The global closed die forging market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-strength, precision-engineered metal components across aerospace, automotive, oil & gas, and power generation industries. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global forging market—encompassing both open and closed die processes—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, with closed die forging commanding a significant share due to its superior dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties. Similarly, Grand View Research valued the global forging market at USD 107.5 billion in 2022 and forecasts a CAGR of 6.5% from 2023 to 2030, citing technological advancements and increasing adoption of forged components in lightweight vehicle design and renewable energy systems. This growth trajectory underscores the critical role of closed die forging in modern manufacturing, elevating a select group of manufacturers to global leadership through scale, innovation, and vertical integration. The following list highlights the top 10 closed die forging manufacturers shaping this expanding industry.
Top 10 Closed Die Forging Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Closed Die Forging Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1995
Website: laube.com
Key Highlights: Closed Die Forgings are revolutionizing the manufacturing world by providing high-strength, high-precision components across various industries….
#2 Viking Forge Closed Die Forging
Domain Est. 1998
Website: viking-forge.com
Key Highlights: Viking Forge is the leader in hot, closed die, near net forgings. Our tight tolerance forging process reduces the amount of machine stock required on various ……
#3 Closed Die Forging Presses
Domain Est. 1998
Website: macrodynepress.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Closed Die Forging Hydraulic and Servo Presses. Manufacture parts with high throughput, consistent tolerances and minimal scrap….
#4 Walker Forge: Closed Die Forgings
Domain Est. 1998
Website: walkerforge.com
Key Highlights: Walker Forge manufactures steel & aluminum closed die forgings. Offering an in house metallurgical lab for fast service & certified engineers. Call today!…
#5 Canton Drop Forge: Closed Die Forging Company
Domain Est. 2001
Website: cantondropforge.com
Key Highlights: As a renowned forging manufacturer, we specialize in producing high-quality closed die forgings and drop forgings tailored for high-performance applications….
#6 Trinity Forge
Domain Est. 1996
Website: trinityforge.com
Key Highlights: In fact, when times are busy, Trinity Forge can design and custom build your die, and ship your parts faster than competitors can deliver from existing tooling….
#7 Scot Forge
Domain Est. 1997
Website: scotforge.com
Key Highlights: Recognized as the industry leader in open die forging and rolled ring forging, we’re the world’s premier provider of high-quality metal forging solutions….
#8 Closed Die Hot Forging
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cornellforge.com
Key Highlights: Closed die hot forging is a process where heated metal is shaped into strong, precise parts using custom dies. At Cornell Forge, we are a ……
#9 Closed Die Forgings
Domain Est. 2002
Website: buntyllc.com
Key Highlights: CLOSED DIE FORGINGS. Often known as “impression die forging”, closed die forging involves two or more dies containing impressions brought together….
#10 Forge Resources Group
Domain Est. 2006
Website: forgeresourcesgroup.com
Key Highlights: We supply custom closed-die forgings in carbon, alloy and stainless steels, aluminum, and other non-ferrous grades from our forging cells….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Closed Die Forging
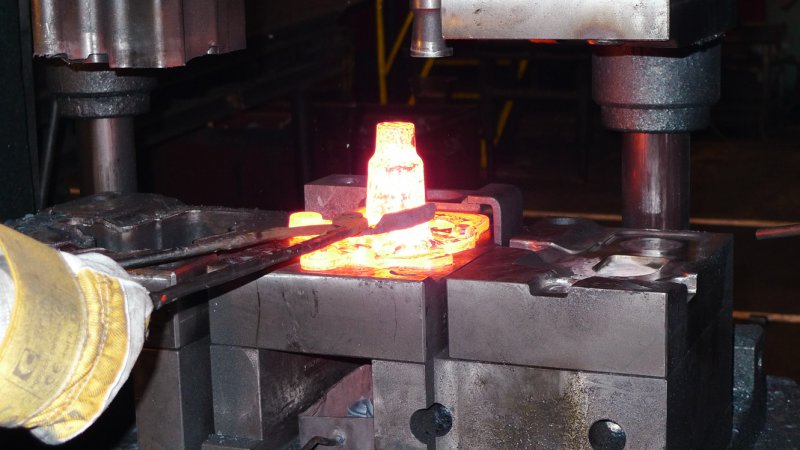

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Closed Die Forging
The closed die forging market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and global economic dynamics. Key trends shaping the sector include:
1. Rising Demand from High-Performance Industries:
The aerospace, defense, and renewable energy sectors will remain primary growth drivers. Stringent requirements for lightweight, high-strength components—especially turbine blades, landing gear, and wind turbine shafts—will increase reliance on closed die forging for its superior grain structure and mechanical properties. The push for fuel-efficient aircraft and electric vehicles (EVs) will further boost demand for forged aluminum and titanium components.
2. Technological Integration and Automation:
By 2026, digitalization will be deeply embedded in forging operations. Adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as AI-driven process optimization, real-time monitoring via IoT sensors, and digital twins—will enhance precision, reduce scrap rates, and improve energy efficiency. Automated forging lines and robotics will become standard, addressing labor shortages and improving consistency in high-volume production.
3. Material Innovation and Sustainability Focus:
There will be growing use of advanced alloys, including high-strength steels, nickel-based superalloys, and lightweight materials like titanium and aluminum. Simultaneously, environmental regulations will push forging companies toward sustainable practices. This includes investment in energy-efficient induction heating, closed-loop cooling systems, and recycling of scale and scrap to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) targets.
4. Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience:
Geopolitical factors and the post-pandemic emphasis on supply chain security will accelerate nearshoring and reshoring, particularly in North America and Europe. While Asia-Pacific (especially China and India) will maintain dominance due to manufacturing scale, Western markets will invest in localized forging capacity for critical industries like defense and aerospace, reducing dependency on offshore suppliers.
5. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships:
Market competition and the high cost of advanced technology will drive consolidation among forging companies. Smaller players may be acquired by larger firms seeking expanded capabilities or geographic reach. Strategic partnerships with OEMs and material suppliers will become essential to co-develop next-generation components and ensure material traceability and quality.
In summary, the 2026 closed die forging market will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and resilience—cementing its role in manufacturing mission-critical components across high-tech industries.
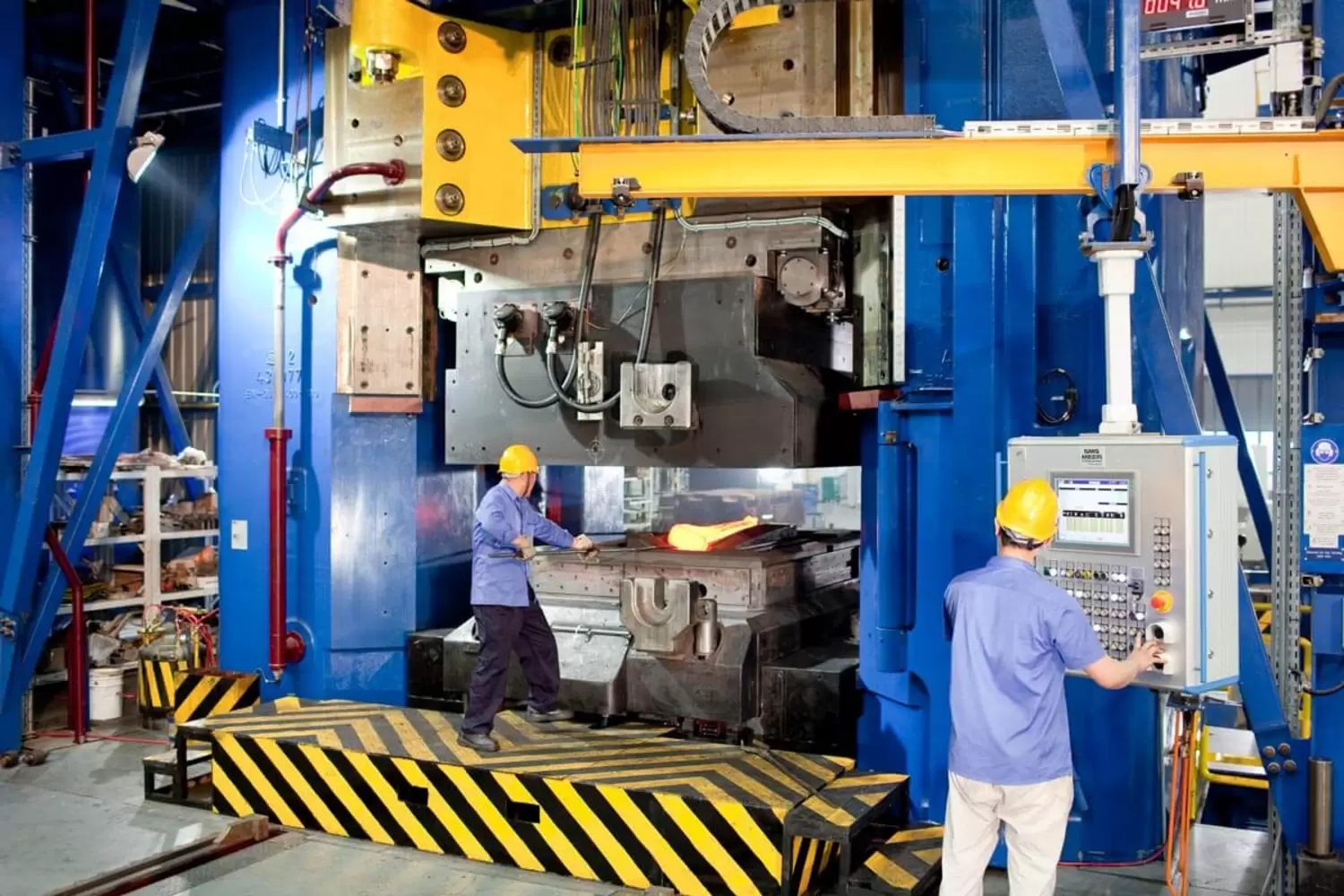

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Closed Die Forging (Quality, IP)
Sourcing closed die forging components presents several critical challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to production delays, compromised product performance, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly assess a forging supplier’s capabilities, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100), and track record can result in inconsistent quality. Buyers often overlook audits of the supplier’s process controls, inspection methods, and material traceability systems, leading to defects such as incorrect grain flow, dimensional inaccuracies, or internal voids.
Poor Material Traceability and Certification
Many suppliers do not provide full material test reports (MTRs) or maintain proper heat traceability, increasing the risk of using substandard or incorrect alloy materials. This is particularly problematic in industries like aerospace or oil and gas, where material properties are mission-critical.
Insufficient Dimensional and Process Control
Closed die forgings require tight tolerances and precise die design. Sourcing from suppliers with outdated tooling or weak statistical process control (SPC) practices can lead to high scrap rates, rework, and non-compliance with engineering specifications.
Inconsistent Post-Forging Treatments
Heat treatment is essential to achieve desired mechanical properties. Suppliers may outsource this step without proper oversight, leading to inconsistent hardness, poor fatigue resistance, or non-uniform microstructure—issues that may not be detected until component failure.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Lack of Formal IP Agreements
Many sourcing engagements proceed without clear contractual terms protecting design ownership, proprietary forging processes, or tooling rights. This exposes buyers to IP theft or unauthorized use of dies and specifications by the supplier or third parties.
Unsecured Tooling Ownership and Access
Forging dies are expensive and often custom-designed. If ownership is not explicitly transferred or secured, suppliers may retain control, potentially using the tooling to produce parts for competitors or withholding access during disputes.
Inadequate Protection in High-Risk Geographies
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of design replication or reverse engineering. Without robust legal safeguards and local counsel, buyers may find it difficult to pursue remedies for IP infringement.
Insufficient Control Over Technical Documentation
Sharing CAD models, forging plans, or process sheets without confidentiality agreements or digital rights management can lead to unauthorized dissemination. Suppliers may also claim co-ownership of improvements made during production, complicating long-term IP strategy.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier selection, comprehensive contractual protections, rigorous quality audits, and proactive IP management throughout the sourcing lifecycle.
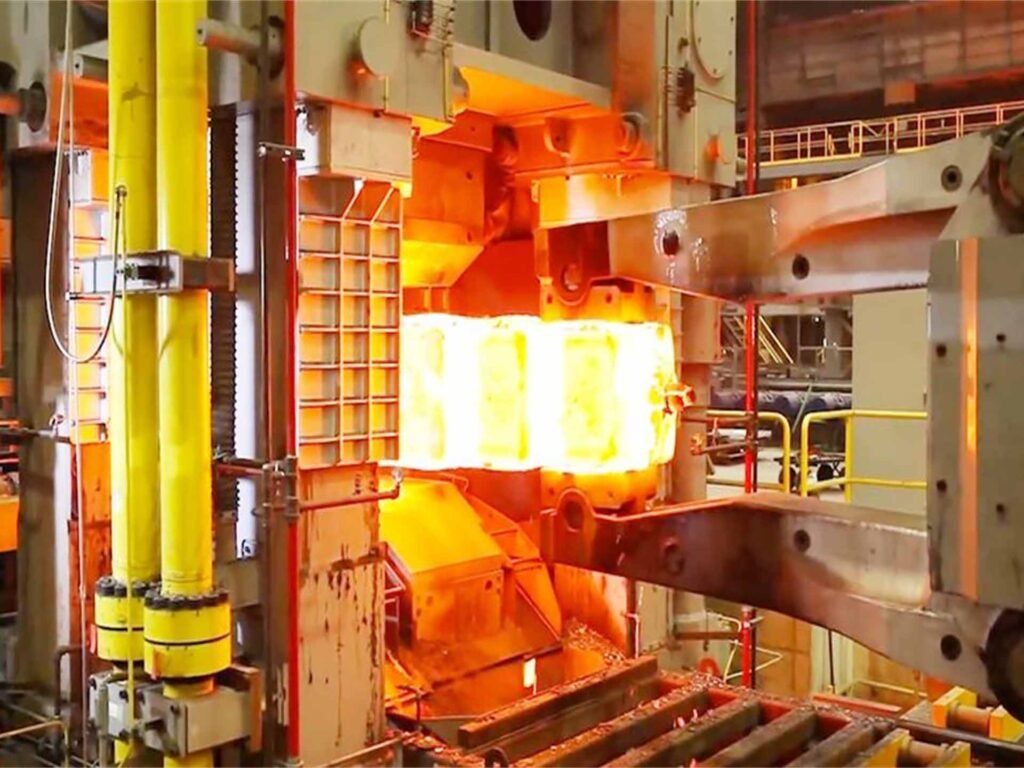
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Closed Die Forging
Overview of Closed Die Forging
Closed die forging, also known as impression die forging, involves shaping metal within a die cavity using compressive forces. This process produces high-strength components used in aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and power generation industries. Due to the stringent performance requirements of these sectors, logistics and regulatory compliance are critical throughout the supply chain.
Material Sourcing & Traceability
Material integrity begins with responsible sourcing. Forged components must use certified raw materials (e.g., alloy steels, stainless steels, titanium) traceable to mill certifications (e.g., MTRs/CMTRs). Suppliers must comply with industry standards such as ASTM, ASME, or AMS. Dual sourcing and long-term supplier agreements help mitigate supply chain disruptions.
Transportation & Handling
Forged parts are often heavy and sensitive to damage. Use secure crating, moisture barriers, and protective coatings during transit. Coordinate with carriers experienced in heavy industrial freight, including flatbed trucks, rail, or ocean freight for international shipments. Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory practices to prevent material degradation.
Facility Compliance Requirements
Forging facilities must adhere to local and international regulations:
– OSHA (U.S.) / HSE (UK): Workplace safety standards for high-pressure equipment, heat exposure, and material handling.
– ISO 9001: Quality management systems for process control and documentation.
– ISO 14001: Environmental management to control emissions, waste heat, and lubricant disposal.
– IATF 16949: Required for automotive supply chains.
– AS9100: Mandatory for aerospace components, including full traceability and inspection documentation.
Regulatory Standards for Forged Components
Compliance with material and dimensional standards is non-negotiable:
– ASTM A694, A105, A182: For carbon and alloy steel forgings.
– API 6A, 16A: For oil and gas wellhead and valve components.
– AMS 2750: Pyrometric requirements for furnace calibration.
– NADCAP: Special process accreditation for non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection.
Documentation & Certification
Each forged part must be accompanied by comprehensive documentation:
– Material Test Reports (MTRs)
– Heat traceability records
– Dimensional inspection reports (CMM data)
– NDT reports
– Conformance certificates (e.g., FAA 8130-3, EN 10204 3.1/3.2)
Digital record-keeping systems (ERP or QMS) ensure audit readiness and support rapid recalls if necessary.
International Trade & Export Compliance
When shipping forged products globally:
– Classify items under the correct HS Code (e.g., 7318.15 for forged steel fasteners).
– Comply with ITAR/EAR if handling defense-related or dual-use materials.
– Ensure adherence to REACH (EU) and RoHS directives regarding hazardous substances.
– Maintain accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Packaging & Labeling Standards
Packaging must protect parts from corrosion and physical damage. Use VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) papers, desiccants, and tamper-evident seals. Label each package with:
– Part number and revision
– Heat/lot number
– Net weight and handling instructions
– Barcodes or RFID tags for inventory tracking
Quality Audits & Continuous Improvement
Conduct regular internal and third-party audits to verify compliance. Address non-conformances through root cause analysis (e.g., 8D reports). Engage in continuous improvement through Lean and Six Sigma methodologies to reduce waste and improve on-time delivery performance.
Risk Management & Contingency Planning
Identify supply chain risks such as raw material shortages, geopolitical issues, or equipment downtime. Maintain safety stock for critical items and develop alternative supplier strategies. Ensure business continuity plans include forging process validation and requalification procedures.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance in closed die forging require integrated management of materials, processes, documentation, and regulations. By adhering to industry standards and maintaining rigorous traceability, forging operations can ensure product integrity, meet customer requirements, and remain competitive in global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Closed Die Forging
In conclusion, sourcing closed die forging offers a reliable and efficient solution for producing high-strength, precision-engineered metal components across industries such as automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, and heavy machinery. The process provides significant advantages, including excellent dimensional accuracy, enhanced mechanical properties due to grain flow optimization, and reduced material waste, making it both cost-effective and sustainable in high-volume production scenarios.
When selecting a supplier, key considerations such as material expertise, in-house capability, quality certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100), capacity for post-forging operations (e.g., heat treatment, machining), and adherence to strict quality control standards are crucial to ensure product integrity and performance. Additionally, geographic proximity, lead times, and the supplier’s experience in your specific industry can greatly influence overall supply chain efficiency.
Ultimately, a well-strategized sourcing approach to closed die forging enables manufacturers to achieve superior product quality, improved reliability, and long-term cost savings—making it an essential element of advanced manufacturing operations.