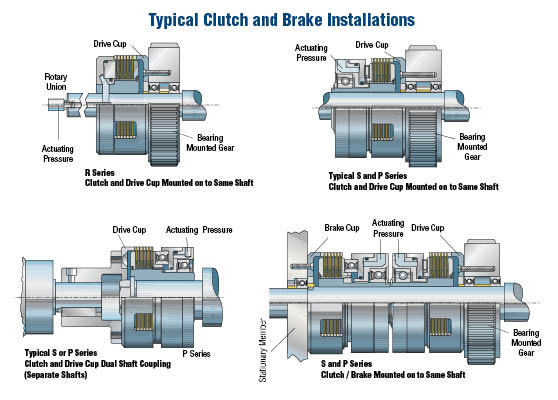
The global clutch and brake manufacturing market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand from automotive, industrial machinery, and transportation sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global clutch market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% between 2023 and 2028, fueled by rising vehicle production and the adoption of advanced transmission technologies. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global brake system market was valued at USD 27.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030, supported by stringent safety regulations and the proliferation of electric vehicles. As these markets evolve, innovation in materials, efficiency, and smart integration is shaping the competitive landscape. In this dynamic environment, leading clutch brake manufacturers are emerging through technological excellence, global reach, and a commitment to performance and safety. Below are the top seven manufacturers driving progress in this critical sector.
Top 7 Clutch Brake Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Brake and Clutch Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cjmco.com
Key Highlights: Carlyle Johnson is a leading industrial brake and clutch manufacturer. For over 100 years we have designed and manufactured clutch, brake and power transmission ……
#2 Industrial clutches and brakes
Domain Est. 1995
Website: danfoss.com
Key Highlights: Airflex industrial clutches and brakes are world-renowned for their superior performance, long life and high quality. These outstanding drivetrain products ……
#3 Alltorq
Domain Est. 2009
Website: alltorq.com
Key Highlights: The PT TECH range includes an extensive Torque Limiter collection along with Hydraulic Power Take Off Clutches, Hydraulic Wet Brakes, Caliper Disc Brakes….
#4 Friction Clutch
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nexengroup.com
Key Highlights: Nexen’s Clutch-brake combos are available with spring or air engagement and shaft, flange, or foot mounting styles. Easily mounts to NEMA and IEC motors….
#5 Performance Clutch Kits, Flywheels
Domain Est. 1999
Website: phoenixfriction.com
Key Highlights: We are the industry leader in bringing you solid flywheel conversion kits for all your towing and performance needs. There are up to six levels of performance….
#6 EBC Brakes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ebcbrakes.com
Key Highlights: EBC Brakes are a leading brake company offering brakes, pads, calipers, brake lines, discs & rotors for Automotive, Motorcycle, Mountain Bike & Racing….
#7 Carlisle Brake & Friction
Domain Est. 2011
Website: carlislecbf.com
Key Highlights: Carlisle Brake & Friction is a leading global solutions provider of high performance and severe duty brake, clutch and transmission applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Clutch Brake

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Clutch Brakes
The global clutch brake market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial automation, advancements in vehicle electrification, and increasing demand for energy-efficient motion control systems. As industries prioritize precision, reliability, and sustainability, clutch brakes—critical components in power transmission systems—are undergoing technological refinement and broader application integration.
1. Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics
By 2026, the continued expansion of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 is expected to boost demand for high-performance clutch brakes. These components are essential in automated assembly lines, packaging machines, and robotics, where rapid engagement/disengagement and precise torque control are required. Electromagnetic and servo-controlled clutch brakes are gaining traction due to their compatibility with digital control systems and IoT-enabled monitoring.
2. Shift Toward Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
The automotive sector, particularly electric and hybrid vehicle (EV/HEV) production, will influence clutch brake innovation. While traditional friction-based clutch systems are less prevalent in full EVs, hybrid models and performance EVs still rely on advanced clutch brakes for regenerative braking integration and dual-clutch transmission (DCT) systems. Lightweight, heat-resistant materials and compact designs are expected to dominate product development.
3. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers toward energy-efficient clutch brake solutions. By 2026, expect wider adoption of low-energy electromagnetic models and regenerative braking systems that minimize power consumption and reduce mechanical wear. Eco-friendly materials and recyclable components will also become distinguishing market features.
4. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Japan, will remain the largest market for clutch brakes due to robust industrial growth and automotive manufacturing. North America and Europe will see steady demand driven by automation in aerospace, material handling, and renewable energy sectors such as wind turbines, which use clutch brakes in pitch control systems.
5. Technological Innovation and Material Advancements
Advancements in composite materials, such as carbon-ceramic and advanced polymers, will enhance the thermal stability and durability of clutch brakes. Integration with predictive maintenance technologies—using sensors and AI analytics—will allow real-time monitoring of wear and performance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
6. Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The market is likely to experience consolidation, with key players such as Altra Industrial Motion, Mayr Antriebstechnik, and Siemens expanding through strategic partnerships, R&D investments, and acquisitions. Differentiation will increasingly rely on customization, digital integration, and technical support services.
In conclusion, by 2026, the clutch brake market will be shaped by digitalization, electrification, and sustainability trends. Companies that innovate in smart, efficient, and adaptable clutch brake systems will be best positioned to capture growth across industrial and transportation sectors.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Clutch Brakes: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing clutch brakes—especially for industrial, automotive, or heavy machinery applications—can present several challenges, particularly when it comes to ensuring quality and avoiding intellectual property (IP) issues. Buyers and procurement teams must be vigilant to avoid common pitfalls that could lead to performance failures, legal disputes, or supply chain disruptions.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Specifications
One of the most frequent quality issues arises from suppliers using substandard materials to cut costs. Clutch brakes are subjected to high stress, heat, and wear, so materials must meet precise engineering standards. Sourcing components with incorrect alloy compositions, poor heat treatment, or insufficient hardness can lead to premature failure and safety risks.
Lack of Certification and Testing
Many suppliers, particularly in low-cost regions, may not provide proper quality certifications such as ISO 9001 or component-specific testing reports (e.g., torque testing, thermal cycling, endurance). Without verifiable test data, buyers risk integrating unproven parts into critical systems, increasing the likelihood of field failures.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Clutch brakes require tight dimensional tolerances to ensure proper engagement, disengagement, and heat dissipation. Poorly controlled manufacturing processes can result in inconsistent part dimensions, leading to misalignment, excessive wear, or reduced service life.
Counterfeit or Recycled Components
In some supply chains, especially through third-party distributors, there is a risk of receiving counterfeit parts or refurbished units misrepresented as new. These components often fail under load and lack traceability, making root cause analysis difficult.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Designs
Many clutch brake designs are protected by patents covering specific mechanisms, materials, or configurations. Sourcing generic or “compatible” replacements from manufacturers who replicate patented features without licensing can expose the buyer to legal liability for IP infringement, even if unintentional.
Lack of Design Ownership Clarity
When working with contract manufacturers or OEMs, it’s essential to clarify who owns the design and tooling rights. Ambiguity in contracts can lead to disputes over design replication, aftermarket support, or future production rights, especially if transitioning suppliers.
Reverse-Engineered Products
Some suppliers offer clutch brakes that are reverse-engineered from branded originals. While functionally similar, these products may infringe on design patents or trade dress rights. Buyers may unknowingly purchase such parts and face legal action or be forced to recall equipment.
Insufficient Documentation for IP Compliance
Proper sourcing requires suppliers to provide documentation confirming freedom to operate (FTO) or IP indemnification. Without these assurances, companies risk introducing infringing components into their products, potentially resulting in injunctions or costly litigation.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Conduct thorough supplier audits, including facility visits and quality system reviews.
- Require material certifications, performance test data, and traceability for all critical components.
- Perform independent validation testing on sample units before full-scale procurement.
- Engage legal counsel to review IP rights and ensure compliance, especially when sourcing “compatible” parts.
- Include IP indemnification clauses in supplier contracts to shift liability for infringement claims.
By addressing both quality and IP concerns proactively, companies can reduce risk, ensure reliability, and protect their brand and legal standing when sourcing clutch brakes.
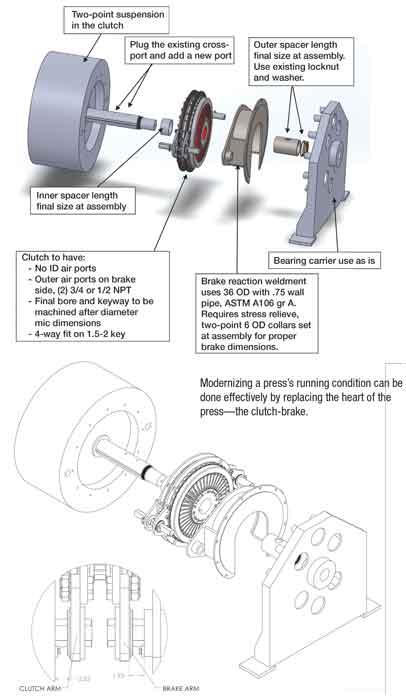
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Clutch Brake
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, import/export, and regulatory adherence of Clutch Brake components. Proper management ensures seamless operations, avoids delays, and maintains legal and safety standards.
Product Classification & Documentation
Accurate classification and documentation are foundational for international shipping and customs clearance. Clutch Brakes are typically categorized under mechanical power transmission components.
- HS Code: Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code—common classifications include 8483.60 (transmission shafts and cranks, bearing housings) or 8708.39 (parts for vehicle braking systems), depending on application.
- Commercial Invoice: Must include detailed product description, quantity, unit price, total value, country of origin, and Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW).
- Packing List: Specify packaging type, gross/net weight, dimensions, and lot/serial numbers if applicable.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN).
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging safeguards Clutch Brakes during transit and meets environmental and safety standards.
- Protection: Use anti-corrosion wrapping (VCI paper), foam inserts, or wooden crates for heavy-duty components to prevent mechanical damage.
- Labeling: Include handling labels (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), product ID, batch number, and weight.
- Hazardous Materials: Confirm Clutch Brakes do not contain restricted substances (e.g., certain lubricants). If present, comply with IATA/IMDG regulations.
Transportation & Shipping Modes
Select appropriate transport methods based on volume, urgency, and destination.
- Freight Options:
- Air Freight: For urgent or low-volume shipments; higher cost but faster delivery.
- Ocean Freight (FCL/LCL): Cost-effective for bulk shipments; plan for longer lead times.
- Ground Transport: Suitable for regional distribution; ensure secure loading and tie-downs.
- Temperature & Humidity Control: Store and transport in dry, climate-controlled environments to prevent rust or material degradation.
Import/Export Compliance
Ensure adherence to national and international trade regulations.
- Export Controls: Verify if Clutch Brakes are subject to export restrictions (e.g., dual-use items under EAR or ITAR).
- Customs Clearance: Provide accurate documentation to avoid delays. Use a licensed customs broker if required.
- Duties & Taxes: Calculate applicable tariffs, VAT, or GST based on destination country and HS code.
Regulatory & Safety Standards
Compliance with industry standards ensures product safety and market access.
- ISO Standards: Follow ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) where applicable.
- Automotive Standards: If used in vehicles, comply with ISO 26262 (functional safety) or regional norms like FMVSS (U.S.) or ECE (Europe).
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Confirm absence of restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in materials.
- OSHA & WHMIS (North America): Ensure workplace safety compliance during handling and storage.
Traceability & Recordkeeping
Maintain detailed records for audit readiness and supply chain transparency.
- Batch Tracking: Implement a system to trace manufacturing date, supplier data, and shipping history.
- Retention Period: Retain logistics and compliance documents for a minimum of 5–7 years, per customs and regulatory requirements.
Sustainability & End-of-Life Compliance
Address environmental responsibilities throughout the product lifecycle.
- WEEE Directive (EU): Register as a producer if selling in Europe; support recycling programs.
- Packaging Waste: Use recyclable materials and comply with local packaging waste regulations.
- Carbon Reporting: Monitor and report logistics-related emissions if required by corporate or regulatory policy.
Adhering to this guide ensures efficient logistics operations and full compliance with global regulatory frameworks for Clutch Brake distribution. Regular audits and staff training are recommended to maintain standards.
Conclusion on Sourcing Clutch Brakes
Sourcing clutch brakes requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, cost efficiency, supplier reliability, and long-term supply chain sustainability. After evaluating various suppliers, material options, manufacturing standards, and application-specific needs, it is evident that selecting the right clutch brake involves more than just comparing prices. Critical factors such as durability, thermal performance, response time, and compatibility with existing machinery must be prioritized.
Partnering with reputable suppliers who adhere to international quality certifications (such as ISO standards) ensures product consistency and reliability. Additionally, considering local versus global sourcing options can impact lead times, logistical costs, and responsiveness to demand fluctuations. Building strong relationships with a diversified supplier base also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
In conclusion, an effective clutch brake sourcing strategy should integrate technical evaluation, cost analysis, supplier vetting, and risk management. By doing so, organizations can secure high-performance components that enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and support long-term maintenance goals. Continuous monitoring and periodic re-evaluation of sourcing practices will further ensure alignment with evolving industry standards and business objectives.