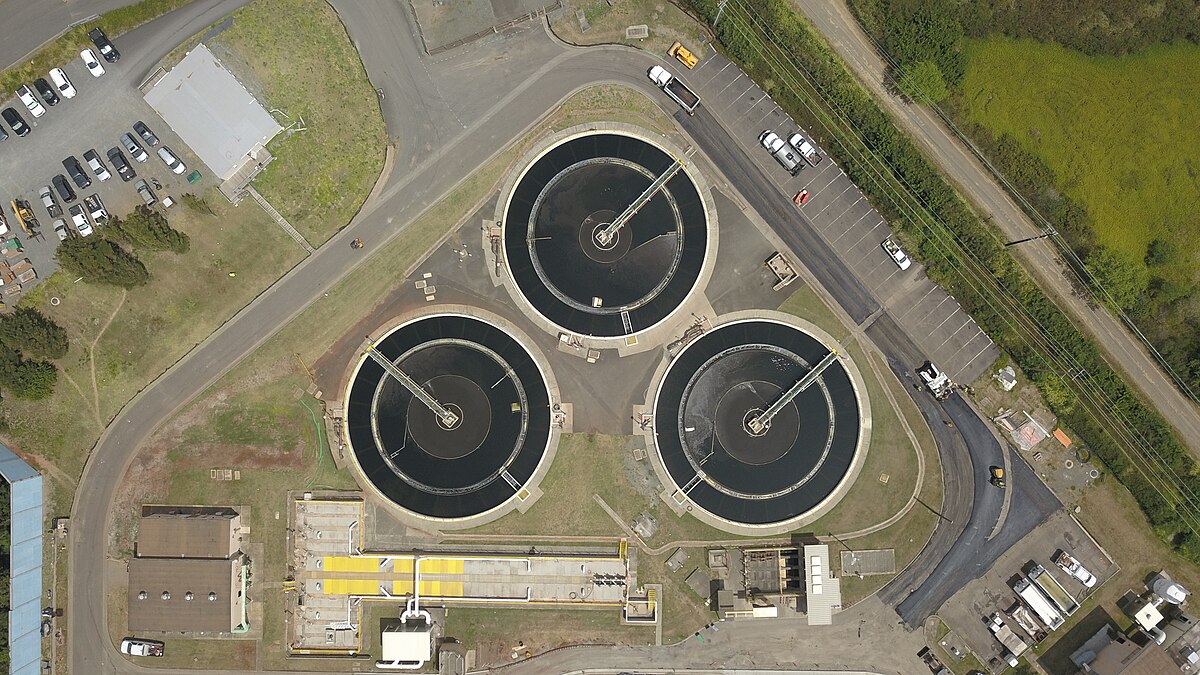
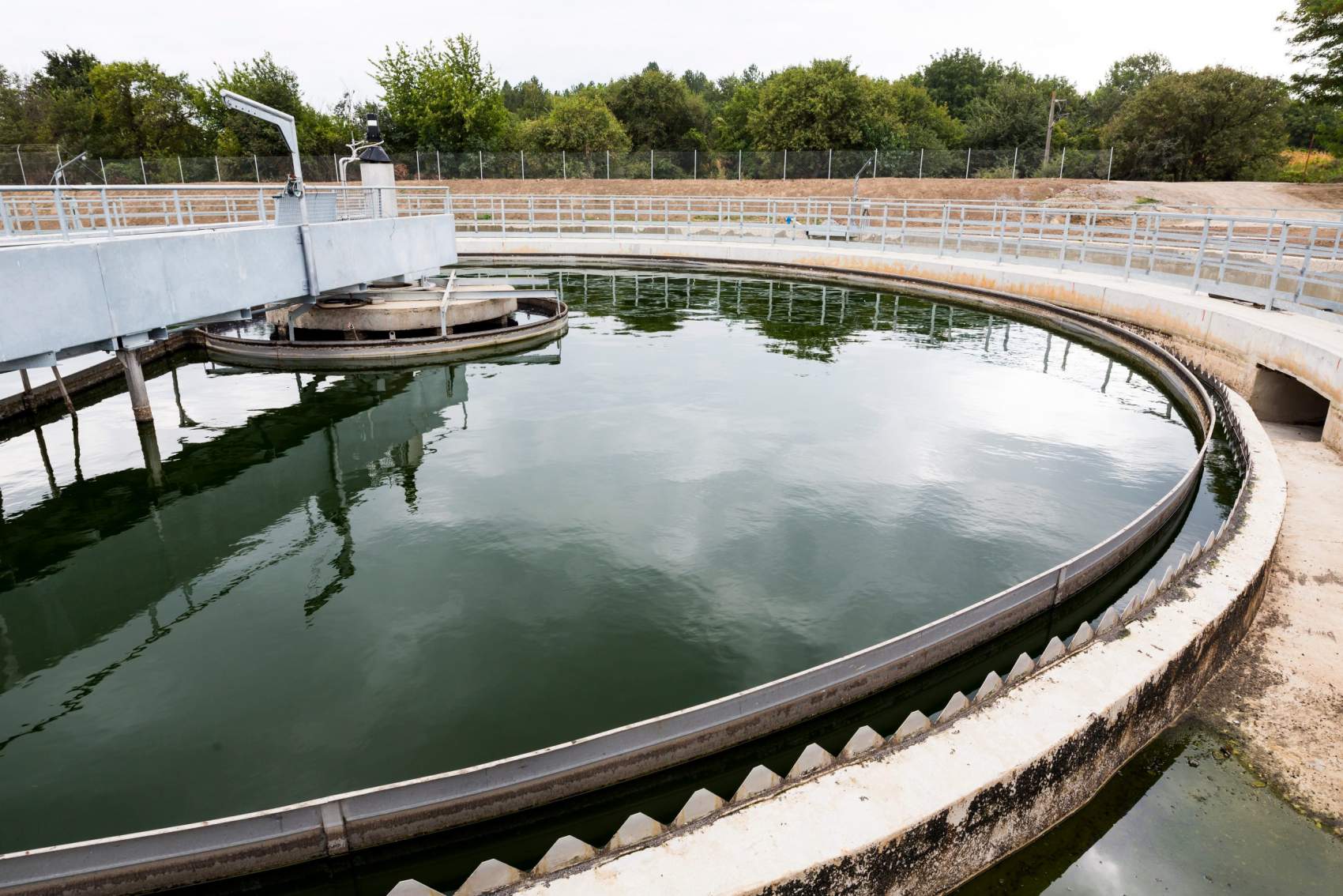
The global clarifier tank market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising industrial wastewater treatment demands and stringent environmental regulations. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the Water Treatment Equipment Market—of which clarifier tanks are a critical component—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global industrial wastewater treatment market, a key end-user segment for clarifier systems, was valued at USD 49.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2030. With increasing urbanization, industrialization, and a growing focus on water reuse, the demand for efficient clarifier tank solutions has never been higher. As industries across food and beverage, municipal water, chemical processing, and mining prioritize sustainable water management, selecting reliable clarifier tank manufacturers becomes essential. Based on market presence, technological innovation, global footprint, and customer reviews, we’ve compiled a data-driven list of the top 10 clarifier tank manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Clarifier Tank Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Lamella Clarifier Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metchem.com
Key Highlights: Met-Chem is a manufacturer and supplier of clarifiers, filter presses & wastewater treatment systems. View our large inventory of new and used clarifiers….
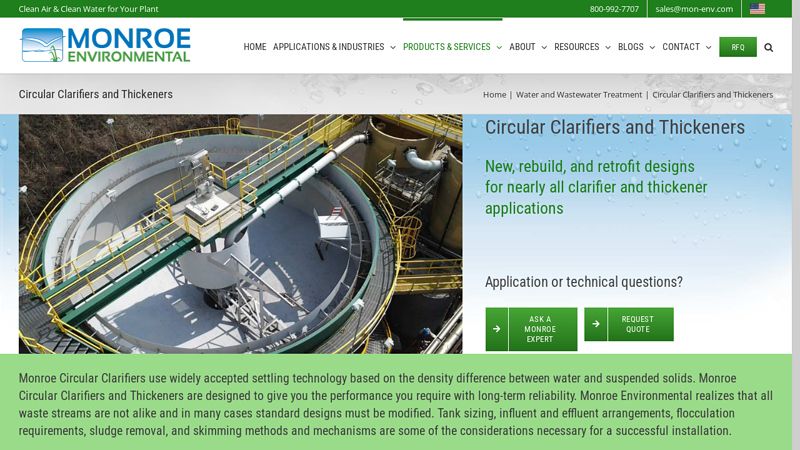
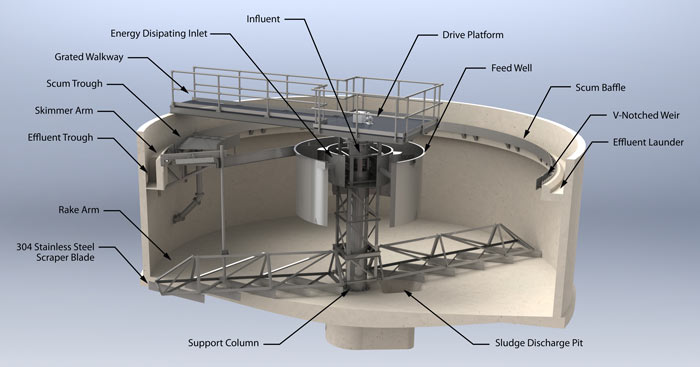
#2 Circular Clarifiers and Thickeners
Domain Est. 1999
Website: monroeenvironmental.com
Key Highlights: Monroe Environmental builds Primary and Secondary Circular Clarifiers for industrial and municipal wastewater treatment, as well as Flocculating Clarifiers….
#3 Clarifiers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jensenprecast.com
Key Highlights: Our clarifier tanks help to support environmentally responsible wastewater treatment practices in a variety of applications….
#4 Clarifiers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: napier-reid.com
Key Highlights: Napier-Reid’s clarifiers provide a size and type to fit any plant requirement. The application-oriented design assures an economical performance….
#5 Clarifiers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: advancetank.com
Key Highlights: Advance Tank has several clarifiers and thickeners operating throughout the United States. We have more than 45 years experience in water and wastewater ……
#6 Clarifiers & Thickeners
Domain Est. 1998
Website: deltank.com
Key Highlights: The DEL Clarifier/Thickener is ideal for dredge dewatering projects utilizing a Total Clean System and geotextile tubes, or any other combination of dewatering ……
#7 Clarifiers for Water Treatment
Domain Est. 2002
Website: watertechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Our clarifier water treatments effectively clarify, soften, thicken, and remove metal. Browse our clarifier systems and learn more about Veolia’s water ……
#8 Water Clarifiers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: clearwaterind.com
Key Highlights: Our manufactured water clarifier technologies include traditional sedimentation, ballasted flocculation, and dissolved air flotation (DAF)….
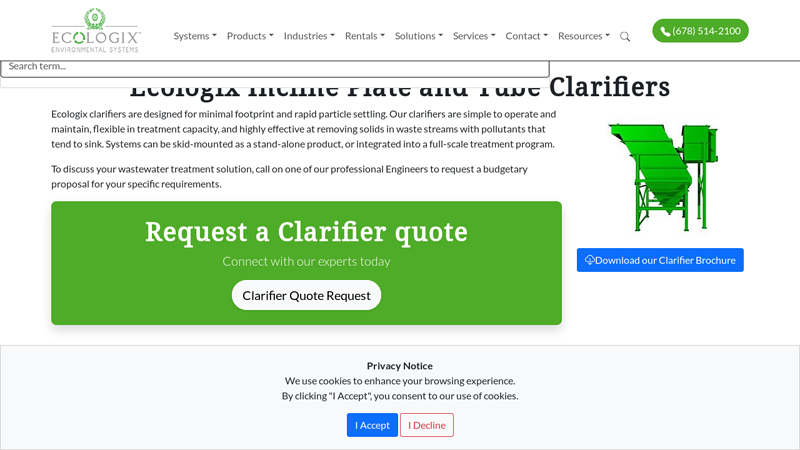
#9 Ecologix Incline Plate and Tube Clarifiers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ecologixsystems.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.8 (19) Ecologix clarifiers are designed for minimal footprint and rapid particle settling. Our clarifiers are simple to operate and maintain, flexible in treatment ……
#10 Solids CONTACT CLARIFIER
Domain Est. 2020
Website: westechwater.com
Key Highlights: Solids Contact Clarifiers for water treatment settle solids quicker, provide better clarity, and reduce chemical usage….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Clarifier Tank

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Clarifier Tanks
The global clarifier tank market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by increasing demand for clean water, stricter environmental regulations, and advancements in water treatment technologies. Clarifier tanks—used primarily in municipal wastewater treatment, industrial effluent management, and drinking water purification—are undergoing a shift toward enhanced efficiency, automation, and sustainability. Below is an in-depth analysis of key market trends expected to shape the clarifier tank industry in 2026.
1. Growing Demand from Municipal and Industrial Sectors
Urbanization and population growth are placing immense pressure on municipal water infrastructure. By 2026, many developing and emerging economies are expected to invest heavily in expanding wastewater treatment capacity, directly boosting demand for clarifier tanks. Simultaneously, industries such as food and beverage, pulp and paper, chemicals, and power generation are implementing zero-liquid discharge (ZLD) policies, increasing the need for advanced clarification systems.
2. Regulatory Drivers and Environmental Compliance
Environmental agencies worldwide, including the U.S. EPA, EU Commission, and China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment, are enforcing stricter discharge limits for suspended solids and pollutants. These regulations are compelling municipalities and industries to upgrade aging infrastructure with high-efficiency clarifier tanks. In 2026, compliance with standards such as the EU Water Framework Directive and the U.S. Clean Water Act will remain key market drivers.
3. Adoption of Advanced Clarifier Technologies
The market is shifting from conventional circular and rectangular clarifiers toward high-rate and dissolved air flotation (DAF) clarifiers, which offer smaller footprints, faster settling rates, and improved performance. By 2026, innovations such as lamella plate clarifiers and automated sludge withdrawal systems will gain traction due to their space efficiency and lower operational costs—especially in urban and space-constrained facilities.
4. Integration of IoT and Smart Monitoring
Smart water management systems are becoming essential. Leading manufacturers are incorporating IoT-enabled sensors, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance features into clarifier tanks. These technologies allow operators to optimize chemical dosing, monitor sludge levels, and reduce energy consumption. By 2026, smart clarifiers are expected to capture a growing share of the market, particularly in North America and Europe.
5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability is a central theme in water infrastructure planning. Clarifier tanks with energy-efficient drive mechanisms, corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., fiberglass-reinforced plastic and stainless steel), and lower chemical usage are increasingly preferred. Additionally, modular and prefabricated clarifier systems are gaining popularity due to reduced construction time and lower environmental impact.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific: Expected to be the fastest-growing region due to rapid industrialization, urban development, and government initiatives like India’s Namami Gange and China’s Sponge Cities program.
- North America and Europe: Driven by infrastructure modernization and regulatory upgrades, with strong emphasis on retrofitting existing plants.
- Middle East & Africa: Rising investments in desalination and municipal wastewater reuse projects will support clarifier tank demand.
7. Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The market is moderately fragmented, with key players such as Evoqua Water Technologies, Xylem Inc., SUEZ, and AECOM investing in R&D and strategic partnerships. Mergers and acquisitions are expected to increase by 2026 as companies aim to expand their technological portfolios and geographic reach.
Conclusion
By 2026, the clarifier tank market will be shaped by technological innovation, regulatory pressures, and the global push for sustainable water management. The integration of smart technologies, demand for compact and efficient systems, and regional infrastructure investments will define growth trajectories. Stakeholders who prioritize energy efficiency, automation, and compliance will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this evolving market.
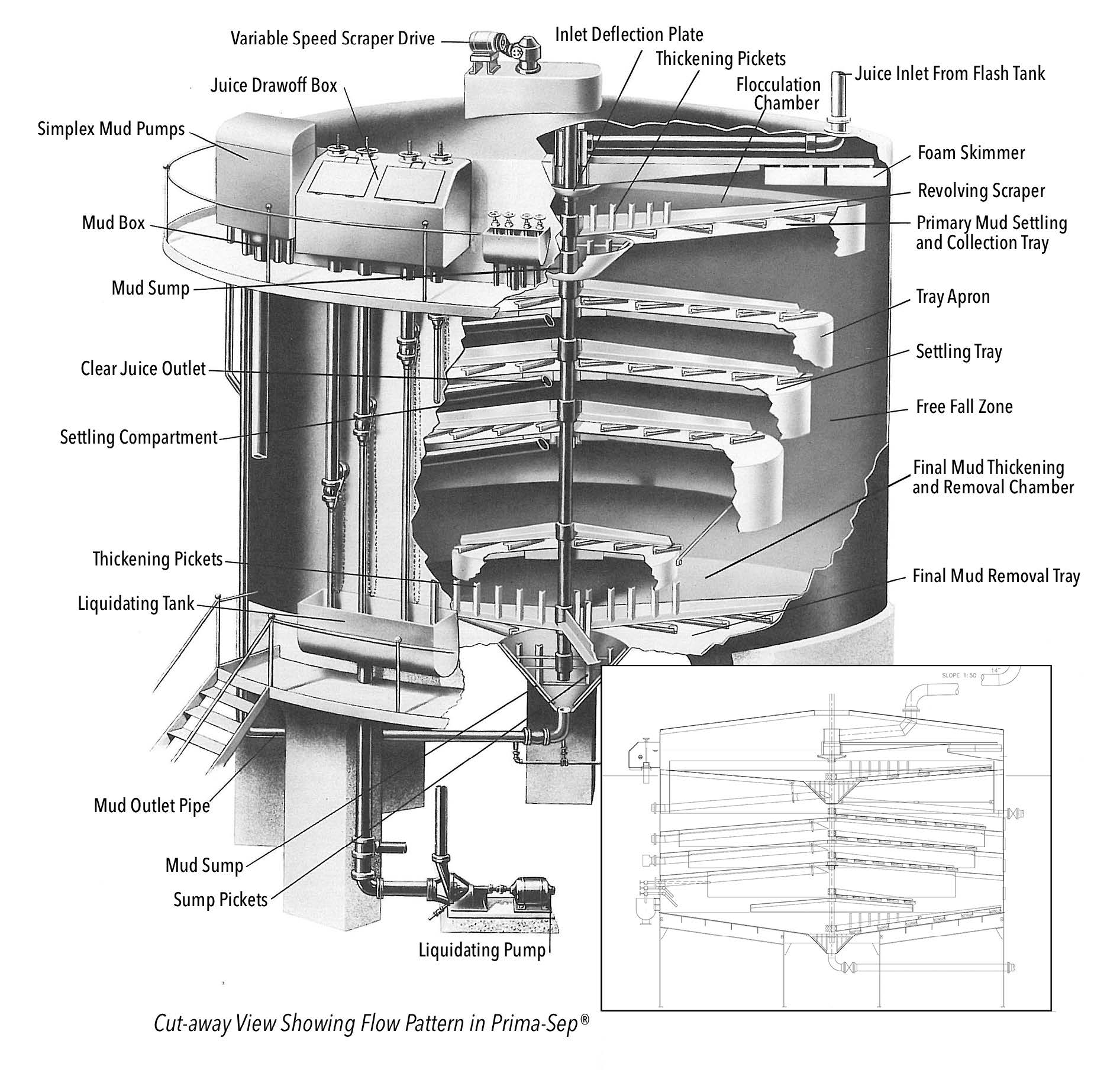
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Clarifier Tanks: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing clarifier tanks—critical components in water and wastewater treatment—can be fraught with challenges, especially when balancing cost, performance, and legal compliance. Two key areas where organizations often encounter significant pitfalls are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to system inefficiencies, costly failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Material Specifications
A frequent issue is sourcing tanks made from substandard materials. For example, using low-grade stainless steel or improperly coated carbon steel can lead to premature corrosion, leaks, and contamination risks. Buyers may accept suppliers’ claims without verifying material certifications (e.g., mill test reports), resulting in tanks that fail under operational stress. -
Poor Fabrication and Welding Standards
Clarifier tanks must withstand hydraulic loads, weather, and chemical exposure. Poor welding—such as incomplete penetration, lack of weld inspection, or non-compliance with ASME or AWS standards—can compromise structural integrity. Suppliers from regions with lax quality control may cut corners, leading to on-site failures during commissioning. -
Lack of Third-Party Inspection and Certification
Skipping independent quality audits or third-party inspections (e.g., by organizations like DNV, TÜV, or Bureau Veritas) increases the risk of receiving non-compliant equipment. Without documented proof of conformity to design standards (e.g., AWWA D100), buyers have limited recourse if defects emerge post-installation. -
Inconsistent Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Clarifier tanks require precise alignment for feed wells, launders, and sludge collection mechanisms. Poor manufacturing tolerances can lead to misalignment, turbulence, short-circuiting, and reduced settling efficiency. This often becomes apparent only during installation, causing costly delays and retrofits. -
Insufficient Testing and Commissioning Documentation
Some suppliers deliver tanks without proper hydrostatic testing, leak testing, or performance validation under simulated conditions. Missing documentation makes it difficult to verify performance claims and exposes the buyer to operational risks after installation.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
-
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Designs
Some suppliers may replicate patented clarifier designs—such as specific baffle configurations, sludge removal mechanisms, or energy-efficient drive systems—without licensing. Purchasing such equipment can inadvertently involve the buyer in IP infringement, potentially leading to legal liability, import seizures, or forced system modifications. -
Lack of IP Clarity in Design-Build Contracts
When working with engineering suppliers on custom clarifier designs, contracts often fail to clearly define IP ownership. This ambiguity can result in disputes over who owns the design improvements, process know-how, or digital models—hindering future modifications or replication. -
Reverse Engineering and Design Theft
In global sourcing, especially from regions with weak IP enforcement, there is a risk that supplier partners may reverse engineer a purchased clarifier and resell it as their own. Without robust contractual safeguards and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), original innovators lose competitive advantage. -
Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Components
Some clarifier tanks incorporate proprietary components (e.g., patented skimmer arms or scraper drives). Suppliers may substitute these with counterfeit or unlicensed versions to cut costs. This not only violates IP rights but also compromises reliability and voids warranties on original equipment. -
Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier IP Compliance
Buyers often focus on price and delivery timelines while neglecting to audit a supplier’s IP practices. Failing to request proof of design licenses, patent clearances, or original equipment manufacturer (OEM) authorizations exposes projects to legal and operational risks.
Mitigation Strategies
- Require detailed material traceability and fabrication records.
- Engage independent inspectors during manufacturing.
- Conduct factory acceptance tests (FAT) with performance benchmarks.
- Perform IP due diligence: verify design patents, request licensing documentation, and include IP indemnity clauses in contracts.
- Work with reputable suppliers who respect IP rights and adhere to international quality standards.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns during procurement, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally defensible clarifier tank installations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Clarifier Tank
This guide outlines the key logistical considerations and compliance requirements associated with the handling, transportation, installation, operation, and maintenance of clarifier tanks in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment applications.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all activities related to clarifier tanks adhere to relevant local, national, and international regulations. Key compliance areas include:
- Environmental Protection Regulations: Comply with standards set by agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), European Union Water Framework Directive, or equivalent bodies to prevent water pollution and ensure effluent quality meets discharge limits.
- Permitting Requirements: Obtain necessary permits for construction, operation, and discharge, including National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits in the U.S. or Environment Agency permits in the UK.
- Health and Safety Standards: Follow OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) or equivalent safety regulations during installation, maintenance, and operation to protect workers from hazards such as confined space entry, chemical exposure, and mechanical risks.
- Structural and Engineering Codes: Design and construct clarifier tanks in accordance with ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers), AWWA (American Water Works Association), or other applicable engineering standards to ensure structural integrity and long-term performance.
Transportation and Handling Logistics
Proper planning is essential for the safe and efficient transport and handling of clarifier tank components:
- Site Assessment: Conduct a thorough site evaluation to ensure access roads, crane placement, and foundation conditions support delivery and installation of large tank sections or pre-assembled units.
- Transportation Mode: Coordinate between flatbed trucks, heavy haul carriers, or barge transport depending on tank size, weight, and site location. Ensure compliance with road weight and dimension regulations.
- Packaging and Protection: Secure all components against weather, corrosion, and physical damage during transit. Use protective coatings, crating, and moisture barriers as needed.
- Lifting and Rigging: Use certified rigging equipment and trained personnel for offloading and positioning. Follow manufacturer-recommended lift points and procedures to avoid structural damage.
Installation Procedures
Adhere to engineered plans and manufacturer specifications during installation:
- Foundation Preparation: Ensure the base is level, compacted, and constructed according to design specifications to prevent settling or misalignment.
- Assembly Sequence: Follow the approved assembly sequence for bolted, welded, or concrete tanks. Perform quality checks at each stage, including weld inspections and alignment verification.
- Alignment and Leveling: Precisely level the tank shell and rotating mechanisms (e.g., scraper bridges) to ensure optimal hydraulic performance and mechanical longevity.
- Commissioning: Conduct hydrostatic testing for leaks, verify drive mechanisms, and calibrate instrumentation (e.g., level sensors, sludge blanket detectors) before operational startup.
Operational Compliance and Monitoring
Maintain continuous compliance during tank operation:
- Effluent Monitoring: Regularly test and document effluent quality (e.g., TSS, BOD, turbidity) to ensure compliance with discharge permits.
- Process Control: Implement procedures for optimal chemical dosing, sludge withdrawal rates, and hydraulic loading to maintain clarifier performance.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain logs of inspections, maintenance, process parameters, and regulatory reports for audit readiness.
- Spill Prevention and Response: Develop and implement SPCC (Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure) plans or equivalent protocols to address potential leaks or overflows.
Maintenance and Decommissioning
Ensure long-term reliability and compliance through proactive maintenance and proper end-of-life procedures:
- Routine Inspections: Schedule periodic inspections of structural components, coatings, mechanical drives, and sludge collection systems.
- Corrosion Protection: Reapply protective coatings or cathodic protection systems as needed, particularly in aggressive environments.
- Sludge Management: Handle and dispose of accumulated sludge in accordance with hazardous waste regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.) if applicable.
- Decommissioning Plan: When retiring a clarifier tank, follow environmental regulations for cleaning, decontamination, dismantling, and site restoration. Properly dispose of materials and document all activities.
Adherence to this logistics and compliance guide ensures the safe, legal, and efficient lifecycle management of clarifier tanks, protecting both the environment and operational integrity.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Clarifier Tank
Sourcing a clarifier tank is a critical decision that directly impacts the efficiency, reliability, and long-term performance of a water or wastewater treatment system. After a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, material quality, manufacturer reputation, lifecycle costs, and after-sales support, it is evident that selecting the right clarifier tank involves more than just comparing initial prices. Key factors such as tank design (e.g., circular vs. rectangular), material durability (e.g., stainless steel, fiberglass, or concrete), compatibility with existing infrastructure, and compliance with environmental and safety standards must be prioritized.
Additionally, engaging suppliers with proven experience, strong references, and comprehensive service offerings—such as installation assistance, maintenance support, and performance guarantees—ensures long-term operational success. The chosen clarifier tank should not only meet current treatment demands but also allow for scalability and adaptability as future needs evolve.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing decision—based on technical suitability, total cost of ownership, and supplier reliability—will result in improved water clarity, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced system sustainability. Investing time and resources into selecting the right clarifier tank is essential for achieving optimal treatment outcomes and ensuring regulatory compliance.