The global closed-cell foam market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and HVAC industries for high-performance insulation and energy-efficient materials. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the closed-cell foam market was valued at USD 29.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% through 2029. This expansion is fueled by stringent energy efficiency regulations, increased infrastructure development, and the material’s superior thermal resistance, moisture barrier properties, and durability compared to open-cell alternatives. As sustainability and performance standards continue to rise, manufacturers are investing in innovative formulations and scalable production technologies. In this competitive landscape, a select group of leading companies are emerging through strategic expansions, R&D advancements, and global supply chain integration—shaping the future of the closed-cell foam industry.
Top 10 Closed Cellular Foam Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Foam Factory, Inc.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: foambymail.com
Key Highlights: We proudly offer traditional foam products like cushions, insulation, and packaging materials, as well as memory foam and latex mattresses, toppers, and even ……
#2 Styrofoam™ Brand XPS Insulation
Domain Est. 1987
Website: dupont.com
Key Highlights: Its unique closed-cell structure and rigid foam board technology enables XPS to meet core thermal, moisture, air and vapor performance requirements. The ……
#3 Worldwide Foam
Domain Est. 2008
Website: worldwidefoam.com
Key Highlights: We offer one-day lead time from our seven strategic locations while providing the widest ranges of closed cell cross-linked polyethylene foam….
#4 Zotefoams
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zotefoams.com
Key Highlights: Zotefoams offers lightweight, high-performance AZOTE and ZOTEK foam solutions for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries….
#5 SWD Urethane
Domain Est. 1996
Website: swdurethane.com
Key Highlights: From our start in 1972, our passion for building science and spray foam innovation has guided everything we do….
#6 Closed Cell Foam Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: insulfab.net
Key Highlights: Closed cell foam and sponge rubber products have been used for gasketing, cushioning, insulating, and padding applications for years….
#7 Aeroflex USA
Domain Est. 2000
Website: aeroflexusa.com
Key Highlights: Closed-Cell Elastomeric Foam Insulation uniquely formulated for success in mechanical, refrigeration, HVAC, and plumbing systems….
#8 Accufoam
Domain Est. 2014
Website: accufoam.com
Key Highlights: High-performance spray foam insulation made in America. Accufoam delivers industry-leading open and closed cell systems engineered for superior efficiency, ……
#9 Elastochem
Domain Est. 2015
Website: elastochem.com
Key Highlights: Great Buildings Start With Great materials. Canadian-made spray foam insulation & coating systems for building efficiency & performance….
#10 Enverge® Spray Foam
Domain Est. 2023
Website: envergesprayfoam.com
Key Highlights: Enverge® is driven by a dedication to support spray foam professionals with top tier manufacturing & technical support. … Closed Cell Products · Specialty ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Closed Cellular Foam
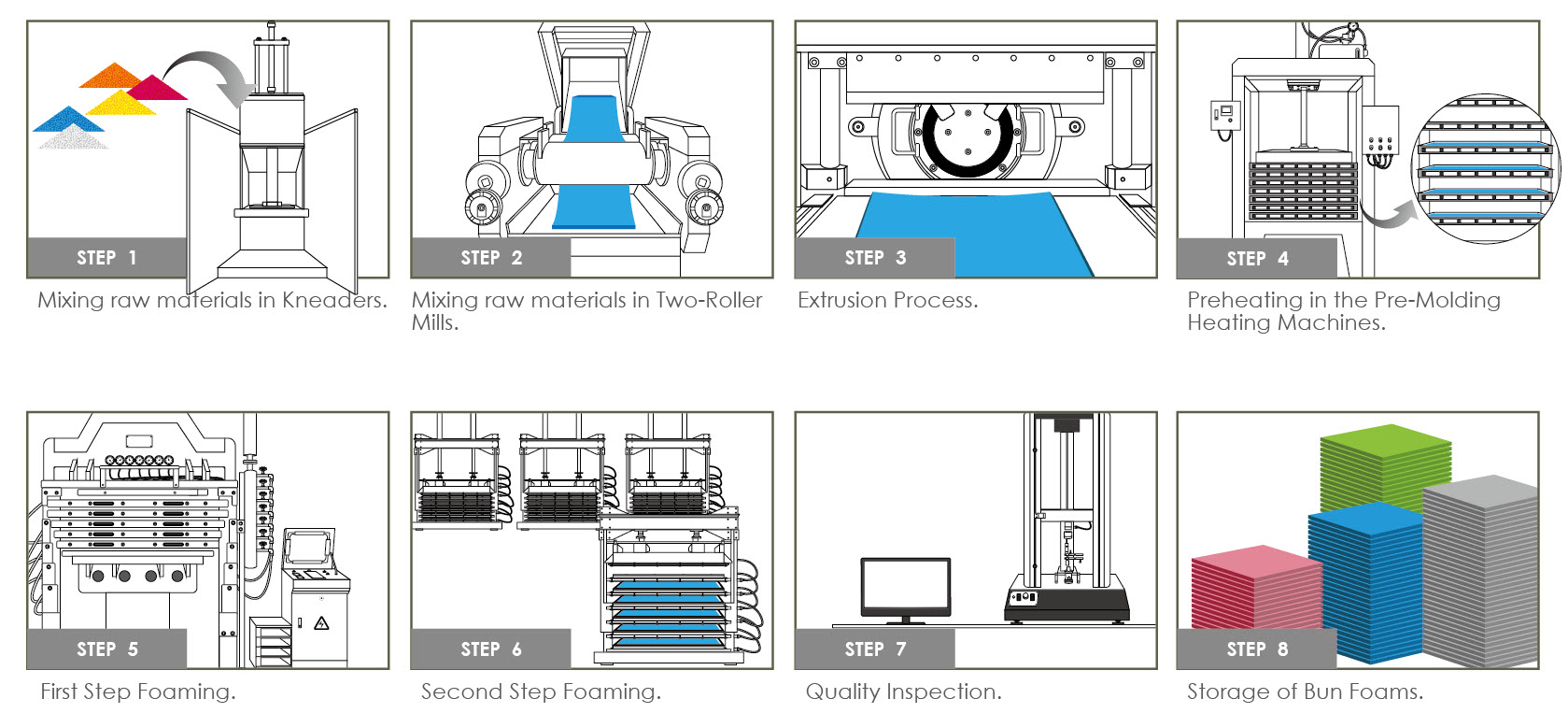
H2: Projected Market Trends for Closed Cellular Foam in 2026
The global closed cellular foam market is anticipated to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across key end-use industries such as automotive, construction, packaging, and consumer goods. This H2 analysis outlines the major trends expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
-
Expansion in Automotive Applications
Closed cellular foam, particularly based on materials like EPDM, TPE, and polyolefins, is witnessing rising adoption in the automotive sector for sealing, insulation, and vibration damping. With the continued shift toward lightweight vehicles and electric vehicles (EVs), manufacturers are leveraging closed cellular foam for thermal and acoustic insulation. By 2026, increasing EV production, especially in North America, Europe, and China, is expected to boost foam demand due to the need for battery insulation and noise reduction in quieter electric drivetrains. -
Growth in Green and Energy-Efficient Construction
The construction industry is increasingly adopting closed cellular foam for insulation in walls, roofs, and HVAC systems due to its excellent thermal resistance, moisture resistance, and durability. Regulatory pressures to meet energy efficiency standards—such as the EU’s Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) and U.S. DOE insulation requirements—are accelerating the use of high-performance foams. By 2026, rising infrastructure development in emerging economies and retrofitting projects in developed regions will further expand market opportunities. -
Sustainability and Bio-Based Material Innovation
Environmental concerns are pushing manufacturers to develop sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based foams. By 2026, the market is expected to see increased R&D investment in bio-based and recyclable closed cellular foams. Companies are exploring foams derived from renewable resources (e.g., plant-based polyols) and enhancing recyclability through chemical recycling technologies. Regulatory frameworks such as the EU Green Deal will likely favor eco-friendly foam solutions, influencing product development and consumer preferences. -
Technological Advancements in Foam Manufacturing
Innovations in foaming technologies—such as supercritical fluid foaming and microcellular injection molding—are enabling the production of foams with finer cell structures, improved mechanical properties, and reduced material usage. These advancements not only enhance performance but also lower production costs and environmental impact. By 2026, smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 integration are expected to optimize supply chains and improve customization for niche applications. -
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Asia-Pacific is projected to remain the largest market for closed cellular foam by 2026, driven by industrial growth in China, India, and Southeast Asia. However, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to diversify production bases and adopt nearshoring strategies, particularly in North America and Eastern Europe. This shift aims to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers and improve delivery timelines. -
Increased Demand in Packaging and Consumer Electronics
The packaging sector, especially for protective and temperature-sensitive shipments (e.g., pharmaceuticals, electronics), is adopting closed cell foams for their cushioning and insulating properties. Similarly, consumer electronics manufacturers are using these foams for internal component protection and heat management. The surge in e-commerce and demand for durable, lightweight packaging will further fuel market growth.
In conclusion, the closed cellular foam market in 2026 will be shaped by technological innovation, sustainability imperatives, and evolving industry needs. Companies that prioritize eco-friendly materials, advanced manufacturing, and regional diversification are likely to gain a competitive advantage in this dynamic landscape.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Closed Cell Foam (Quality & IP)
Sourcing Closed Cell Foam (CCF) requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, or legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Specification of Material Properties
Failing to define precise technical requirements (e.g., density, compressive strength, thermal conductivity, water absorption, and cell structure) can result in receiving substandard foam. Suppliers may meet nominal specifications but deliver inconsistent or non-compliant batches if tolerances and test methods (e.g., ASTM D1621, D2856) are not clearly defined.
Overlooking Long-Term Performance and Environmental Resistance
Short-term lab tests may not reflect real-world aging. Pitfalls include not verifying resistance to UV exposure, temperature cycling, moisture ingress, or chemical exposure—especially critical in construction, marine, or outdoor applications. Foam that degrades prematurely can compromise system integrity.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes and Batch Variability
CCF quality heavily depends on production control. Sourcing from suppliers without robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of inconsistent cell structure, density variation, or poor bonding—leading to delamination or reduced insulation performance.
Insufficient Supplier Qualification and Audits
Relying solely on datasheets without conducting on-site audits or requesting production samples can hide issues like outdated equipment, poor raw material sourcing, or lack of in-process testing. Vetting suppliers through independent lab testing of samples is essential.
Misunderstanding Material Compatibility
Closed cell foam may interact poorly with adhesives, coatings, or adjacent materials. For example, certain blowing agents or polymer bases can outgas or inhibit curing, leading to bond failures. Compatibility testing under end-use conditions is often overlooked.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unintentional Use of Patented Formulations or Processes
Many high-performance CCFs rely on proprietary resin blends, blowing agents (e.g., HFOs), or manufacturing techniques protected by patents. Sourcing foam without verifying freedom-to-operate risks infringement claims, especially when importing or selling in regulated markets (e.g., EU, US).
Lack of IP Clarity in Custom or Private-Label Agreements
When co-developing or branding foam products, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Suppliers may retain rights to formulations or tooling, limiting your ability to switch manufacturers or scale production.
Dependency on Proprietary Technologies with Limited Licensing
Some advanced foams (e.g., low-GWP blown, fire-retardant variants) depend on patented technologies requiring licensing. Sourcing such materials without confirming appropriate sublicensing rights can expose your business to legal or supply risks.
Inadequate Documentation and Chain of Title
Poor record-keeping regarding material origins, supplier warranties, or technical disclosures can complicate IP defense or compliance audits. Ensure all sourcing agreements include IP indemnification clauses and clear documentation of material composition.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can secure reliable, high-performance closed cell foam supplies while minimizing technical and legal risks.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Closed Cell Foam
Closed cell foam is a widely used material in insulation, packaging, marine, and construction industries due to its high compressive strength, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation properties. Proper logistics and compliance handling are critical to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and product integrity throughout the supply chain.
1. Classification & Regulatory Identification
- Chemical Composition: Typically made from polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PU), ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), or neoprene.
- Hazard Classification: Generally classified as non-hazardous under transportation regulations if not treated with flame retardants or other regulated substances.
- UN Number: Not applicable (N/A) for non-treated foams; however, treated or flammable variants may require classification (e.g., UN 3499 for self-reactive substances if applicable).
- GHS/SDS Compliance: A Safety Data Sheet (SDS) in accordance with GHS (Globally Harmonized System) must be available, especially if the foam contains additives.
2. Packaging & Handling
- Packaging: Supplied in rolls, sheets, or custom-cut forms. Must be wrapped in moisture-resistant film (e.g., polyethylene) to prevent water absorption during transit.
- Palletization: Securely strapped and stretch-wrapped on standard wooden or plastic pallets (1200 x 1000 mm or 48″ x 40″).
- Labeling:
- Product name and specification
- Batch/lot number
- Manufacturer information
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Protect from Moisture”, “Do Not Stack Excessively”)
- Handling Precautions: Use mechanical lifting equipment for heavy rolls; avoid sharp tools that may puncture material.
3. Storage Conditions
- Environment: Store indoors in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area.
- Temperature: 10°C to 30°C (50°F to 86°F); avoid prolonged exposure to temperatures above 60°C (140°F).
- UV Exposure: Protect from direct sunlight and UV radiation to prevent degradation.
- Stacking: Limit stack height to prevent deformation (typically no more than 2–3 pallets high).
4. Transportation Requirements
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, rail, sea, and air freight.
- Non-Hazardous Transport: When untreated, closed cell foam is generally not regulated as dangerous goods under:
- ADR (Road, Europe)
- IMDG Code (Sea)
- IATA DGR (Air)
- Flame-Retardant Treated Foam: May require classification under Class 4.1 (Flammable Solids) or Class 9 (Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods) depending on test results (e.g., ASTM E84, FMVSS 302).
- Documentation: Commercial invoice, packing list, and SDS must accompany shipments. Certificates of compliance (e.g., REACH, RoHS) may be required for international trade.
5. Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Confirm that all chemical components are registered under REACH. No SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) above threshold.
- RoHS (EU): Applicable if foam is used in electrical/electronic equipment. Must not contain restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium, PBDEs).
- California Proposition 65: Ensure no listed chemicals (e.g., certain flame retardants) are present above safe harbor levels.
- TSCA (USA): Comply with Toxic Substances Control Act; confirm all chemicals are listed on the TSCA Inventory.
- Fire Safety Standards:
- ASTM E84 / UL 723: Surface burning characteristics (flame spread and smoke index)
- NFPA 286: Fire propagation in interior finishes
- FMVSS 302: Flammability of interior materials (automotive)
6. Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Recyclability: Limited recyclability; PE and EVA foams may be mechanically recycled in specialized facilities.
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local regulations. May be disposed of in licensed landfills if non-hazardous.
- Incineration: Must be conducted in facilities with emission controls due to potential release of toxic fumes (especially chlorinated foams like neoprene).
7. Import/Export Documentation
- HS Code Example: 3921.13 (Foils, sheets, film, and strips of polymers, cellular)
- Certificates Required:
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
- Material Compliance Statement (e.g., RoHS, REACH)
- Phytosanitary certificate (if wooden pallets used and required by destination country)
8. Best Practices Summary
- Always verify foam formulation and treatment before transport.
- Maintain SDS and compliance documentation across the supply chain.
- Use protective packaging to prevent physical and environmental damage.
- Train personnel on safe handling and emergency procedures.
- Monitor regulatory updates in target markets.
By adhering to these logistics and compliance guidelines, companies can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient distribution of closed cell foam products globally.
In conclusion, sourcing closed-cell foam requires careful consideration of material specifications, intended application, and supplier capabilities. Closed-cell foams offer superior strength, moisture resistance, thermal insulation, and durability compared to open-cell variants, making them ideal for applications in construction, automotive, marine, HVAC, and packaging industries. When sourcing, it is essential to evaluate factors such as density, compression resistance, temperature range, chemical resistance, and compliance with industry standards (e.g., ASTM, UL, ISO).
Engaging with reliable suppliers who provide consistent quality, technical support, and scalable production capacity is crucial. Additionally, considerations around cost-efficiency, lead times, environmental impact, and availability of customized solutions should inform the final sourcing decision. By conducting thorough due diligence and aligning material properties with project requirements, organizations can ensure optimal performance, longevity, and value when integrating closed-cell foam into their products or processes.