The global closed cell foam pad market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as construction, automotive, packaging, and HVAC. According to Grand View Research, the global foam materials market was valued at USD 87.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030, with closed cell foams accounting for a significant share due to their superior thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and structural durability. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects continued growth in specialty foam segments, citing increased infrastructure development and stricter energy efficiency standards as key drivers. As demand surges, manufacturers are scaling production, innovating in material formulations, and expanding geographic reach. In this competitive landscape, nine key players have emerged as leaders in closed cell foam pad manufacturing—delivering high-performance solutions across industrial and consumer applications.
Top 9 Closed Cell Foam Pad Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Polyethylene Foam
Domain Est. 2000
Website: foambymail.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $75 21-day returnsFoam Factory, Inc. is your source for a wide range of cost-effective closed-cell polyethylene foam products! From sheets in a variety of formul…
#2 Our Products
Domain Est. 2008
Website: worldwidefoam.com
Key Highlights: Worldwide Foam stocks a wide variety of closed-cell elastomeric foams, in bun and roll formats. Our list of OEM foam products is one of the most diverse in the ……
#3 Z Lite Original Foam Sleeping Pad
Domain Est. 1995
Website: cascadedesigns.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.7 (83) Lightest, most compact closed-cell foam pad. Extra Durable: Virtually indestructible, the proprietary closed-cell foam provides lasting, economical comfo…
#4 Zotefoams
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zotefoams.com
Key Highlights: Zotefoams offers lightweight, high-performance AZOTE and ZOTEK foam solutions for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries….
#5 Hibco Foam Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hibco.com
Key Highlights: Durable closed-cell foam is chemical, water, heat and impact resistant · Available in 2 to 8 lbs./cu. · C.I.D. · Ideal for military packaging, GSA packaging, ……
#6 Flexible Foams
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americanexcelsior.com
Key Highlights: Flexible foam can provide protection in packaging, comfort in furniture and support in medical and athletic applications….
#7 Closed Cell Foam & Padding, EVA & Polyethylene Foam
Domain Est. 1999
Website: foamorder.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.3 (76) FoamOrder is your resource for closed cell foam and padding. We offer a variety of foam types including Polyethylene, EVA and closed cell in different …..
#8 closed
Domain Est. 2001
Website: thefoamfactory.com
Key Highlights: Polyethylene foam is a strong, resilient closed-cell foam. Ideally suited as the material or part of a material required in products requiring a shock ……
#9 Sustainability
Domain Est. 2001
Website: schmitzfoam.com
Key Highlights: The closed-cell foam doesn’t absorb water and remains flexible in any climate regardless of its original purpose. It does so for a very long period….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Closed Cell Foam Pad
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Closed Cell Foam Pad
The global Closed Cell Foam Pad market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand across key industries, and growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency. Below are the major trends shaping the market:
-
Expanding Applications in Construction and Infrastructure
By 2026, closed cell foam pads are expected to gain broader adoption in the construction sector, particularly for flooring underlayment, roofing, and insulation. Their moisture resistance, durability, and thermal performance make them ideal for both residential and commercial applications, especially in regions with extreme climates. -
Rising Demand in the Sports and Flooring Industry
The sports, leisure, and fitness sectors are increasingly using closed cell foam pads as shock-absorbing layers in gym floors, playgrounds, and athletic tracks. As health and wellness infrastructure expands globally, demand for high-performance, low-maintenance materials like closed cell foam will grow steadily. -
Growth in Automotive and Transportation Applications
The automotive industry is adopting closed cell foam pads for noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) control, as well as insulation in electric vehicles (EVs). With the EV market expanding rapidly, lightweight and thermally efficient materials such as closed cell foam will see increased integration in vehicle design. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Material Innovation
Environmental regulations and consumer demand are pushing manufacturers to develop bio-based or recyclable closed cell foam solutions. By 2026, companies that invest in sustainable production methods and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations are expected to gain a competitive edge. -
Regional Market Shifts and Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, will lead market growth due to rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and industrial expansion. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, driven by building energy efficiency standards and retrofitting projects. -
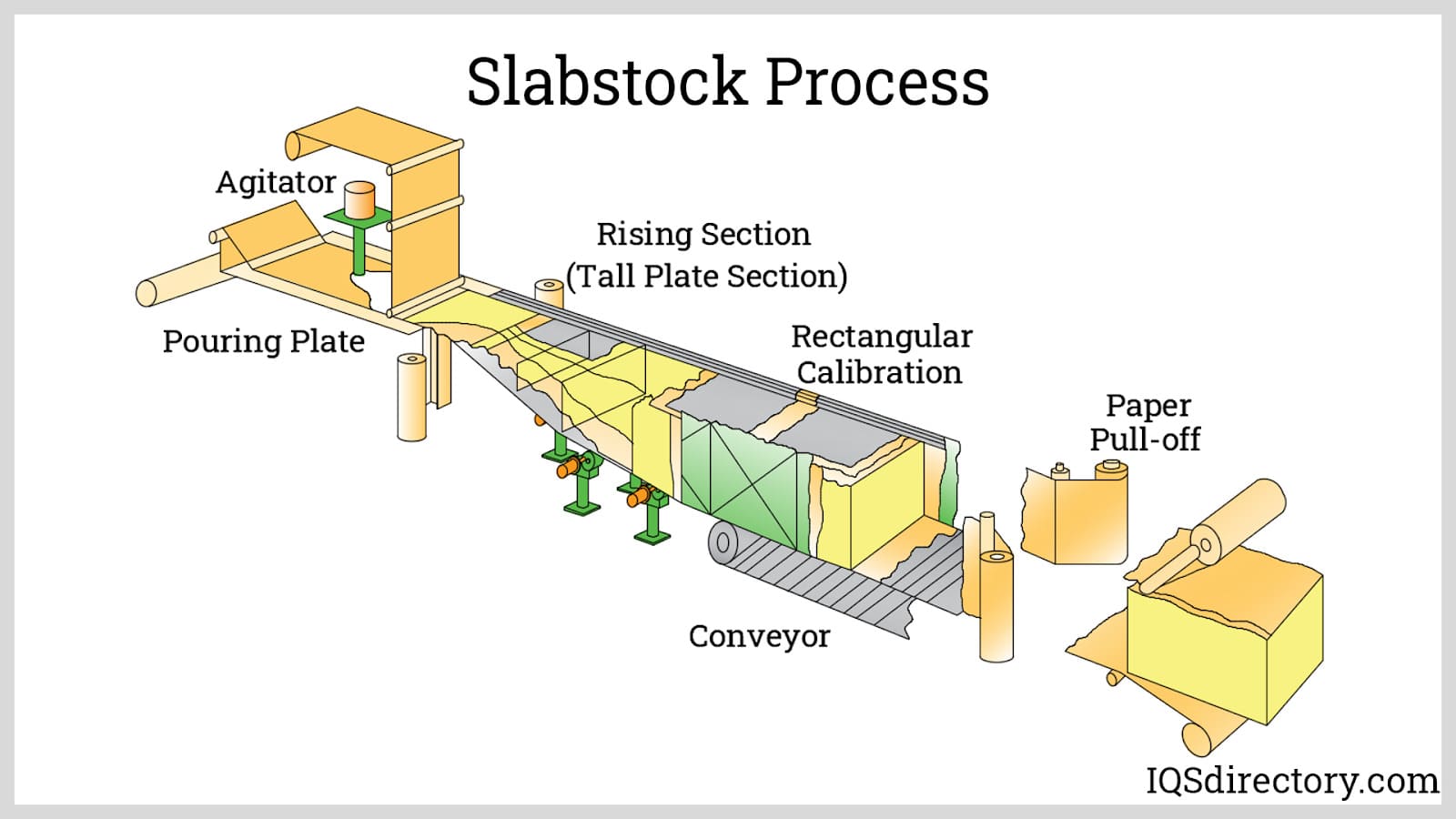
Technological Advancements in Foam Manufacturing
Innovations in cross-linking technologies, foaming agents, and extrusion processes are improving the performance and cost-efficiency of closed cell foam pads. These advancements will enable tailored solutions for specific industry needs, such as higher compression resistance or enhanced fire retardancy. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Volatility
Fluctuations in petrochemical feedstock prices may impact production costs. As a result, companies are expected to diversify supply chains and explore alternative raw materials to ensure consistent output and pricing stability by 2026.
In summary, the Closed Cell Foam Pad market in 2026 will be characterized by diversified applications, regional growth imbalances, and a strong push toward sustainability and performance optimization. Companies that align with these trends through innovation and strategic market positioning are likely to dominate the landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Closed Cell Foam Pads (Quality, IP)
Sourcing closed cell foam pads involves navigating a range of potential issues, particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Avoiding these pitfalls is essential to ensure product performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term business integrity.
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Specifications
One of the most frequent challenges is receiving foam pads that fail to meet required physical or chemical specifications. Suppliers—especially lower-cost or less-established ones—may deliver materials with inconsistent density, incorrect thickness, inadequate compression resistance, or poor closed-cell structure integrity. This can result in premature product failure, reduced insulation performance, or non-compliance with industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). Buyers should insist on material certifications, batch testing, and third-party validation to mitigate this risk.
Misrepresentation of Foam Properties
Some suppliers exaggerate or misstate key performance attributes such as temperature resistance, waterproofing, or UV stability. For instance, a foam may be marketed as suitable for outdoor use but degrade rapidly under sunlight due to insufficient UV stabilizers. This misrepresentation can lead to product recalls or warranty claims. Conducting independent lab testing and requiring detailed technical data sheets (TDS) and safety data sheets (SDS) helps verify claims.
Lack of Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
Without clear traceability, it becomes difficult to ensure consistent quality or respond effectively to defects. Sourcing from suppliers with opaque supply chains increases the risk of receiving recycled or off-spec materials blended into the final product. Establishing supplier audits and requiring documentation of raw material sources promotes accountability and quality control.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing foam pads from manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement can expose buyers to legal risks. Some suppliers may offer pads that replicate patented designs, cell structures, or proprietary formulations without authorization. Using such products—even unknowingly—can lead to infringement lawsuits, import bans, or reputational damage. It is critical to perform due diligence on supplier IP practices, request proof of design freedom-to-operate, and include IP indemnification clauses in contracts.
Inadequate Regulatory Compliance
Closed cell foams used in specific applications (e.g., medical devices, transportation, building insulation) must comply with fire safety (e.g., UL 94, FMVSS 302), environmental (e.g., REACH, RoHS), or food-contact regulations. Suppliers may claim compliance without proper certification. Buyers should verify compliance documentation and conduct periodic audits to ensure adherence.
Hidden Tooling and Minimum Order Volume Traps
Some suppliers offer low per-unit pricing but lock buyers into high minimum order quantities (MOQs) or non-negotiable tooling costs. This can lead to excess inventory or limited design flexibility. Clarifying MOQs, tooling ownership, and scalability options during negotiations helps avoid long-term constraints.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls through rigorous vetting, contractual safeguards, and ongoing quality monitoring, companies can secure reliable, high-performance closed cell foam pads while protecting their intellectual property and brand reputation.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Closed Cell Foam Pad
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling, transportation, storage, and disposal of Closed Cell Foam Pads (e.g., EVA, PE, PU foam used for insulation, packaging, marine applications, camping, etc.).
H2: Regulatory Compliance
- Chemical Regulations:
- REACH (EU): Verify the foam material and any additives (flame retardants, colorants, blowing agents) are registered under REACH. Obtain a valid Supplier Declaration of Conformity (SDoC) from the manufacturer. Check for Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) on the Candidate List; notification may be required if present above thresholds.
- RoHS (EU & China): Ensure compliance for electrical/electronic applications. Verify absence of restricted substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr6+, PBB, PBDE, DEHP, BBP, DBP, DIBP) above maximum concentration values.
- TSCA (USA): Confirm compliance with the Toxic Substances Control Act. Ensure chemicals used are listed on the TSCA Inventory or are exempt.
- Proposition 65 (California, USA): Check if any components require a warning label for carcinogens or reproductive toxins. Labeling may be mandatory for products sold in California.
- Flame Retardancy Standards: If applicable, ensure foam meets relevant standards (e.g., FMVSS 302 for automotive, ASTM E84 for building materials, specific marine regulations). Documentation (test reports) is crucial.
- Product Safety & Labeling:
- General Product Safety Directives (GPSD – EU, CPSA – USA): Ensure the product is safe for its intended use. Maintain technical documentation (design, testing, risk assessment).
- Labeling Requirements: Include mandatory markings: Manufacturer/importer name & address, product identification (batch/lot number), CE marking (if applicable within EU), RoHS marking (if applicable), Prop 65 warnings (if required), country of origin, and any specific hazard symbols (e.g., flammability if highly flammable).
- Environmental Regulations:
- WEEE (EU): If the foam is integral to an electrical/electronic device, WEEE compliance obligations may apply to the final product.
- Packaging Waste Directives (EU, US States): If the foam is used as packaging, compliance with take-back and recycling schemes may be required.
- Disposal Regulations: Understand local regulations for disposal as non-hazardous municipal solid waste or potential recycling pathways. Avoid landfill where possible. Note: Burning foam (especially PVC-based or containing flame retardants) can release toxic fumes (dioxins, HCl) and is generally illegal and environmentally hazardous.
- Country-Specific Regulations: Research requirements in target markets (e.g., CCC in China, KC in South Korea, INMETRO in Brazil). Customs may require specific certifications.
H2: Transportation & Logistics
- Classification & Documentation:
- UN Number & Hazard Class: Closed cell foam pads are typically NOT classified as hazardous materials for transport unless they are treated with specific flammable liquids, contain residual flammable blowing agents, or are highly flammable solid sheets meeting specific test criteria. Crucially: Obtain a Transport Safety Data Sheet (TSDS) or Safety Data Sheet (SDS) from the manufacturer/supplier. This document is mandatory and will confirm if the specific product requires hazardous classification (e.g., Class 4.1 Flammable Solid). Do not assume it’s non-hazardous without verification.
- Proper Shipping Name (PSN): If classified as hazardous, use the correct PSN as per the SDS (e.g., “POLYMERIZABLE LIQUID, STABILIZED, N.O.S.” if residual monomer, “FLAMMABLE SOLID, N.O.S.” if highly flammable). If non-hazardous, no specific PSN is needed.
- Air (IATA DGR) & Ocean (IMDG Code): Follow regulations strictly if hazardous. For non-hazardous foam, standard cargo rules apply, but proper packaging is still essential.
- Packaging:
- Protection: Protect pads from moisture, dirt, oil, solvents, and physical damage (tearing, compression). Use durable plastic bags, shrink wrap, or corrugated cardboard boxes. Avoid direct contact with incompatible materials.
- Stacking & Securing: Design packaging for efficient stacking without crushing lower layers. Use pallets (standard sizes: EUR, ISO) and secure loads with stretch wrap, straps, or banding to prevent shifting during transit. Clearly mark “This Way Up” and “Fragile” if necessary.
- Marking: Include shipping marks, handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Protect from Sunlight”), UN number (if hazardous), and any required hazard labels (if applicable) on outer packaging.
- Storage:
- Environment: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight, heat sources (radiators, boilers), open flames, and sparks. High temperatures can degrade foam and increase flammability risk.
- Stacking: Store vertically or flat, avoiding excessive height that could crush lower pads. Follow manufacturer’s stacking recommendations.
- Separation: Keep away from strong oxidizing agents, flammable liquids, and corrosive substances. Do not store near welding or cutting operations.
- Handling:
- Use appropriate PPE (gloves, safety glasses) to prevent skin irritation from dust or sharp edges during cutting/unpacking.
- Use mechanical aids (hand trucks, forklifts) for heavy or bulky loads to prevent manual handling injuries.
- Avoid dragging rolls/sheets to prevent surface damage.
- Customs & Trade:
- Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading/air waybills.
- Determine correct HS (Harmonized System) Code for the foam pad (e.g., often 3921.19 for plates/sheets of other plastics). This affects tariffs and import requirements.
- Obtain necessary import/export licenses or permits if required by destination country.
- Ensure compliance with Incoterms® rules agreed upon with the buyer/seller.
H2: Key Action Steps
- Obtain SDS/TSDS: This is the foundational document. Request it from your supplier for every specific foam product.
- Verify Hazard Classification: Use the SDS to definitively determine if the foam is hazardous for transport. Consult a dangerous goods expert if unsure.
- Check Target Market Regulations: Research REACH, RoHS, Prop 65, flammability standards, and labeling requirements for each country you sell into.
- Implement Proper Packaging: Design packaging for protection, stability, and clear marking.
- Train Staff: Ensure warehouse, logistics, and sales personnel understand handling, storage, and compliance requirements.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep SDS, test reports (flammability, RoHS, REACH), SDoCs, and shipping records readily available.
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Regulations and foam compositions vary significantly. Always consult the specific Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for your product and seek advice from qualified regulatory, safety, and logistics professionals for your specific situation and jurisdictions.
Conclusion for Sourcing Closed Cell Foam Pads
After thorough evaluation of market suppliers, product specifications, cost considerations, and performance requirements, sourcing closed cell foam pads from a reliable and quality-focused supplier is essential to ensure durability, water resistance, and structural integrity in end-use applications. The selected supplier should offer consistent material quality, meet industry standards (such as ASTM or ISO specifications), and provide scalable production capacity to support ongoing project needs. Additionally, factors such as environmental compliance, lead times, and logistical support play a critical role in the overall sourcing decision.
In conclusion, a balanced approach that prioritizes quality, cost-efficiency, and supply chain reliability will enable successful integration of closed cell foam pads into the intended application—whether for insulation, marine, automotive, or outdoor gear use. Establishing a long-term partnership with a vetted supplier will not only ensure product consistency but also support innovation and responsiveness to future material needs.