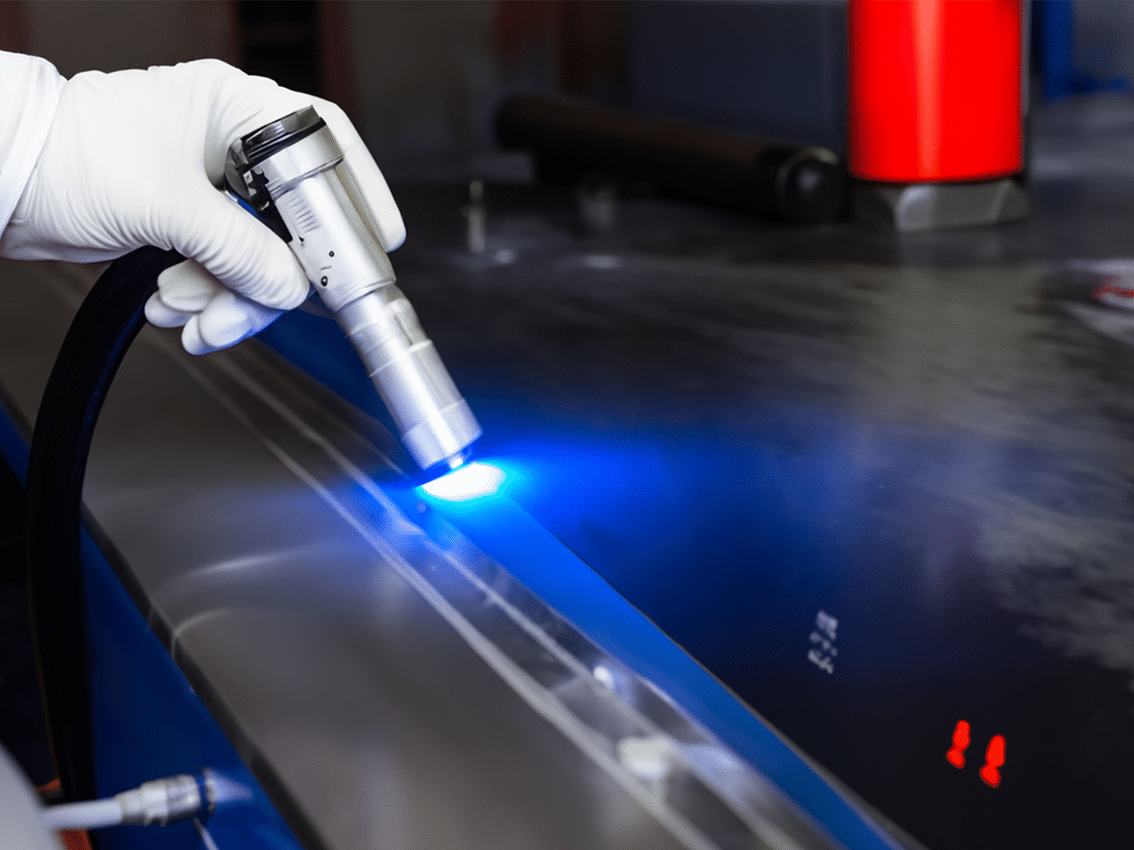
The global laser cleaning market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly, precision-based cleaning solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heritage conservation. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 647.1 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of laser cleaning as a non-abrasive, chemical-free alternative to traditional methods, alongside advancements in fiber laser technology. As industrial players seek sustainable and efficient surface preparation techniques, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront of innovation and commercial deployment. These leading companies are not only expanding their product portfolios but also investing heavily in R&D to enhance efficiency, portability, and automation in laser cleaning systems. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and global reach, the following analysis identifies the top 10 cleaning with laser light manufacturers shaping the future of industrial maintenance and precision surface treatment.
Top 10 Cleaning With Laser Light Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 P-laser Industrial laser cleaning
Website: p-laser.com
Key Highlights: we engineer and manufacture the most advanced—and most powerful—pulsed industrial laser cleaning systems on the market, built for both manual and automated ……
#2 Clean Laser Systems
Website: cleanlaser.de
Key Highlights: IPG | cleanLASER has been developing and producing high-precision laser systems for cleaning and industrial surface treatment for more than 20 years….
#3 Laser Cleaning
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Elevate production quality with laser cleaning technology: remove dust, rust, and imperfections efficiently, reducing costs and improving precision….
#4 SHARK P CL Industrial Laser Cleaning Machines (100
Website: pulsar-laser.com
Key Highlights: SHARK P CL is an industrial pulsed laser cleaning machine series by PULSAR Laser with outputs from 100 W to 1000 W, air-cooled up to 500 W….
#5 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics is the world leader of fiber laser technology, providing the most innovative and productive laser solutions for any industry application….
#6 Laser Cleaning and Laser Ablation Systems
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Remove rust and surface contaminants with our laser cleaning & laser ablation systems. Experience superior cleaning tech, automation, and eco-friendly ……
#7 Laser cleaning
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: How to achieve the perfect weld seam: laser cleaning allows you to very gently clean metal components of dirt, as well as oxidation and functional layers….
#8 Laser Cleaning
Website: irisndt.com
Key Highlights: Some sections of the originally coated plate were laser cleaned while others were media blasted before being recoated. The clean surfaces were subjected to ……
#9 Netalux
Website: netalux.com
Key Highlights: Discover our award-winning Laser Cleaning Solutions for the world’s most demanding industries. Discover our products and global service now….
#10 Laser Cleaning Technologies
Website: lasercleaningtechnologies.com
Key Highlights: We offer the only fiber-coupled, compact, mobile or stationary laser cleaning units, with 20 to 1600watts of laser power for a wide-range of applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Cleaning With Laser Light

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Cleaning with Laser Light
The global market for cleaning with laser light is poised for transformative growth by 2026, driven by technological innovation, environmental regulations, and rising demand across key industries. Laser cleaning, also known as laser ablation, utilizes high-intensity laser beams to remove contaminants, oxides, coatings, and rust from surfaces without damaging the underlying material. This non-contact, eco-friendly method is gaining traction as a superior alternative to traditional cleaning techniques such as sandblasting, chemical solvents, and dry ice blasting.
1. Increasing Adoption in Manufacturing and Automotive Sectors
By 2026, the manufacturing and automotive industries are expected to be the largest adopters of laser cleaning technology. The precision and repeatability of laser systems make them ideal for tasks such as weld preparation, surface activation before bonding, and maintenance of molds and tools. Automotive manufacturers are increasingly integrating laser cleaning into production lines to improve weld quality and reduce defects, contributing significantly to market expansion.
2. Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Stringent environmental regulations are accelerating the shift toward sustainable industrial practices. Unlike chemical or abrasive cleaning methods, laser cleaning produces no secondary waste, requires no consumables, and eliminates the need for hazardous solvents. Governments worldwide are tightening emissions and waste disposal standards, positioning laser cleaning as a compliant and future-proof solution. This regulatory tailwind is expected to boost adoption, especially in Europe and North America.
3. Advancements in Portable and Fiber Laser Systems
Technological advancements—particularly in fiber laser efficiency, portability, and affordability—are making laser cleaning more accessible. By 2026, lightweight, handheld laser cleaning devices are anticipated to dominate the market, enabling use in field applications such as shipbuilding, aerospace maintenance, and heritage restoration. Improved user interfaces, safety features, and integration with robotics further enhance operational efficiency and adoption rates.
4. Growth in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors are increasingly utilizing laser cleaning for precision maintenance of turbine blades, aircraft fuselages, and military equipment. The ability to remove corrosion and coatings without substrate damage is critical in these high-stakes environments. Increased defense spending and aircraft fleet expansions globally are expected to drive demand for reliable, high-performance cleaning solutions.
5. Expansion in Asia-Pacific Markets
While Europe and North America currently lead in laser cleaning adoption, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to be the fastest-growing market by 2026. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in advanced manufacturing and automation, creating strong demand for laser-based technologies. Government support for green manufacturing and industrial modernization further supports market penetration.
6. Cost Reduction and ROI Improvements
Historically, high upfront costs limited laser cleaning adoption. However, by 2026, declining prices of laser components and increased competition among suppliers are expected to lower entry barriers. Combined with long-term savings from reduced downtime, lower maintenance, and elimination of consumables, the return on investment (ROI) for laser cleaning systems is becoming increasingly compelling.
7. Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Laser cleaning systems are being integrated into smart manufacturing ecosystems, with capabilities for real-time monitoring, data logging, and predictive maintenance. By 2026, AI-powered laser cleaning robots and IoT-enabled devices are expected to become standard in automated production environments, further improving efficiency and scalability.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for cleaning with laser light is characterized by rapid technological adoption, regulatory support, and expanding applications across industries. With its environmental benefits, precision, and growing cost-effectiveness, laser cleaning is set to become a cornerstone of modern industrial maintenance and manufacturing processes.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Cleaning with Laser Light (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser cleaning technology offers significant advantages, but it also presents critical challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to financial loss, operational inefficiencies, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Performance Inconsistencies
Many suppliers, especially those in emerging markets, may lack rigorous quality control systems, resulting in inconsistent laser cleaning performance. Units might fail to meet stated specifications for power output, beam quality, or cleaning speed. This can lead to incomplete cleaning, surface damage, or accelerated equipment wear. Always demand third-party test reports, conduct on-site demonstrations under real-world conditions, and verify compliance with international standards (e.g., IEC, CE) before procurement.
Inadequate or Misrepresented Technical Documentation
Suppliers may provide incomplete, outdated, or misleading technical documentation, including maintenance manuals, safety protocols, and integration specs. This can hinder proper operation, increase downtime, and create safety hazards. Ensure all documentation is comprehensive, available in your required language, and aligns with the delivered system. Request software/firmware version logs and update policies during due diligence.
Weak Intellectual Property Protection and Infringement Risks
Laser cleaning systems often incorporate proprietary optics, control algorithms, and software. Sourcing from manufacturers with weak or unclear IP ownership can expose buyers to infringement claims. Some low-cost vendors may use copied designs or unauthorized components. Conduct IP audits, require proof of patents or trademarks, and include IP indemnification clauses in contracts to mitigate legal exposure.
Lack of Genuine Spare Parts and Long-Term Support
After-sales support is crucial for laser systems, yet many suppliers fail to provide reliable access to authentic spare parts or technical assistance. Counterfeit or substandard replacement parts can degrade system performance and void warranties. Confirm the supplier’s service network, spare parts availability, and software update roadmap before purchasing. Avoid suppliers who do not offer service level agreements (SLAs).
Hidden Software Limitations and Licensing Traps
Advanced laser cleaning systems rely on software for automation and optimization. Some vendors impose restrictive licensing models, charge exorbitant fees for updates, or limit functionality unless additional modules are purchased. Ensure full transparency on software capabilities, licensing terms, and update policies. Where possible, negotiate perpetual licenses or open integration protocols.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—prioritizing verified quality, thorough documentation, clear IP rights, and long-term support—buyers can ensure a reliable and legally secure investment in laser cleaning technology.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Cleaning With Laser Light
Overview of Laser Cleaning Technology
Laser cleaning is a non-abrasive, environmentally friendly method that uses pulsed laser beams to remove contaminants such as rust, paint, oxides, and grease from surfaces without damaging the underlying material. This technique is widely used in industries including automotive, aerospace, heritage restoration, and manufacturing. Due to its precision and chemical-free process, laser cleaning offers significant advantages over traditional methods. However, its deployment requires careful attention to logistics, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Equipment Handling and Transportation
Laser cleaning systems vary in size from portable handheld units to large fixed installations. Proper handling and transportation are essential to maintain equipment integrity and operator safety.
- Packaging and Protection: Always use manufacturer-recommended packaging, especially for mirrors, lenses, and fiber-optic components, which are sensitive to shock and contamination.
- Environmental Conditions: Transport equipment in climate-controlled vehicles to avoid condensation, extreme temperatures, and humidity that could damage optical and electronic components.
- Secure Mounting: During transit, secure lasers and power units to prevent movement. Use padded crating for long-distance or international shipping.
- Battery and Power Units: If the system includes rechargeable batteries, ensure compliance with IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium-ion batteries during air or sea transport.
Site Requirements and Setup
Before deploying a laser cleaning system, evaluate the operational site to ensure compatibility and safety.
- Power Supply: Confirm availability of correct voltage, phase, and grounding as specified by the manufacturer. Use uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) where power fluctuations are common.
- Space and Ventilation: Provide adequate workspace with clearance around the equipment. Ensure proper ventilation or fume extraction systems are in place to manage vaporized contaminants.
- Environmental Controls: Avoid operation in environments with excessive dust, moisture, or temperature extremes unless the equipment is rated for such conditions.
- Stable Surface: Mount the laser and control unit on a stable, vibration-free surface to maintain beam accuracy and system longevity.
Safety Protocols and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Laser cleaning poses hazards including eye and skin exposure, fumes, and electrical risks. Strict safety measures are mandatory.
- Laser Safety Classification: Most industrial laser cleaners fall under Class 4—high-power lasers capable of causing fires and serious injury. Comply with IEC 60825-1 and ANSI Z136.1 standards.
- Controlled Access: Designate a laser-controlled area with warning signs, interlocks, and barriers to prevent unauthorized access during operation.
- PPE Requirements:
- Laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength (e.g., 1064 nm for Nd:YAG lasers).
- Flame-resistant clothing.
- Respiratory protection (e.g., N95 or P100 masks) when cleaning hazardous materials like lead-based paint or cadmium coatings.
- Protective gloves and face shields as needed.
- Eye Safety: Never view the laser beam directly or its reflections. Use beam shutters and enclosures whenever possible.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to local, national, and international regulations is critical for legal and safe operation.
- Laser Safety Regulations: Follow national laser safety standards (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK, DGUV in Germany). Appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) for oversight in industrial settings.
- Environmental Regulations: Comply with EPA, REACH, or local waste disposal laws when handling removed contaminants. Use HEPA-filtered vacuum systems to capture airborne particulates.
- Workplace Health and Safety: Follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910 or equivalent regulations regarding machine guarding, electrical safety, and hazard communication.
- Permits and Documentation: Maintain records of equipment certification, operator training, maintenance logs, and safety audits. Some jurisdictions require permits for Class 4 laser use.
Operator Training and Certification
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate laser cleaning equipment.
- Technical Training: Operators must understand laser parameters (pulse frequency, power, spot size), material interactions, and system operation.
- Safety Training: Include emergency shutdown procedures, first aid for laser exposure, and fire response.
- Certification: Provide formal certification upon completion of training, and require periodic refresher courses.
- Competency Assessment: Regularly evaluate operator skills and adherence to protocols.
Maintenance and Calibration
Proper maintenance ensures performance, safety, and regulatory compliance.
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct routine checks of cooling systems, optics, cables, and safety interlocks.
- Optical Cleaning: Clean lenses and mirrors with approved materials to avoid coating damage.
- Calibration: Calibrate the laser output and beam alignment according to manufacturer guidelines, typically every 6–12 months.
- Software Updates: Keep control software up to date to benefit from safety enhancements and performance improvements.
Waste Management and Environmental Considerations
The debris generated during laser cleaning must be managed responsibly.
- Fume Extraction: Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems with HEPA and activated carbon filters to capture particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Waste Classification: Test removed materials (e.g., paint chips, rust) for hazardous substances. Dispose of waste through licensed hazardous waste handlers if required.
- Spill Containment: Prepare spill kits and containment procedures for any accidental release of hazardous residues.
- Sustainability Benefits: Document reduced chemical usage and waste volume compared to abrasive or solvent-based methods to support ESG reporting.
Emergency Procedures
Prepare for potential incidents with clear response protocols.
- Laser Incident: In case of beam exposure, immediately cease operation, assess injuries, and seek medical attention. Report incidents to the LSO and regulatory bodies if required.
- Fire Response: Keep Class C fire extinguishers nearby. Laser cleaning can ignite flammable residues or substrates.
- Power Failure: Ensure safe shutdown procedures and protect data/logs during outages.
- Evacuation Plan: Establish evacuation routes and assembly points for the work area.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance and support audits.
- Equipment Logs: Track maintenance, calibration, and repairs.
- Training Records: Archive operator certifications and training dates.
- Incident Reports: Document any safety or operational incidents with root cause analysis.
- Compliance Certificates: Keep copies of equipment CE, FDA, or other regulatory certifications.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures safe, efficient, and legally sound deployment of laser cleaning technology across industrial and commercial applications.
Conclusion: Sourcing Cleaning with Laser Light
Laser cleaning has emerged as a highly effective, precise, and environmentally friendly solution for surface cleaning across various industries, including manufacturing, heritage conservation, automotive, and aerospace. By utilizing focused laser beams to remove contaminants such as rust, paint, oxides, and oil without damaging the underlying substrate, this technology offers significant advantages over traditional cleaning methods like sandblasting or chemical treatments.
One of the key benefits of laser cleaning is its non-abrasive and non-contact nature, which preserves the integrity of delicate materials and complex geometries. It also eliminates the need for consumables and hazardous chemicals, reducing both operational costs and environmental impact. Additionally, laser cleaning systems are highly automated and can be integrated into production lines, improving efficiency and consistency.
Despite higher initial investment costs and the need for trained operators, the long-term savings, improved safety, and compliance with environmental regulations make laser cleaning a compelling choice for modern industrial applications. As technological advancements continue to enhance laser performance and reduce equipment costs, the adoption of laser cleaning is expected to grow significantly.
In conclusion, sourcing laser cleaning technology represents a forward-thinking investment in sustainable, efficient, and high-precision cleaning solutions. Companies that embrace this innovation position themselves at the forefront of industrial advancement, achieving superior cleaning results while meeting environmental and operational excellence goals.