights: Okuma America Corporation helps users gain competitive advantage through the open possibilities of our CNC machine tools and advanced technologies….
#8 CNC Machine Tools Distributor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: absolutemachine.com
Key Highlights: Absolute Machine Tools is a master importer and distributor of CNC machine tools throughout North America. Comprehensive Metal Cutting and Automation Products….
#9 to Mazak Corporation
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mazak.com
Key Highlights: Total Solution for Automation Systems. Automation systems for machining centers. Automation systems for turning centers. Build your Mazak Ez Machine….
#10 DN Solutions
Domain Est. 2017
Website: dn-solutions.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to official website of DN Solutions! Here you can view our wide range of products from the very latest machines to our most popular models….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cnc Turning Center
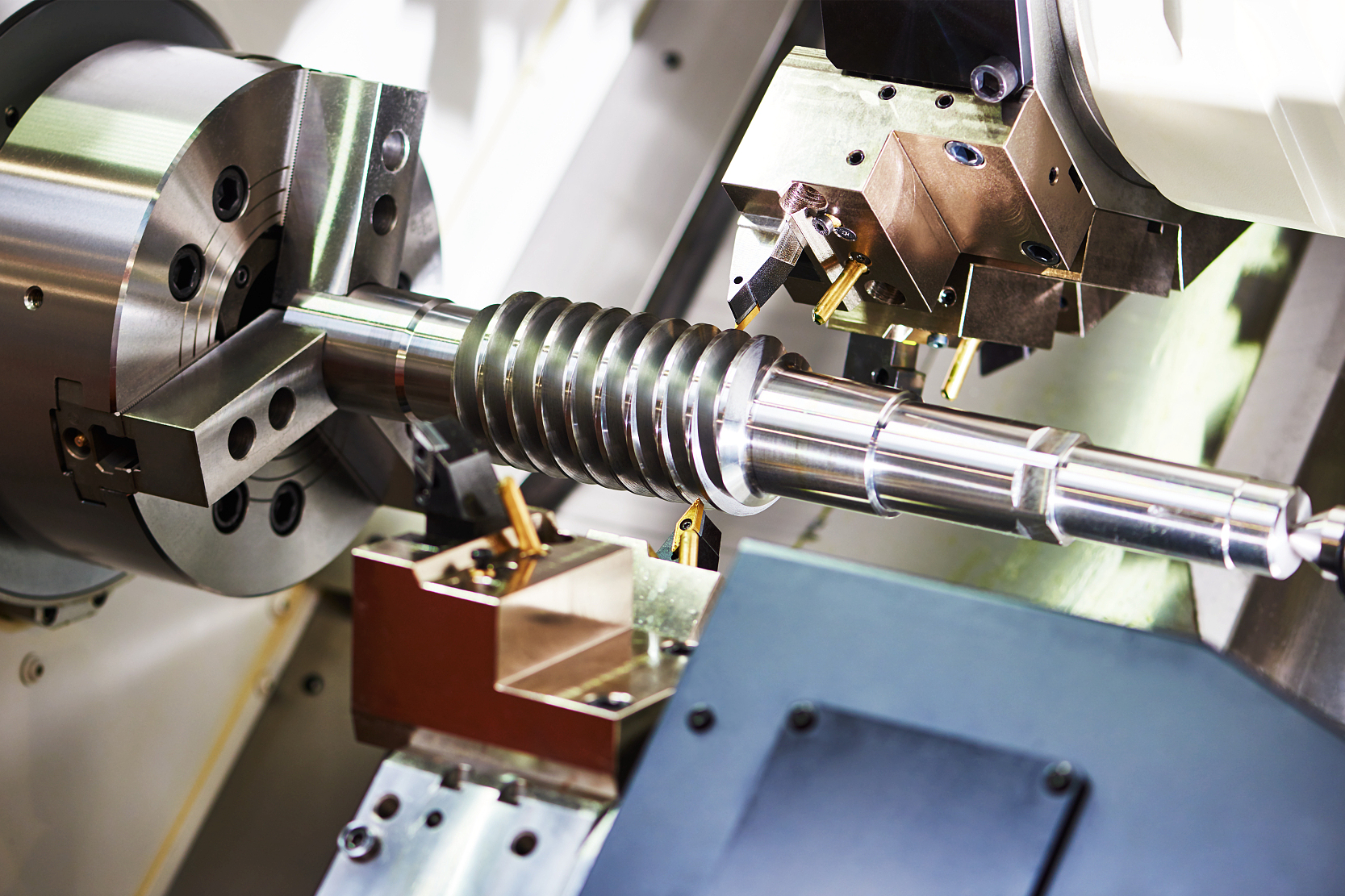
2026 Market Trends for CNC Turning Centers: A Strategic Outlook
By 2026, the global CNC Turning Center market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and shifting global economic dynamics. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
Increased Adoption of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 Integration
CNC Turning Centers will increasingly feature embedded IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and cloud connectivity. This shift enables predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and seamless integration with MES and ERP systems. Machine learning algorithms will optimize cutting parameters and reduce cycle times, enhancing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and supporting lights-out manufacturing operations.
Rise of Hybrid and Multi-Tasking Machines
Demand for machines combining turning with milling, grinding, or additive manufacturing capabilities will grow. These multi-tasking CNC Turning Centers reduce setup times, improve accuracy, and streamline production of complex parts—especially critical in aerospace, medical, and energy sectors. By 2026, hybrid models will capture a larger market share as manufacturers prioritize flexibility and efficiency.
Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will push OEMs to design energy-efficient CNC Turning Centers with lower power consumption, reduced coolant usage, and recyclable components. Regenerative drives, optimized spindle designs, and closed-loop cooling systems will become standard features, helping end-users meet carbon reduction targets.
Expansion in High-Precision and Micro-Machining Applications
Growing demand in medical devices, electronics, and optics will drive innovation in precision turning. CNC Turning Centers capable of micron-level tolerances and handling miniature components will see increased investment, particularly in Asia-Pacific markets where electronics manufacturing is expanding rapidly.
Geopolitical Shifts and Regional Manufacturing Resilience
Ongoing supply chain realignments and “nearshoring” trends—especially in North America and Europe—will boost demand for CNC Turning Centers as companies localize production. This trend is expected to benefit domestic machine tool builders and encourage investments in automation to offset labor shortages.
Workforce Development and User-Friendly Interfaces
As the skilled labor gap persists, CNC Turning Centers will feature more intuitive, AI-assisted interfaces, augmented reality (AR) for setup and troubleshooting, and simplified programming through conversational interfaces. These advancements will lower the barrier to entry and improve operator productivity.
In conclusion, the 2026 CNC Turning Center market will be defined by intelligence, integration, and efficiency. Manufacturers who embrace digitalization, sustainability, and versatility will be best positioned to lead in this evolving industrial ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a CNC Turning Center (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a CNC Turning Center involves critical decisions that can significantly impact production quality, operational efficiency, and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking key factors can lead to costly mistakes. Below are the most common pitfalls related to quality and IP:
Poor Machine Build Quality and Component Selection
Many buyers focus on price and overlook build quality. Low-cost machines often use inferior linear guides, spindles, or ball screws that wear quickly, resulting in reduced accuracy, frequent downtime, and higher total cost of ownership. Always verify component brands, construction materials, and manufacturing tolerances before purchasing.
Inadequate Accuracy and Repeatability Verification
Not all CNC lathes deliver the precision they advertise. Some suppliers exaggerate specifications or fail to provide test reports (e.g., laser calibration data). Always request third-party inspection reports or conduct on-site performance testing to validate stated accuracy and repeatability under actual operating conditions.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines require maintenance. Sourcing from suppliers with limited local support or poor spare parts logistics can lead to extended downtime. Ensure the supplier offers timely technical assistance, training, and a reliable supply chain for critical components.
Insufficient Verification of Software and Control Systems
The CNC control system (e.g., Fanuc, Siemens, Mitsubishi) directly affects usability and machining performance. Counterfeit or outdated software may be installed to cut costs, reducing functionality and supportability. Confirm the authenticity of the control system and ensure compatibility with your existing programming standards and tooling.
Intellectual Property Risks from Reverse-Engineered Machines
Some manufacturers, especially in certain regions, produce CNC machines that closely mimic branded models using reverse engineering. These clones may infringe on patents and trademarks, exposing your company to legal liability if you purchase or operate them. Always verify the originality of the machine design and request documentation proving legitimate IP ownership.
Unprotected Program and Design Data
When outsourcing production or allowing machine suppliers remote access for diagnostics, there’s a risk of unauthorized access to proprietary CNC programs, toolpaths, and product designs. Ensure contracts include strict data protection clauses and use encrypted communication and access controls to safeguard sensitive IP.
Failure to Audit Supplier Manufacturing Practices
Without on-site audits, it’s difficult to assess a supplier’s quality control processes, worker training, and adherence to international standards (e.g., ISO 9001). Unverified suppliers may cut corners during assembly or calibration, compromising long-term machine reliability.
Overlooking Compliance with Regional Safety and Environmental Standards
Machines not certified to local standards (e.g., CE, UL, ANSI) can pose safety risks and may be barred from operation. Non-compliant machines might also lack proper electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) shielding, risking interference with other equipment and potential IP data leaks through signal transmission.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, clear supplier vetting, and proactive IP protection strategies to ensure both machine performance and legal compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for CNC Turning Center
Incoming Material Handling
Ensure all raw materials (bar stock, blanks, etc.) are received with proper documentation, including material certifications (e.g., mill test reports), quantity verification, and inspection for damage. Store materials in designated, labeled areas to prevent mix-ups and environmental degradation. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to reduce obsolescence and maintain material traceability.
Material Traceability & Documentation
Maintain full traceability of materials from receipt through production. Assign batch/heat numbers and log them in the production tracking system. Required documentation includes material certificates, purchase orders, and inspection records. This traceability is critical for compliance with ISO 9001, AS9100 (if applicable), and customer-specific requirements.
Work-in-Progress (WIP) Flow Management
Organize the CNC turning center layout to support efficient WIP movement. Use clearly marked staging areas, visual management tools (e.g., Kanban boards), and standardized work instructions to minimize bottlenecks and errors. Ensure each workpiece is accompanied by a traveler or routing sheet that logs operations, tooling used, and inspection checkpoints.
Tooling & Fixture Logistics
Maintain an organized tool crib with a digital or manual log for tool issuance, calibration, and lifecycle tracking. Regularly audit tooling inventory to ensure availability and accuracy. Calibrate probes, tool setters, and measuring equipment per a documented schedule to comply with quality standards and prevent non-conformance.
Finished Goods Inspection & Release
Conduct final inspections per customer drawings and internal quality plans. Use calibrated measurement equipment (e.g., micrometers, CMM) and document results in inspection reports. Only release parts that meet all specifications and have complete documentation. Non-conforming parts must be quarantined and processed through a formal non-conformance report (NCR) system.
Packaging & Outgoing Shipment
Package finished parts according to customer specifications to prevent damage during transit. Include proper labeling with part number, revision, quantity, batch/heat number, and handling instructions. Generate shipping documents (packing list, bill of lading, certificate of conformance) and ensure compliance with export regulations if shipping internationally (e.g., ITAR, EAR).
Regulatory & Industry Compliance
Adhere to relevant standards such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (for automotive), or AS9100 (for aerospace). Maintain documented procedures for internal audits, corrective actions, and management reviews. Ensure environmental compliance with local regulations regarding coolant disposal, metal shavings (swarf) handling, and waste oil management.
Record Retention & Audit Preparedness
Retain all production, inspection, calibration, and material records for the duration specified by quality standards or customer contracts (typically 10+ years for aerospace). Store records electronically or physically in a secure, organized system. Conduct regular internal audits to verify compliance and prepare for external audits by customers or certification bodies.
Continuous Improvement & Corrective Actions
Use non-conformance data and customer feedback to drive corrective and preventive actions (CAPA). Implement lean manufacturing principles to reduce waste and improve turnaround time. Regularly review logistics and compliance processes to ensure ongoing alignment with best practices and regulatory updates.
Conclusion for Sourcing a CNC Turning Center
Sourcing a CNC turning center is a strategic investment that significantly impacts manufacturing efficiency, product quality, and long-term operational scalability. After thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier credibility, cost considerations, after-sales support, and alignment with production requirements, the selected CNC turning center demonstrates optimal performance, reliability, and return on investment.
Key factors such as precision, automation capabilities, ease of integration into existing workflows, and future serviceability were prioritized to ensure seamless operations and adaptability to evolving production demands. Additionally, choosing a reputable supplier with a strong service network ensures timely maintenance, operator training, and technical support—critical elements for minimizing downtime and maximizing uptime.
In conclusion, the procurement of this CNC turning center positions the organization to enhance productivity, maintain competitive advantage, and meet stringent quality standards. With proper implementation and ongoing maintenance, this equipment will serve as a cornerstone of manufacturing excellence for years to come.